Jiangtong Li
Cross-Paradigm Graph Backdoor Attacks with Promptable Subgraph Triggers
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks(GNNs) are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, where adversaries implant malicious triggers to manipulate model predictions. Existing trigger generators are often simplistic in structure and overly reliant on specific features, confining them to a single graph learning paradigm, such as graph supervised learning, graph contrastive learning, or graph prompt learning. This specialized design, which aligns the trigger with one learning objective, results in poor transferability when applied to other learning paradigms. For instance, triggers generated for the graph supervised learning paradigm perform poorly when tested within graph contrastive learning or graph prompt learning environments. Furthermore, these simple generators often fail to utilize complex structural information or node diversity within the graph data. These constraints limit the attack success rates of such methods in general testing scenarios. Therefore, to address these limitations, we propose Cross-Paradigm Graph Backdoor Attacks with Promptable Subgraph Triggers(CP-GBA), a new transferable graph backdoor attack that employs graph prompt learning(GPL) to train a set of universal subgraph triggers. First, we distill a compact yet expressive trigger set from target graphs, which is structured as a queryable repository, by jointly enforcing class-awareness, feature richness, and structural fidelity. Second, we conduct the first exploration of the theoretical transferability of GPL to train these triggers under prompt-based objectives, enabling effective generalization to diverse and unseen test-time paradigms. Extensive experiments across multiple real-world datasets and defense scenarios show that CP-GBA achieves state-of-the-art attack success rates.
EEG-FM-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for the Systematic Evaluation of EEG Foundation Models
Aug 25, 2025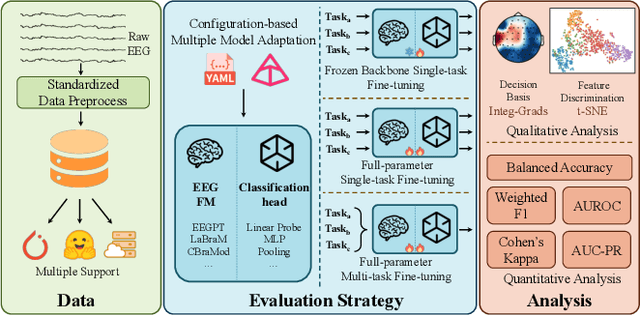
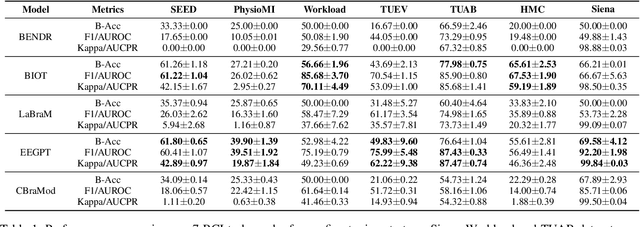
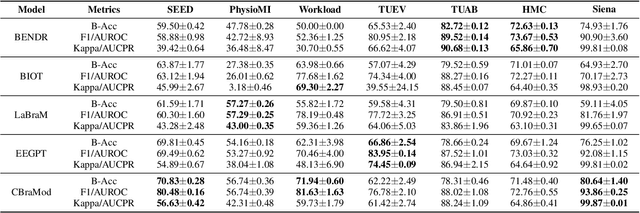
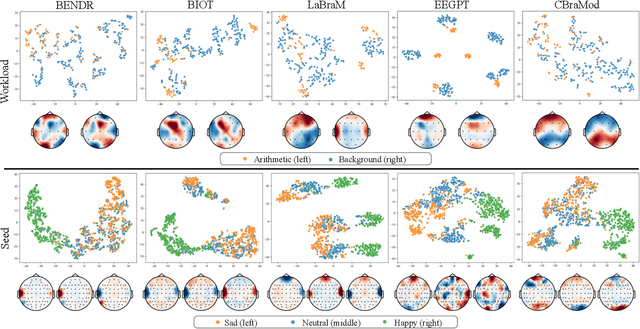
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) foundation models are poised to significantly advance brain signal analysis by learning robust representations from large-scale, unlabeled datasets. However, their rapid proliferation has outpaced the development of standardized evaluation benchmarks, which complicates direct model comparisons and hinders systematic scientific progress. This fragmentation fosters scientific inefficiency and obscures genuine architectural advancements. To address this critical gap, we introduce EEG-FM-Bench, the first comprehensive benchmark for the systematic and standardized evaluation of EEG foundation models (EEG-FMs). Our contributions are threefold: (1) we curate a diverse suite of downstream tasks and datasets from canonical EEG paradigms, implementing standardized processing and evaluation protocols within a unified open-source framework; (2) we benchmark prominent state-of-the-art foundation models to establish comprehensive baseline results for a clear comparison of the current landscape; (3) we perform qualitative analyses of the learned representations to provide insights into model behavior and inform future architectural design. Through extensive experiments, we find that fine-grained spatio-temporal feature interaction, multitask unified training and neuropsychological priors would contribute to enhancing model performance and generalization capabilities. By offering a unified platform for fair comparison and reproducible research, EEG-FM-Bench seeks to catalyze progress and guide the community toward the development of more robust and generalizable EEG-FMs. Code is released at https://github.com/xw1216/EEG-FM-Bench.
CFBenchmark-MM: Chinese Financial Assistant Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Model
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have rapidly evolved with the growth of Large Language Models (LLMs) and are now applied in various fields. In finance, the integration of diverse modalities such as text, charts, and tables is crucial for accurate and efficient decision-making. Therefore, an effective evaluation system that incorporates these data types is essential for advancing financial application. In this paper, we introduce CFBenchmark-MM, a Chinese multimodal financial benchmark with over 9,000 image-question pairs featuring tables, histogram charts, line charts, pie charts, and structural diagrams. Additionally, we develop a staged evaluation system to assess MLLMs in handling multimodal information by providing different visual content step by step. Despite MLLMs having inherent financial knowledge, experimental results still show limited efficiency and robustness in handling multimodal financial context. Further analysis on incorrect responses reveals the misinterpretation of visual content and the misunderstanding of financial concepts are the primary issues. Our research validates the significant, yet underexploited, potential of MLLMs in financial analysis, highlighting the need for further development and domain-specific optimization to encourage the enhanced use in financial domain.
FinLMM-R1: Enhancing Financial Reasoning in LMM through Scalable Data and Reward Design
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) demonstrate significant cross-modal reasoning capabilities. However, financial applications face challenges due to the lack of high-quality multimodal reasoning datasets and the inefficiency of existing training paradigms for reasoning enhancement. To address these issues, we propose an integrated framework, FinLMM-R1, combining an automated and scalable pipeline for data construction with enhanced training strategies to improve the multimodal reasoning of LMM. The Automated and Scalable Pipeline (ASP) resolves textual-visual misalignment in financial reports through a separate paradigm of question-answer generation and image-question alignment, ensuring data integrity and extraction efficiency. Through ASP, we collect 89,378 aligned image-question pairs from 23,397 financial reports, covering tasks such as arithmetic reasoning, statistics reasoning, financial explanation, and financial knowledge. Moreover, we introduce the Thinking with Adversarial Reward in LMM (TAR-LMM), extending the prior two-stage training framework [1] with additional reward mechanisms. In the first stage, we focus on text-only tasks with format and accuracy rewards to guide the model in generating well-structured thinking contents. In the second stage, we construct multi-image contrastive samples with additional reward components including image selection, thinking content length, and adversarial reward to jointly optimize the LMM across visual perception, reasoning efficiency, and logical coherence. Extensive experiments on 7 benchmarks show ASP-derived dataset and training framework significantly improve answer accuracy and reasoning depth over existing reasoning LMMs in both general and financial multimodal contexts.
ALFEE: Adaptive Large Foundation Model for EEG Representation
May 07, 2025Abstract:While foundation models excel in text, image, and video domains, the critical biological signals, particularly electroencephalography(EEG), remain underexplored. EEG benefits neurological research with its high temporal resolution, operational practicality, and safety profile. However, low signal-to-noise ratio, inter-subject variability, and cross-paradigm differences hinder the generalization of current models. Existing methods often employ simplified strategies, such as a single loss function or a channel-temporal joint representation module, and suffer from a domain gap between pretraining and evaluation tasks that compromises efficiency and adaptability. To address these limitations, we propose the Adaptive Large Foundation model for EEG signal representation(ALFEE) framework, a novel hybrid transformer architecture with two learning stages for robust EEG representation learning. ALFEE employs a hybrid attention that separates channel-wise feature aggregation from temporal dynamics modeling, enabling robust EEG representation with variable channel configurations. A channel encoder adaptively compresses variable channel information, a temporal encoder captures task-guided evolution, and a hybrid decoder reconstructs signals in both temporal and frequency domains. During pretraining, ALFEE optimizes task prediction, channel and temporal mask reconstruction, and temporal forecasting to enhance multi-scale and multi-channel representation. During fine-tuning, a full-model adaptation with a task-specific token dictionary and a cross-attention layer boosts performance across multiple tasks. After 25,000 hours of pretraining, extensive experimental results on six downstream EEG tasks demonstrate the superior performance of ALFEE over existing models. Our ALFEE framework establishes a scalable foundation for biological signal analysis with implementation at https://github.com/xw1216/ALFEE.
Align and Aggregate: Compositional Reasoning with Video Alignment and Answer Aggregation for Video Question-Answering
Jul 03, 2024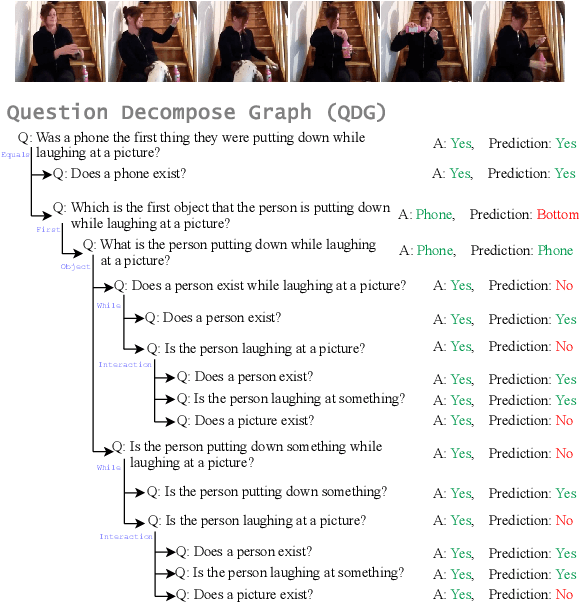
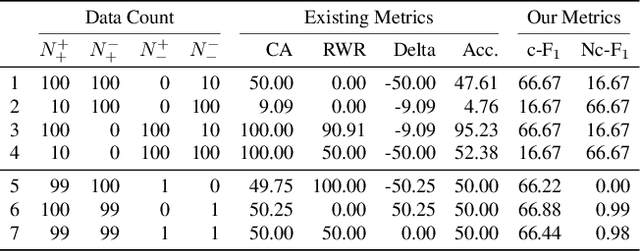
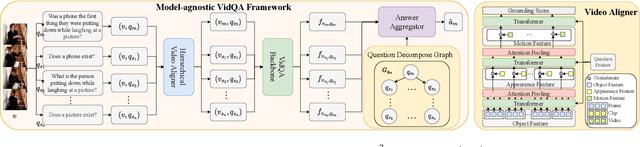
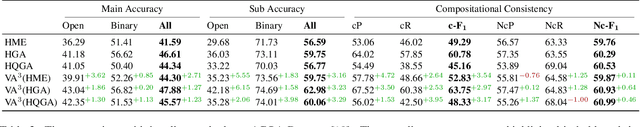
Abstract:Despite the recent progress made in Video Question-Answering (VideoQA), these methods typically function as black-boxes, making it difficult to understand their reasoning processes and perform consistent compositional reasoning. To address these challenges, we propose a \textit{model-agnostic} Video Alignment and Answer Aggregation (VA$^{3}$) framework, which is capable of enhancing both compositional consistency and accuracy of existing VidQA methods by integrating video aligner and answer aggregator modules. The video aligner hierarchically selects the relevant video clips based on the question, while the answer aggregator deduces the answer to the question based on its sub-questions, with compositional consistency ensured by the information flow along question decomposition graph and the contrastive learning strategy. We evaluate our framework on three settings of the AGQA-Decomp dataset with three baseline methods, and propose new metrics to measure the compositional consistency of VidQA methods more comprehensively. Moreover, we propose a large language model (LLM) based automatic question decomposition pipeline to apply our framework to any VidQA dataset. We extend MSVD and NExT-QA datasets with it to evaluate our VA$^3$ framework on broader scenarios. Extensive experiments show that our framework improves both compositional consistency and accuracy of existing methods, leading to more interpretable real-world VidQA models.
* 10 pages,CVPR
Multi-Patch Prediction: Adapting LLMs for Time Series Representation Learning
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:In this study, we present aLLM4TS, an innovative framework that adapts Large Language Models (LLMs) for time-series representation learning. Central to our approach is that we reconceive time-series forecasting as a self-supervised, multi-patch prediction task, which, compared to traditional mask-and-reconstruction methods, captures temporal dynamics in patch representations more effectively. Our strategy encompasses two-stage training: (i). a causal continual pre-training phase on various time-series datasets, anchored on next patch prediction, effectively syncing LLM capabilities with the intricacies of time-series data; (ii). fine-tuning for multi-patch prediction in the targeted time-series context. A distinctive element of our framework is the patch-wise decoding layer, which departs from previous methods reliant on sequence-level decoding. Such a design directly transposes individual patches into temporal sequences, thereby significantly bolstering the model's proficiency in mastering temporal patch-based representations. aLLM4TS demonstrates superior performance in several downstream tasks, proving its effectiveness in deriving temporal representations with enhanced transferability and marking a pivotal advancement in the adaptation of LLMs for time-series analysis.
CFBenchmark: Chinese Financial Assistant Benchmark for Large Language Model
Nov 10, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated great potential in the financial domain. Thus, it becomes important to assess the performance of LLMs in the financial tasks. In this work, we introduce CFBenchmark, to evaluate the performance of LLMs for Chinese financial assistant. The basic version of CFBenchmark is designed to evaluate the basic ability in Chinese financial text processing from three aspects~(\emph{i.e.} recognition, classification, and generation) including eight tasks, and includes financial texts ranging in length from 50 to over 1,800 characters. We conduct experiments on several LLMs available in the literature with CFBenchmark-Basic, and the experimental results indicate that while some LLMs show outstanding performance in specific tasks, overall, there is still significant room for improvement in basic tasks of financial text processing with existing models. In the future, we plan to explore the advanced version of CFBenchmark, aiming to further explore the extensive capabilities of language models in more profound dimensions as a financial assistant in Chinese. Our codes are released at https://github.com/TongjiFinLab/CFBenchmark.
CFGPT: Chinese Financial Assistant with Large Language Model
Sep 22, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated great potential in natural language processing tasks within the financial domain. In this work, we present a Chinese Financial Generative Pre-trained Transformer framework, named CFGPT, which includes a dataset~(CFData) for pre-training and supervised fine-tuning, a financial LLM~(CFLLM) to adeptly manage financial texts, and a deployment framework~(CFAPP) designed to navigate real-world financial applications. The CFData comprising both a pre-training dataset and a supervised fine-tuning dataset, where the pre-training dataset collates Chinese financial data and analytics, alongside a smaller subset of general-purpose text with 584M documents and 141B tokens in total, and the supervised fine-tuning dataset is tailored for six distinct financial tasks, embodying various facets of financial analysis and decision-making with 1.5M instruction pairs and 1.5B tokens in total. The CFLLM, which is based on InternLM-7B to balance the model capability and size, is trained on CFData in two stage, continued pre-training and supervised fine-tuning. The CFAPP is centered on large language models (LLMs) and augmented with additional modules to ensure multifaceted functionality in real-world application. Our codes are released at https://github.com/TongjiFinLab/CFGPT.
Deep Image Harmonization in Dual Color Spaces
Aug 05, 2023Abstract:Image harmonization is an essential step in image composition that adjusts the appearance of composite foreground to address the inconsistency between foreground and background. Existing methods primarily operate in correlated $RGB$ color space, leading to entangled features and limited representation ability. In contrast, decorrelated color space (e.g., $Lab$) has decorrelated channels that provide disentangled color and illumination statistics. In this paper, we explore image harmonization in dual color spaces, which supplements entangled $RGB$ features with disentangled $L$, $a$, $b$ features to alleviate the workload in harmonization process. The network comprises a $RGB$ harmonization backbone, an $Lab$ encoding module, and an $Lab$ control module. The backbone is a U-Net network translating composite image to harmonized image. Three encoders in $Lab$ encoding module extract three control codes independently from $L$, $a$, $b$ channels, which are used to manipulate the decoder features in harmonization backbone via $Lab$ control module. Our code and model are available at \href{https://github.com/bcmi/DucoNet-Image-Harmonization}{https://github.com/bcmi/DucoNet-Image-Harmonization}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge