Yudi Zhang
ScribbleSense: Generative Scribble-Based Texture Editing with Intent Prediction
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Interactive 3D model texture editing presents enhanced opportunities for creating 3D assets, with freehand drawing style offering the most intuitive experience. However, existing methods primarily support sketch-based interactions for outlining, while the utilization of coarse-grained scribble-based interaction remains limited. Furthermore, current methodologies often encounter challenges due to the abstract nature of scribble instructions, which can result in ambiguous editing intentions and unclear target semantic locations. To address these issues, we propose ScribbleSense, an editing method that combines multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and image generation models to effectively resolve these challenges. We leverage the visual capabilities of MLLMs to predict the editing intent behind the scribbles. Once the semantic intent of the scribble is discerned, we employ globally generated images to extract local texture details, thereby anchoring local semantics and alleviating ambiguities concerning the target semantic locations. Experimental results indicate that our method effectively leverages the strengths of MLLMs, achieving state-of-the-art interactive editing performance for scribble-based texture editing.
C-TLSAN: Content-Enhanced Time-Aware Long- and Short-Term Attention Network for Personalized Recommendation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Sequential recommender systems aim to model users' evolving preferences by capturing patterns in their historical interactions. Recent advances in this area have leveraged deep neural networks and attention mechanisms to effectively represent sequential behaviors and time-sensitive interests. In this work, we propose C-TLSAN (Content-Enhanced Time-Aware Long- and Short-Term Attention Network), an extension of the TLSAN architecture that jointly models long- and short-term user preferences while incorporating semantic content associated with items, such as product descriptions. C-TLSAN enriches the recommendation pipeline by embedding textual content linked to users' historical interactions directly into both long-term and short-term attention layers. This allows the model to learn from both behavioral patterns and rich item content, enhancing user and item representations across temporal dimensions. By fusing sequential signals with textual semantics, our approach improves the expressiveness and personalization capacity of recommendation systems. We conduct extensive experiments on large-scale Amazon datasets, benchmarking C-TLSAN against state-of-the-art baselines, including recent sequential recommenders based on Large Language Models (LLMs), which represent interaction history and predictions in text form. Empirical results demonstrate that C-TLSAN consistently outperforms strong baselines in next-item prediction tasks. Notably, it improves AUC by 1.66%, Recall@10 by 93.99%, and Precision@10 by 94.80% on average over the best-performing baseline (TLSAN) across 10 Amazon product categories. These results highlight the value of integrating content-aware enhancements into temporal modeling frameworks for sequential recommendation. Our code is available at https://github.com/booml247/cTLSAN.
MiniCPM4: Ultra-Efficient LLMs on End Devices
Jun 09, 2025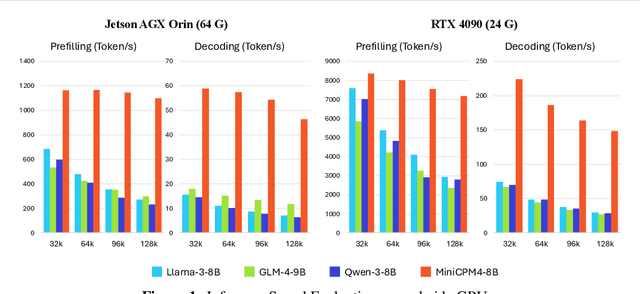

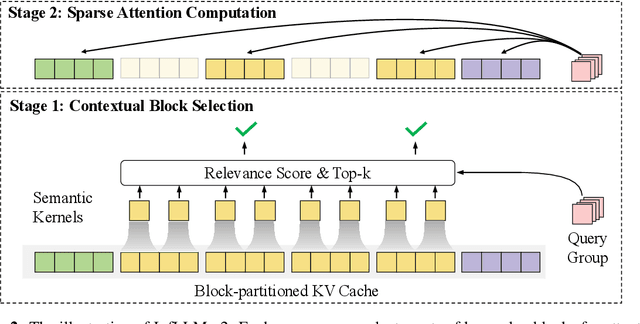
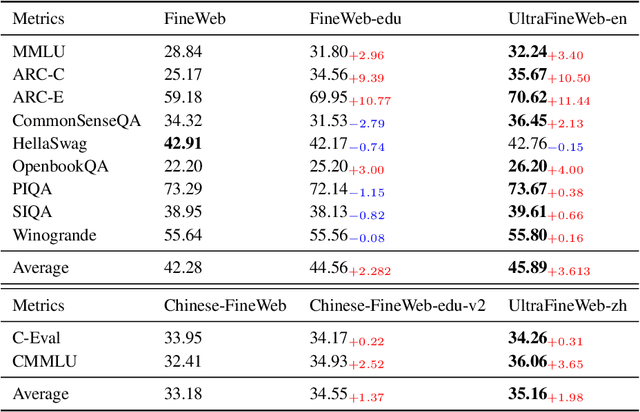
Abstract:This paper introduces MiniCPM4, a highly efficient large language model (LLM) designed explicitly for end-side devices. We achieve this efficiency through systematic innovation in four key dimensions: model architecture, training data, training algorithms, and inference systems. Specifically, in terms of model architecture, we propose InfLLM v2, a trainable sparse attention mechanism that accelerates both prefilling and decoding phases for long-context processing. Regarding training data, we propose UltraClean, an efficient and accurate pre-training data filtering and generation strategy, and UltraChat v2, a comprehensive supervised fine-tuning dataset. These datasets enable satisfactory model performance to be achieved using just 8 trillion training tokens. Regarding training algorithms, we propose ModelTunnel v2 for efficient pre-training strategy search, and improve existing post-training methods by introducing chunk-wise rollout for load-balanced reinforcement learning and data-efficient tenary LLM, BitCPM. Regarding inference systems, we propose CPM.cu that integrates sparse attention, model quantization, and speculative sampling to achieve efficient prefilling and decoding. To meet diverse on-device requirements, MiniCPM4 is available in two versions, with 0.5B and 8B parameters, respectively. Sufficient evaluation results show that MiniCPM4 outperforms open-source models of similar size across multiple benchmarks, highlighting both its efficiency and effectiveness. Notably, MiniCPM4-8B demonstrates significant speed improvements over Qwen3-8B when processing long sequences. Through further adaptation, MiniCPM4 successfully powers diverse applications, including trustworthy survey generation and tool use with model context protocol, clearly showcasing its broad usability.
Speculative Decoding Meets Quantization: Compatibility Evaluation and Hierarchical Framework Design
May 29, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding and quantization effectively accelerate memory-bound inference of large language models. Speculative decoding mitigates the memory bandwidth bottleneck by verifying multiple tokens within a single forward pass, which increases computational effort. Quantization achieves this optimization by compressing weights and activations into lower bit-widths and also reduces computations via low-bit matrix multiplications. To further leverage their strengths, we investigate the integration of these two techniques. Surprisingly, experiments applying the advanced speculative decoding method EAGLE-2 to various quantized models reveal that the memory benefits from 4-bit weight quantization are diminished by the computational load from speculative decoding. Specifically, verifying a tree-style draft incurs significantly more time overhead than a single-token forward pass on 4-bit weight quantized models. This finding led to our new speculative decoding design: a hierarchical framework that employs a small model as an intermediate stage to turn tree-style drafts into sequence drafts, leveraging the memory access benefits of the target quantized model. Experimental results show that our hierarchical approach achieves a 2.78$\times$ speedup across various tasks for the 4-bit weight Llama-3-70B model on an A100 GPU, outperforming EAGLE-2 by 1.31$\times$. Code available at https://github.com/AI9Stars/SpecMQuant.
Consistent Image Layout Editing with Diffusion Models
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Despite the great success of large-scale text-to-image diffusion models in image generation and image editing, existing methods still struggle to edit the layout of real images. Although a few works have been proposed to tackle this problem, they either fail to adjust the layout of images, or have difficulty in preserving visual appearance of objects after the layout adjustment. To bridge this gap, this paper proposes a novel image layout editing method that can not only re-arrange a real image to a specified layout, but also can ensure the visual appearance of the objects consistent with their appearance before editing. Concretely, the proposed method consists of two key components. Firstly, a multi-concept learning scheme is used to learn the concepts of different objects from a single image, which is crucial for keeping visual consistency in the layout editing. Secondly, it leverages the semantic consistency within intermediate features of diffusion models to project the appearance information of objects to the desired regions directly. Besides, a novel initialization noise design is adopted to facilitate the process of re-arranging the layout. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms previous works in both layout alignment and visual consistency for the task of image layout editing
Distill Not Only Data but Also Rewards: Can Smaller Language Models Surpass Larger Ones?
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Distilling large language models (LLMs) typically involves transferring the teacher model's responses through supervised fine-tuning (SFT). However, this approach neglects the potential to distill both data (output content) and reward signals (quality evaluations). Extracting reliable reward signals directly from teacher models is challenging, as LLMs are optimized for generation rather than evaluation, often resulting in biased or inconsistent assessments. To address this limitation, we propose a novel distillation pipeline that transfers both responses and rewards. Our method generates pseudo-rewards through a self-supervised mechanism that leverages the inherent structure of both teacher and student responses, enabling reward learning without explicit external evaluation. The reward model subsequently guides reinforcement learning (RL), allowing iterative refinement of the student model after an SFT warm-up phase. Experiments on GSM8K and MMLU-PRO demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms traditional SFT-based approaches, enabling student models to surpass the performance of their teachers. This work highlights the potential for scalable, efficient distillation through structured self-supervised reward learning, reducing dependence on external reward supervision.
FR-Spec: Accelerating Large-Vocabulary Language Models via Frequency-Ranked Speculative Sampling
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Speculative sampling has emerged as an important technique for accelerating the auto-regressive generation process of large language models (LLMs) by utilizing a draft-then-verify mechanism to produce multiple tokens per forward pass. While state-of-the-art speculative sampling methods use only a single layer and a language modeling (LM) head as the draft model to achieve impressive layer compression, their efficiency gains are substantially reduced for large-vocabulary LLMs, such as Llama-3-8B with a vocabulary of 128k tokens. To address this, we present FR-Spec, a frequency-ranked speculative sampling framework that optimizes draft candidate selection through vocabulary space compression. By constraining the draft search to a frequency-prioritized token subset, our method reduces LM Head computation overhead by 75% while ensuring the equivalence of the final output distribution. Experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate an average of 1.12$\times$ speedup over the state-of-the-art speculative sampling method EAGLE-2.
Large Action Models: From Inception to Implementation
Dec 13, 2024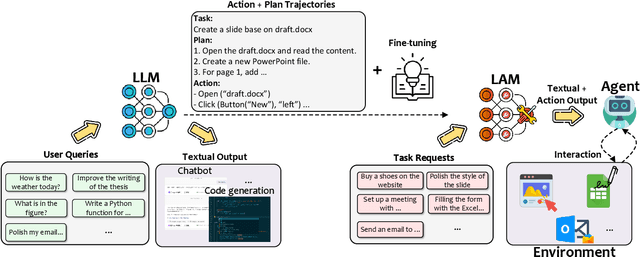

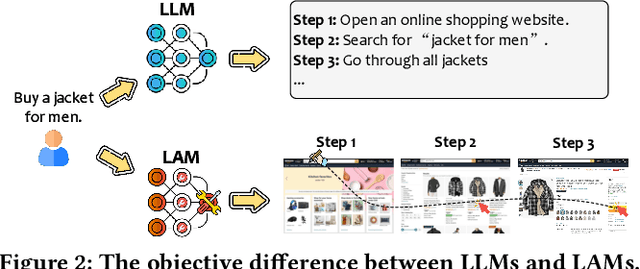

Abstract:As AI continues to advance, there is a growing demand for systems that go beyond language-based assistance and move toward intelligent agents capable of performing real-world actions. This evolution requires the transition from traditional Large Language Models (LLMs), which excel at generating textual responses, to Large Action Models (LAMs), designed for action generation and execution within dynamic environments. Enabled by agent systems, LAMs hold the potential to transform AI from passive language understanding to active task completion, marking a significant milestone in the progression toward artificial general intelligence. In this paper, we present a comprehensive framework for developing LAMs, offering a systematic approach to their creation, from inception to deployment. We begin with an overview of LAMs, highlighting their unique characteristics and delineating their differences from LLMs. Using a Windows OS-based agent as a case study, we provide a detailed, step-by-step guide on the key stages of LAM development, including data collection, model training, environment integration, grounding, and evaluation. This generalizable workflow can serve as a blueprint for creating functional LAMs in various application domains. We conclude by identifying the current limitations of LAMs and discussing directions for future research and industrial deployment, emphasizing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in realizing the full potential of LAMs in real-world applications. The code for the data collection process utilized in this paper is publicly available at: https://github.com/microsoft/UFO/tree/main/dataflow, and comprehensive documentation can be found at https://microsoft.github.io/UFO/dataflow/overview/.
RuAG: Learned-rule-augmented Generation for Large Language Models
Nov 04, 2024

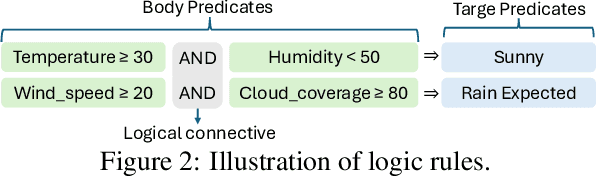

Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) have gained attention for their ability to enhance LLMs' reasoning by incorporating external knowledge but suffer from limited contextual window size, leading to insufficient information injection. To this end, we propose a novel framework, RuAG, to automatically distill large volumes of offline data into interpretable first-order logic rules, which are injected into LLMs to boost their reasoning capabilities. Our method begins by formulating the search process relying on LLMs' commonsense, where LLMs automatically define head and body predicates. Then, RuAG applies Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to address the combinational searching space and efficiently discover logic rules from data. The resulting logic rules are translated into natural language, allowing targeted knowledge injection and seamless integration into LLM prompts for LLM's downstream task reasoning. We evaluate our framework on public and private industrial tasks, including natural language processing, time-series, decision-making, and industrial tasks, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing LLM's capability over diverse tasks.
Enabling Real-Time Conversations with Minimal Training Costs
Sep 18, 2024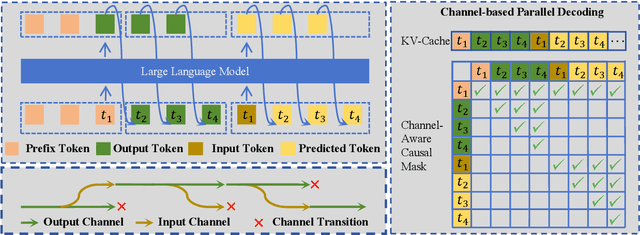
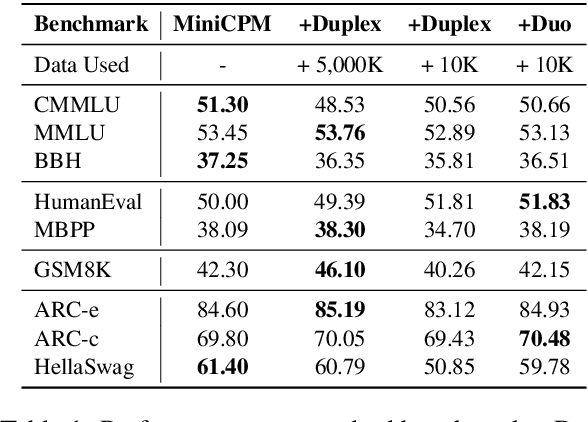
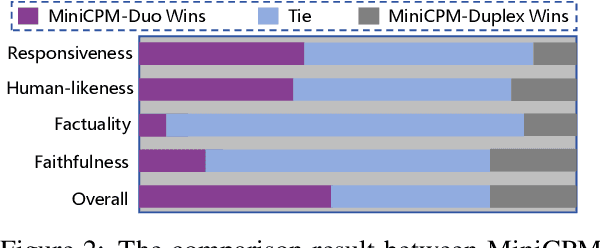
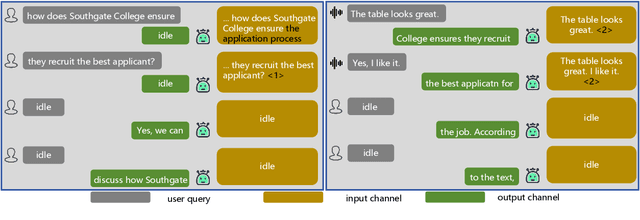
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated the ability to improve human efficiency through conversational interactions. Conventional LLM-powered dialogue systems, operating on a turn-based paradigm, preclude real-time interaction during response generation. To address this limitation, researchers have proposed duplex models. These models can dynamically adapt to user input, facilitating real-time interactive feedback. However, these methods typically require substantial computational resources to acquire the ability. To reduce overhead, this paper presents a new duplex decoding approach that enhances LLMs with duplex ability, requiring minimal additional training. Specifically, our method employs parallel decoding of queries and responses in conversations, effectively implementing a channel-division-multiplexing decoding strategy. Experimental results indicate that our proposed method significantly enhances the naturalness and human-likeness of user-AI interactions with minimal training costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge