Yu-Xiong Wang
InterPrior: Scaling Generative Control for Physics-Based Human-Object Interactions
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Humans rarely plan whole-body interactions with objects at the level of explicit whole-body movements. High-level intentions, such as affordance, define the goal, while coordinated balance, contact, and manipulation can emerge naturally from underlying physical and motor priors. Scaling such priors is key to enabling humanoids to compose and generalize loco-manipulation skills across diverse contexts while maintaining physically coherent whole-body coordination. To this end, we introduce InterPrior, a scalable framework that learns a unified generative controller through large-scale imitation pretraining and post-training by reinforcement learning. InterPrior first distills a full-reference imitation expert into a versatile, goal-conditioned variational policy that reconstructs motion from multimodal observations and high-level intent. While the distilled policy reconstructs training behaviors, it does not generalize reliably due to the vast configuration space of large-scale human-object interactions. To address this, we apply data augmentation with physical perturbations, and then perform reinforcement learning finetuning to improve competence on unseen goals and initializations. Together, these steps consolidate the reconstructed latent skills into a valid manifold, yielding a motion prior that generalizes beyond the training data, e.g., it can incorporate new behaviors such as interactions with unseen objects. We further demonstrate its effectiveness for user-interactive control and its potential for real robot deployment.
Capturing Visual Environment Structure Correlates with Control Performance
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The choice of visual representation is key to scaling generalist robot policies. However, direct evaluation via policy rollouts is expensive, even in simulation. Existing proxy metrics focus on the representation's capacity to capture narrow aspects of the visual world, like object shape, limiting generalization across environments. In this paper, we take an analytical perspective: we probe pretrained visual encoders by measuring how well they support decoding of environment state -- including geometry, object structure, and physical attributes -- from images. Leveraging simulation environments with access to ground-truth state, we show that this probing accuracy strongly correlates with downstream policy performance across diverse environments and learning settings, significantly outperforming prior metrics and enabling efficient representation selection. More broadly, our study provides insight into the representational properties that support generalizable manipulation, suggesting that learning to encode the latent physical state of the environment is a promising objective for control.
Walk through Paintings: Egocentric World Models from Internet Priors
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:What if a video generation model could not only imagine a plausible future, but the correct one, accurately reflecting how the world changes with each action? We address this question by presenting the Egocentric World Model (EgoWM), a simple, architecture-agnostic method that transforms any pretrained video diffusion model into an action-conditioned world model, enabling controllable future prediction. Rather than training from scratch, we repurpose the rich world priors of Internet-scale video models and inject motor commands through lightweight conditioning layers. This allows the model to follow actions faithfully while preserving realism and strong generalization. Our approach scales naturally across embodiments and action spaces, ranging from 3-DoF mobile robots to 25-DoF humanoids, where predicting egocentric joint-angle-driven dynamics is substantially more challenging. The model produces coherent rollouts for both navigation and manipulation tasks, requiring only modest fine-tuning. To evaluate physical correctness independently of visual appearance, we introduce the Structural Consistency Score (SCS), which measures whether stable scene elements evolve consistently with the provided actions. EgoWM improves SCS by up to 80 percent over prior state-of-the-art navigation world models, while achieving up to six times lower inference latency and robust generalization to unseen environments, including navigation inside paintings.
3DGS-Drag: Dragging Gaussians for Intuitive Point-Based 3D Editing
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:The transformative potential of 3D content creation has been progressively unlocked through advancements in generative models. Recently, intuitive drag editing with geometric changes has attracted significant attention in 2D editing yet remains challenging for 3D scenes. In this paper, we introduce 3DGS-Drag -- a point-based 3D editing framework that provides efficient, intuitive drag manipulation of real 3D scenes. Our approach bridges the gap between deformation-based and 2D-editing-based 3D editing methods, addressing their limitations to geometry-related content editing. We leverage two key innovations: deformation guidance utilizing 3D Gaussian Splatting for consistent geometric modifications and diffusion guidance for content correction and visual quality enhancement. A progressive editing strategy further supports aggressive 3D drag edits. Our method enables a wide range of edits, including motion change, shape adjustment, inpainting, and content extension. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of 3DGS-Drag in various scenes, achieving state-of-the-art performance in geometry-related 3D content editing. Notably, the editing is efficient, taking 10 to 20 minutes on a single RTX 4090 GPU.
Visual Backdoor Attacks on MLLM Embodied Decision Making via Contrastive Trigger Learning
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have advanced embodied agents by enabling direct perception, reasoning, and planning task-oriented actions from visual inputs. However, such vision driven embodied agents open a new attack surface: visual backdoor attacks, where the agent behaves normally until a visual trigger appears in the scene, then persistently executes an attacker-specified multi-step policy. We introduce BEAT, the first framework to inject such visual backdoors into MLLM-based embodied agents using objects in the environments as triggers. Unlike textual triggers, object triggers exhibit wide variation across viewpoints and lighting, making them difficult to implant reliably. BEAT addresses this challenge by (1) constructing a training set that spans diverse scenes, tasks, and trigger placements to expose agents to trigger variability, and (2) introducing a two-stage training scheme that first applies supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and then our novel Contrastive Trigger Learning (CTL). CTL formulates trigger discrimination as preference learning between trigger-present and trigger-free inputs, explicitly sharpening the decision boundaries to ensure precise backdoor activation. Across various embodied agent benchmarks and MLLMs, BEAT achieves attack success rates up to 80%, while maintaining strong benign task performance, and generalizes reliably to out-of-distribution trigger placements. Notably, compared to naive SFT, CTL boosts backdoor activation accuracy up to 39% under limited backdoor data. These findings expose a critical yet unexplored security risk in MLLM-based embodied agents, underscoring the need for robust defenses before real-world deployment.
Dexplore: Scalable Neural Control for Dexterous Manipulation from Reference-Scoped Exploration
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Hand-object motion-capture (MoCap) repositories offer large-scale, contact-rich demonstrations and hold promise for scaling dexterous robotic manipulation. Yet demonstration inaccuracies and embodiment gaps between human and robot hands limit the straightforward use of these data. Existing methods adopt a three-stage workflow, including retargeting, tracking, and residual correction, which often leaves demonstrations underused and compound errors across stages. We introduce Dexplore, a unified single-loop optimization that jointly performs retargeting and tracking to learn robot control policies directly from MoCap at scale. Rather than treating demonstrations as ground truth, we use them as soft guidance. From raw trajectories, we derive adaptive spatial scopes, and train with reinforcement learning to keep the policy in-scope while minimizing control effort and accomplishing the task. This unified formulation preserves demonstration intent, enables robot-specific strategies to emerge, improves robustness to noise, and scales to large demonstration corpora. We distill the scaled tracking policy into a vision-based, skill-conditioned generative controller that encodes diverse manipulation skills in a rich latent representation, supporting generalization across objects and real-world deployment. Taken together, these contributions position Dexplore as a principled bridge that transforms imperfect demonstrations into effective training signals for dexterous manipulation.
InterAct: Advancing Large-Scale Versatile 3D Human-Object Interaction Generation
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:While large-scale human motion capture datasets have advanced human motion generation, modeling and generating dynamic 3D human-object interactions (HOIs) remain challenging due to dataset limitations. Existing datasets often lack extensive, high-quality motion and annotation and exhibit artifacts such as contact penetration, floating, and incorrect hand motions. To address these issues, we introduce InterAct, a large-scale 3D HOI benchmark featuring dataset and methodological advancements. First, we consolidate and standardize 21.81 hours of HOI data from diverse sources, enriching it with detailed textual annotations. Second, we propose a unified optimization framework to enhance data quality by reducing artifacts and correcting hand motions. Leveraging the principle of contact invariance, we maintain human-object relationships while introducing motion variations, expanding the dataset to 30.70 hours. Third, we define six benchmarking tasks and develop a unified HOI generative modeling perspective, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Extensive experiments validate the utility of our dataset as a foundational resource for advancing 3D human-object interaction generation. To support continued research in this area, the dataset is publicly available at https://github.com/wzyabcas/InterAct, and will be actively maintained.
Virtual Fitting Room: Generating Arbitrarily Long Videos of Virtual Try-On from a Single Image -- Technical Preview
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:We introduce the Virtual Fitting Room (VFR), a novel video generative model that produces arbitrarily long virtual try-on videos. Our VFR models long video generation tasks as an auto-regressive, segment-by-segment generation process, eliminating the need for resource-intensive generation and lengthy video data, while providing the flexibility to generate videos of arbitrary length. The key challenges of this task are twofold: ensuring local smoothness between adjacent segments and maintaining global temporal consistency across different segments. To address these challenges, we propose our VFR framework, which ensures smoothness through a prefix video condition and enforces consistency with the anchor video -- a 360-degree video that comprehensively captures the human's wholebody appearance. Our VFR generates minute-scale virtual try-on videos with both local smoothness and global temporal consistency under various motions, making it a pioneering work in long virtual try-on video generation.
Dress&Dance: Dress up and Dance as You Like It - Technical Preview
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:We present Dress&Dance, a video diffusion framework that generates high quality 5-second-long 24 FPS virtual try-on videos at 1152x720 resolution of a user wearing desired garments while moving in accordance with a given reference video. Our approach requires a single user image and supports a range of tops, bottoms, and one-piece garments, as well as simultaneous tops and bottoms try-on in a single pass. Key to our framework is CondNet, a novel conditioning network that leverages attention to unify multi-modal inputs (text, images, and videos), thereby enhancing garment registration and motion fidelity. CondNet is trained on heterogeneous training data, combining limited video data and a larger, more readily available image dataset, in a multistage progressive manner. Dress&Dance outperforms existing open source and commercial solutions and enables a high quality and flexible try-on experience.
Towards Formal Verification of LLM-Generated Code from Natural Language Prompts
Jul 17, 2025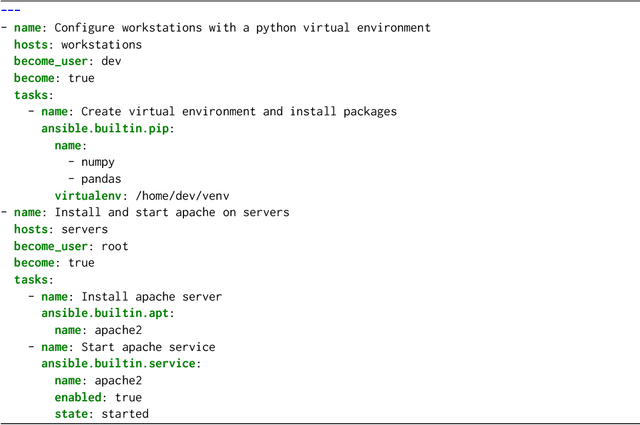
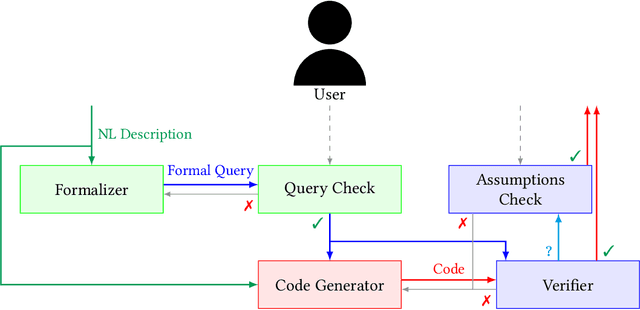
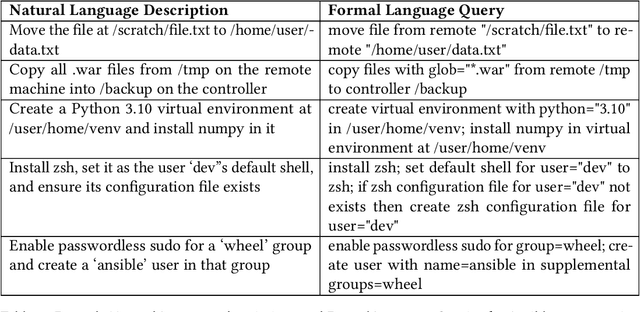
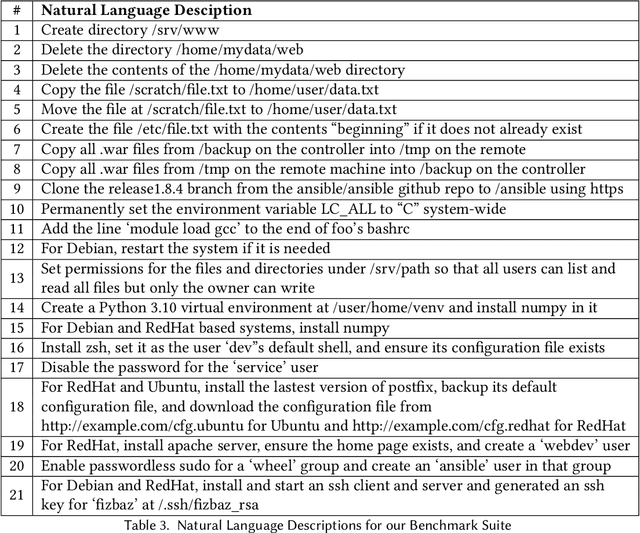
Abstract:In the past few years LLMs have emerged as a tool that can aid programmers by taking natural language descriptions and generating code based on it. However, LLMs often generate incorrect code that users need to fix and the literature suggests users often struggle to detect these errors. In this work we seek to offer formal guarantees of correctness to LLM generated code; such guarantees could improve the experience of using AI Code Assistants and potentially enable natural language programming for users with little or no programming knowledge. To address this challenge we propose to incorporate a formal query language that can represent a user's intent in a formally defined but natural language-like manner that a user can confirm matches their intent. Then, using such a query we propose to verify LLM generated code to ensure it matches the user's intent. We implement these ideas in our system, Astrogator, for the Ansible programming language which includes such a formal query language, a calculus for representing the behavior of Ansible programs, and a symbolic interpreter which is used for the verification. On a benchmark suite of 21 code-generation tasks, our verifier is able to verify correct code in 83% of cases and identify incorrect code in 92%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge