Jianyuan Zhong
Ehsan
Mathesis: Towards Formal Theorem Proving from Natural Languages
Jun 08, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models show strong promise for formal reasoning. However, most LLM-based theorem provers have long been constrained by the need for expert-written formal statements as inputs, limiting their applicability to real-world problems expressed in natural language. We tackle this gap with Mathesis, the first end-to-end theorem proving pipeline processing informal problem statements. It contributes Mathesis-Autoformalizer, the first autoformalizer using reinforcement learning to enhance the formalization ability of natural language problems, aided by our novel LeanScorer framework for nuanced formalization quality assessment. It also proposes a Mathesis-Prover, which generates formal proofs from the formalized statements. To evaluate the real-world applicability of end-to-end formal theorem proving, we introduce Gaokao-Formal, a benchmark of 488 complex problems from China's national college entrance exam. Our approach is carefully designed, with a thorough study of each component. Experiments demonstrate Mathesis's effectiveness, with the autoformalizer outperforming the best baseline by 22% in pass-rate on Gaokao-Formal. The full system surpasses other model combinations, achieving 64% accuracy on MiniF2F with pass@32 and a state-of-the-art 18% on Gaokao-Formal.
Solve-Detect-Verify: Inference-Time Scaling with Flexible Generative Verifier
May 17, 2025
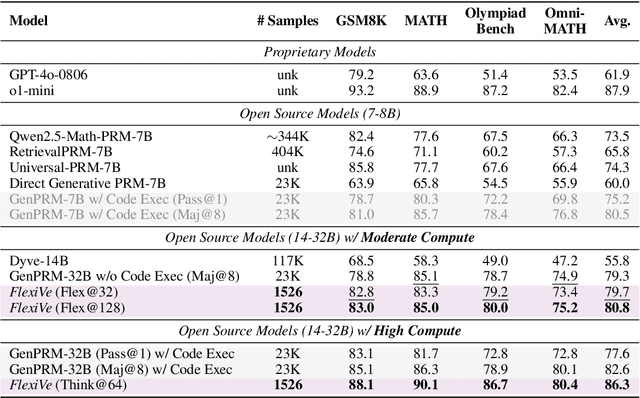
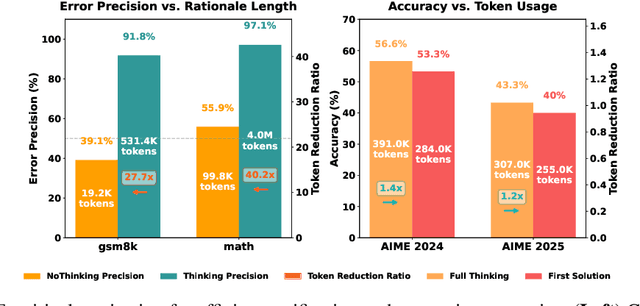
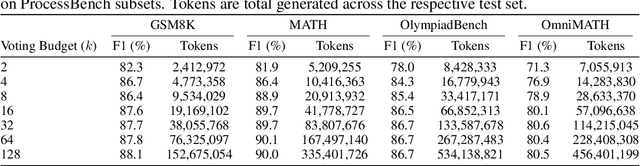
Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning for complex tasks inherently involves a trade-off between solution accuracy and computational efficiency. The subsequent step of verification, while intended to improve performance, further complicates this landscape by introducing its own challenging trade-off: sophisticated Generative Reward Models (GenRMs) can be computationally prohibitive if naively integrated with LLMs at test-time, while simpler, faster methods may lack reliability. To overcome these challenges, we introduce FlexiVe, a novel generative verifier that flexibly balances computational resources between rapid, reliable fast thinking and meticulous slow thinking using a Flexible Allocation of Verification Budget strategy. We further propose the Solve-Detect-Verify pipeline, an efficient inference-time scaling framework that intelligently integrates FlexiVe, proactively identifying solution completion points to trigger targeted verification and provide focused solver feedback. Experiments show FlexiVe achieves superior accuracy in pinpointing errors within reasoning traces on ProcessBench. Furthermore, on challenging mathematical reasoning benchmarks (AIME 2024, AIME 2025, and CNMO), our full approach outperforms baselines like self-consistency in reasoning accuracy and inference efficiency. Our system offers a scalable and effective solution to enhance LLM reasoning at test time.
DeepCircuitX: A Comprehensive Repository-Level Dataset for RTL Code Understanding, Generation, and PPA Analysis
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces DeepCircuitX, a comprehensive repository-level dataset designed to advance RTL (Register Transfer Level) code understanding, generation, and power-performance-area (PPA) analysis. Unlike existing datasets that are limited to either file-level RTL code or physical layout data, DeepCircuitX provides a holistic, multilevel resource that spans repository, file, module, and block-level RTL code. This structure enables more nuanced training and evaluation of large language models (LLMs) for RTL-specific tasks. DeepCircuitX is enriched with Chain of Thought (CoT) annotations, offering detailed descriptions of functionality and structure at multiple levels. These annotations enhance its utility for a wide range of tasks, including RTL code understanding, generation, and completion. Additionally, the dataset includes synthesized netlists and PPA metrics, facilitating early-stage design exploration and enabling accurate PPA prediction directly from RTL code. We demonstrate the dataset's effectiveness on various LLMs finetuned with our dataset and confirm the quality with human evaluations. Our results highlight DeepCircuitX as a critical resource for advancing RTL-focused machine learning applications in hardware design automation.Our data is available at https://zeju.gitbook.io/lcm-team.
DeepGate3: Towards Scalable Circuit Representation Learning
Jul 15, 2024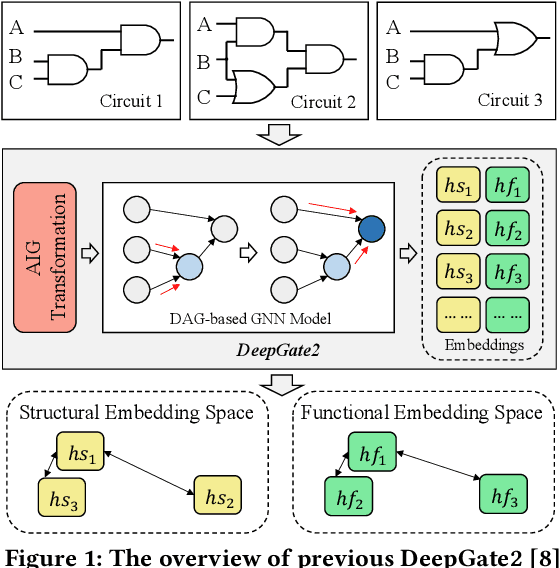
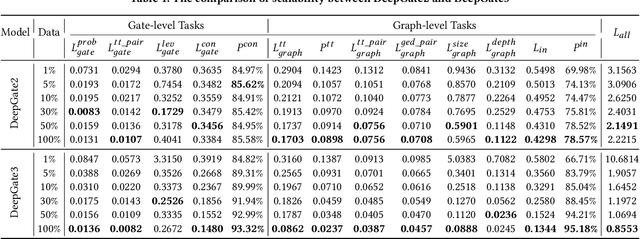
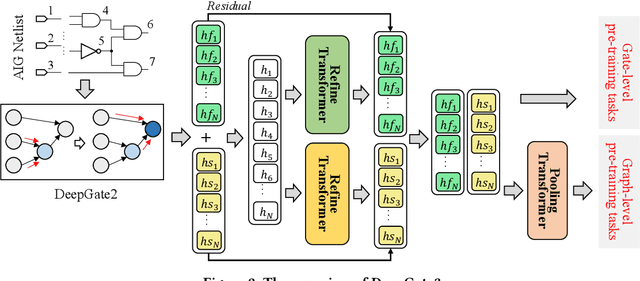
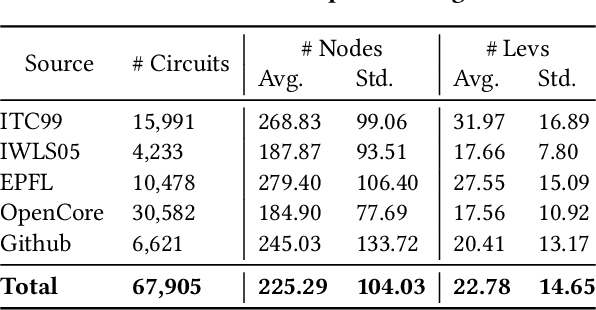
Abstract:Circuit representation learning has shown promising results in advancing the field of Electronic Design Automation (EDA). Existing models, such as DeepGate Family, primarily utilize Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to encode circuit netlists into gate-level embeddings. However, the scalability of GNN-based models is fundamentally constrained by architectural limitations, impacting their ability to generalize across diverse and complex circuit designs. To address these challenges, we introduce DeepGate3, an enhanced architecture that integrates Transformer modules following the initial GNN processing. This novel architecture not only retains the robust gate-level representation capabilities of its predecessor, DeepGate2, but also enhances them with the ability to model subcircuits through a novel pooling transformer mechanism. DeepGate3 is further refined with multiple innovative supervision tasks, significantly enhancing its learning process and enabling superior representation of both gate-level and subcircuit structures. Our experiments demonstrate marked improvements in scalability and generalizability over traditional GNN-based approaches, establishing a significant step forward in circuit representation learning technology.
Beyond Trend and Periodicity: Guiding Time Series Forecasting with Textual Cues
May 22, 2024Abstract:This work introduces a novel Text-Guided Time Series Forecasting (TGTSF) task. By integrating textual cues, such as channel descriptions and dynamic news, TGTSF addresses the critical limitations of traditional methods that rely purely on historical data. To support this task, we propose TGForecaster, a robust baseline model that fuses textual cues and time series data using cross-attention mechanisms. We then present four meticulously curated benchmark datasets to validate the proposed framework, ranging from simple periodic data to complex, event-driven fluctuations. Our comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that TGForecaster consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance, highlighting the transformative potential of incorporating textual information into time series forecasting. This work not only pioneers a novel forecasting task but also establishes a new benchmark for future research, driving advancements in multimodal data integration for time series models.
GuardT2I: Defending Text-to-Image Models from Adversarial Prompts
Mar 03, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in Text-to-Image (T2I) models have raised significant safety concerns about their potential misuse for generating inappropriate or Not-Safe-For-Work (NSFW) contents, despite existing countermeasures such as NSFW classifiers or model fine-tuning for inappropriate concept removal. Addressing this challenge, our study unveils GuardT2I, a novel moderation framework that adopts a generative approach to enhance T2I models' robustness against adversarial prompts. Instead of making a binary classification, GuardT2I utilizes a Large Language Model (LLM) to conditionally transform text guidance embeddings within the T2I models into natural language for effective adversarial prompt detection, without compromising the models' inherent performance. Our extensive experiments reveal that GuardT2I outperforms leading commercial solutions like OpenAI-Moderation and Microsoft Azure Moderator by a significant margin across diverse adversarial scenarios.
SpeechBrain: A General-Purpose Speech Toolkit
Jun 08, 2021
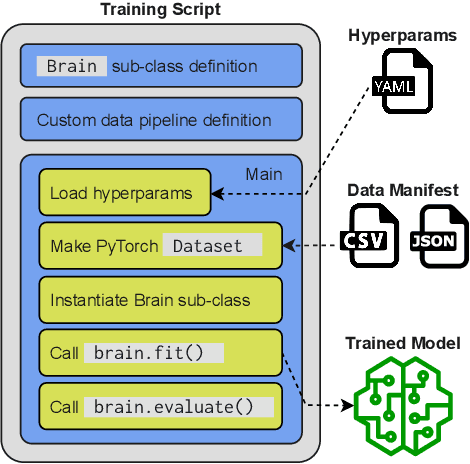

Abstract:SpeechBrain is an open-source and all-in-one speech toolkit. It is designed to facilitate the research and development of neural speech processing technologies by being simple, flexible, user-friendly, and well-documented. This paper describes the core architecture designed to support several tasks of common interest, allowing users to naturally conceive, compare and share novel speech processing pipelines. SpeechBrain achieves competitive or state-of-the-art performance in a wide range of speech benchmarks. It also provides training recipes, pretrained models, and inference scripts for popular speech datasets, as well as tutorials which allow anyone with basic Python proficiency to familiarize themselves with speech technologies.
Attention is All You Need in Speech Separation
Oct 25, 2020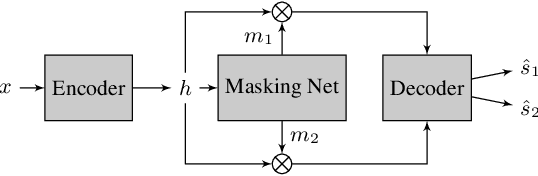
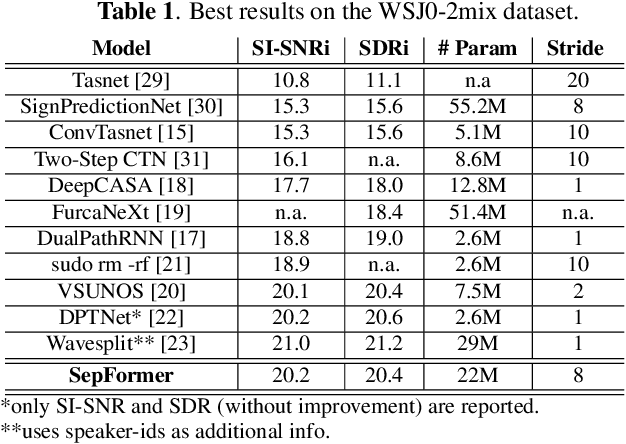
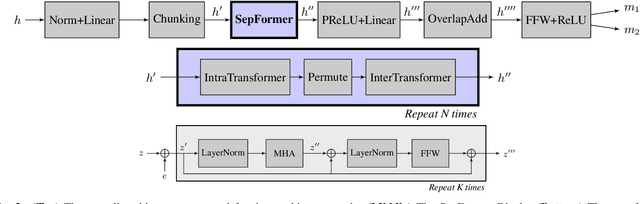
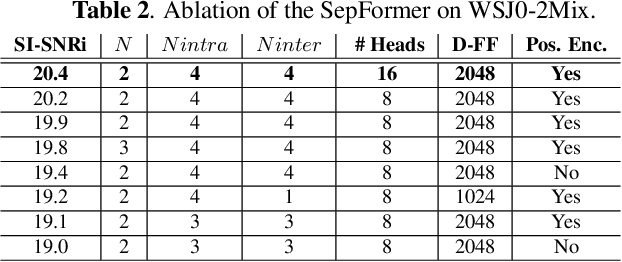
Abstract:Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) have long been the dominant architecture in sequence-to-sequence learning. RNNs, however, are inherently sequential models that do not allow parallelization of their computations. Transformers are emerging as a natural alternative to standard RNNs, replacing recurrent computations with a multi-head attention mechanism. In this paper, we propose the `SepFormer', a novel RNN-free Transformer-based neural network for speech separation. The SepFormer learns short and long-term dependencies with a multi-scale approach that employs transformers. The proposed model matches or overtakes the state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the standard WSJ0-2/3mix datasets. It indeed achieves an SI-SNRi of 20.2 dB on WSJ0-2mix matching the SOTA, and an SI-SNRi of 17.6 dB on WSJ0-3mix, a SOTA result. The SepFormer inherits the parallelization advantages of Transformers and achieves a competitive performance even when downsampling the encoded representation by a factor of 8. It is thus significantly faster and it is less memory-demanding than the latest RNN-based systems.
Multi-task self-supervised learning for Robust Speech Recognition
Jan 25, 2020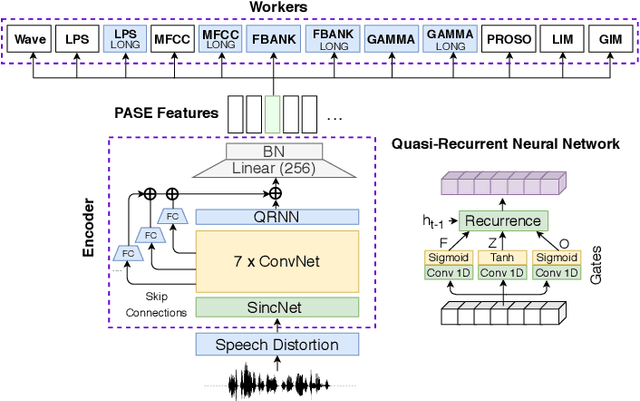
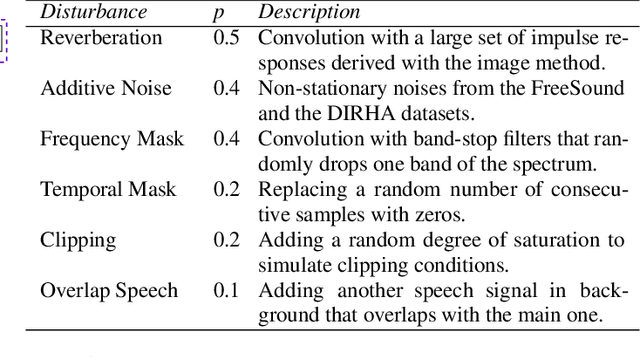
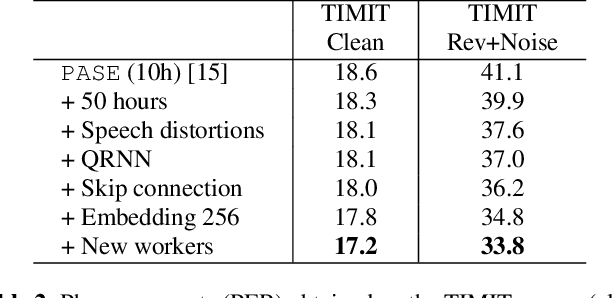
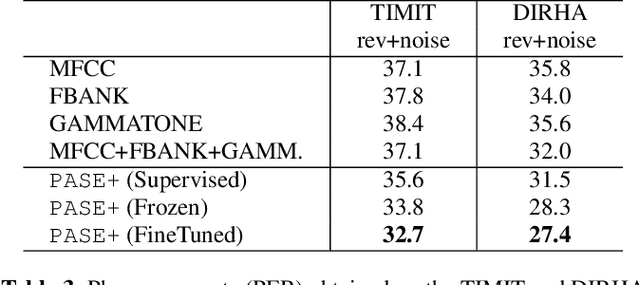
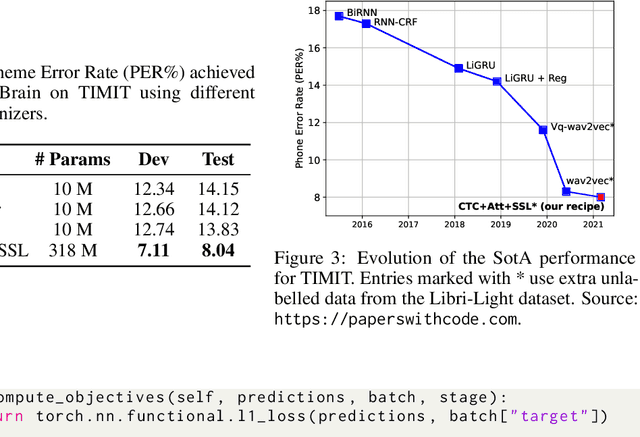
Abstract:Despite the growing interest in unsupervised learning, extracting meaningful knowledge from unlabelled audio remains an open challenge. To take a step in this direction, we recently proposed a problem-agnostic speech encoder (PASE), that combines a convolutional encoder followed by multiple neural networks, called workers, tasked to solve self-supervised problems (i.e., ones that do not require manual annotations as ground truth). PASE was shown to capture relevant speech information, including speaker voice-print and phonemes. This paper proposes PASE+, an improved version of PASE for robust speech recognition in noisy and reverberant environments. To this end, we employ an online speech distortion module, that contaminates the input signals with a variety of random disturbances. We then propose a revised encoder that better learns short- and long-term speech dynamics with an efficient combination of recurrent and convolutional networks. Finally, we refine the set of workers used in self-supervision to encourage better cooperation. Results on TIMIT, DIRHA and CHiME-5 show that PASE+ significantly outperforms both the previous version of PASE as well as common acoustic features. Interestingly, PASE+ learns transferable representations suitable for highly mismatched acoustic conditions.
UR-FUNNY: A Multimodal Language Dataset for Understanding Humor
Apr 14, 2019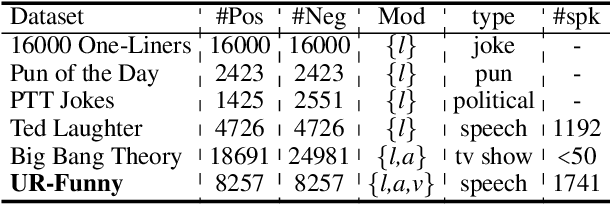
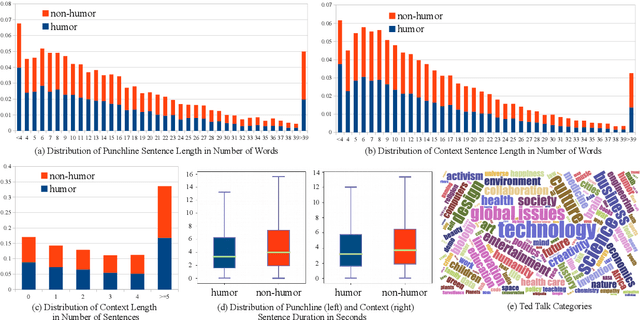
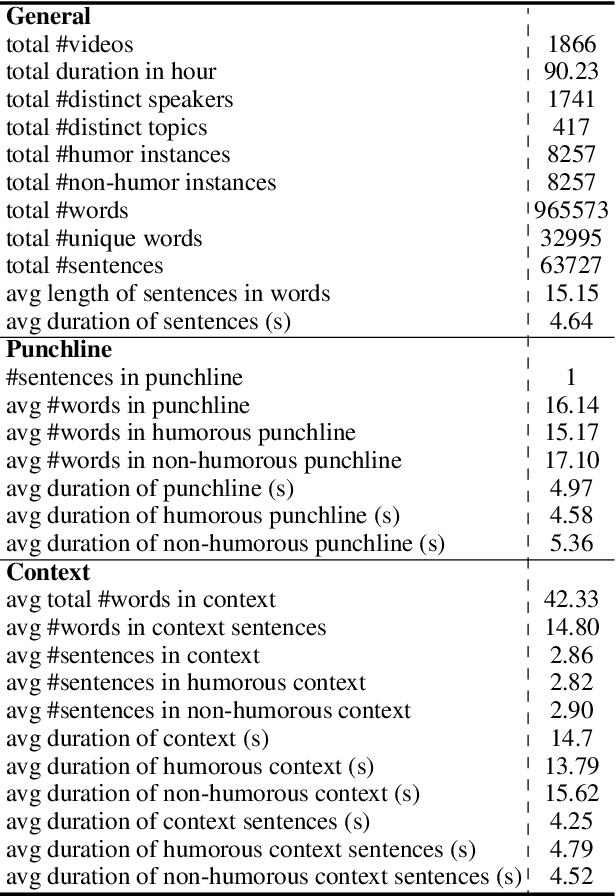
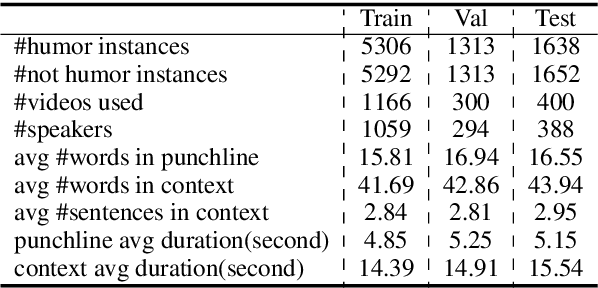
Abstract:Humor is a unique and creative communicative behavior displayed during social interactions. It is produced in a multimodal manner, through the usage of words (text), gestures (vision) and prosodic cues (acoustic). Understanding humor from these three modalities falls within boundaries of multimodal language; a recent research trend in natural language processing that models natural language as it happens in face-to-face communication. Although humor detection is an established research area in NLP, in a multimodal context it is an understudied area. This paper presents a diverse multimodal dataset, called UR-FUNNY, to open the door to understanding multimodal language used in expressing humor. The dataset and accompanying studies, present a framework in multimodal humor detection for the natural language processing community. UR-FUNNY is publicly available for research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge