Sanghun Kim
Bidirectional Temporal Diffusion Model for Temporally Consistent Human Animation
Jul 19, 2023
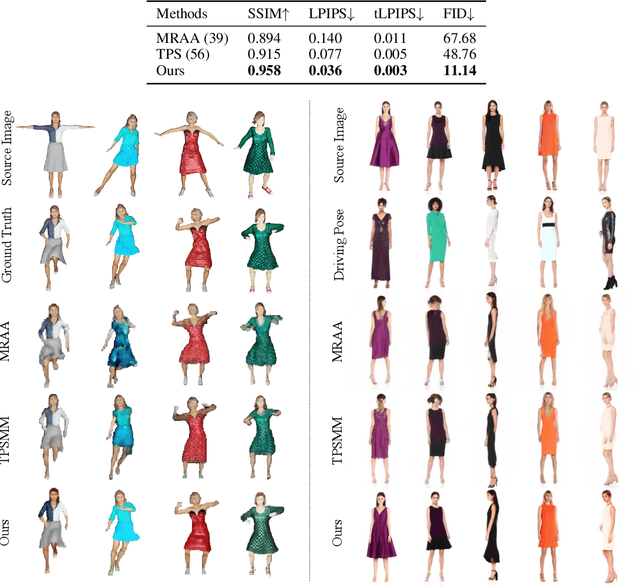
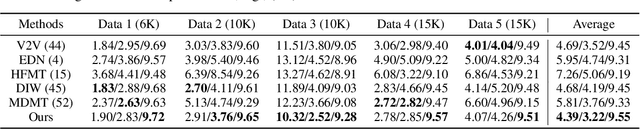
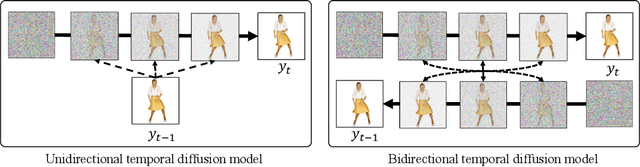
Abstract:We introduce a method to generate temporally coherent human animation from a single image, a video, or a random noise. This problem has been formulated as modeling of an auto-regressive generation, i.e., to regress past frames to decode future frames. However, such unidirectional generation is highly prone to motion drifting over time, generating unrealistic human animation with significant artifacts such as appearance distortion. We claim that bidirectional temporal modeling enforces temporal coherence on a generative network by largely suppressing the motion ambiguity of human appearance. To prove our claim, we design a novel human animation framework using a denoising diffusion model: a neural network learns to generate the image of a person by denoising temporal Gaussian noises whose intermediate results are cross-conditioned bidirectionally between consecutive frames. In the experiments, our method demonstrates strong performance compared to existing unidirectional approaches with realistic temporal coherence
Unrealistic Feature Suppression for Generative Adversarial Networks
Jul 23, 2021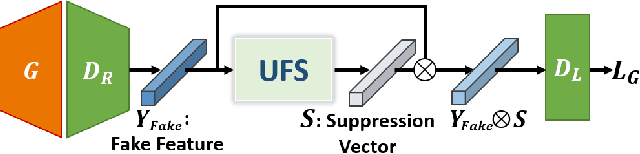



Abstract:Due to the unstable nature of minimax game between generator and discriminator, improving the performance of GANs is a challenging task. Recent studies have shown that selected high-quality samples in training improve the performance of GANs. However, sampling approaches which discard samples show limitations in some aspects such as the speed of training and optimality of the networks. In this paper we propose unrealistic feature suppression (UFS) module that keeps high-quality features and suppresses unrealistic features. UFS module keeps the training stability of networks and improves the quality of generated images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of UFS module on various models such as WGAN-GP, SNGAN, and BigGAN. By using UFS module, we achieved better Frechet inception distance and inception score compared to various baseline models. We also visualize how effectively our UFS module suppresses unrealistic features through class activation maps.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge