Fangkai Yang
NVIDIA Corporation
Closing the Loop: Universal Repository Representation with RPG-Encoder
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Current repository agents encounter a reasoning disconnect due to fragmented representations, as existing methods rely on isolated API documentation or dependency graphs that lack semantic depth. We consider repository comprehension and generation to be inverse processes within a unified cycle: generation expands intent into implementation, while comprehension compresses implementation back into intent. To address this, we propose RPG-Encoder, a framework that generalizes the Repository Planning Graph (RPG) from a static generative blueprint into a unified, high-fidelity representation. RPG-Encoder closes the reasoning loop through three mechanisms: (1) Encoding raw code into the RPG that combines lifted semantic features with code dependencies; (2) Evolving the topology incrementally to decouple maintenance costs from repository scale, reducing overhead by 95.7%; and (3) Operating as a unified interface for structure-aware navigation. In evaluations, RPG-Encoder establishes state-of-the-art localization performance on SWE-bench Verified with 93.7% Acc@5 and exceeds the best baseline by over 10% in localization accuracy on SWE-bench Live Lite. These results highlight our superior fine-grained precision in complex codebases. Furthermore, it achieves 98.5% reconstruction coverage on RepoCraft, confirming RPG's high-fidelity capacity to mirror the original codebase and closing the loop between intent and implementation.
AdaptFlow: Adaptive Workflow Optimization via Meta-Learning
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have sparked growing interest in agentic workflows, which are structured sequences of LLM invocations intended to solve complex tasks. However, existing approaches often rely on static templates or manually designed workflows, which limit adaptability to diverse tasks and hinder scalability. We propose AdaptFlow, a natural language-based meta-learning framework inspired by model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML). AdaptFlow learns a generalizable workflow initialization that enables rapid subtask-level adaptation. It employs a bi-level optimization scheme: the inner loop refines the workflow for a specific subtask using LLM-generated feedback, while the outer loop updates the shared initialization to perform well across tasks. This setup allows AdaptFlow to generalize effectively to unseen tasks by adapting the initialized workflow through language-guided modifications. Evaluated across question answering, code generation, and mathematical reasoning benchmarks, AdaptFlow consistently outperforms both manually crafted and automatically searched baselines, achieving state-of-the-art results with strong generalization across tasks and models. The source code and data are available at https://github.com/microsoft/DKI_LLM/tree/AdaptFlow/AdaptFlow.
RePrompt: Reasoning-Augmented Reprompting for Text-to-Image Generation via Reinforcement Learning
May 23, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress in text-to-image (T2I) generation, existing models often struggle to faithfully capture user intentions from short and under-specified prompts. While prior work has attempted to enhance prompts using large language models (LLMs), these methods frequently generate stylistic or unrealistic content due to insufficient grounding in visual semantics and real-world composition. Inspired by recent advances in reasoning for language model, we propose RePrompt, a novel reprompting framework that introduces explicit reasoning into the prompt enhancement process via reinforcement learning. Instead of relying on handcrafted rules or stylistic rewrites, our method trains a language model to generate structured, self-reflective prompts by optimizing for image-level outcomes. The tailored reward models assesse the generated images in terms of human preference, semantic alignment, and visual composition, providing indirect supervision to refine prompt generation. Our approach enables end-to-end training without human-annotated data. Experiments on GenEval and T2I-Compbench show that RePrompt significantly boosts spatial layout fidelity and compositional generalization across diverse T2I backbones, establishing new state-of-the-art results.
UFO2: The Desktop AgentOS
Apr 20, 2025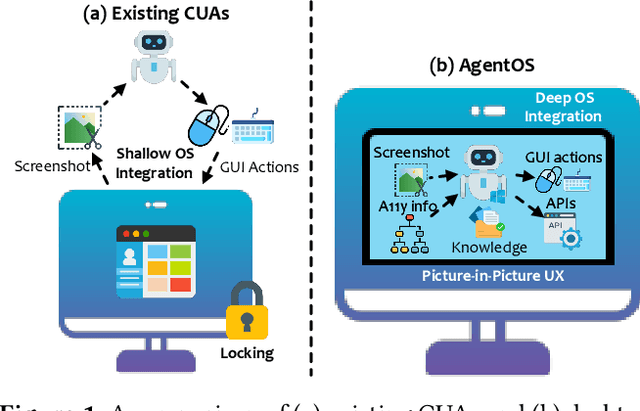
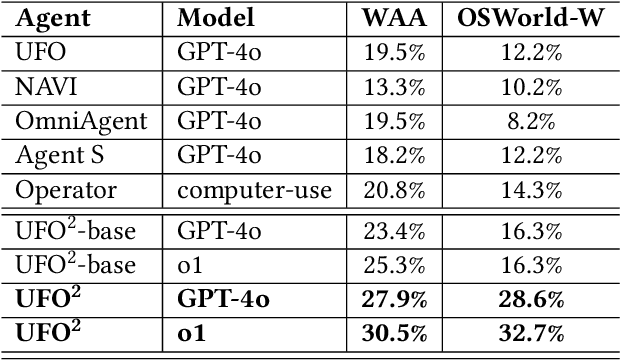
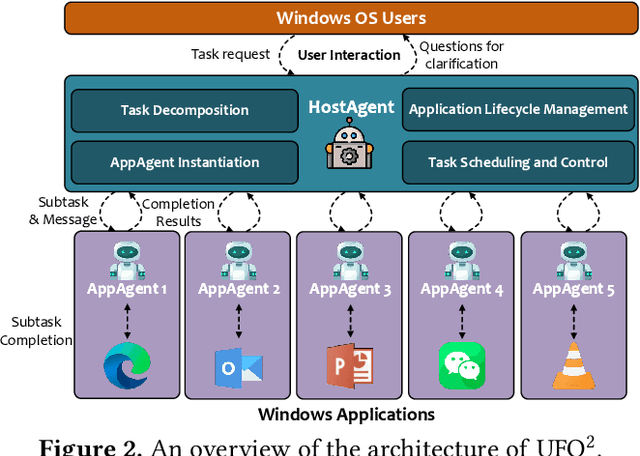
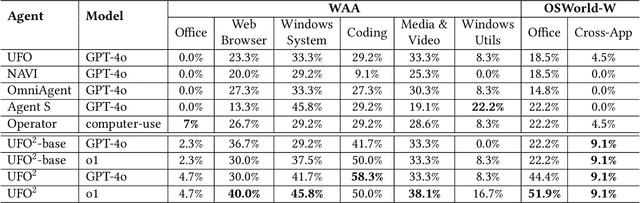
Abstract:Recent Computer-Using Agents (CUAs), powered by multimodal large language models (LLMs), offer a promising direction for automating complex desktop workflows through natural language. However, most existing CUAs remain conceptual prototypes, hindered by shallow OS integration, fragile screenshot-based interaction, and disruptive execution. We present UFO2, a multiagent AgentOS for Windows desktops that elevates CUAs into practical, system-level automation. UFO2 features a centralized HostAgent for task decomposition and coordination, alongside a collection of application-specialized AppAgent equipped with native APIs, domain-specific knowledge, and a unified GUI--API action layer. This architecture enables robust task execution while preserving modularity and extensibility. A hybrid control detection pipeline fuses Windows UI Automation (UIA) with vision-based parsing to support diverse interface styles. Runtime efficiency is further enhanced through speculative multi-action planning, reducing per-step LLM overhead. Finally, a Picture-in-Picture (PiP) interface enables automation within an isolated virtual desktop, allowing agents and users to operate concurrently without interference. We evaluate UFO2 across over 20 real-world Windows applications, demonstrating substantial improvements in robustness and execution accuracy over prior CUAs. Our results show that deep OS integration unlocks a scalable path toward reliable, user-aligned desktop automation.
VEM: Environment-Free Exploration for Training GUI Agent with Value Environment Model
Feb 26, 2025
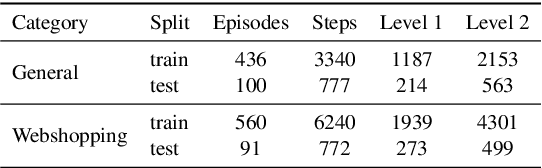
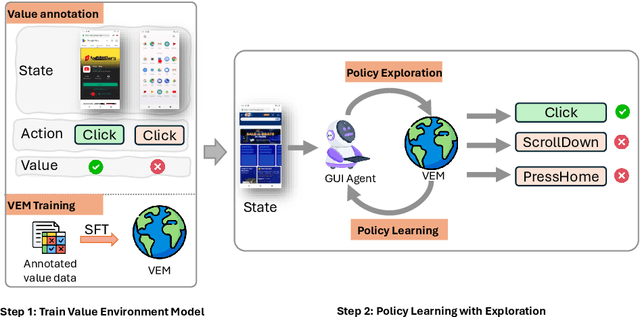

Abstract:Training Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) agents via Reinforcement Learning (RL) faces critical challenges: environment-based RL requires costly interactions, while environment-free methods struggle with distribution shift and reward generalization. We propose an environment-free RL framework that decouples value estimation from policy optimization by leveraging a pretrained Value Environment Model (VEM). VEM predicts state-action values directly from offline data, distilling human-like priors about GUI interaction outcomes without requiring next-state prediction or environmental feedback. This avoids compounding errors and enhances resilience to UI changes by focusing on semantic reasoning (e.g., Does this action advance the user's goal?). The framework operates in two stages: (1) pretraining VEM to estimate long-term action utilities and (2) guiding policy exploration with frozen VEM signals, enabling layout-agnostic GUI automation. Evaluated on Android-in-the-Wild benchmarks, VEM achieves state-of-the-art performance in both offline and online settings, outperforming environment-free baselines significantly and matching environment-based approaches without interaction costs. Importantly, VEM demonstrates that semantic-aware value estimation can achieve comparable performance with online-trained methods.
Lean and Mean: Decoupled Value Policy Optimization with Global Value Guidance
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)-based Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) is essential for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. It requires joint training of an actor and critic with a pretrained, fixed reward model for guidance. This approach increases computational complexity and instability due to actor-critic interdependence. Additionally, PPO lacks access to true environment rewards in LLM tasks, limiting its adaptability. Under such conditions, pretraining a value model or a reward model becomes equivalent, as both provide fixed supervisory signals without new ground-truth feedback. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{Decoupled Value Policy Optimization (DVPO)}, a lean framework that replaces traditional reward modeling with a pretrained \emph{global value model (GVM)}. The GVM is conditioned on policy trajectories and predicts token-level return-to-go estimates. By decoupling value model from policy training (via frozen GVM-driven RL objectives), DVPO eliminates actor-critic interdependence, reducing GPU memory usage by 40\% and training time by 35\% compared to conventional RLHF. Experiments across benchmarks show DVPO outperforms efficient RLHF methods (e.g., DPO) while matching state-of-the-art PPO in performance.
Enabling Autonomic Microservice Management through Self-Learning Agents
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:The increasing complexity of modern software systems necessitates robust autonomic self-management capabilities. While Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate potential in this domain, they often face challenges in adapting their general knowledge to specific service contexts. To address this limitation, we propose ServiceOdyssey, a self-learning agent system that autonomously manages microservices without requiring prior knowledge of service-specific configurations. By leveraging curriculum learning principles and iterative exploration, ServiceOdyssey progressively develops a deep understanding of operational environments, reducing dependence on human input or static documentation. A prototype built with the Sock Shop microservice demonstrates the potential of this approach for autonomic microservice management.
Skeleton-Guided-Translation: A Benchmarking Framework for Code Repository Translation with Fine-Grained Quality Evaluation
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:The advancement of large language models has intensified the need to modernize enterprise applications and migrate legacy systems to secure, versatile languages. However, existing code translation benchmarks primarily focus on individual functions, overlooking the complexities involved in translating entire repositories, such as maintaining inter-module coherence and managing dependencies. While some recent repository-level translation benchmarks attempt to address these challenges, they still face limitations, including poor maintainability and overly coarse evaluation granularity, which make them less developer-friendly. We introduce Skeleton-Guided-Translation, a framework for repository-level Java to C# code translation with fine-grained quality evaluation. It uses a two-step process: first translating the repository's structural "skeletons", then translating the full repository guided by these skeletons. Building on this, we present TRANSREPO-BENCH, a benchmark of high quality open-source Java repositories and their corresponding C# skeletons, including matching unit tests and build configurations. Our unit tests are fixed and can be applied across multiple or incremental translations without manual adjustments, enhancing automation and scalability in evaluations. Additionally, we develop fine-grained evaluation metrics that assess translation quality at the individual test case level, addressing traditional binary metrics' inability to distinguish when build failures cause all tests to fail. Evaluations using TRANSREPO-BENCH highlight key challenges and advance more accurate repository level code translation.
WarriorCoder: Learning from Expert Battles to Augment Code Large Language Models
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Despite recent progress achieved by code large language models (LLMs), their remarkable abilities are largely dependent on fine-tuning on the high-quality data, posing challenges for data collection and annotation. To address this, current methods often design various data flywheels to gather complex code instructions, enabling models to handle more intricate tasks. However, these approaches typically rely on off-the-shelf datasets and data augmentation from the limited pool of proprietary LLMs (e.g., Claude, GPT4, and so on), which limits the diversity of the constructed data and makes it prone to systemic biases. In this paper, we propose WarriorCoder which learns from expert battles to address these limitations. Specifically, we create an arena for current expert code LLMs, where each model challenges and responds to others' challenges, with evaluations conducted by uninvolved judge models. This competitive framework generates novel training data constructed from scratch, harnessing the strengths of all participants. Experimental results demonstrate that WarriorCoder achieves competitive performance compared to previous methods, even without relying on proprietary LLMs.
Large Action Models: From Inception to Implementation
Dec 13, 2024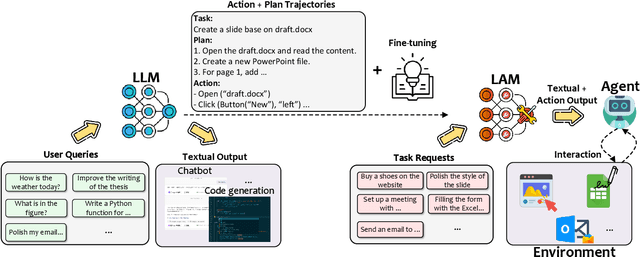

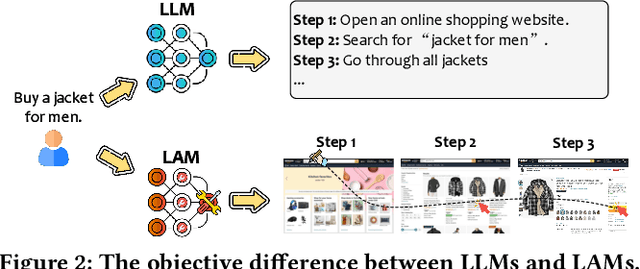

Abstract:As AI continues to advance, there is a growing demand for systems that go beyond language-based assistance and move toward intelligent agents capable of performing real-world actions. This evolution requires the transition from traditional Large Language Models (LLMs), which excel at generating textual responses, to Large Action Models (LAMs), designed for action generation and execution within dynamic environments. Enabled by agent systems, LAMs hold the potential to transform AI from passive language understanding to active task completion, marking a significant milestone in the progression toward artificial general intelligence. In this paper, we present a comprehensive framework for developing LAMs, offering a systematic approach to their creation, from inception to deployment. We begin with an overview of LAMs, highlighting their unique characteristics and delineating their differences from LLMs. Using a Windows OS-based agent as a case study, we provide a detailed, step-by-step guide on the key stages of LAM development, including data collection, model training, environment integration, grounding, and evaluation. This generalizable workflow can serve as a blueprint for creating functional LAMs in various application domains. We conclude by identifying the current limitations of LAMs and discussing directions for future research and industrial deployment, emphasizing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in realizing the full potential of LAMs in real-world applications. The code for the data collection process utilized in this paper is publicly available at: https://github.com/microsoft/UFO/tree/main/dataflow, and comprehensive documentation can be found at https://microsoft.github.io/UFO/dataflow/overview/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge