SeungKyu Lee
Segment Anything Model Meets Glass: Mirror and Transparent Objects Cannot Be Easily Detected
Apr 29, 2023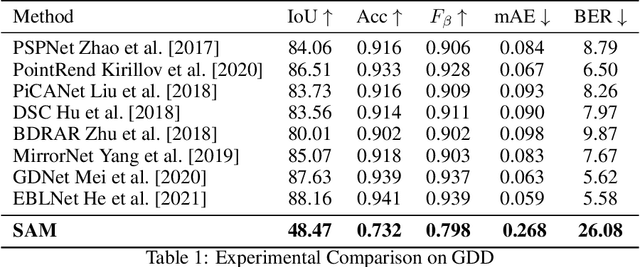
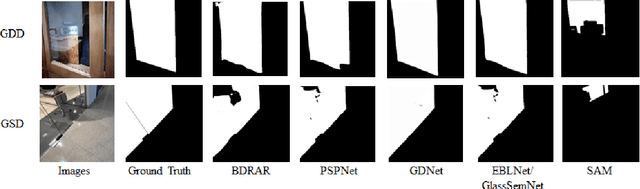
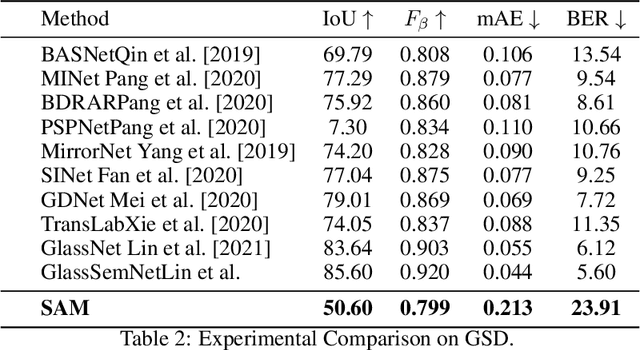

Abstract:Meta AI Research has recently released SAM (Segment Anything Model) which is trained on a large segmentation dataset of over 1 billion masks. As a foundation model in the field of computer vision, SAM (Segment Anything Model) has gained attention for its impressive performance in generic object segmentation. Despite its strong capability in a wide range of zero-shot transfer tasks, it remains unknown whether SAM can detect things in challenging setups like transparent objects. In this work, we perform an empirical evaluation of two glass-related challenging scenarios: mirror and transparent objects. We found that SAM often fails to detect the glass in both scenarios, which raises concern for deploying the SAM in safety-critical situations that have various forms of glass.
Unrealistic Feature Suppression for Generative Adversarial Networks
Jul 23, 2021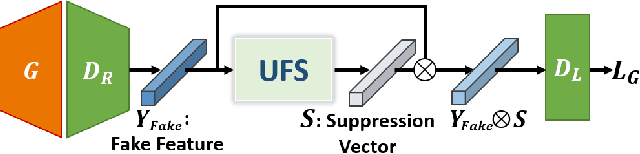



Abstract:Due to the unstable nature of minimax game between generator and discriminator, improving the performance of GANs is a challenging task. Recent studies have shown that selected high-quality samples in training improve the performance of GANs. However, sampling approaches which discard samples show limitations in some aspects such as the speed of training and optimality of the networks. In this paper we propose unrealistic feature suppression (UFS) module that keeps high-quality features and suppresses unrealistic features. UFS module keeps the training stability of networks and improves the quality of generated images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of UFS module on various models such as WGAN-GP, SNGAN, and BigGAN. By using UFS module, we achieved better Frechet inception distance and inception score compared to various baseline models. We also visualize how effectively our UFS module suppresses unrealistic features through class activation maps.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge