Yunhao Zhou
DynamicRTL: RTL Representation Learning for Dynamic Circuit Behavior
Nov 12, 2025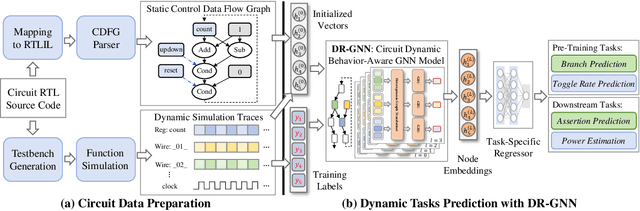
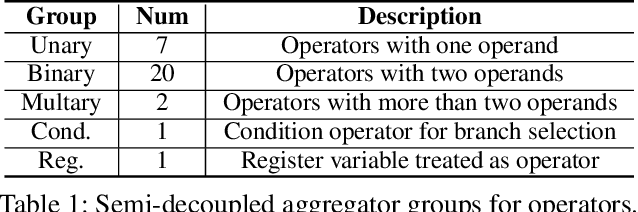
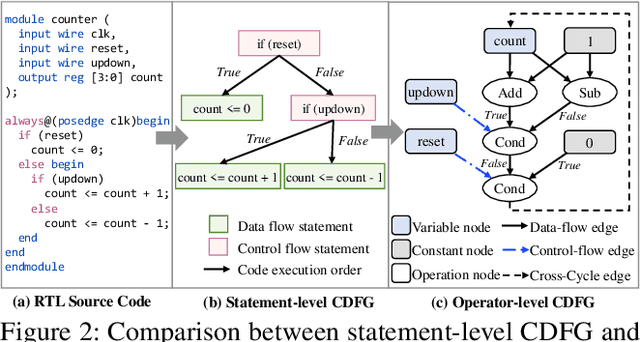
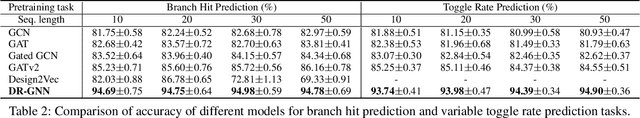
Abstract:There is a growing body of work on using Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to learn representations of circuits, focusing primarily on their static characteristics. However, these models fail to capture circuit runtime behavior, which is crucial for tasks like circuit verification and optimization. To address this limitation, we introduce DR-GNN (DynamicRTL-GNN), a novel approach that learns RTL circuit representations by incorporating both static structures and multi-cycle execution behaviors. DR-GNN leverages an operator-level Control Data Flow Graph (CDFG) to represent Register Transfer Level (RTL) circuits, enabling the model to capture dynamic dependencies and runtime execution. To train and evaluate DR-GNN, we build the first comprehensive dynamic circuit dataset, comprising over 6,300 Verilog designs and 63,000 simulation traces. Our results demonstrate that DR-GNN outperforms existing models in branch hit prediction and toggle rate prediction. Furthermore, its learned representations transfer effectively to related dynamic circuit tasks, achieving strong performance in power estimation and assertion prediction.
Speculative Decoding for Verilog: Speed and Quality, All in One
Mar 18, 2025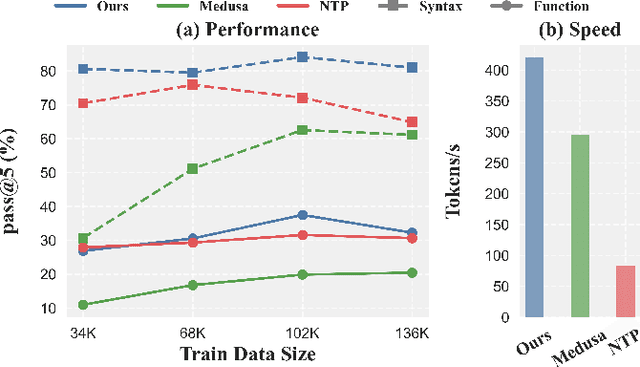
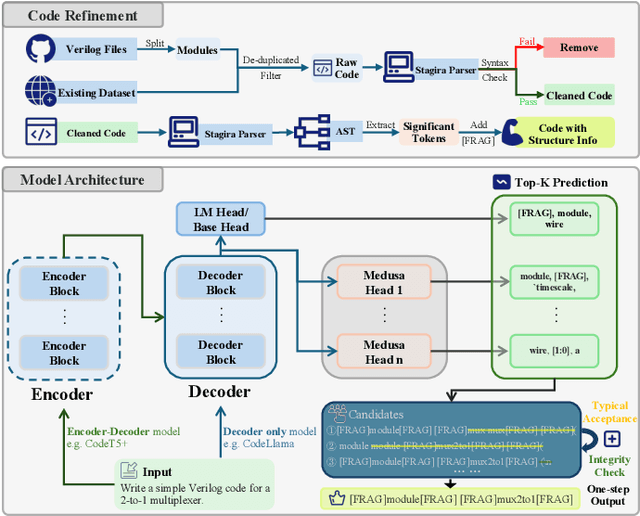
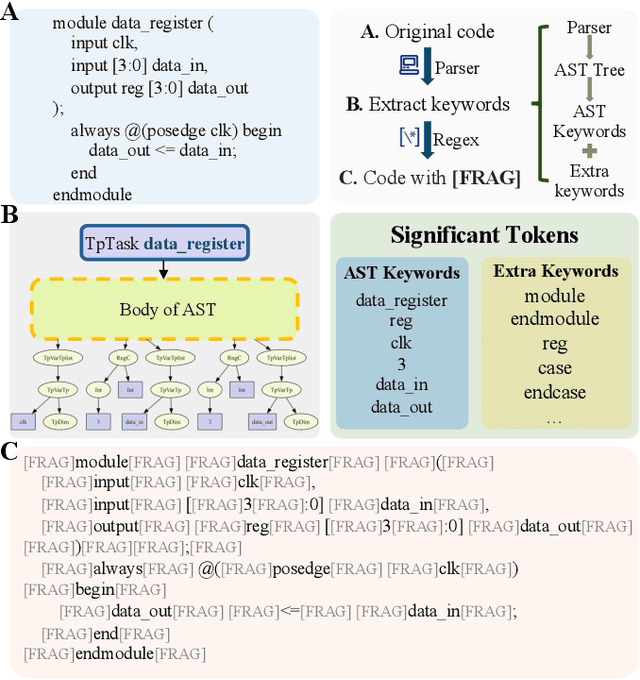
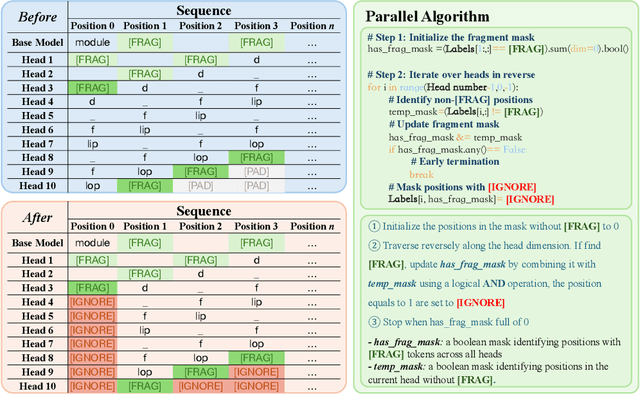
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized code generation tasks across various programming languages. However, the unique characteristics of programming languages, particularly those like Verilog with specific syntax and lower representation in training datasets, pose significant challenges for conventional tokenization and decoding approaches. In this paper, we introduce a novel application of speculative decoding for Verilog code generation, showing that it can improve both inference speed and output quality, effectively achieving speed and quality all in one. Unlike standard LLM tokenization schemes, which often fragment meaningful code structures, our approach aligns decoding stops with syntactically significant tokens, making it easier for models to learn the token distribution. This refinement addresses inherent tokenization issues and enhances the model's ability to capture Verilog's logical constructs more effectively. Our experimental results show that our method achieves up to a 5.05x speedup in Verilog code generation and increases pass@10 functional accuracy on RTLLM by up to 17.19% compared to conventional training strategies. These findings highlight speculative decoding as a promising approach to bridge the quality gap in code generation for specialized programming languages.
DeepCircuitX: A Comprehensive Repository-Level Dataset for RTL Code Understanding, Generation, and PPA Analysis
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces DeepCircuitX, a comprehensive repository-level dataset designed to advance RTL (Register Transfer Level) code understanding, generation, and power-performance-area (PPA) analysis. Unlike existing datasets that are limited to either file-level RTL code or physical layout data, DeepCircuitX provides a holistic, multilevel resource that spans repository, file, module, and block-level RTL code. This structure enables more nuanced training and evaluation of large language models (LLMs) for RTL-specific tasks. DeepCircuitX is enriched with Chain of Thought (CoT) annotations, offering detailed descriptions of functionality and structure at multiple levels. These annotations enhance its utility for a wide range of tasks, including RTL code understanding, generation, and completion. Additionally, the dataset includes synthesized netlists and PPA metrics, facilitating early-stage design exploration and enabling accurate PPA prediction directly from RTL code. We demonstrate the dataset's effectiveness on various LLMs finetuned with our dataset and confirm the quality with human evaluations. Our results highlight DeepCircuitX as a critical resource for advancing RTL-focused machine learning applications in hardware design automation.Our data is available at https://zeju.gitbook.io/lcm-team.
DeepRTL: Bridging Verilog Understanding and Generation with a Unified Representation Model
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have shown significant potential for automating hardware description language (HDL) code generation from high-level natural language instructions. While fine-tuning has improved LLMs' performance in hardware design tasks, prior efforts have largely focused on Verilog generation, overlooking the equally critical task of Verilog understanding. Furthermore, existing models suffer from weak alignment between natural language descriptions and Verilog code, hindering the generation of high-quality, synthesizable designs. To address these issues, we present DeepRTL, a unified representation model that excels in both Verilog understanding and generation. Based on CodeT5+, DeepRTL is fine-tuned on a comprehensive dataset that aligns Verilog code with rich, multi-level natural language descriptions. We also introduce the first benchmark for Verilog understanding and take the initiative to apply embedding similarity and GPT Score to evaluate the models' understanding capabilities. These metrics capture semantic similarity more accurately than traditional methods like BLEU and ROUGE, which are limited to surface-level n-gram overlaps. By adapting curriculum learning to train DeepRTL, we enable it to significantly outperform GPT-4 in Verilog understanding tasks, while achieving performance on par with OpenAI's o1-preview model in Verilog generation tasks.
Natural language is not enough: Benchmarking multi-modal generative AI for Verilog generation
Jul 11, 2024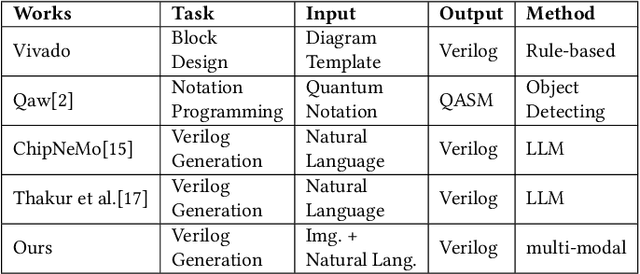
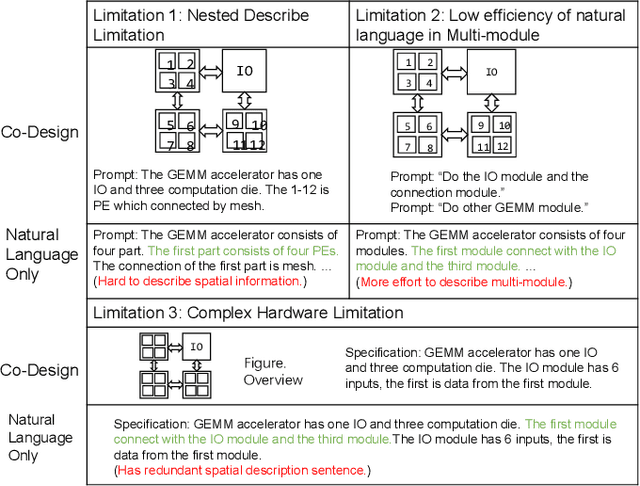
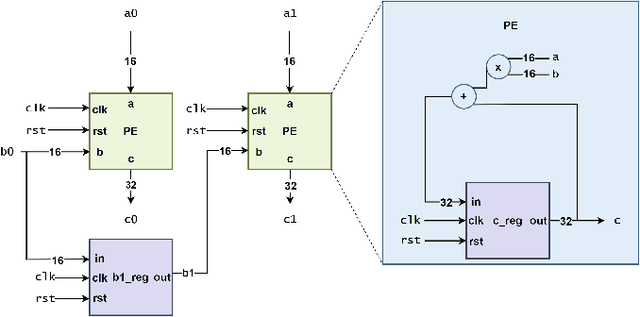
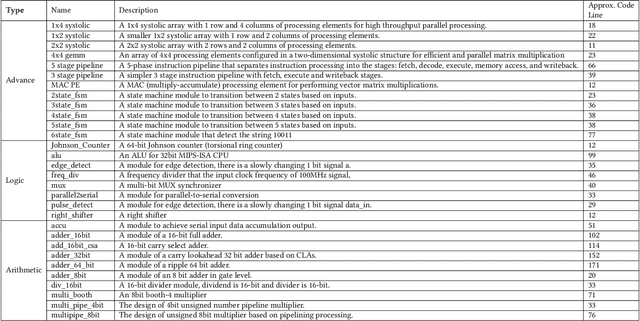
Abstract:Natural language interfaces have exhibited considerable potential in the automation of Verilog generation derived from high-level specifications through the utilization of large language models, garnering significant attention. Nevertheless, this paper elucidates that visual representations contribute essential contextual information critical to design intent for hardware architectures possessing spatial complexity, potentially surpassing the efficacy of natural-language-only inputs. Expanding upon this premise, our paper introduces an open-source benchmark for multi-modal generative models tailored for Verilog synthesis from visual-linguistic inputs, addressing both singular and complex modules. Additionally, we introduce an open-source visual and natural language Verilog query language framework to facilitate efficient and user-friendly multi-modal queries. To evaluate the performance of the proposed multi-modal hardware generative AI in Verilog generation tasks, we compare it with a popular method that relies solely on natural language. Our results demonstrate a significant accuracy improvement in the multi-modal generated Verilog compared to queries based solely on natural language. We hope to reveal a new approach to hardware design in the large-hardware-design-model era, thereby fostering a more diversified and productive approach to hardware design.
Data is all you need: Finetuning LLMs for Chip Design via an Automated design-data augmentation framework
Mar 17, 2024
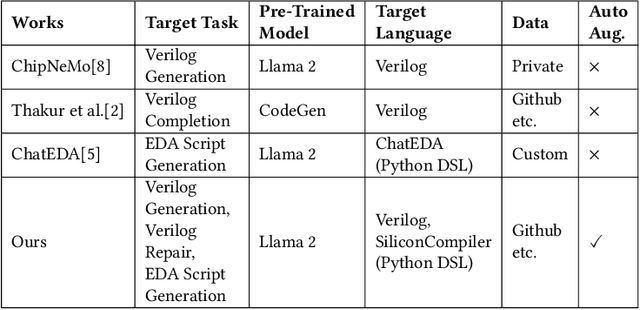


Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have demonstrated their potential for automated generation of hardware description language (HDL) code from high-level prompts. Researchers have utilized fine-tuning to enhance the ability of these large language models (LLMs) in the field of Chip Design. However, the lack of Verilog data hinders further improvement in the quality of Verilog generation by LLMs. Additionally, the absence of a Verilog and Electronic Design Automation (EDA) script data augmentation framework significantly increases the time required to prepare the training dataset for LLM trainers. This paper proposes an automated design-data augmentation framework, which generates high-volume and high-quality natural language aligned with Verilog and EDA scripts. For Verilog generation, it translates Verilog files to an abstract syntax tree and then maps nodes to natural language with a predefined template. For Verilog repair, it uses predefined rules to generate the wrong verilog file and then pairs EDA Tool feedback with the right and wrong verilog file. For EDA Script generation, it uses existing LLM(GPT-3.5) to obtain the description of the Script. To evaluate the effectiveness of our data augmentation method, we finetune Llama2-13B and Llama2-7B models using the dataset generated by our augmentation framework. The results demonstrate a significant improvement in the Verilog generation tasks with LLMs. Moreover, the accuracy of Verilog generation surpasses that of the current state-of-the-art open-source Verilog generation model, increasing from 58.8% to 70.6% with the same benchmark. Our 13B model (ChipGPT-FT) has a pass rate improvement compared with GPT-3.5 in Verilog generation and outperforms in EDA script (i.e., SiliconCompiler) generation with only 200 EDA script data.
Moving Towards Centers: Re-ranking with Attention and Memory for Re-identification
May 04, 2021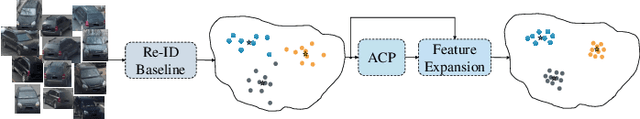
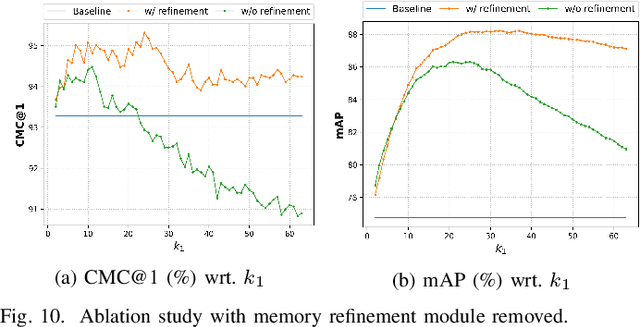
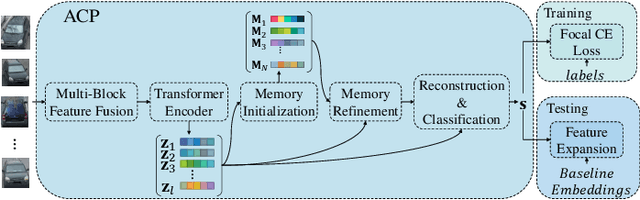
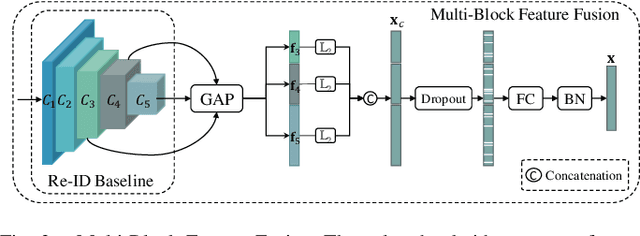
Abstract:Re-ranking utilizes contextual information to optimize the initial ranking list of person or vehicle re-identification (re-ID), which boosts the retrieval performance at post-processing steps. This paper proposes a re-ranking network to predict the correlations between the probe and top-ranked neighbor samples. Specifically, all the feature embeddings of query and gallery images are expanded and enhanced by a linear combination of their neighbors, with the correlation prediction serves as discriminative combination weights. The combination process is equivalent to moving independent embeddings toward the identity centers, improving cluster compactness. For correlation prediction, we first aggregate the contextual information for probe's k-nearest neighbors via the Transformer encoder. Then, we distill and refine the probe-related features into the Contextual Memory cell via attention mechanism. Like humans that retrieve images by not only considering probe images but also memorizing the retrieved ones, the Contextual Memory produces multi-view descriptions for each instance. Finally, the neighbors are reconstructed with features fetched from the Contextual Memory, and a binary classifier predicts their correlations with the probe. Experiments on six widely-used person and vehicle re-ID benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Especially, our method surpasses the state-of-the-art re-ranking approaches on large-scale datasets by a significant margin, i.e., with an average 3.08% CMC@1 and 7.46% mAP improvements on VERI-Wild, MSMT17, and VehicleID datasets.
Rethinking and Designing a High-performing Automatic License Plate Recognition Approach
Nov 30, 2020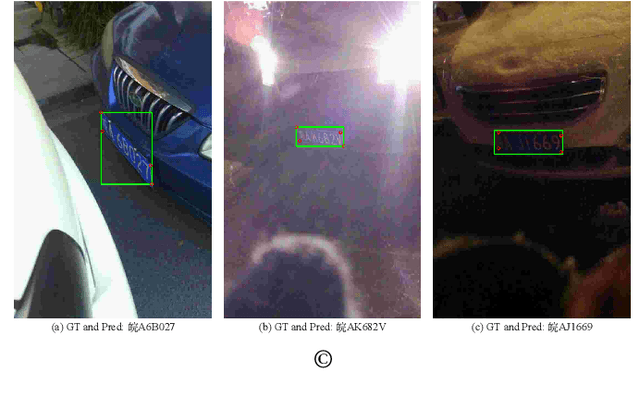
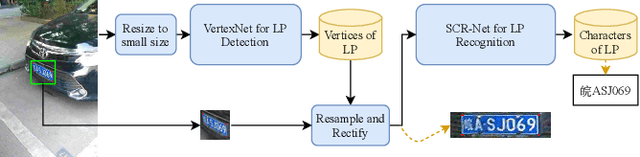
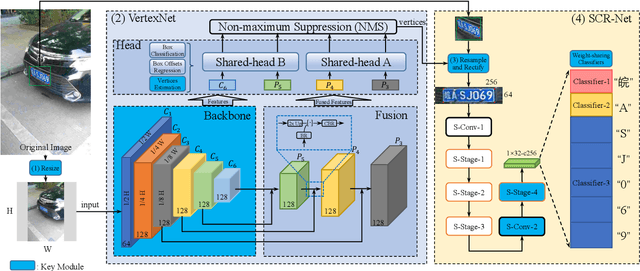
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a real-time and accurate automatic license plate recognition (ALPR) approach. Our study illustrates the outstanding design of ALPR with four insights: (1) the resampling-based cascaded framework is beneficial to both speed and accuracy; (2) the highly efficient license plate recognition should abundant additional character segmentation and recurrent neural network (RNN), but adopt a plain convolutional neural network (CNN); (3) in the case of CNN, taking advantage of vertex information on license plates improves the recognition performance; and (4) the weight-sharing character classifier addresses the lack of training images in small-scale datasets. Based on these insights, we propose a novel ALPR approach, termed VSNet. Specifically, VSNet includes two CNNs, i.e., VertexNet for license plate detection and SCR-Net for license plate recognition, which is integrated in a resampling-based cascaded manner. In VertexNet, we propose an efficient integration block to extract the spatial features of license plates. With vertex supervisory information, we propose a vertex-estimation branch in VertexNet such that license plates can be rectified as the input images of SCR-Net. Moreover, vertex-based data augmentation is employed to diverse the training samples. In SCR-Net, we propose a horizontal encoding technique for left-to-right feature extraction and a weight-sharing classifier for character recognition. Experimental results show that the proposed VSNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods by more than 50% relative improvement on error rate, achieving >99% recognition accuracy on both CCPD and AOLP datasets with 149 FPS inference speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge