Saravan Rajmohan
Memora: A Harmonic Memory Representation Balancing Abstraction and Specificity
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Agent memory systems must accommodate continuously growing information while supporting efficient, context-aware retrieval for downstream tasks. Abstraction is essential for scaling agent memory, yet it often comes at the cost of specificity, obscuring the fine-grained details required for effective reasoning. We introduce Memora, a harmonic memory representation that structurally balances abstraction and specificity. Memora organizes information via its primary abstractions that index concrete memory values and consolidate related updates into unified memory entries, while cue anchors expand retrieval access across diverse aspects of the memory and connect related memories. Building on this structure, we employ a retrieval policy that actively exploits these memory connections to retrieve relevant information beyond direct semantic similarity. Theoretically, we show that standard Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Knowledge Graph (KG)-based memory systems emerge as special cases of our framework. Empirically, Memora establishes a new state-of-the-art on the LoCoMo and LongMemEval benchmarks, demonstrating better retrieval relevance and reasoning effectiveness as memory scales.
GUI-360$^\circ$: A Comprehensive Dataset and Benchmark for Computer-Using Agents
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce GUI-360$^\circ$, a large-scale, comprehensive dataset and benchmark suite designed to advance computer-using agents (CUAs). CUAs present unique challenges and is constrained by three persistent gaps: a scarcity of real-world CUA tasks, the lack of automated collection-and-annotation pipelines for multi-modal trajectories, and the absence of a unified benchmark that jointly evaluates GUI grounding, screen parsing, and action prediction. GUI-360$^\circ$ addresses these gaps with an LLM-augmented, largely automated pipeline for query sourcing, environment-template construction, task instantiation, batched execution, and LLM-driven quality filtering. The released corpus contains over 1.2M executed action steps across thousands of trajectories in popular Windows office applications, and includes full-resolution screenshots, accessibility metadata when available, instantiated goals, intermediate reasoning traces, and both successful and failed action trajectories. The dataset supports three canonical tasks, GUI grounding, screen parsing, and action prediction, and a hybrid GUI+API action space that reflects modern agent designs. Benchmarking state-of-the-art vision--language models on GUI-360$^\circ$ reveals substantial out-of-the-box shortcomings in grounding and action prediction; supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning yield significant gains but do not close the gap to human-level reliability. We release GUI-360$^\circ$ and accompanying code to facilitate reproducible research and accelerate progress on robust desktop CUAs. The full dataset has been made public on https://huggingface.co/datasets/vyokky/GUI-360.
Adapting Web Agents with Synthetic Supervision
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Web agents struggle to adapt to new websites due to the scarcity of environment specific tasks and demonstrations. Recent works have explored synthetic data generation to address this challenge, however, they suffer from data quality issues where synthesized tasks contain hallucinations that cannot be executed, and collected trajectories are noisy with redundant or misaligned actions. In this paper, we propose SynthAgent, a fully synthetic supervision framework that aims at improving synthetic data quality via dual refinement of both tasks and trajectories. Our approach begins by synthesizing diverse tasks through categorized exploration of web elements, ensuring efficient coverage of the target environment. During trajectory collection, we refine tasks when conflicts with actual observations are detected, mitigating hallucinations while maintaining task consistency. After collection, we conduct trajectory refinement with a global context to mitigate potential noise or misalignments. Finally, we fine-tune open-source web agents on the refined synthetic data to adapt them to the target environment. Experimental results demonstrate that SynthAgent outperforms existing synthetic data methods, validating the importance of high-quality synthetic supervision. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/SynthAgent.
GUI-360: A Comprehensive Dataset and Benchmark for Computer-Using Agents
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce GUI-360$^\circ$, a large-scale, comprehensive dataset and benchmark suite designed to advance computer-using agents (CUAs). CUAs present unique challenges and is constrained by three persistent gaps: a scarcity of real-world CUA tasks, the lack of automated collection-and-annotation pipelines for multi-modal trajectories, and the absence of a unified benchmark that jointly evaluates GUI grounding, screen parsing, and action prediction. GUI-360$^\circ$ addresses these gaps with an LLM-augmented, largely automated pipeline for query sourcing, environment-template construction, task instantiation, batched execution, and LLM-driven quality filtering. The released corpus contains over 1.2M executed action steps across thousands of trajectories in popular Windows office applications, and includes full-resolution screenshots, accessibility metadata when available, instantiated goals, intermediate reasoning traces, and both successful and failed action trajectories. The dataset supports three canonical tasks, GUI grounding, screen parsing, and action prediction, and a hybrid GUI+API action space that reflects modern agent designs. Benchmarking state-of-the-art vision--language models on GUI-360$^\circ$ reveals substantial out-of-the-box shortcomings in grounding and action prediction; supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning yield significant gains but do not close the gap to human-level reliability. We release GUI-360$^\circ$ and accompanying code to facilitate reproducible research and accelerate progress on robust desktop CUAs. The full dataset has been made public on https://huggingface.co/datasets/vyokky/GUI-360.
Attention Enhanced Entity Recommendation for Intelligent Monitoring in Cloud Systems
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present DiRecGNN, an attention-enhanced entity recommendation framework for monitoring cloud services at Microsoft. We provide insights on the usefulness of this feature as perceived by the cloud service owners and lessons learned from deployment. Specifically, we introduce the problem of recommending the optimal subset of attributes (dimensions) that should be tracked by an automated watchdog (monitor) for cloud services. To begin, we construct the monitor heterogeneous graph at production-scale. The interaction dynamics of these entities are often characterized by limited structural and engagement information, resulting in inferior performance of state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, traditional methods fail to capture the dependencies between entities spanning a long range due to their homophilic nature. Therefore, we propose an attention-enhanced entity ranking model inspired by transformer architectures. Our model utilizes a multi-head attention mechanism to focus on heterogeneous neighbors and their attributes, and further attends to paths sampled using random walks to capture long-range dependencies. We also employ multi-faceted loss functions to optimize for relevant recommendations while respecting the inherent sparsity of the data. Empirical evaluations demonstrate significant improvements over existing methods, with our model achieving a 43.1% increase in MRR. Furthermore, product teams who consumed these features perceive the feature as useful and rated it 4.5 out of 5.
LEGOMem: Modular Procedural Memory for Multi-agent LLM Systems for Workflow Automation
Oct 06, 2025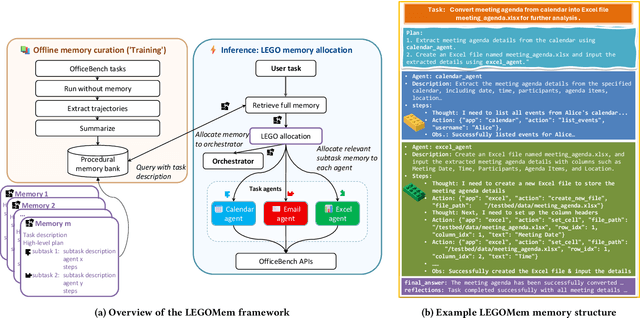
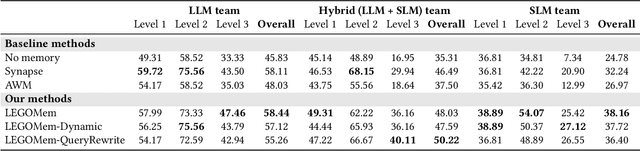
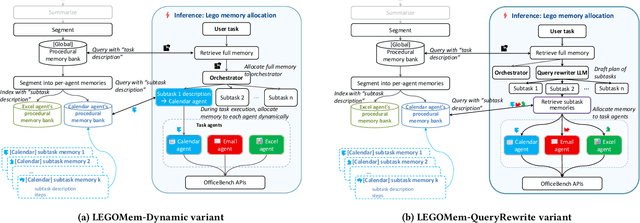
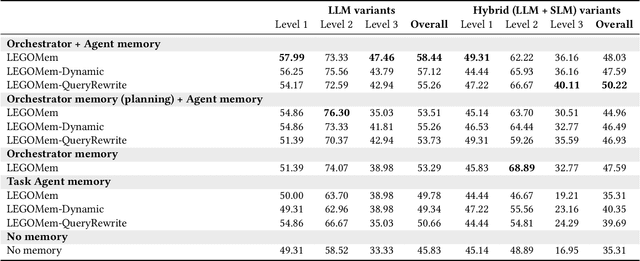
Abstract:We introduce LEGOMem, a modular procedural memory framework for multi-agent large language model (LLM) systems in workflow automation. LEGOMem decomposes past task trajectories into reusable memory units and flexibly allocates them across orchestrators and task agents to support planning and execution. To explore the design space of memory in multi-agent systems, we use LEGOMem as a lens and conduct a systematic study of procedural memory in multi-agent systems, examining where memory should be placed, how it should be retrieved, and which agents benefit most. Experiments on the OfficeBench benchmark show that orchestrator memory is critical for effective task decomposition and delegation, while fine-grained agent memory improves execution accuracy. We find that even teams composed of smaller language models can benefit substantially from procedural memory, narrowing the performance gap with stronger agents by leveraging prior execution traces for more accurate planning and tool use. These results position LEGOMem as both a practical framework for memory-augmented agent systems and a research tool for understanding memory design in multi-agent workflow automation.
ACON: Optimizing Context Compression for Long-horizon LLM Agents
Oct 01, 2025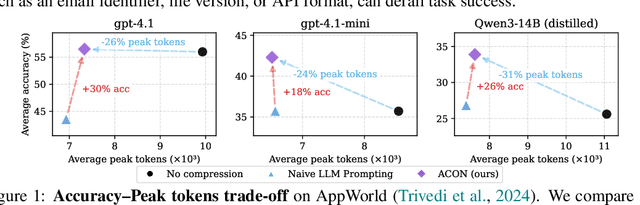
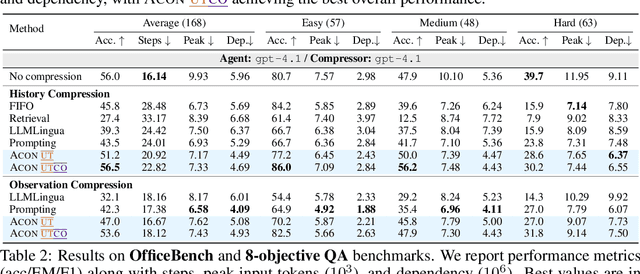
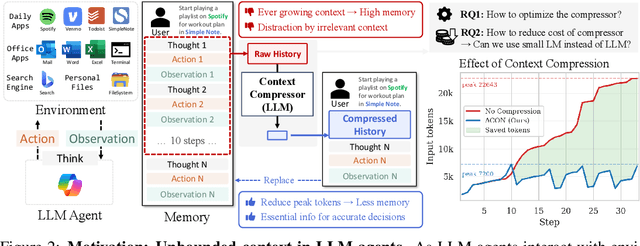
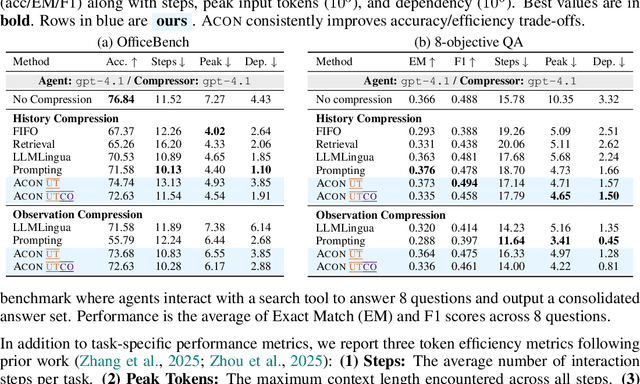
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as agents in dynamic, real-world environments, where success requires both reasoning and effective tool use. A central challenge for agentic tasks is the growing context length, as agents must accumulate long histories of actions and observations. This expansion raises costs and reduces efficiency in long-horizon tasks, yet prior work on context compression has mostly focused on single-step tasks or narrow applications. We introduce Agent Context Optimization (ACON), a unified framework that optimally compresses both environment observations and interaction histories into concise yet informative condensations. ACON leverages compression guideline optimization in natural language space: given paired trajectories where full context succeeds but compressed context fails, capable LLMs analyze the causes of failure, and the compression guideline is updated accordingly. Furthermore, we propose distilling the optimized LLM compressor into smaller models to reduce the overhead of the additional module. Experiments on AppWorld, OfficeBench, and Multi-objective QA show that ACON reduces memory usage by 26-54% (peak tokens) while largely preserving task performance, preserves over 95% of accuracy when distilled into smaller compressors, and enhances smaller LMs as long-horizon agents with up to 46% performance improvement.
OdysseyBench: Evaluating LLM Agents on Long-Horizon Complex Office Application Workflows
Aug 12, 2025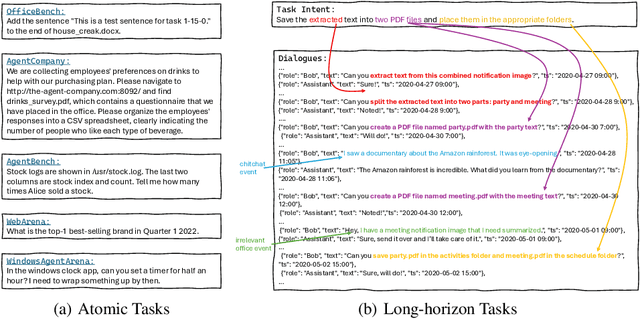
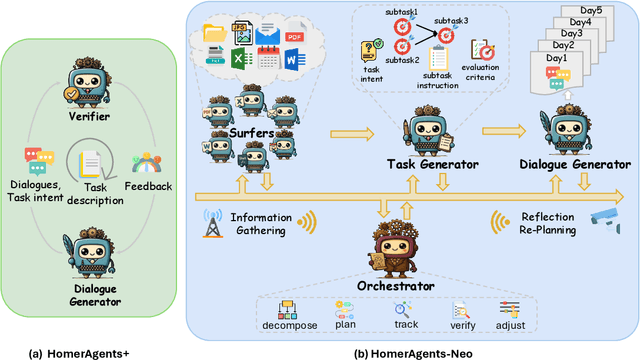
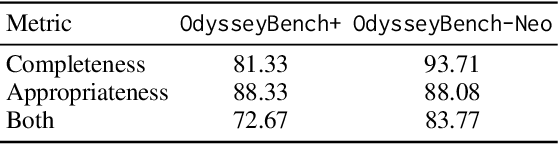
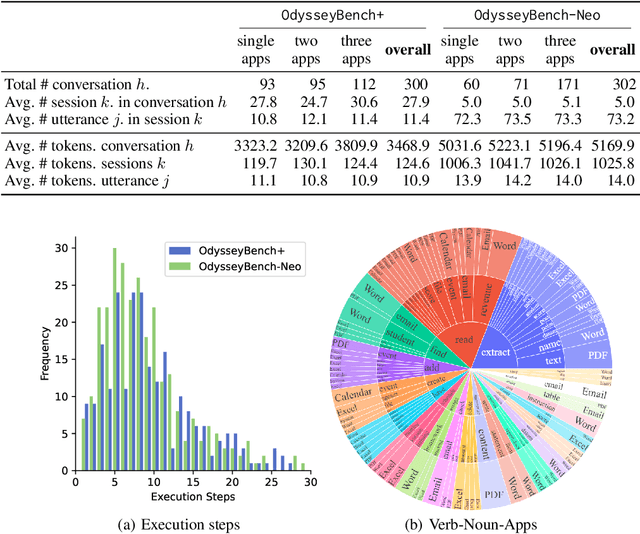
Abstract:Autonomous agents powered by large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications requiring complex, long-horizon workflows. However, existing benchmarks predominantly focus on atomic tasks that are self-contained and independent, failing to capture the long-term contextual dependencies and multi-interaction coordination required in realistic scenarios. To address this gap, we introduce OdysseyBench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLM agents on long-horizon workflows across diverse office applications including Word, Excel, PDF, Email, and Calendar. Our benchmark comprises two complementary splits: OdysseyBench+ with 300 tasks derived from real-world use cases, and OdysseyBench-Neo with 302 newly synthesized complex tasks. Each task requires agent to identify essential information from long-horizon interaction histories and perform multi-step reasoning across various applications. To enable scalable benchmark creation, we propose HomerAgents, a multi-agent framework that automates the generation of long-horizon workflow benchmarks through systematic environment exploration, task generation, and dialogue synthesis. Our extensive evaluation demonstrates that OdysseyBench effectively challenges state-of-the-art LLM agents, providing more accurate assessment of their capabilities in complex, real-world contexts compared to existing atomic task benchmarks. We believe that OdysseyBench will serve as a valuable resource for advancing the development and evaluation of LLM agents in real-world productivity scenarios. In addition, we release OdysseyBench and HomerAgents to foster research along this line.
AdaptFlow: Adaptive Workflow Optimization via Meta-Learning
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have sparked growing interest in agentic workflows, which are structured sequences of LLM invocations intended to solve complex tasks. However, existing approaches often rely on static templates or manually designed workflows, which limit adaptability to diverse tasks and hinder scalability. We propose AdaptFlow, a natural language-based meta-learning framework inspired by model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML). AdaptFlow learns a generalizable workflow initialization that enables rapid subtask-level adaptation. It employs a bi-level optimization scheme: the inner loop refines the workflow for a specific subtask using LLM-generated feedback, while the outer loop updates the shared initialization to perform well across tasks. This setup allows AdaptFlow to generalize effectively to unseen tasks by adapting the initialized workflow through language-guided modifications. Evaluated across question answering, code generation, and mathematical reasoning benchmarks, AdaptFlow consistently outperforms both manually crafted and automatically searched baselines, achieving state-of-the-art results with strong generalization across tasks and models. The source code and data are available at https://github.com/microsoft/DKI_LLM/tree/AdaptFlow/AdaptFlow.
Enhancing Reasoning Capabilities of Small Language Models with Blueprints and Prompt Template Search
Jun 10, 2025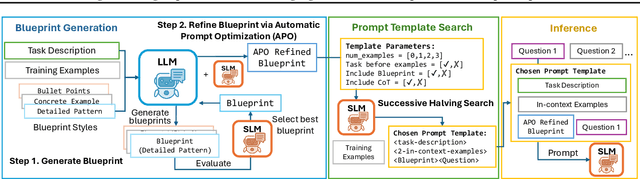
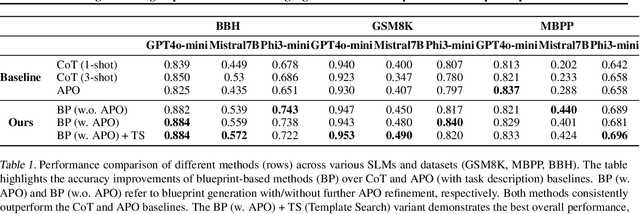
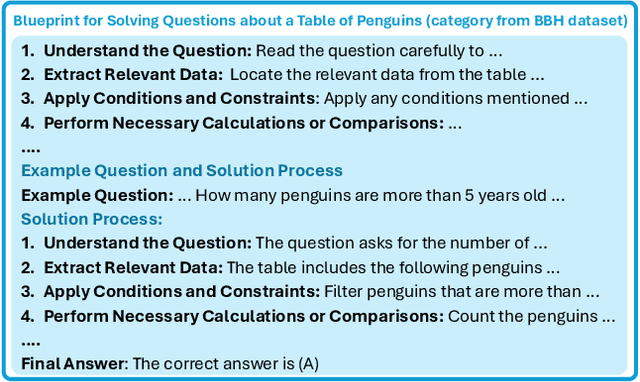
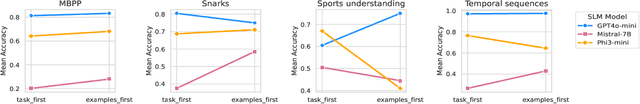
Abstract:Small language models (SLMs) offer promising and efficient alternatives to large language models (LLMs). However, SLMs' limited capacity restricts their reasoning capabilities and makes them sensitive to prompt variations. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework that enhances SLM reasoning capabilities through LLM generated blueprints. The blueprints provide structured, high-level reasoning guides that help SLMs systematically tackle related problems. Furthermore, our framework integrates a prompt template search mechanism to mitigate the SLMs' sensitivity to prompt variations. Our framework demonstrates improved SLM performance across various tasks, including math (GSM8K), coding (MBPP), and logic reasoning (BBH). Our approach improves the reasoning capabilities of SLMs without increasing model size or requiring additional training, offering a lightweight and deployment-friendly solution for on-device or resource-constrained environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge