Qihan Huang
Boosting MLLM Reasoning with Text-Debiased Hint-GRPO
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:MLLM reasoning has drawn widespread research for its excellent problem-solving capability. Current reasoning methods fall into two types: PRM, which supervises the intermediate reasoning steps, and ORM, which supervises the final results. Recently, DeepSeek-R1 has challenged the traditional view that PRM outperforms ORM, which demonstrates strong generalization performance using an ORM method (i.e., GRPO). However, current MLLM's GRPO algorithms still struggle to handle challenging and complex multimodal reasoning tasks (e.g., mathematical reasoning). In this work, we reveal two problems that impede the performance of GRPO on the MLLM: Low data utilization and Text-bias. Low data utilization refers to that GRPO cannot acquire positive rewards to update the MLLM on difficult samples, and text-bias is a phenomenon that the MLLM bypasses image condition and solely relies on text condition for generation after GRPO training. To tackle these problems, this work proposes Hint-GRPO that improves data utilization by adaptively providing hints for samples of varying difficulty, and text-bias calibration that mitigates text-bias by calibrating the token prediction logits with image condition in test-time. Experiment results on three base MLLMs across eleven datasets demonstrate that our proposed methods advance the reasoning capability of original MLLM by a large margin, exhibiting superior performance to existing MLLM reasoning methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/hqhQAQ/Hint-GRPO.
CustomVideoX: 3D Reference Attention Driven Dynamic Adaptation for Zero-Shot Customized Video Diffusion Transformers
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Customized generation has achieved significant progress in image synthesis, yet personalized video generation remains challenging due to temporal inconsistencies and quality degradation. In this paper, we introduce CustomVideoX, an innovative framework leveraging the video diffusion transformer for personalized video generation from a reference image. CustomVideoX capitalizes on pre-trained video networks by exclusively training the LoRA parameters to extract reference features, ensuring both efficiency and adaptability. To facilitate seamless interaction between the reference image and video content, we propose 3D Reference Attention, which enables direct and simultaneous engagement of reference image features with all video frames across spatial and temporal dimensions. To mitigate the excessive influence of reference image features and textual guidance on generated video content during inference, we implement the Time-Aware Reference Attention Bias (TAB) strategy, dynamically modulating reference bias over different time steps. Additionally, we introduce the Entity Region-Aware Enhancement (ERAE) module, aligning highly activated regions of key entity tokens with reference feature injection by adjusting attention bias. To thoroughly evaluate personalized video generation, we establish a new benchmark, VideoBench, comprising over 50 objects and 100 prompts for extensive assessment. Experimental results show that CustomVideoX significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of video consistency and quality.
PatchDPO: Patch-level DPO for Finetuning-free Personalized Image Generation
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Finetuning-free personalized image generation can synthesize customized images without test-time finetuning, attracting wide research interest owing to its high efficiency. Current finetuning-free methods simply adopt a single training stage with a simple image reconstruction task, and they typically generate low-quality images inconsistent with the reference images during test-time. To mitigate this problem, inspired by the recent DPO (i.e., direct preference optimization) technique, this work proposes an additional training stage to improve the pre-trained personalized generation models. However, traditional DPO only determines the overall superiority or inferiority of two samples, which is not suitable for personalized image generation because the generated images are commonly inconsistent with the reference images only in some local image patches. To tackle this problem, this work proposes PatchDPO that estimates the quality of image patches within each generated image and accordingly trains the model. To this end, PatchDPO first leverages the pre-trained vision model with a proposed self-supervised training method to estimate the patch quality. Next, PatchDPO adopts a weighted training approach to train the model with the estimated patch quality, which rewards the image patches with high quality while penalizing the image patches with low quality. Experiment results demonstrate that PatchDPO significantly improves the performance of multiple pre-trained personalized generation models, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on both single-object and multi-object personalized image generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/hqhQAQ/PatchDPO.
LG-CAV: Train Any Concept Activation Vector with Language Guidance
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Concept activation vector (CAV) has attracted broad research interest in explainable AI, by elegantly attributing model predictions to specific concepts. However, the training of CAV often necessitates a large number of high-quality images, which are expensive to curate and thus limited to a predefined set of concepts. To address this issue, we propose Language-Guided CAV (LG-CAV) to harness the abundant concept knowledge within the certain pre-trained vision-language models (e.g., CLIP). This method allows training any CAV without labeled data, by utilizing the corresponding concept descriptions as guidance. To bridge the gap between vision-language model and the target model, we calculate the activation values of concept descriptions on a common pool of images (probe images) with vision-language model and utilize them as language guidance to train the LG-CAV. Furthermore, after training high-quality LG-CAVs related to all the predicted classes in the target model, we propose the activation sample reweighting (ASR), serving as a model correction technique, to improve the performance of the target model in return. Experiments on four datasets across nine architectures demonstrate that LG-CAV achieves significantly superior quality to previous CAV methods given any concept, and our model correction method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing concept-based methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/hqhQAQ/LG-CAV.
Resolving Multi-Condition Confusion for Finetuning-Free Personalized Image Generation
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Personalized text-to-image generation methods can generate customized images based on the reference images, which have garnered wide research interest. Recent methods propose a finetuning-free approach with a decoupled cross-attention mechanism to generate personalized images requiring no test-time finetuning. However, when multiple reference images are provided, the current decoupled cross-attention mechanism encounters the object confusion problem and fails to map each reference image to its corresponding object, thereby seriously limiting its scope of application. To address the object confusion problem, in this work we investigate the relevance of different positions of the latent image features to the target object in diffusion model, and accordingly propose a weighted-merge method to merge multiple reference image features into the corresponding objects. Next, we integrate this weighted-merge method into existing pre-trained models and continue to train the model on a multi-object dataset constructed from the open-sourced SA-1B dataset. To mitigate object confusion and reduce training costs, we propose an object quality score to estimate the image quality for the selection of high-quality training samples. Furthermore, our weighted-merge training framework can be employed on single-object generation when a single object has multiple reference images. The experiments verify that our method achieves superior performance to the state-of-the-arts on the Concept101 dataset and DreamBooth dataset of multi-object personalized image generation, and remarkably improves the performance on single-object personalized image generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/hqhQAQ/MIP-Adapter.
MS-Diffusion: Multi-subject Zero-shot Image Personalization with Layout Guidance
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in text-to-image generation models have dramatically enhanced the generation of photorealistic images from textual prompts, leading to an increased interest in personalized text-to-image applications, particularly in multi-subject scenarios. However, these advances are hindered by two main challenges: firstly, the need to accurately maintain the details of each referenced subject in accordance with the textual descriptions; and secondly, the difficulty in achieving a cohesive representation of multiple subjects in a single image without introducing inconsistencies. To address these concerns, our research introduces the MS-Diffusion framework for layout-guided zero-shot image personalization with multi-subjects. This innovative approach integrates grounding tokens with the feature resampler to maintain detail fidelity among subjects. With the layout guidance, MS-Diffusion further improves the cross-attention to adapt to the multi-subject inputs, ensuring that each subject condition acts on specific areas. The proposed multi-subject cross-attention orchestrates harmonious inter-subject compositions while preserving the control of texts. Comprehensive quantitative and qualitative experiments affirm that this method surpasses existing models in both image and text fidelity, promoting the development of personalized text-to-image generation.
On the Concept Trustworthiness in Concept Bottleneck Models
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs), which break down the reasoning process into the input-to-concept mapping and the concept-to-label prediction, have garnered significant attention due to their remarkable interpretability achieved by the interpretable concept bottleneck. However, despite the transparency of the concept-to-label prediction, the mapping from the input to the intermediate concept remains a black box, giving rise to concerns about the trustworthiness of the learned concepts (i.e., these concepts may be predicted based on spurious cues). The issue of concept untrustworthiness greatly hampers the interpretability of CBMs, thereby hindering their further advancement. To conduct a comprehensive analysis on this issue, in this study we establish a benchmark to assess the trustworthiness of concepts in CBMs. A pioneering metric, referred to as concept trustworthiness score, is proposed to gauge whether the concepts are derived from relevant regions. Additionally, an enhanced CBM is introduced, enabling concept predictions to be made specifically from distinct parts of the feature map, thereby facilitating the exploration of their related regions. Besides, we introduce three modules, namely the cross-layer alignment (CLA) module, the cross-image alignment (CIA) module, and the prediction alignment (PA) module, to further enhance the concept trustworthiness within the elaborated CBM. The experiments on five datasets across ten architectures demonstrate that without using any concept localization annotations during training, our model improves the concept trustworthiness by a large margin, meanwhile achieving superior accuracy to the state-of-the-arts. Our code is available at https://github.com/hqhQAQ/ProtoCBM.
Is ProtoPNet Really Explainable? Evaluating and Improving the Interpretability of Prototypes
Dec 12, 2022Abstract:ProtoPNet and its follow-up variants (ProtoPNets) have attracted broad research interest for their intrinsic interpretability from prototypes and comparable accuracy to non-interpretable counterparts. However, it has been recently found that the interpretability of prototypes can be corrupted due to the semantic gap between similarity in latent space and that in input space. In this work, we make the first attempt to quantitatively evaluate the interpretability of prototype-based explanations, rather than solely qualitative evaluations by some visualization examples, which can be easily misled by cherry picks. To this end, we propose two evaluation metrics, termed consistency score and stability score, to evaluate the explanation consistency cross images and the explanation robustness against perturbations, both of which are essential for explanations taken into practice. Furthermore, we propose a shallow-deep feature alignment (SDFA) module and a score aggregation (SA) module to improve the interpretability of prototypes. We conduct systematical evaluation experiments and substantial discussions to uncover the interpretability of existing ProtoPNets. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves significantly superior performance to the state-of-the-arts, under both the conventional qualitative evaluations and the proposed quantitative evaluations, in both accuracy and interpretability. Codes are available at https://github.com/hqhQAQ/EvalProtoPNet.
ProtoPFormer: Concentrating on Prototypical Parts in Vision Transformers for Interpretable Image Recognition
Aug 22, 2022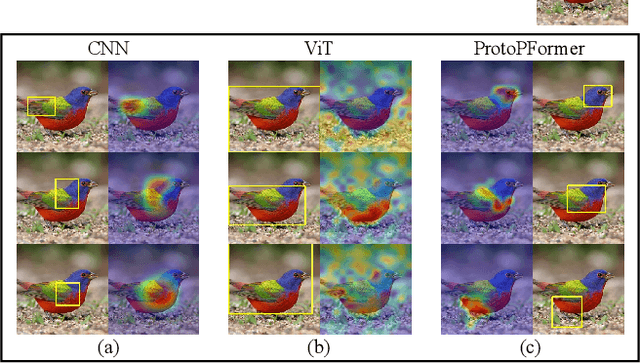
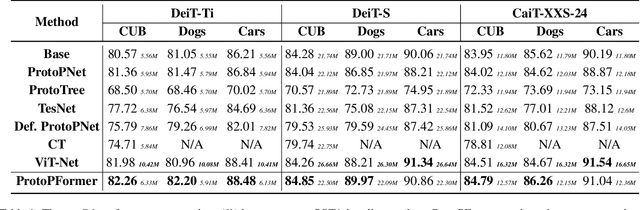
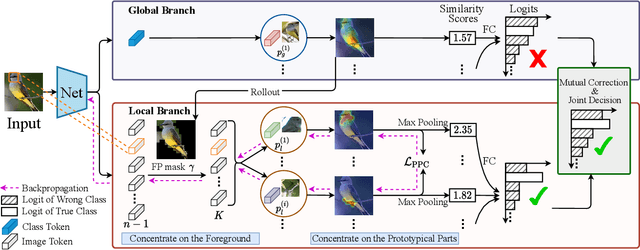
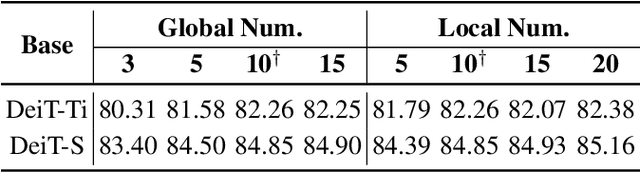
Abstract:Prototypical part network (ProtoPNet) has drawn wide attention and boosted many follow-up studies due to its self-explanatory property for explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). However, when directly applying ProtoPNet on vision transformer (ViT) backbones, learned prototypes have a ''distraction'' problem: they have a relatively high probability of being activated by the background and pay less attention to the foreground. The powerful capability of modeling long-term dependency makes the transformer-based ProtoPNet hard to focus on prototypical parts, thus severely impairing its inherent interpretability. This paper proposes prototypical part transformer (ProtoPFormer) for appropriately and effectively applying the prototype-based method with ViTs for interpretable image recognition. The proposed method introduces global and local prototypes for capturing and highlighting the representative holistic and partial features of targets according to the architectural characteristics of ViTs. The global prototypes are adopted to provide the global view of objects to guide local prototypes to concentrate on the foreground while eliminating the influence of the background. Afterwards, local prototypes are explicitly supervised to concentrate on their respective prototypical visual parts, increasing the overall interpretability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed global and local prototypes can mutually correct each other and jointly make final decisions, which faithfully and transparently reason the decision-making processes associatively from the whole and local perspectives, respectively. Moreover, ProtoPFormer consistently achieves superior performance and visualization results over the state-of-the-art (SOTA) prototype-based baselines. Our code has been released at https://github.com/zju-vipa/ProtoPFormer.
A Survey of Deep Learning for Low-Shot Object Detection
Dec 10, 2021



Abstract:Object detection is a fundamental task in computer vision and image processing. Current deep learning based object detectors have been highly successful with abundant labeled data. But in real life, it is not guaranteed that each object category has enough labeled samples for training. These large object detectors are easy to overfit when the training data is limited. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce few-shot learning and zero-shot learning into object detection, which can be named low-shot object detection together. Low-Shot Object Detection (LSOD) aims to detect objects from a few or even zero labeled data, which can be categorized into few-shot object detection (FSOD) and zero-shot object detection (ZSD), respectively. This paper conducts a comprehensive survey for deep learning based FSOD and ZSD. First, this survey classifies methods for FSOD and ZSD into different categories and discusses the pros and cons of them. Second, this survey reviews dataset settings and evaluation metrics for FSOD and ZSD, then analyzes the performance of different methods on these benchmarks. Finally, this survey discusses future challenges and promising directions for FSOD and ZSD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge