Yongliang Wang
HierLoc: Hyperbolic Entity Embeddings for Hierarchical Visual Geolocation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Visual geolocalization, the task of predicting where an image was taken, remains challenging due to global scale, visual ambiguity, and the inherently hierarchical structure of geography. Existing paradigms rely on either large-scale retrieval, which requires storing a large number of image embeddings, grid-based classifiers that ignore geographic continuity, or generative models that diffuse over space but struggle with fine detail. We introduce an entity-centric formulation of geolocation that replaces image-to-image retrieval with a compact hierarchy of geographic entities embedded in Hyperbolic space. Images are aligned directly to country, region, subregion, and city entities through Geo-Weighted Hyperbolic contrastive learning by directly incorporating haversine distance into the contrastive objective. This hierarchical design enables interpretable predictions and efficient inference with 240k entity embeddings instead of over 5 million image embeddings on the OSV5M benchmark, on which our method establishes a new state-of-the-art performance. Compared to the current methods in the literature, it reduces mean geodesic error by 19.5\%, while improving the fine-grained subregion accuracy by 43%. These results demonstrate that geometry-aware hierarchical embeddings provide a scalable and conceptually new alternative for global image geolocation.
GeoSceneGraph: Geometric Scene Graph Diffusion Model for Text-guided 3D Indoor Scene Synthesis
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Methods that synthesize indoor 3D scenes from text prompts have wide-ranging applications in film production, interior design, video games, virtual reality, and synthetic data generation for training embodied agents. Existing approaches typically either train generative models from scratch or leverage vision-language models (VLMs). While VLMs achieve strong performance, particularly for complex or open-ended prompts, smaller task-specific models remain necessary for deployment on resource-constrained devices such as extended reality (XR) glasses or mobile phones. However, many generative approaches that train from scratch overlook the inherent graph structure of indoor scenes, which can limit scene coherence and realism. Conversely, methods that incorporate scene graphs either demand a user-provided semantic graph, which is generally inconvenient and restrictive, or rely on ground-truth relationship annotations, limiting their capacity to capture more varied object interactions. To address these challenges, we introduce GeoSceneGraph, a method that synthesizes 3D scenes from text prompts by leveraging the graph structure and geometric symmetries of 3D scenes, without relying on predefined relationship classes. Despite not using ground-truth relationships, GeoSceneGraph achieves performance comparable to methods that do. Our model is built on equivariant graph neural networks (EGNNs), but existing EGNN approaches are typically limited to low-dimensional conditioning and are not designed to handle complex modalities such as text. We propose a simple and effective strategy for conditioning EGNNs on text features, and we validate our design through ablation studies.
LADB: Latent Aligned Diffusion Bridges for Semi-Supervised Domain Translation
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models excel at generating high-quality outputs but face challenges in data-scarce domains, where exhaustive retraining or costly paired data are often required. To address these limitations, we propose Latent Aligned Diffusion Bridges (LADB), a semi-supervised framework for sample-to-sample translation that effectively bridges domain gaps using partially paired data. By aligning source and target distributions within a shared latent space, LADB seamlessly integrates pretrained source-domain diffusion models with a target-domain Latent Aligned Diffusion Model (LADM), trained on partially paired latent representations. This approach enables deterministic domain mapping without the need for full supervision. Compared to unpaired methods, which often lack controllability, and fully paired approaches that require large, domain-specific datasets, LADB strikes a balance between fidelity and diversity by leveraging a mixture of paired and unpaired latent-target couplings. Our experimental results demonstrate superior performance in depth-to-image translation under partial supervision. Furthermore, we extend LADB to handle multi-source translation (from depth maps and segmentation masks) and multi-target translation in a class-conditioned style transfer task, showcasing its versatility in handling diverse and heterogeneous use cases. Ultimately, we present LADB as a scalable and versatile solution for real-world domain translation, particularly in scenarios where data annotation is costly or incomplete.
Learning Dual-Arm Coordination for Grasping Large Flat Objects
Apr 04, 2025



Abstract:Grasping large flat objects, such as books or keyboards lying horizontally, presents significant challenges for single-arm robotic systems, often requiring extra actions like pushing objects against walls or moving them to the edge of a surface to facilitate grasping. In contrast, dual-arm manipulation, inspired by human dexterity, offers a more refined solution by directly coordinating both arms to lift and grasp the object without the need for complex repositioning. In this paper, we propose a model-free deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework to enable dual-arm coordination for grasping large flat objects. We utilize a large-scale grasp pose detection model as a backbone to extract high-dimensional features from input images, which are then used as the state representation in a reinforcement learning (RL) model. A CNN-based Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm with shared Actor-Critic layers is employed to learn coordinated dual-arm grasp actions. The system is trained and tested in Isaac Gym and deployed to real robots. Experimental results demonstrate that our policy can effectively grasp large flat objects without requiring additional maneuvers. Furthermore, the policy exhibits strong generalization capabilities, successfully handling unseen objects. Importantly, it can be directly transferred to real robots without fine-tuning, consistently outperforming baseline methods.
Stick to Facts: Towards Fidelity-oriented Product Description Generation
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Different from other text generation tasks, in product description generation, it is of vital importance to generate faithful descriptions that stick to the product attribute information. However, little attention has been paid to this problem. To bridge this gap, we propose a model named Fidelity-oriented Product Description Generator (FPDG). FPDG takes the entity label of each word into account, since the product attribute information is always conveyed by entity words. Specifically, we first propose a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) decoder based on the Entity-label-guided Long Short-Term Memory (ELSTM) cell, taking both the embedding and the entity label of each word as input. Second, we establish a keyword memory that stores the entity labels as keys and keywords as values, allowing FPDG to attend to keywords by attending to their entity labels. Experiments conducted on a large-scale real-world product description dataset show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of both traditional generation metrics and human evaluations. Specifically, FPDG increases the fidelity of the generated descriptions by 25%.
Learning Dual-Arm Push and Grasp Synergy in Dense Clutter
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Robotic grasping in densely cluttered environments is challenging due to scarce collision-free grasp affordances. Non-prehensile actions can increase feasible grasps in cluttered environments, but most research focuses on single-arm rather than dual-arm manipulation. Policies from single-arm systems fail to fully leverage the advantages of dual-arm coordination. We propose a target-oriented hierarchical deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework that learns dual-arm push-grasp synergy for grasping objects to enhance dexterous manipulation in dense clutter. Our framework maps visual observations to actions via a pre-trained deep learning backbone and a novel CNN-based DRL model, trained with Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), to develop a dual-arm push-grasp strategy. The backbone enhances feature mapping in densely cluttered environments. A novel fuzzy-based reward function is introduced to accelerate efficient strategy learning. Our system is developed and trained in Isaac Gym and then tested in simulations and on a real robot. Experimental results show that our framework effectively maps visual data to dual push-grasp motions, enabling the dual-arm system to grasp target objects in complex environments. Compared to other methods, our approach generates 6-DoF grasp candidates and enables dual-arm push actions, mimicking human behavior. Results show that our method efficiently completes tasks in densely cluttered environments. https://sites.google.com/view/pg4da/home
BezierFormer: A Unified Architecture for 2D and 3D Lane Detection
Apr 25, 2024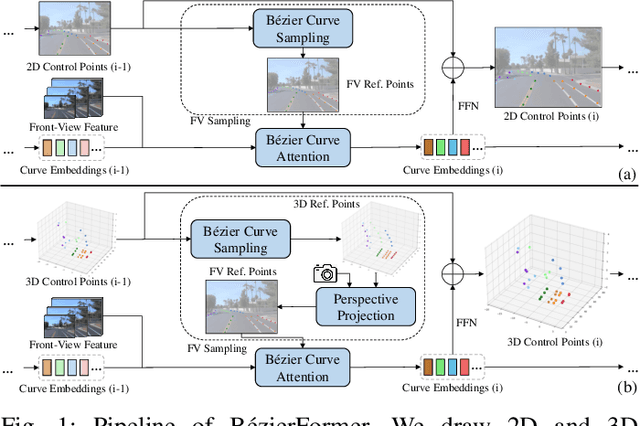
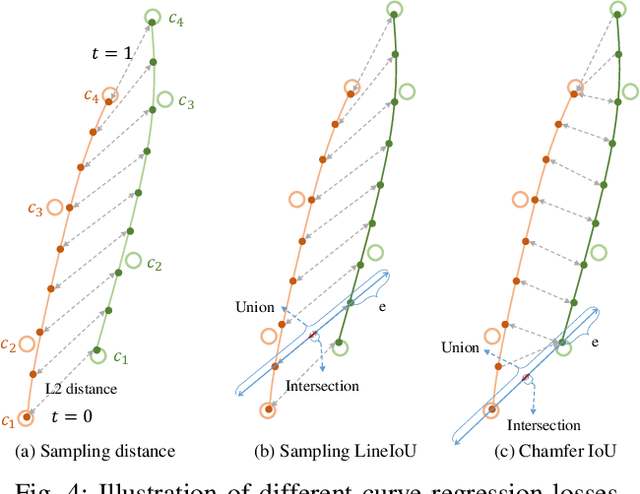
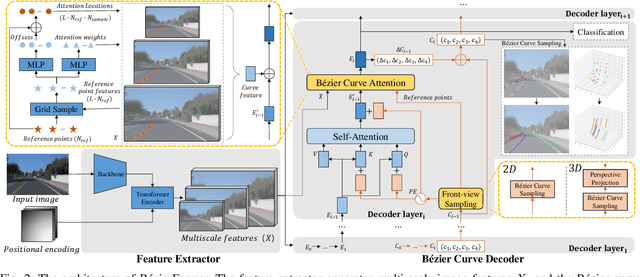
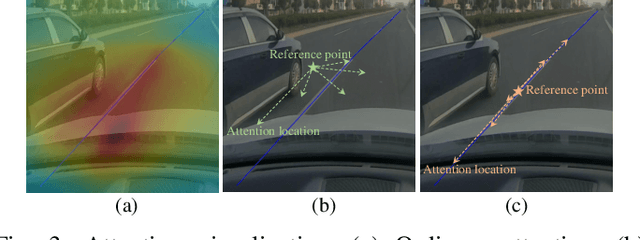

Abstract:Lane detection has made significant progress in recent years, but there is not a unified architecture for its two sub-tasks: 2D lane detection and 3D lane detection. To fill this gap, we introduce B\'{e}zierFormer, a unified 2D and 3D lane detection architecture based on B\'{e}zier curve lane representation. B\'{e}zierFormer formulate queries as B\'{e}zier control points and incorporate a novel B\'{e}zier curve attention mechanism. This attention mechanism enables comprehensive and accurate feature extraction for slender lane curves via sampling and fusing multiple reference points on each curve. In addition, we propose a novel Chamfer IoU-based loss which is more suitable for the B\'{e}zier control points regression. The state-of-the-art performance of B\'{e}zierFormer on widely-used 2D and 3D lane detection benchmarks verifies its effectiveness and suggests the worthiness of further exploration.
Box2Poly: Memory-Efficient Polygon Prediction of Arbitrarily Shaped and Rotated Text
Sep 20, 2023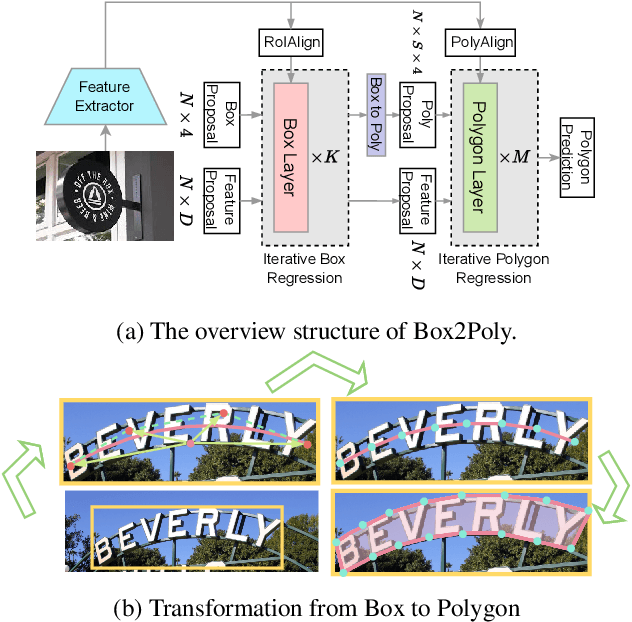
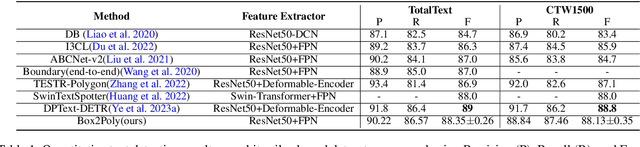
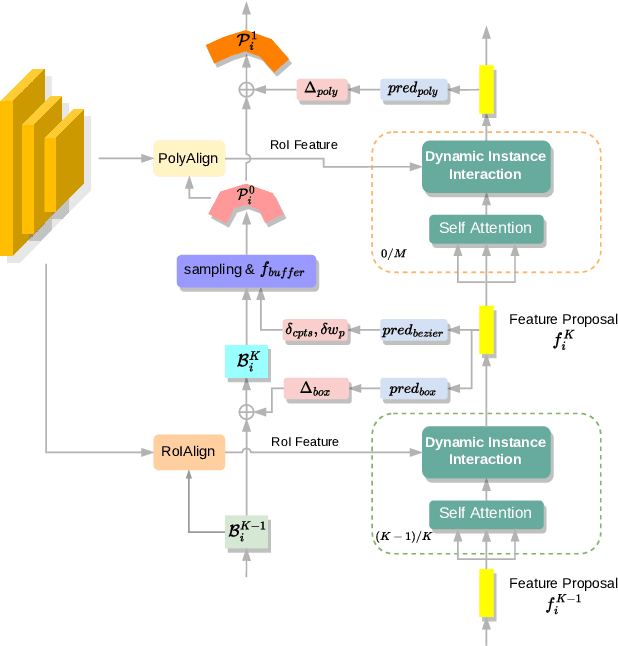

Abstract:Recently, Transformer-based text detection techniques have sought to predict polygons by encoding the coordinates of individual boundary vertices using distinct query features. However, this approach incurs a significant memory overhead and struggles to effectively capture the intricate relationships between vertices belonging to the same instance. Consequently, irregular text layouts often lead to the prediction of outlined vertices, diminishing the quality of results. To address these challenges, we present an innovative approach rooted in Sparse R-CNN: a cascade decoding pipeline for polygon prediction. Our method ensures precision by iteratively refining polygon predictions, considering both the scale and location of preceding results. Leveraging this stabilized regression pipeline, even employing just a single feature vector to guide polygon instance regression yields promising detection results. Simultaneously, the leverage of instance-level feature proposal substantially enhances memory efficiency (>50% less vs. the state-of-the-art method DPText-DETR) and reduces inference speed (>40% less vs. DPText-DETR) with minor performance drop on benchmarks.
NeMO: Neural Map Growing System for Spatiotemporal Fusion in Bird's-Eye-View and BDD-Map Benchmark
Jun 07, 2023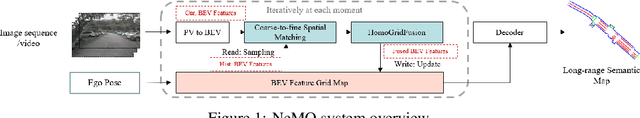

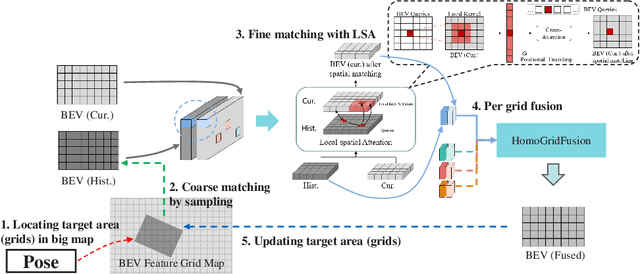

Abstract:Vision-centric Bird's-Eye View (BEV) representation is essential for autonomous driving systems (ADS). Multi-frame temporal fusion which leverages historical information has been demonstrated to provide more comprehensive perception results. While most research focuses on ego-centric maps of fixed settings, long-range local map generation remains less explored. This work outlines a new paradigm, named NeMO, for generating local maps through the utilization of a readable and writable big map, a learning-based fusion module, and an interaction mechanism between the two. With an assumption that the feature distribution of all BEV grids follows an identical pattern, we adopt a shared-weight neural network for all grids to update the big map. This paradigm supports the fusion of longer time series and the generation of long-range BEV local maps. Furthermore, we release BDD-Map, a BDD100K-based dataset incorporating map element annotations, including lane lines, boundaries, and pedestrian crossing. Experiments on the NuScenes and BDD-Map datasets demonstrate that NeMO outperforms state-of-the-art map segmentation methods. We also provide a new scene-level BEV map evaluation setting along with the corresponding baseline for a more comprehensive comparison.
Towards Personalized Review Summarization by Modeling Historical Reviews from Customer and Product Separately
Jan 27, 2023Abstract:Review summarization is a non-trivial task that aims to summarize the main idea of the product review in the E-commerce website. Different from the document summary which only needs to focus on the main facts described in the document, review summarization should not only summarize the main aspects mentioned in the review but also reflect the personal style of the review author. Although existing review summarization methods have incorporated the historical reviews of both customer and product, they usually simply concatenate and indiscriminately model this two heterogeneous information into a long sequence. Moreover, the rating information can also provide a high-level abstraction of customer preference, it has not been used by the majority of methods. In this paper, we propose the Heterogeneous Historical Review aware Review Summarization Model (HHRRS) which separately models the two types of historical reviews with the rating information by a graph reasoning module with a contrastive loss. We employ a multi-task framework that conducts the review sentiment classification and summarization jointly. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of HHRRS on both tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge