Xuyang Chen
Driving with DINO: Vision Foundation Features as a Unified Bridge for Sim-to-Real Generation in Autonomous Driving
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Driven by the emergence of Controllable Video Diffusion, existing Sim2Real methods for autonomous driving video generation typically rely on explicit intermediate representations to bridge the domain gap. However, these modalities face a fundamental Consistency-Realism Dilemma. Low-level signals (e.g., edges, blurred images) ensure precise control but compromise realism by "baking in" synthetic artifacts, whereas high-level priors (e.g., depth, semantics, HDMaps) facilitate photorealism but lack the structural detail required for consistent guidance. In this work, we present Driving with DINO (DwD), a novel framework that leverages Vision Foundation Module (VFM) features as a unified bridge between the simulation and real-world domains. We first identify that these features encode a spectrum of information, from high-level semantics to fine-grained structure. To effectively utilize this, we employ Principal Subspace Projection to discard the high-frequency elements responsible for "texture baking," while concurrently introducing Random Channel Tail Drop to mitigate the structural loss inherent in rigid dimensionality reduction, thereby reconciling realism with control consistency. Furthermore, to fully leverage DINOv3's high-resolution capabilities for enhancing control precision, we introduce a learnable Spatial Alignment Module that adapts these high-resolution features to the diffusion backbone. Finally, we propose a Causal Temporal Aggregator employing causal convolutions to explicitly preserve historical motion context when integrating frame-wise DINO features, which effectively mitigates motion blur and guarantees temporal stability. Project page: https://albertchen98.github.io/DwD-project/
Semantic Transmission Framework in Direct Satellite Communications
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Insufficient link budget has become a bottleneck problem for direct access in current satellite communications. In this paper, we develop a semantic transmission framework for direct satellite communications as an effective and viable solution to tackle this problem. To measure the tradeoffs between communication, computation, and generation quality, we introduce a semantic efficiency metric with optimized weights. The optimization aims to maximize the average semantic efficiency metric by jointly optimizing transmission mode selection, satellite-user association, ISL task migration, denoising steps, and adaptive weights, which is a complex nonlinear integer programming problem. To maximize the average semantic efficiency metric, we propose a decision-assisted REINFORCE++ algorithm that utilizes feasibility-aware action space and a critic-free stabilized policy update. Numerical results show that the proposed algorithm achieves higher semantic efficiency than baselines.
Data Fusion-Enhanced Decision Transformer for Stable Cross-Domain Generalization
Nov 12, 2025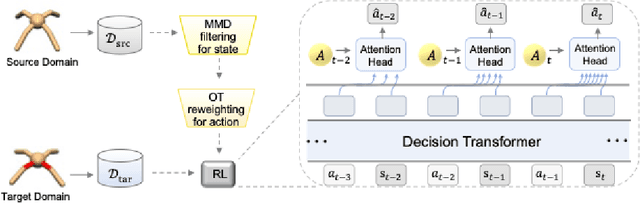
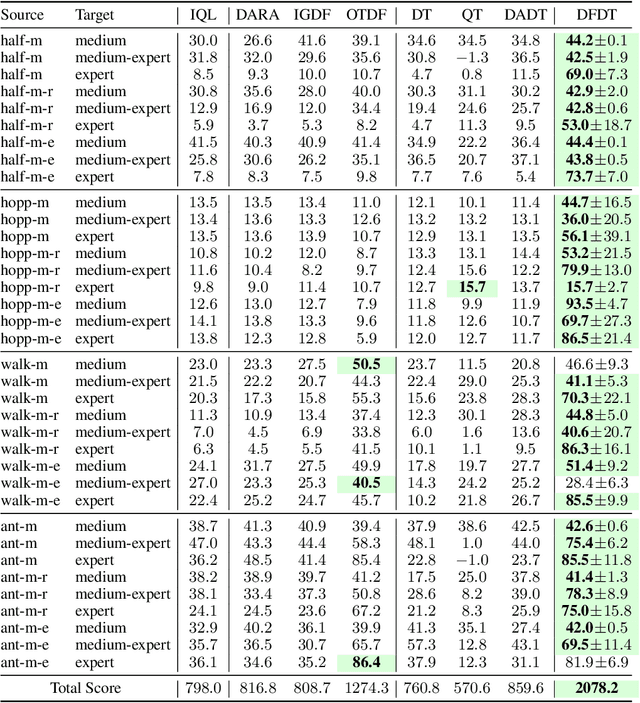
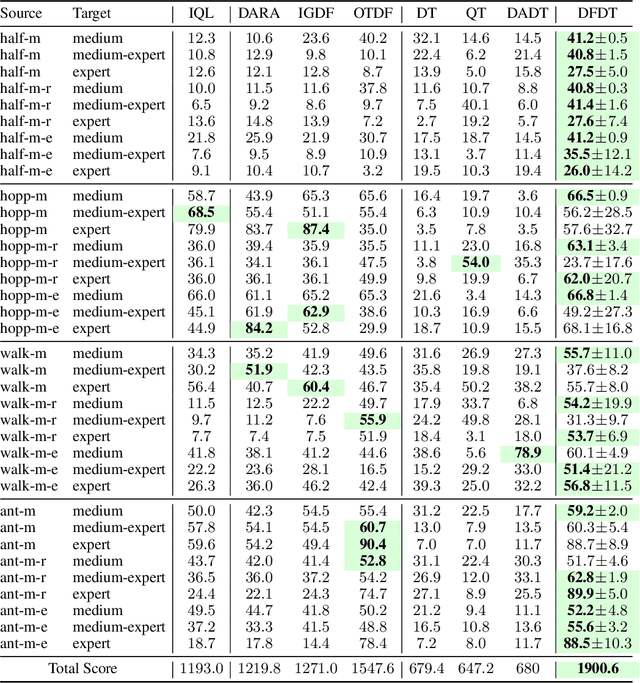
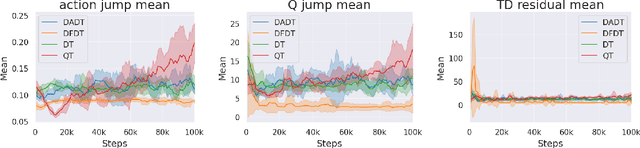
Abstract:Cross-domain shifts present a significant challenge for decision transformer (DT) policies. Existing cross-domain policy adaptation methods typically rely on a single simple filtering criterion to select source trajectory fragments and stitch them together. They match either state structure or action feasibility. However, the selected fragments still have poor stitchability: state structures can misalign, the return-to-go (RTG) becomes incomparable when the reward or horizon changes, and actions may jump at trajectory junctions. As a result, RTG tokens lose continuity, which compromises DT's inference ability. To tackle these challenges, we propose Data Fusion-Enhanced Decision Transformer (DFDT), a compact pipeline that restores stitchability. Particularly, DFDT fuses scarce target data with selectively trusted source fragments via a two-level data filter, maximum mean discrepancy (MMD) mismatch for state-structure alignment, and optimal transport (OT) deviation for action feasibility. It then trains on a feasibility-weighted fusion distribution. Furthermore, DFDT replaces RTG tokens with advantage-conditioned tokens, which improves the continuity of the semantics in the token sequence. It also applies a $Q$-guided regularizer to suppress junction value and action jumps. Theoretically, we provide bounds that tie state value and policy performance gaps to the MMD-mismatch and OT-deviation measures, and show that the bounds tighten as these two measures shrink. We show that DFDT improves return and stability over strong offline RL and sequence-model baselines across gravity, kinematic, and morphology shifts on D4RL-style control tasks, and further corroborate these gains with token-stitching and sequence-semantics stability analyses.
MeSS: City Mesh-Guided Outdoor Scene Generation with Cross-View Consistent Diffusion
Aug 21, 2025Abstract:Mesh models have become increasingly accessible for numerous cities; however, the lack of realistic textures restricts their application in virtual urban navigation and autonomous driving. To address this, this paper proposes MeSS (Meshbased Scene Synthesis) for generating high-quality, styleconsistent outdoor scenes with city mesh models serving as the geometric prior. While image and video diffusion models can leverage spatial layouts (such as depth maps or HD maps) as control conditions to generate street-level perspective views, they are not directly applicable to 3D scene generation. Video diffusion models excel at synthesizing consistent view sequences that depict scenes but often struggle to adhere to predefined camera paths or align accurately with rendered control videos. In contrast, image diffusion models, though unable to guarantee cross-view visual consistency, can produce more geometry-aligned results when combined with ControlNet. Building on this insight, our approach enhances image diffusion models by improving cross-view consistency. The pipeline comprises three key stages: first, we generate geometrically consistent sparse views using Cascaded Outpainting ControlNets; second, we propagate denser intermediate views via a component dubbed AGInpaint; and third, we globally eliminate visual inconsistencies (e.g., varying exposure) using the GCAlign module. Concurrently with generation, a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) scene is reconstructed by initializing Gaussian balls on the mesh surface. Our method outperforms existing approaches in both geometric alignment and generation quality. Once synthesized, the scene can be rendered in diverse styles through relighting and style transfer techniques.
QoE Optimization for Semantic Self-Correcting Video Transmission in Multi-UAV Networks
Jul 09, 2025
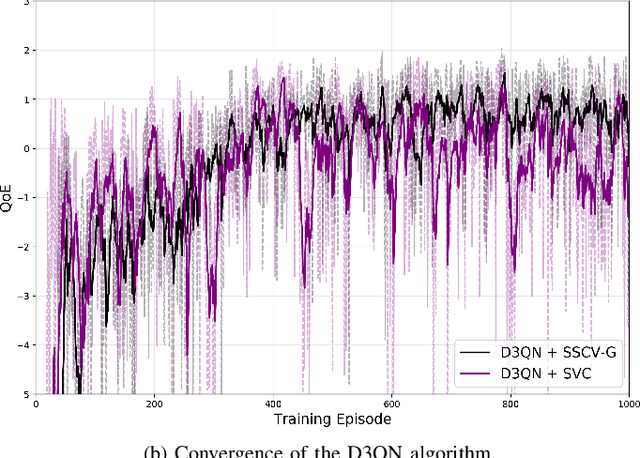
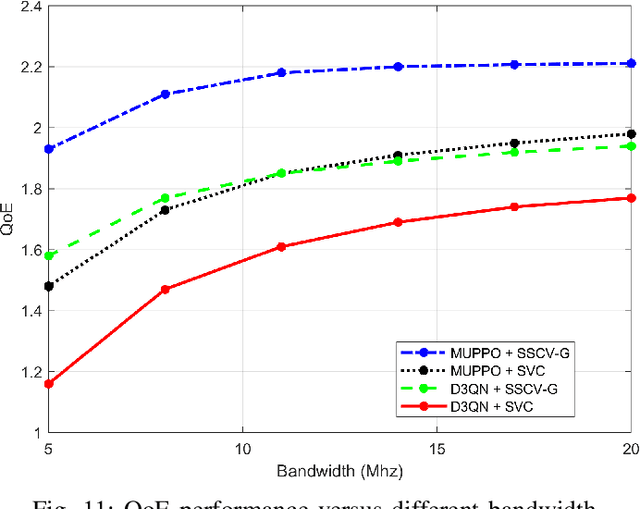
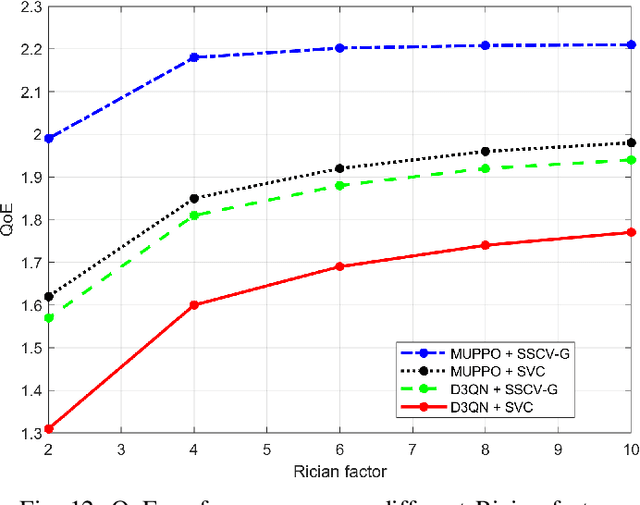
Abstract:Real-time unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) video streaming is essential for time-sensitive applications, including remote surveillance, emergency response, and environmental monitoring. However, it faces challenges such as limited bandwidth, latency fluctuations, and high packet loss. To address these issues, we propose a novel semantic self-correcting video transmission framework with ultra-fine bitrate granularity (SSCV-G). In SSCV-G, video frames are encoded into a compact semantic codebook space, and the transmitter adaptively sends a subset of semantic indices based on bandwidth availability, enabling fine-grained bitrate control for improved bandwidth efficiency. At the receiver, a spatio-temporal vision transformer (ST-ViT) performs multi-frame joint decoding to reconstruct dropped semantic indices by modeling intra- and inter-frame dependencies. To further improve performance under dynamic network conditions, we integrate a multi-user proximal policy optimization (MUPPO) reinforcement learning scheme that jointly optimizes communication resource allocation and semantic bitrate selection to maximize user Quality of Experience (QoE). Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SSCV-G significantly outperforms state-of-the-art video codecs in coding efficiency, bandwidth adaptability, and packet loss robustness. Moreover, the proposed MUPPO-based QoE optimization consistently surpasses existing benchmarks.
Taming OOD Actions for Offline Reinforcement Learning: An Advantage-Based Approach
May 08, 2025Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) aims to learn decision-making policies from fixed datasets without online interactions, providing a practical solution where online data collection is expensive or risky. However, offline RL often suffers from distribution shift, resulting in inaccurate evaluation and substantial overestimation on out-of-distribution (OOD) actions. To address this, existing approaches incorporate conservatism by indiscriminately discouraging all OOD actions, thereby hindering the agent's ability to generalize and exploit beneficial ones. In this paper, we propose Advantage-based Diffusion Actor-Critic (ADAC), a novel method that systematically evaluates OOD actions using the batch-optimal value function. Based on this evaluation, ADAC defines an advantage function to modulate the Q-function update, enabling more precise assessment of OOD action quality. We design a custom PointMaze environment and collect datasets to visually reveal that advantage modulation can effectively identify and select superior OOD actions. Extensive experiments show that ADAC achieves state-of-the-art performance on almost all tasks in the D4RL benchmark, with particularly clear margins on the more challenging tasks.
Global Optimality of Single-Timescale Actor-Critic under Continuous State-Action Space: A Study on Linear Quadratic Regulator
May 02, 2025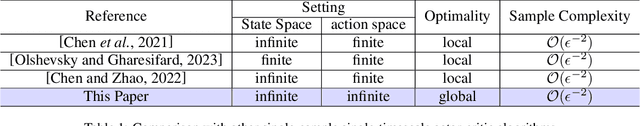
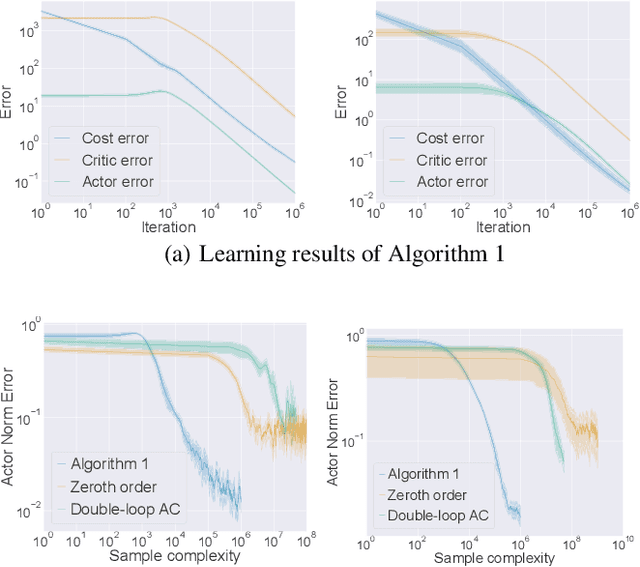
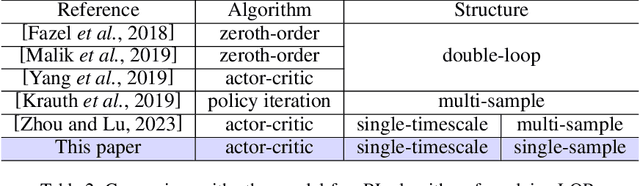
Abstract:Actor-critic methods have achieved state-of-the-art performance in various challenging tasks. However, theoretical understandings of their performance remain elusive and challenging. Existing studies mostly focus on practically uncommon variants such as double-loop or two-timescale stepsize actor-critic algorithms for simplicity. These results certify local convergence on finite state- or action-space only. We push the boundary to investigate the classic single-sample single-timescale actor-critic on continuous (infinite) state-action space, where we employ the canonical linear quadratic regulator (LQR) problem as a case study. We show that the popular single-timescale actor-critic can attain an epsilon-optimal solution with an order of epsilon to -2 sample complexity for solving LQR on the demanding continuous state-action space. Our work provides new insights into the performance of single-timescale actor-critic, which further bridges the gap between theory and practice.
VIPO: Value Function Inconsistency Penalized Offline Reinforcement Learning
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) learns effective policies from pre-collected datasets, offering a practical solution for applications where online interactions are risky or costly. Model-based approaches are particularly advantageous for offline RL, owing to their data efficiency and generalizability. However, due to inherent model errors, model-based methods often artificially introduce conservatism guided by heuristic uncertainty estimation, which can be unreliable. In this paper, we introduce VIPO, a novel model-based offline RL algorithm that incorporates self-supervised feedback from value estimation to enhance model training. Specifically, the model is learned by additionally minimizing the inconsistency between the value learned directly from the offline data and the one estimated from the model. We perform comprehensive evaluations from multiple perspectives to show that VIPO can learn a highly accurate model efficiently and consistently outperform existing methods. It offers a general framework that can be readily integrated into existing model-based offline RL algorithms to systematically enhance model accuracy. As a result, VIPO achieves state-of-the-art performance on almost all tasks in both D4RL and NeoRL benchmarks.
The Communication and Computation Trade-off in Wireless Semantic Communications
Apr 14, 2025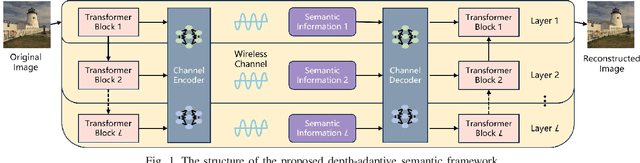
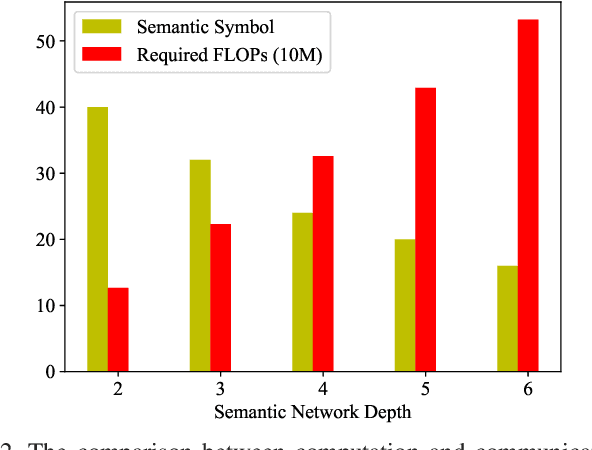
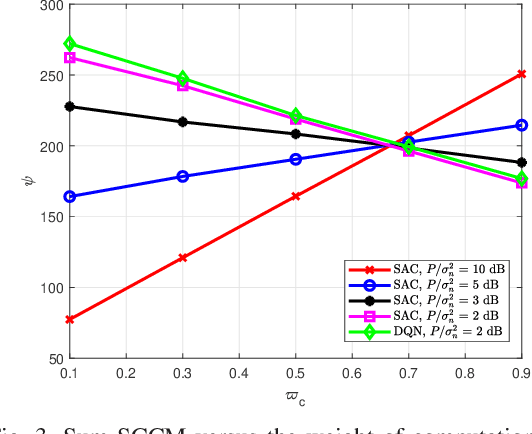
Abstract:Semantic communications have emerged as a crucial research direction for future wireless communication networks. However, as wireless systems become increasingly complex, the demands for computation and communication resources in semantic communications continue to grow rapidly. This paper investigates the trade-off between computation and communication in wireless semantic communications, taking into consideration transmission task delay and performance constraints within the semantic communication framework. We propose a novel tradeoff metric to analyze the balance between computation and communication in semantic transmissions and employ the deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithm to minimize this metric, thereby reducing the cost associated with balancing computation and communication. Through simulations, we analyze the tradeoff between computation and communication and demonstrate the effectiveness of optimizing this trade-off metric.
Preference-Guided Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Exploration
Jul 09, 2024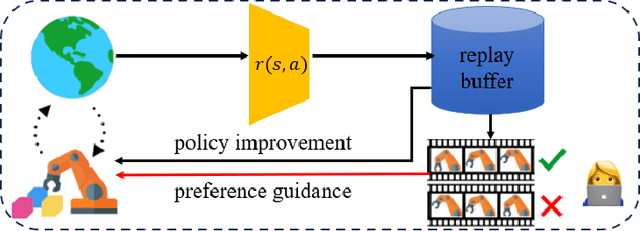
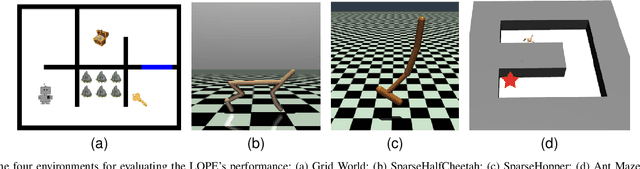
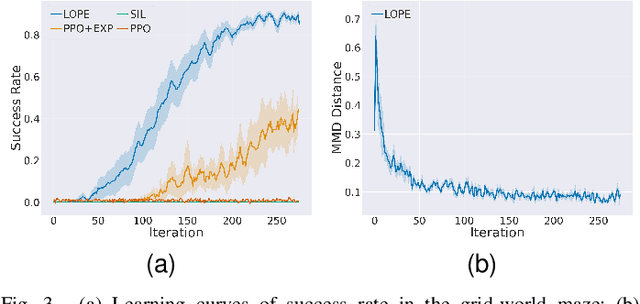
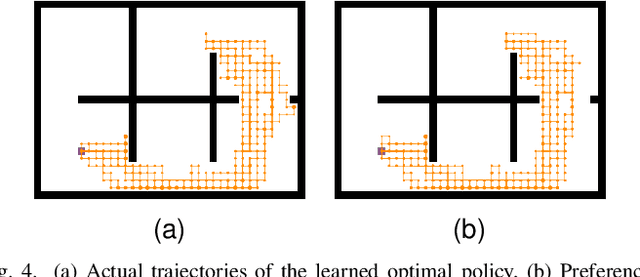
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate preference-based reinforcement learning (PbRL) that allows reinforcement learning (RL) agents to learn from human feedback. This is particularly valuable when defining a fine-grain reward function is not feasible. However, this approach is inefficient and impractical for promoting deep exploration in hard-exploration tasks with long horizons and sparse rewards. To tackle this issue, we introduce LOPE: Learning Online with trajectory Preference guidancE, an end-to-end preference-guided RL framework that enhances exploration efficiency in hard-exploration tasks. Our intuition is that LOPE directly adjusts the focus of online exploration by considering human feedback as guidance, avoiding learning a separate reward model from preferences. Specifically, LOPE includes a two-step sequential policy optimization process consisting of trust-region-based policy improvement and preference guidance steps. We reformulate preference guidance as a novel trajectory-wise state marginal matching problem that minimizes the maximum mean discrepancy distance between the preferred trajectories and the learned policy. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical analysis to characterize the performance improvement bound and evaluate the LOPE's effectiveness. When assessed in various challenging hard-exploration environments, LOPE outperforms several state-of-the-art methods regarding convergence rate and overall performance. The code used in this study is available at \url{https://github.com/buaawgj/LOPE}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge