Yuxuan Bian
IC-Custom: Diverse Image Customization via In-Context Learning
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Image customization, a crucial technique for industrial media production, aims to generate content that is consistent with reference images. However, current approaches conventionally separate image customization into position-aware and position-free customization paradigms and lack a universal framework for diverse customization, limiting their applications across various scenarios. To overcome these limitations, we propose IC-Custom, a unified framework that seamlessly integrates position-aware and position-free image customization through in-context learning. IC-Custom concatenates reference images with target images to a polyptych, leveraging DiT's multi-modal attention mechanism for fine-grained token-level interactions. We introduce the In-context Multi-Modal Attention (ICMA) mechanism with learnable task-oriented register tokens and boundary-aware positional embeddings to enable the model to correctly handle different task types and distinguish various inputs in polyptych configurations. To bridge the data gap, we carefully curated a high-quality dataset of 12k identity-consistent samples with 8k from real-world sources and 4k from high-quality synthetic data, avoiding the overly glossy and over-saturated synthetic appearance. IC-Custom supports various industrial applications, including try-on, accessory placement, furniture arrangement, and creative IP customization. Extensive evaluations on our proposed ProductBench and the publicly available DreamBench demonstrate that IC-Custom significantly outperforms community workflows, closed-source models, and state-of-the-art open-source approaches. IC-Custom achieves approximately 73% higher human preference across identity consistency, harmonicity, and text alignment metrics, while training only 0.4% of the original model parameters. Project page: https://liyaowei-stu.github.io/project/IC_Custom
VideoPainter: Any-length Video Inpainting and Editing with Plug-and-Play Context Control
Mar 07, 2025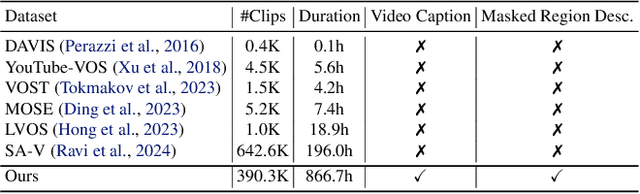
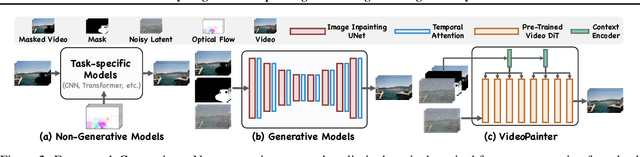
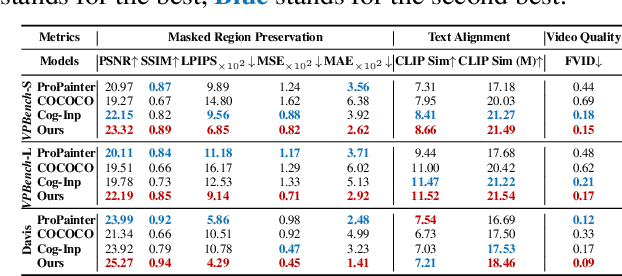
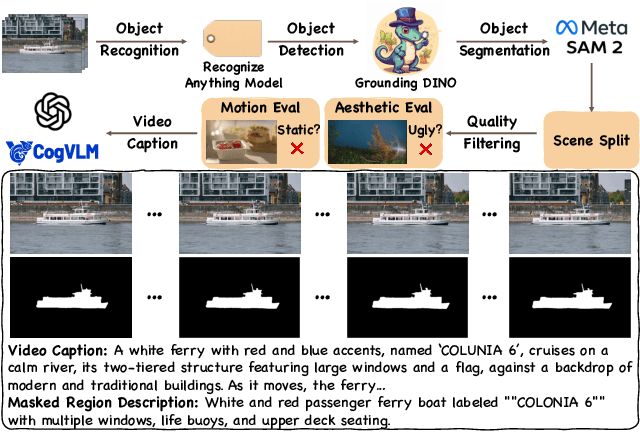
Abstract:Video inpainting, which aims to restore corrupted video content, has experienced substantial progress. Despite these advances, existing methods, whether propagating unmasked region pixels through optical flow and receptive field priors, or extending image-inpainting models temporally, face challenges in generating fully masked objects or balancing the competing objectives of background context preservation and foreground generation in one model, respectively. To address these limitations, we propose a novel dual-stream paradigm VideoPainter that incorporates an efficient context encoder (comprising only 6% of the backbone parameters) to process masked videos and inject backbone-aware background contextual cues to any pre-trained video DiT, producing semantically consistent content in a plug-and-play manner. This architectural separation significantly reduces the model's learning complexity while enabling nuanced integration of crucial background context. We also introduce a novel target region ID resampling technique that enables any-length video inpainting, greatly enhancing our practical applicability. Additionally, we establish a scalable dataset pipeline leveraging current vision understanding models, contributing VPData and VPBench to facilitate segmentation-based inpainting training and assessment, the largest video inpainting dataset and benchmark to date with over 390K diverse clips. Using inpainting as a pipeline basis, we also explore downstream applications including video editing and video editing pair data generation, demonstrating competitive performance and significant practical potential. Extensive experiments demonstrate VideoPainter's superior performance in both any-length video inpainting and editing, across eight key metrics, including video quality, mask region preservation, and textual coherence.
BrushEdit: All-In-One Image Inpainting and Editing
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Image editing has advanced significantly with the development of diffusion models using both inversion-based and instruction-based methods. However, current inversion-based approaches struggle with big modifications (e.g., adding or removing objects) due to the structured nature of inversion noise, which hinders substantial changes. Meanwhile, instruction-based methods often constrain users to black-box operations, limiting direct interaction for specifying editing regions and intensity. To address these limitations, we propose BrushEdit, a novel inpainting-based instruction-guided image editing paradigm, which leverages multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and image inpainting models to enable autonomous, user-friendly, and interactive free-form instruction editing. Specifically, we devise a system enabling free-form instruction editing by integrating MLLMs and a dual-branch image inpainting model in an agent-cooperative framework to perform editing category classification, main object identification, mask acquisition, and editing area inpainting. Extensive experiments show that our framework effectively combines MLLMs and inpainting models, achieving superior performance across seven metrics including mask region preservation and editing effect coherence.
Adding Multimodal Controls to Whole-body Human Motion Generation
Aug 04, 2024
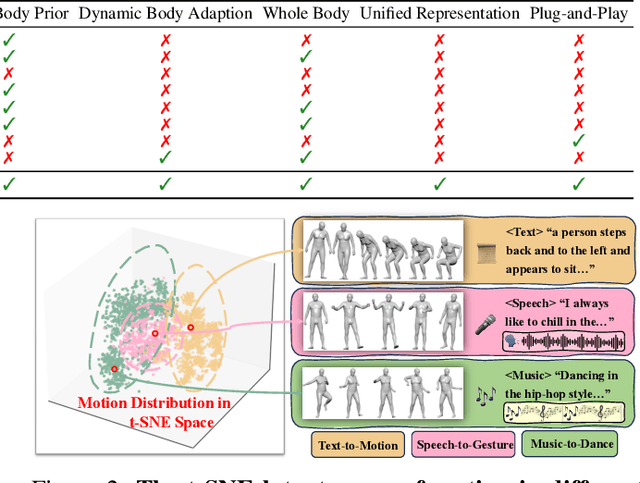
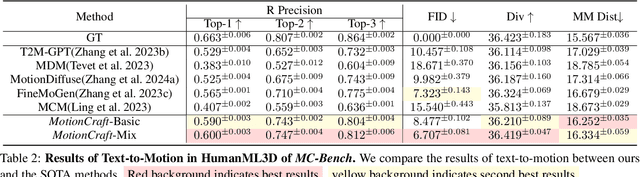
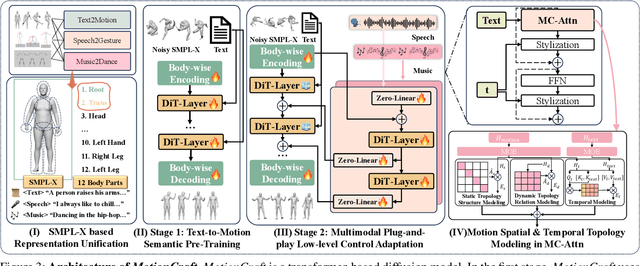
Abstract:Whole-body multimodal motion generation, controlled by text, speech, or music, has numerous applications including video generation and character animation. However, employing a unified model to accomplish various generation tasks with different condition modalities presents two main challenges: motion distribution drifts across different generation scenarios and the complex optimization of mixed conditions with varying granularity. Furthermore, inconsistent motion formats in existing datasets further hinder effective multimodal motion generation. In this paper, we propose ControlMM, a unified framework to Control whole-body Multimodal Motion generation in a plug-and-play manner. To effectively learn and transfer motion knowledge across different motion distributions, we propose ControlMM-Attn, for parallel modeling of static and dynamic human topology graphs. To handle conditions with varying granularity, ControlMM employs a coarse-to-fine training strategy, including stage-1 text-to-motion pre-training for semantic generation and stage-2 multimodal control adaptation for conditions of varying low-level granularity. To address existing benchmarks' varying motion format limitations, we introduce ControlMM-Bench, the first publicly available multimodal whole-body human motion generation benchmark based on the unified whole-body SMPL-X format. Extensive experiments show that ControlMM achieves state-of-the-art performance across various standard motion generation tasks. Our website is at https://yxbian23.github.io/ControlMM.
Adding Multi-modal Controls to Whole-body Human Motion Generation
Jul 30, 2024



Abstract:Whole-body multi-modal motion generation, controlled by text, speech, or music, has numerous applications including video generation and character animation. However, employing a unified model to accomplish various generation tasks with different condition modalities presents two main challenges: motion distribution drifts across different generation scenarios and the complex optimization of mixed conditions with varying granularity. Furthermore, inconsistent motion formats in existing datasets further hinder effective multi-modal motion generation. In this paper, we propose ControlMM, a unified framework to Control whole-body Multi-modal Motion generation in a plug-and-play manner. To effectively learn and transfer motion knowledge across different motion distributions, we propose ControlMM-Attn, for parallel modeling of static and dynamic human topology graphs. To handle conditions with varying granularity, ControlMM employs a coarse-to-fine training strategy, including stage-1 text-to-motion pre-training for semantic generation and stage-2 multi-modal control adaptation for conditions of varying low-level granularity. To address existing benchmarks' varying motion format limitations, we introduce ControlMM-Bench, the first publicly available multi-modal whole-body human motion generation benchmark based on the unified whole-body SMPL-X format. Extensive experiments show that ControlMM achieves state-of-the-art performance across various standard motion generation tasks. Our website is at https://yxbian23.github.io/ControlMM.
Image Inpainting Models are Effective Tools for Instruction-guided Image Editing
Jul 18, 2024

Abstract:This is the technique report for the winning solution of the CVPR2024 GenAI Media Generation Challenge Workshop's Instruction-guided Image Editing track. Instruction-guided image editing has been largely studied in recent years. The most advanced methods, such as SmartEdit and MGIE, usually combine large language models with diffusion models through joint training, where the former provides text understanding ability, and the latter provides image generation ability. However, in our experiments, we find that simply connecting large language models and image generation models through intermediary guidance such as masks instead of joint fine-tuning leads to a better editing performance and success rate. We use a 4-step process IIIE (Inpainting-based Instruction-guided Image Editing): editing category classification, main editing object identification, editing mask acquisition, and image inpainting. Results show that through proper combinations of language models and image inpainting models, our pipeline can reach a high success rate with satisfying visual quality.
Beyond Trend and Periodicity: Guiding Time Series Forecasting with Textual Cues
May 22, 2024Abstract:This work introduces a novel Text-Guided Time Series Forecasting (TGTSF) task. By integrating textual cues, such as channel descriptions and dynamic news, TGTSF addresses the critical limitations of traditional methods that rely purely on historical data. To support this task, we propose TGForecaster, a robust baseline model that fuses textual cues and time series data using cross-attention mechanisms. We then present four meticulously curated benchmark datasets to validate the proposed framework, ranging from simple periodic data to complex, event-driven fluctuations. Our comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that TGForecaster consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance, highlighting the transformative potential of incorporating textual information into time series forecasting. This work not only pioneers a novel forecasting task but also establishes a new benchmark for future research, driving advancements in multimodal data integration for time series models.
BrushNet: A Plug-and-Play Image Inpainting Model with Decomposed Dual-Branch Diffusion
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:Image inpainting, the process of restoring corrupted images, has seen significant advancements with the advent of diffusion models (DMs). Despite these advancements, current DM adaptations for inpainting, which involve modifications to the sampling strategy or the development of inpainting-specific DMs, frequently suffer from semantic inconsistencies and reduced image quality. Addressing these challenges, our work introduces a novel paradigm: the division of masked image features and noisy latent into separate branches. This division dramatically diminishes the model's learning load, facilitating a nuanced incorporation of essential masked image information in a hierarchical fashion. Herein, we present BrushNet, a novel plug-and-play dual-branch model engineered to embed pixel-level masked image features into any pre-trained DM, guaranteeing coherent and enhanced image inpainting outcomes. Additionally, we introduce BrushData and BrushBench to facilitate segmentation-based inpainting training and performance assessment. Our extensive experimental analysis demonstrates BrushNet's superior performance over existing models across seven key metrics, including image quality, mask region preservation, and textual coherence.
Multi-Patch Prediction: Adapting LLMs for Time Series Representation Learning
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:In this study, we present aLLM4TS, an innovative framework that adapts Large Language Models (LLMs) for time-series representation learning. Central to our approach is that we reconceive time-series forecasting as a self-supervised, multi-patch prediction task, which, compared to traditional mask-and-reconstruction methods, captures temporal dynamics in patch representations more effectively. Our strategy encompasses two-stage training: (i). a causal continual pre-training phase on various time-series datasets, anchored on next patch prediction, effectively syncing LLM capabilities with the intricacies of time-series data; (ii). fine-tuning for multi-patch prediction in the targeted time-series context. A distinctive element of our framework is the patch-wise decoding layer, which departs from previous methods reliant on sequence-level decoding. Such a design directly transposes individual patches into temporal sequences, thereby significantly bolstering the model's proficiency in mastering temporal patch-based representations. aLLM4TS demonstrates superior performance in several downstream tasks, proving its effectiveness in deriving temporal representations with enhanced transferability and marking a pivotal advancement in the adaptation of LLMs for time-series analysis.
Direct Inversion: Boosting Diffusion-based Editing with 3 Lines of Code
Oct 19, 2023



Abstract:Text-guided diffusion models have revolutionized image generation and editing, offering exceptional realism and diversity. Specifically, in the context of diffusion-based editing, where a source image is edited according to a target prompt, the process commences by acquiring a noisy latent vector corresponding to the source image via the diffusion model. This vector is subsequently fed into separate source and target diffusion branches for editing. The accuracy of this inversion process significantly impacts the final editing outcome, influencing both essential content preservation of the source image and edit fidelity according to the target prompt. Prior inversion techniques aimed at finding a unified solution in both the source and target diffusion branches. However, our theoretical and empirical analyses reveal that disentangling these branches leads to a distinct separation of responsibilities for preserving essential content and ensuring edit fidelity. Building on this insight, we introduce "Direct Inversion," a novel technique achieving optimal performance of both branches with just three lines of code. To assess image editing performance, we present PIE-Bench, an editing benchmark with 700 images showcasing diverse scenes and editing types, accompanied by versatile annotations and comprehensive evaluation metrics. Compared to state-of-the-art optimization-based inversion techniques, our solution not only yields superior performance across 8 editing methods but also achieves nearly an order of speed-up.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge