Pei Xiao
Secure Intellicise Wireless Network: Agentic AI for Coverless Semantic Steganography Communication
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Semantic Communication (SemCom), leveraging its significant advantages in transmission efficiency and reliability, has emerged as a core technology for constructing future intellicise (intelligent and concise) wireless networks. However, intelligent attacks represented by semantic eavesdropping pose severe challenges to the security of SemCom. To address this challenge, Semantic Steganographic Communication (SemSteCom) achieves ``invisible'' encryption by implicitly embedding private semantic information into cover modality carriers. The state-of-the-art study has further introduced generative diffusion models to directly generate stega images without relying on original cover images, effectively enhancing steganographic capacity. Nevertheless, the recovery process of private images is highly dependent on the guidance of private semantic keys, which may be inferred by intelligent eavesdroppers, thereby introducing new security threats. To address this issue, we propose an Agentic AI-driven SemSteCom (AgentSemSteCom) scheme, which includes semantic extraction, digital token controlled reference image generation, coverless steganography, semantic codec, and optional task-oriented enhancement modules. The proposed AgentSemSteCom scheme obviates the need for both cover images and private semantic keys, thereby boosting steganographic capacity while reinforcing transmission security. The simulation results on open-source datasets verify that, AgentSemSteCom achieves better transmission quality and higher security levels than the baseline scheme.
Large Artificial Intelligence Models for Future Wireless Communications
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:The anticipated integration of large artificial intelligence (AI) models with wireless communications is estimated to usher a transformative wave in the forthcoming information age. As wireless networks grow in complexity, the traditional methodologies employed for optimization and management face increasingly challenges. Large AI models have extensive parameter spaces and enhanced learning capabilities and can offer innovative solutions to these challenges. They are also capable of learning, adapting and optimizing in real-time. We introduce the potential and challenges of integrating large AI models into wireless communications, highlighting existing AIdriven applications and inherent challenges for future large AI models. In this paper, we propose the architecture of large AI models for future wireless communications, introduce their advantages in data analysis, resource allocation and real-time adaptation, discuss the potential challenges and corresponding solutions of energy, architecture design, privacy, security, ethical and regulatory. In addition, we explore the potential future directions of large AI models in wireless communications, laying the groundwork for forthcoming research in this area.
Hypothesize-Then-Verify: Speculative Root Cause Analysis for Microservices with Pathwise Parallelism
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Microservice systems have become the backbone of cloud-native enterprise applications due to their resource elasticity, loosely coupled architecture, and lightweight deployment. Yet, the intrinsic complexity and dynamic runtime interactions of such systems inevitably give rise to anomalies. Ensuring system reliability therefore hinges on effective root cause analysis (RCA), which entails not only localizing the source of anomalies but also characterizing the underlying failures in a timely and interpretable manner. Recent advances in intelligent RCA techniques, particularly those powered by large language models (LLMs), have demonstrated promising capabilities, as LLMs reduce reliance on handcrafted features while offering cross-platform adaptability, task generalization, and flexibility. However, existing LLM-based methods still suffer from two critical limitations: (a) limited exploration diversity, which undermines accuracy, and (b) heavy dependence on large-scale LLMs, which results in slow inference. To overcome these challenges, we propose SpecRCA, a speculative root cause analysis framework for microservices that adopts a \textit{hypothesize-then-verify} paradigm. SpecRCA first leverages a hypothesis drafting module to rapidly generate candidate root causes, and then employs a parallel root cause verifier to efficiently validate them. Preliminary experiments on the AIOps 2022 dataset demonstrate that SpecRCA achieves superior accuracy and efficiency compared to existing approaches, highlighting its potential as a practical solution for scalable and interpretable RCA in complex microservice environments.
Semantic Transmission Framework in Direct Satellite Communications
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Insufficient link budget has become a bottleneck problem for direct access in current satellite communications. In this paper, we develop a semantic transmission framework for direct satellite communications as an effective and viable solution to tackle this problem. To measure the tradeoffs between communication, computation, and generation quality, we introduce a semantic efficiency metric with optimized weights. The optimization aims to maximize the average semantic efficiency metric by jointly optimizing transmission mode selection, satellite-user association, ISL task migration, denoising steps, and adaptive weights, which is a complex nonlinear integer programming problem. To maximize the average semantic efficiency metric, we propose a decision-assisted REINFORCE++ algorithm that utilizes feasibility-aware action space and a critic-free stabilized policy update. Numerical results show that the proposed algorithm achieves higher semantic efficiency than baselines.
Ultra-Massive MIMO with Orthogonal Chirp Division Multiplexing for Near-Field Sensing and Communication Integration
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:This paper integrates the emerging ultra-massive multiple-input multiple-output (UM-MIMO) technique with orthogonal chirp division multiplexing (OCDM) waveform to tackle the challenging near-field integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) problem. Specifically, we conceive a comprehensive ISAC architecture, where an UM-MIMO base station adopts OCDM waveform for communications and a co-located sensing receiver adopts the frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) detection principle to simplify the associated hardware. For sensing tasks, several OCDM subcarriers, namely, dedicated sensing subcarriers (DSSs), are each transmitted through a dedicated sensing antenna (DSA) within the transmit antenna array. By judiciously designing the DSS selection scheme and optimizing receiver parameters, the FMCW-based sensing receiver can decouple the echo signals from different DSAs with significantly reduced hardware complexity. This setup enables the estimation of ranges and velocities of near-field targets in an antenna-pairwise manner. Moreover, by leveraging the spatial diversity of UM-MIMO, we introduce the concept of virtual bistatic sensing (VIBS), which incorporates the estimates from multiple antenna pairs to achieve high-accuracy target positioning and three-dimensional velocity measurement. The VIBS paradigm is immune to hostile channel environments characterized by spatial non-stationarity and uncorrelated multipath environment. Furthermore, the channel estimation of UM-MIMO OCDM systems enhanced by the sensing results is investigated. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed ISAC scheme enhances sensing accuracy, and also benefits communication performance.
A Secure Affine Frequency Division Multiplexing for Wireless Communication Systems
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) has garnered significant attention due to its superior performance in high-mobility scenarios, coupled with multiple waveform parameters that provide greater degrees of freedom for system design. This paper introduces a novel secure affine frequency division multiplexing (SE-AFDM) system, which advances prior designs by dynamically varying an AFDM pre-chirp parameter to enhance physical-layer security. In the SE-AFDM system, the pre-chirp parameter is dynamically generated from a codebook controlled by a long-period pseudo-noise (LPPN) sequence. Instead of applying spreading in the data domain, our parameter-domain spreading approach provides additional security while maintaining reliability and high spectrum efficiency. We also propose a synchronization framework to solve the problem of reliably and rapidly synchronizing the time-varying parameter in fast time-varying channels. The theoretical derivations prove that unsynchronized eavesdroppers cannot eliminate the nonlinear impact of the time-varying parameter and further provide useful guidance for codebook design. Simulation results demonstrate the security advantages of the proposed SE-AFDM system in high-mobility scenarios, while our hardware prototype validates the effectiveness of the proposed synchronization framework.
A Survey on Parallel Text Generation: From Parallel Decoding to Diffusion Language Models
Aug 12, 2025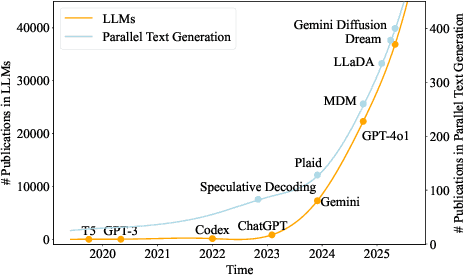
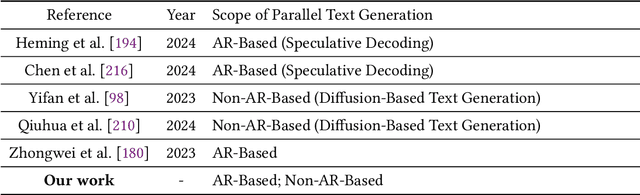
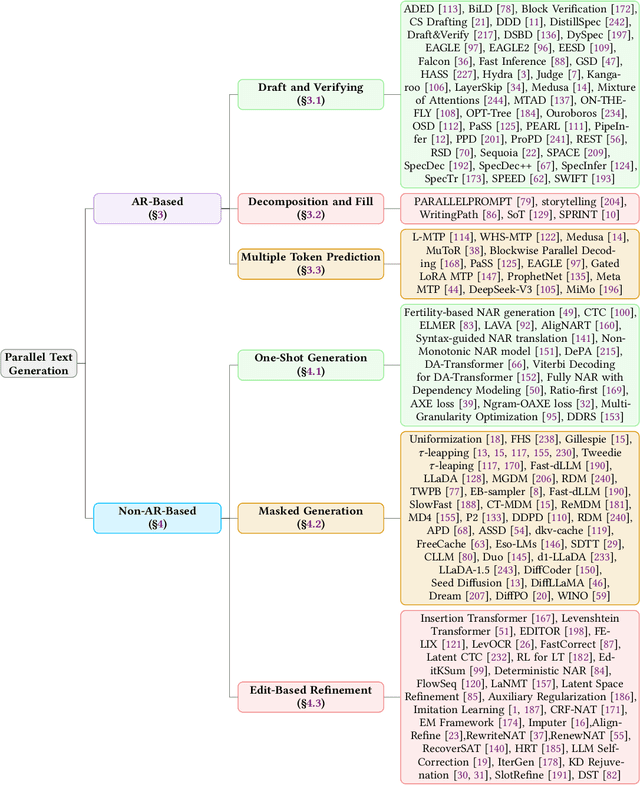
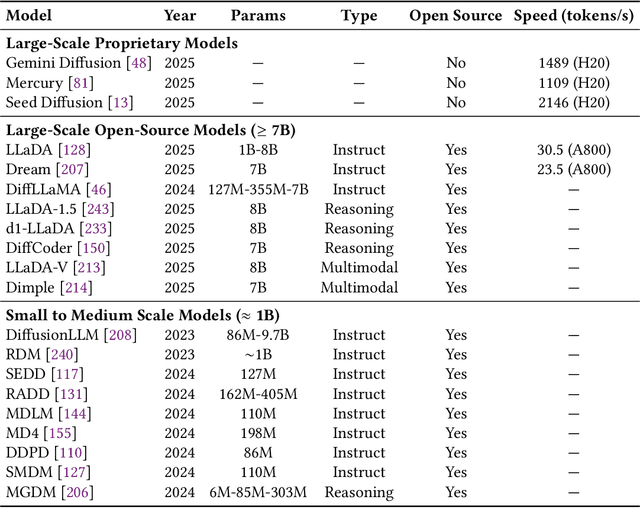
Abstract:As text generation has become a core capability of modern Large Language Models (LLMs), it underpins a wide range of downstream applications. However, most existing LLMs rely on autoregressive (AR) generation, producing one token at a time based on previously generated context-resulting in limited generation speed due to the inherently sequential nature of the process. To address this challenge, an increasing number of researchers have begun exploring parallel text generation-a broad class of techniques aimed at breaking the token-by-token generation bottleneck and improving inference efficiency. Despite growing interest, there remains a lack of comprehensive analysis on what specific techniques constitute parallel text generation and how they improve inference performance. To bridge this gap, we present a systematic survey of parallel text generation methods. We categorize existing approaches into AR-based and Non-AR-based paradigms, and provide a detailed examination of the core techniques within each category. Following this taxonomy, we assess their theoretical trade-offs in terms of speed, quality, and efficiency, and examine their potential for combination and comparison with alternative acceleration strategies. Finally, based on our findings, we highlight recent advancements, identify open challenges, and outline promising directions for future research in parallel text generation.
Joint Beamforming and Position Optimization for Fluid STAR-RIS-NOMA Assisted Wireless Communication Systems
Jul 09, 2025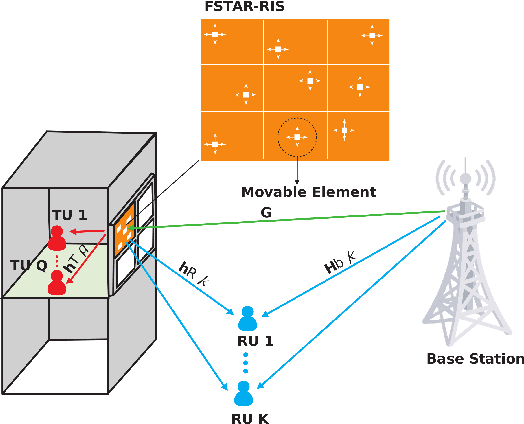
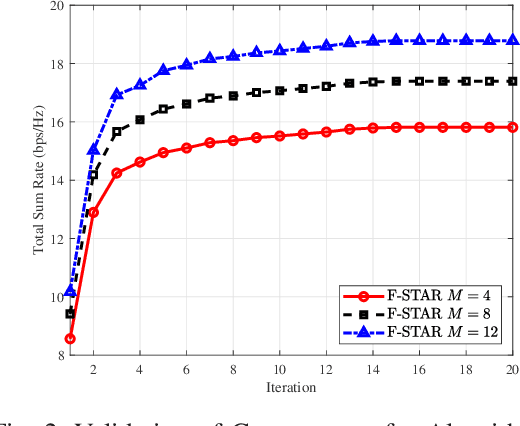
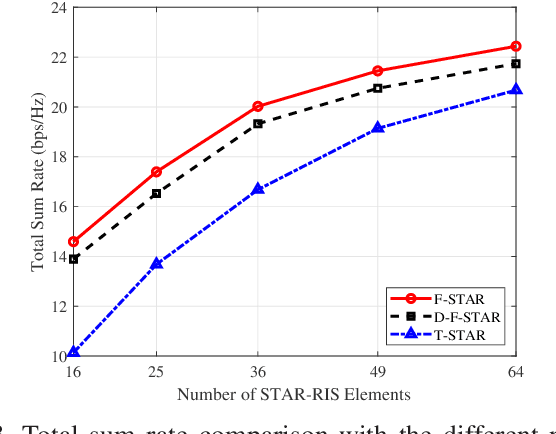
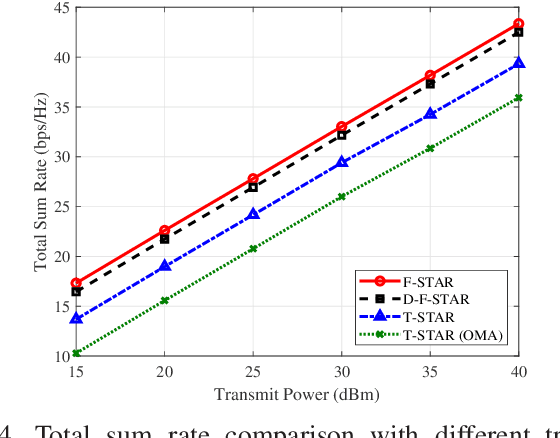
Abstract:To address the limitations of traditional reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) in spatial control capability, this paper introduces the concept of the fluid antenna system (FAS) and proposes a fluid simultaneously transmitting and reflecting RIS (FSTAR-RIS) assisted non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) multi-user communication system. In this system, each FSTAR-RIS element is capable of flexible mobility and can dynamically adjust its position in response to environmental variations, thereby enabling simultaneous service to users in both the transmission and reflection zones. This significantly enhances the system's spatial degrees of freedom (DoF) and service adaptability. To maximize the system's weighted sum-rate, we formulate a non-convex optimization problem that jointly optimizes the base station beamforming, the transmission/reflection coefficients of the FSTAR-RIS, and the element positions. An alternating optimization (AO) algorithm is developed, incorporating successive convex approximation (SCA), semi-definite relaxation (SDR), and majorization-minimization (MM) techniques. In particular, to address the complex channel coupling introduced by the coexistence of direct and FSTAR-RIS paths, the MM framework is employed in the element position optimization subproblem, enabling an efficient iterative solution strategy. Simulation results validate that the proposed system achieves up to a 27% increase in total sum rate compared to traditional STAR-RIS systems and requires approximately 50% fewer RIS elements to attain the same performance, highlighting its effectiveness for cost-efficient large-scale deployment.
Terahertz Chip-Scale Meta-Networks with LSPR Routing: A Theoretical Framework
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Efficient chip-scale interconnects are essential for modern microelectronic-photonic systems, supporting high bandwidth and low-latency processing. Traditional wired links face high resistivity and latency, while millimeter-wave wireless solutions suffer from bandwidth congestion and interference. Terahertz (THz) plasmonic communication, based on surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), offers high data rates and broad bandwidth, and is compatible with nanophotonic platforms. This work introduces a Binary Field-Driven Meta-Routing Method supported by a semi-analytical framework that models the tunable interaction between THz plasmonic phenomena and graphene's electromagnetic properties. By modulating graphene's impedance, the method enables dynamic coupling and routing of localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) across a meta-network, facilitating real-time beam steering in chip-scale systems. Combining analytical conductivity models, coupled-mode theory, and algorithmic control, the approach enables predictive configuration of LSPR-based steering in reconfigurable graphene metasurfaces. Four meta-pixel antenna configurations Y-MetaRouter, MetaSwitcher, Penta-MetaEmitter, and CP-MetaCore are designed to support unidirectional radiation, bi-directional steering, frequency-driven transitions, and circular polarization, respectively. Chemical potential modulation creates reconfigurable LSPR pathways and virtual SPP channels. A Coupled-Mode Theory for Field-Driven LSPR Meta-Networks is proposed to model current distributions and predict far-field characteristics. Results show strong agreement between theory and full-wave simulations. A point-to-point meta-wireless link is analyzed, demonstrating scalability for low-latency, high-performance THz communication in WiNoC and chiplet applications. System-level metrics confirm feasibility for space-constrained, high-speed interconnects.
Widely Linear Augmented Extreme Learning Machine Based Impairments Compensation for Satellite Communications
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Satellite communications are crucial for the evolution beyond fifth-generation networks. However, the dynamic nature of satellite channels and their inherent impairments present significant challenges. In this paper, a novel post-compensation scheme that combines the complex-valued extreme learning machine with augmented hidden layer (CELMAH) architecture and widely linear processing (WLP) is developed to address these issues by exploiting signal impropriety in satellite communications. Although CELMAH shares structural similarities with WLP, it employs a different core algorithm and does not fully exploit the signal impropriety. By incorporating WLP principles, we derive a tailored formulation suited to the network structure and propose the CELM augmented by widely linear least squares (CELM-WLLS) for post-distortion. The proposed approach offers enhanced communication robustness and is highly effective for satellite communication scenarios characterized by dynamic channel conditions and non-linear impairments. CELM-WLLS is designed to improve signal recovery performance and outperform traditional methods such as least square (LS) and minimum mean square error (MMSE). Compared to CELMAH, CELM-WLLS demonstrates approximately 0.8 dB gain in BER performance, and also achieves a two-thirds reduction in computational complexity, making it a more efficient solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge