Victor Ruhle
Memora: A Harmonic Memory Representation Balancing Abstraction and Specificity
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Agent memory systems must accommodate continuously growing information while supporting efficient, context-aware retrieval for downstream tasks. Abstraction is essential for scaling agent memory, yet it often comes at the cost of specificity, obscuring the fine-grained details required for effective reasoning. We introduce Memora, a harmonic memory representation that structurally balances abstraction and specificity. Memora organizes information via its primary abstractions that index concrete memory values and consolidate related updates into unified memory entries, while cue anchors expand retrieval access across diverse aspects of the memory and connect related memories. Building on this structure, we employ a retrieval policy that actively exploits these memory connections to retrieve relevant information beyond direct semantic similarity. Theoretically, we show that standard Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Knowledge Graph (KG)-based memory systems emerge as special cases of our framework. Empirically, Memora establishes a new state-of-the-art on the LoCoMo and LongMemEval benchmarks, demonstrating better retrieval relevance and reasoning effectiveness as memory scales.
Exploring How LLMs Capture and Represent Domain-Specific Knowledge
Apr 24, 2025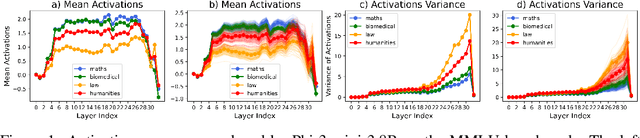

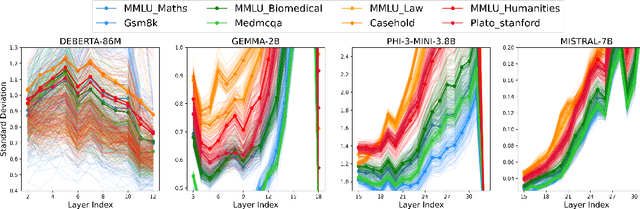

Abstract:We study whether Large Language Models (LLMs) inherently capture domain-specific nuances in natural language. Our experiments probe the domain sensitivity of LLMs by examining their ability to distinguish queries from different domains using hidden states generated during the prefill phase. We reveal latent domain-related trajectories that indicate the model's internal recognition of query domains. We also study the robustness of these domain representations to variations in prompt styles and sources. Our approach leverages these representations for model selection, mapping the LLM that best matches the domain trace of the input query (i.e., the model with the highest performance on similar traces). Our findings show that LLMs can differentiate queries for related domains, and that the fine-tuned model is not always the most accurate. Unlike previous work, our interpretations apply to both closed and open-ended generative tasks
TURBOATTENTION: Efficient Attention Approximation For High Throughputs LLMs
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Large language model (LLM) inference demands significant amount of computation and memory, especially in the key attention mechanism. While techniques, such as quantization and acceleration algorithms, like FlashAttention, have improved efficiency of the overall inference, they address different aspects of the problem: quantization focuses on weight-activation operations, while FlashAttention improves execution but requires high-precision formats. Recent Key-value (KV) cache quantization reduces memory bandwidth but still needs floating-point dequantization for attention operation. We present TurboAttention, a comprehensive approach to enable quantized execution of attention that simultaneously addresses both memory and computational efficiency. Our solution introduces two key innovations: FlashQ, a headwise attention quantization technique that enables both compression of KV cache and quantized execution of activation-activation multiplication, and Sparsity-based Softmax Approximation (SAS), which eliminates the need for dequantization to FP32 during exponentiation operation in attention. Experimental results demonstrate that TurboAttention achieves 1.2-1.8x speedup in attention, reduces the KV cache size by over 4.4x, and enables up to 2.37x maximum throughput over the FP16 baseline while outperforming state-of-the-art quantization and compression techniques across various datasets and models.
Hybrid LLM: Cost-Efficient and Quality-Aware Query Routing
Apr 22, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel in most NLP tasks but also require expensive cloud servers for deployment due to their size, while smaller models that can be deployed on lower cost (e.g., edge) devices, tend to lag behind in terms of response quality. Therefore in this work we propose a hybrid inference approach which combines their respective strengths to save cost and maintain quality. Our approach uses a router that assigns queries to the small or large model based on the predicted query difficulty and the desired quality level. The desired quality level can be tuned dynamically at test time to seamlessly trade quality for cost as per the scenario requirements. In experiments our approach allows us to make up to 40% fewer calls to the large model, with no drop in response quality.
Hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Real-time Composition Assistance
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:Retrieval augmented models show promise in enhancing traditional language models by improving their contextual understanding, integrating private data, and reducing hallucination. However, the processing time required for retrieval augmented large language models poses a challenge when applying them to tasks that require real-time responses, such as composition assistance. To overcome this limitation, we propose the Hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation (HybridRAG) framework that leverages a hybrid setting that combines both client and cloud models. HybridRAG incorporates retrieval-augmented memory generated asynchronously by a Large Language Model (LLM) in the cloud. By integrating this retrieval augmented memory, the client model acquires the capability to generate highly effective responses, benefiting from the LLM's capabilities. Furthermore, through asynchronous memory integration, the client model is capable of delivering real-time responses to user requests without the need to wait for memory synchronization from the cloud. Our experiments on Wikitext and Pile subsets show that HybridRAG achieves lower latency than a cloud-based retrieval-augmented LLM, while outperforming client-only models in utility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge