Vikram Adve
Towards Formal Verification of LLM-Generated Code from Natural Language Prompts
Jul 17, 2025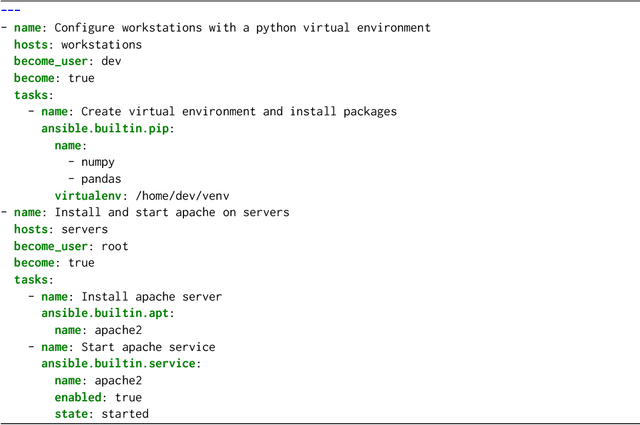
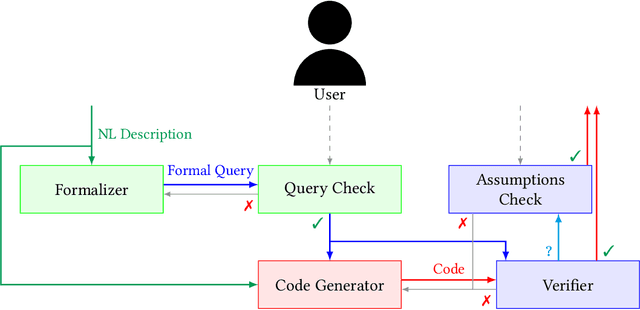
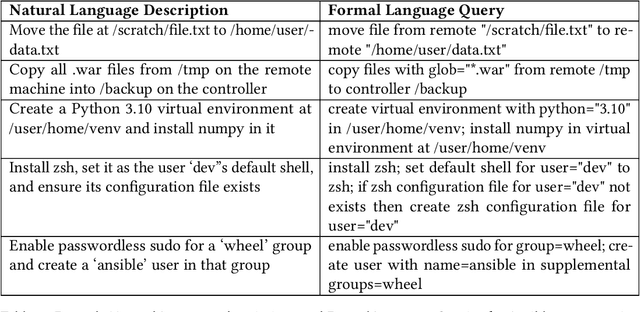
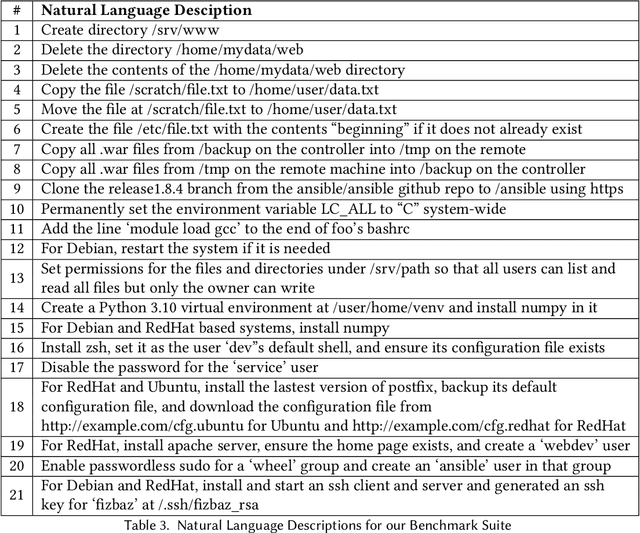
Abstract:In the past few years LLMs have emerged as a tool that can aid programmers by taking natural language descriptions and generating code based on it. However, LLMs often generate incorrect code that users need to fix and the literature suggests users often struggle to detect these errors. In this work we seek to offer formal guarantees of correctness to LLM generated code; such guarantees could improve the experience of using AI Code Assistants and potentially enable natural language programming for users with little or no programming knowledge. To address this challenge we propose to incorporate a formal query language that can represent a user's intent in a formally defined but natural language-like manner that a user can confirm matches their intent. Then, using such a query we propose to verify LLM generated code to ensure it matches the user's intent. We implement these ideas in our system, Astrogator, for the Ansible programming language which includes such a formal query language, a calculus for representing the behavior of Ansible programs, and a symbolic interpreter which is used for the verification. On a benchmark suite of 21 code-generation tasks, our verifier is able to verify correct code in 83% of cases and identify incorrect code in 92%.
LEWIS (LayEr WIse Sparsity) -- A Training Free Guided Model Merging Approach
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:As specialized large language models (LLMs) become increasingly prevalent, model merging methods are being used to combine them to create a single multi-task model without requiring any additional data or training. However, these approaches fall short when the objective of merging is to increase the downstream model's performance on a particular task-specific benchmark. In this work, we propose LEWIS (Layer Wise Sparsity), a guided model-merging framework that uses activation-based layer importance to dynamically adjust layer-wise task-vector sparsity required for the merge process. LEWIS uses a calibration dataset to prioritize critical layers during the task-vector pruning process required for model merging. This approach guides existing merging methods by preserving essential layer-wise task-specific knowledge while ensuring the merged model performs the best at benchmarks resembling the calibration dataset. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of LEWIS with performance improvements of code instruction-following and math-solving models created through model merging up to 4 percent and 11.3 percent, respectively, outperforming unguided data-less model merging approaches that use uniform-sparsity.
Transforming the Hybrid Cloud for Emerging AI Workloads
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:This white paper, developed through close collaboration between IBM Research and UIUC researchers within the IIDAI Institute, envisions transforming hybrid cloud systems to meet the growing complexity of AI workloads through innovative, full-stack co-design approaches, emphasizing usability, manageability, affordability, adaptability, efficiency, and scalability. By integrating cutting-edge technologies such as generative and agentic AI, cross-layer automation and optimization, unified control plane, and composable and adaptive system architecture, the proposed framework addresses critical challenges in energy efficiency, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Incorporating quantum computing as it matures will enable quantum-accelerated simulations for materials science, climate modeling, and other high-impact domains. Collaborative efforts between academia and industry are central to this vision, driving advancements in foundation models for material design and climate solutions, scalable multimodal data processing, and enhanced physics-based AI emulators for applications like weather forecasting and carbon sequestration. Research priorities include advancing AI agentic systems, LLM as an Abstraction (LLMaaA), AI model optimization and unified abstractions across heterogeneous infrastructure, end-to-end edge-cloud transformation, efficient programming model, middleware and platform, secure infrastructure, application-adaptive cloud systems, and new quantum-classical collaborative workflows. These ideas and solutions encompass both theoretical and practical research questions, requiring coordinated input and support from the research community. This joint initiative aims to establish hybrid clouds as secure, efficient, and sustainable platforms, fostering breakthroughs in AI-driven applications and scientific discovery across academia, industry, and society.
Semi-Supervised Object Detection in the Open World
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Existing approaches for semi-supervised object detection assume a fixed set of classes present in training and unlabeled datasets, i.e., in-distribution (ID) data. The performance of these techniques significantly degrades when these techniques are deployed in the open-world, due to the fact that the unlabeled and test data may contain objects that were not seen during training, i.e., out-of-distribution (OOD) data. The two key questions that we explore in this paper are: can we detect these OOD samples and if so, can we learn from them? With these considerations in mind, we propose the Open World Semi-supervised Detection framework (OWSSD) that effectively detects OOD data along with a semi-supervised learning pipeline that learns from both ID and OOD data. We introduce an ensemble based OOD detector consisting of lightweight auto-encoder networks trained only on ID data. Through extensive evalulation, we demonstrate that our method performs competitively against state-of-the-art OOD detection algorithms and also significantly boosts the semi-supervised learning performance in open-world scenarios.
DLVM: A modern compiler infrastructure for deep learning systems
Feb 02, 2018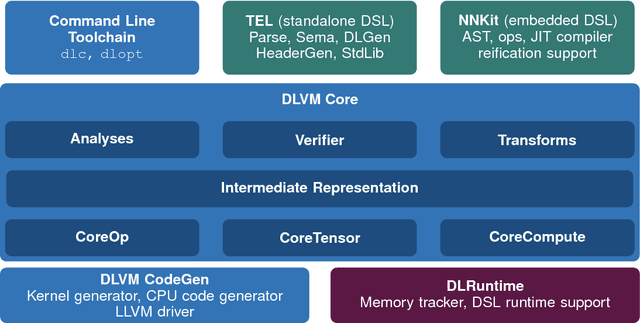
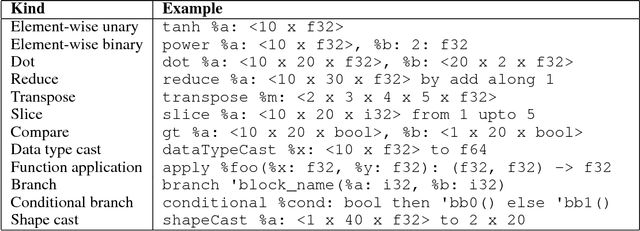
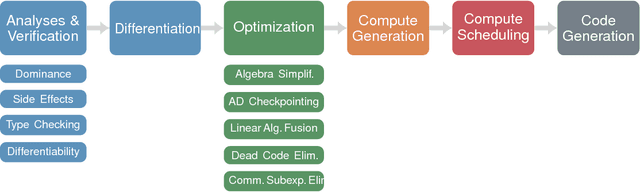

Abstract:Deep learning software demands reliability and performance. However, many of the existing deep learning frameworks are software libraries that act as an unsafe DSL in Python and a computation graph interpreter. We present DLVM, a design and implementation of a compiler infrastructure with a linear algebra intermediate representation, algorithmic differentiation by adjoint code generation, domain-specific optimizations and a code generator targeting GPU via LLVM. Designed as a modern compiler infrastructure inspired by LLVM, DLVM is more modular and more generic than existing deep learning compiler frameworks, and supports tensor DSLs with high expressivity. With our prototypical staged DSL embedded in Swift, we argue that the DLVM system enables a form of modular, safe and performant frameworks for deep learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge