Hang Cui
Strong Linear Baselines Strike Back: Closed-Form Linear Models as Gaussian Process Conditional Density Estimators for TSAD
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Research in time series anomaly detection (TSAD) has largely focused on developing increasingly sophisticated, hard-to-train, and expensive-to-infer neural architectures. We revisit this paradigm and show that a simple linear autoregressive anomaly score with the closed-form solution provided by ordinary least squares (OLS) regression consistently matches or outperforms state-of-the-art deep detectors. From a theoretical perspective, we show that linear models capture a broad class of anomaly types, estimating a finite-history Gaussian process conditional density. From a practical side, across extensive univariate and multivariate benchmarks, the proposed approach achieves superior accuracy while requiring orders of magnitude fewer computational resources. Thus, future research should consistently include strong linear baselines and, more importantly, develop new benchmarks with richer temporal structures pinpointing the advantages of deep learning models.
Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Content Moderation with Large Language Models
Dec 23, 2025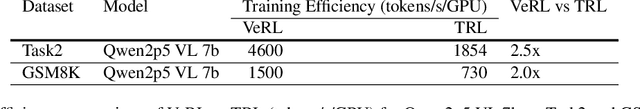
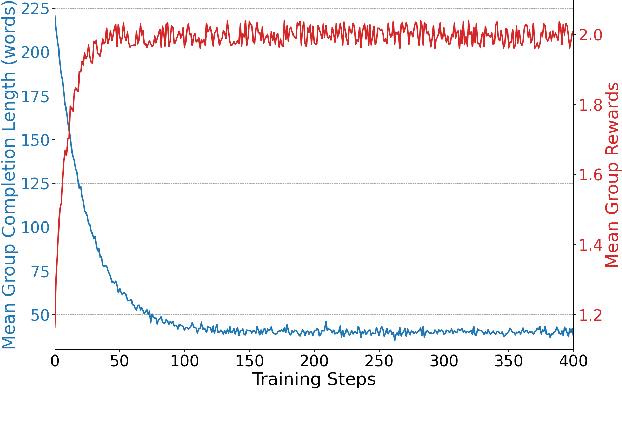
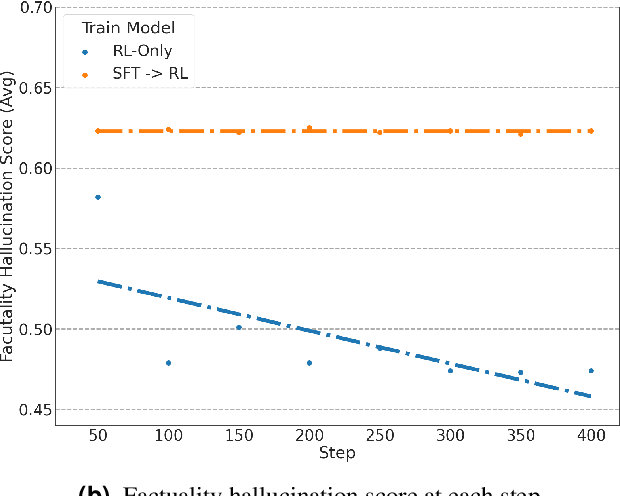
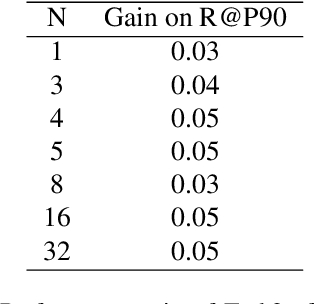
Abstract:Content moderation at scale remains one of the most pressing challenges in today's digital ecosystem, where billions of user- and AI-generated artifacts must be continuously evaluated for policy violations. Although recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong potential for policy-grounded moderation, the practical challenges of training these systems to achieve expert-level accuracy in real-world settings remain largely unexplored, particularly in regimes characterized by label sparsity, evolving policy definitions, and the need for nuanced reasoning beyond shallow pattern matching. In this work, we present a comprehensive empirical investigation of scaling reinforcement learning (RL) for content classification, systematically evaluating multiple RL training recipes and reward-shaping strategies-including verifiable rewards and LLM-as-judge frameworks-to transform general-purpose language models into specialized, policy-aligned classifiers across three real-world content moderation tasks. Our findings provide actionable insights for industrial-scale moderation systems, demonstrating that RL exhibits sigmoid-like scaling behavior in which performance improves smoothly with increased training data, rollouts, and optimization steps before gradually saturating. Moreover, we show that RL substantially improves performance on tasks requiring complex policy-grounded reasoning while achieving up to 100x higher data efficiency than supervised fine-tuning, making it particularly effective in domains where expert annotations are scarce or costly.
ViTs: Teaching Machines to See Time Series Anomalies Like Human Experts
Oct 06, 2025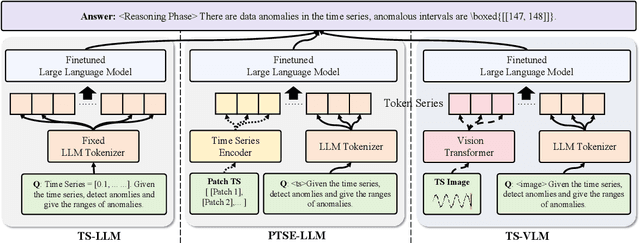
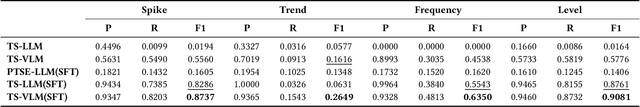
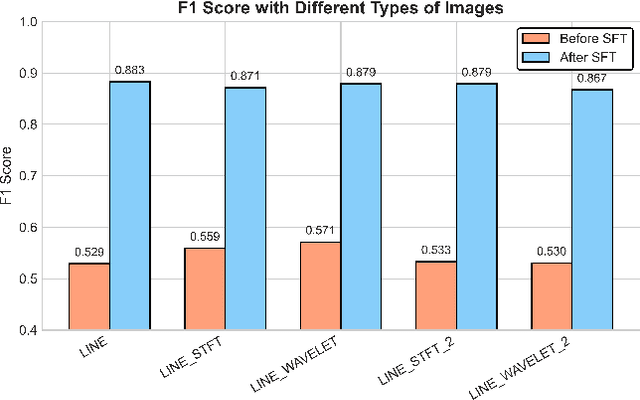
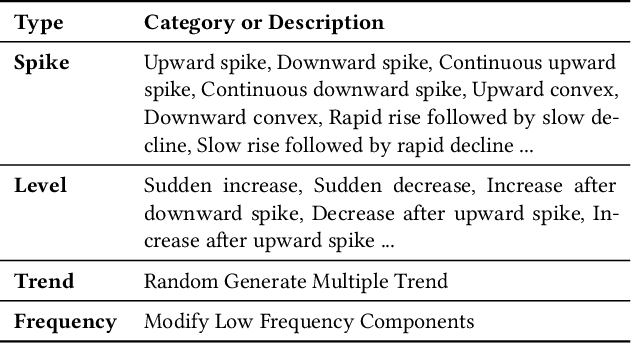
Abstract:Web service administrators must ensure the stability of multiple systems by promptly detecting anomalies in Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Achieving the goal of "train once, infer across scenarios" remains a fundamental challenge for time series anomaly detection models. Beyond improving zero-shot generalization, such models must also flexibly handle sequences of varying lengths during inference, ranging from one hour to one week, without retraining. Conventional approaches rely on sliding-window encoding and self-supervised learning, which restrict inference to fixed-length inputs. Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable zero-shot capabilities across general domains. However, when applied to time series data, they face inherent limitations due to context length. To address this issue, we propose ViTs, a Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based framework that converts time series curves into visual representations. By rescaling time series images, temporal dependencies are preserved while maintaining a consistent input size, thereby enabling efficient processing of arbitrarily long sequences without context constraints. Training VLMs for this purpose introduces unique challenges, primarily due to the scarcity of aligned time series image-text data. To overcome this, we employ an evolutionary algorithm to automatically generate thousands of high-quality image-text pairs and design a three-stage training pipeline consisting of: (1) time series knowledge injection, (2) anomaly detection enhancement, and (3) anomaly reasoning refinement. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ViTs substantially enhance the ability of VLMs to understand and detect anomalies in time series data. All datasets and code will be publicly released at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ViTs-C484/.
FalconWing: An Open-Source Platform for Ultra-Light Fixed-Wing Aircraft Research
May 02, 2025Abstract:We present FalconWing -- an open-source, ultra-lightweight (150 g) fixed-wing platform for autonomy research. The hardware platform integrates a small camera, a standard airframe, offboard computation, and radio communication for manual overrides. We demonstrate FalconWing's capabilities by developing and deploying a purely vision-based control policy for autonomous landing (without IMU or motion capture) using a novel real-to-sim-to-real learning approach. Our learning approach: (1) constructs a photorealistic simulation environment via 3D Gaussian splatting trained on real-world images; (2) identifies nonlinear dynamics from vision-estimated real-flight data; and (3) trains a multi-modal Vision Transformer (ViT) policy through simulation-only imitation learning. The ViT architecture fuses single RGB image with the history of control actions via self-attention, preserving temporal context while maintaining real-time 20 Hz inference. When deployed zero-shot on the hardware platform, this policy achieves an 80% success rate in vision-based autonomous landings. Together with the hardware specifications, we also open-source the system dynamics, the software for photorealistic simulator and the learning approach.
Virtual Node Generation for Node Classification in Sparsely-Labeled Graphs
Sep 12, 2024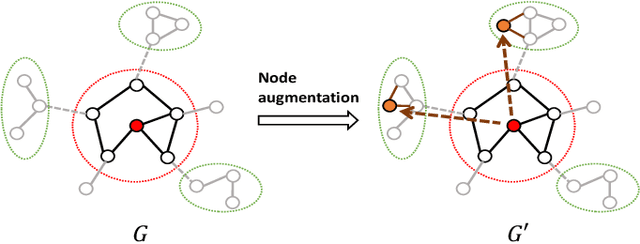
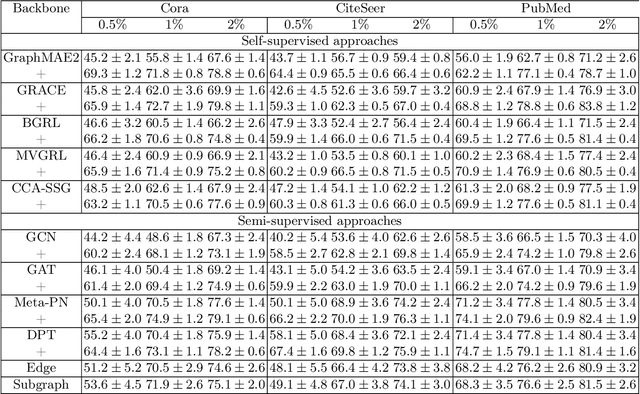
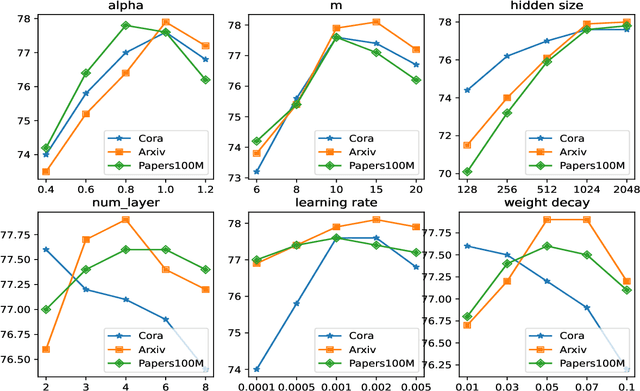
Abstract:In the broader machine learning literature, data-generation methods demonstrate promising results by generating additional informative training examples via augmenting sparse labels. Such methods are less studied in graphs due to the intricate dependencies among nodes in complex topology structures. This paper presents a novel node generation method that infuses a small set of high-quality synthesized nodes into the graph as additional labeled nodes to optimally expand the propagation of labeled information. By simply infusing additional nodes, the framework is orthogonal to the graph learning and downstream classification techniques, and thus is compatible with most popular graph pre-training (self-supervised learning), semi-supervised learning, and meta-learning methods. The contribution lies in designing the generated node set by solving a novel optimization problem. The optimization places the generated nodes in a manner that: (1) minimizes the classification loss to guarantee training accuracy and (2) maximizes label propagation to low-confidence nodes in the downstream task to ensure high-quality propagation. Theoretically, we show that the above dual optimization maximizes the global confidence of node classification. Our Experiments demonstrate statistically significant performance improvements over 14 baselines on 10 publicly available datasets.
TimeSeriesBench: An Industrial-Grade Benchmark for Time Series Anomaly Detection Models
Feb 26, 2024Abstract:Driven by the proliferation of real-world application scenarios and scales, time series anomaly detection (TSAD) has attracted considerable scholarly and industrial interest. However, existing algorithms exhibit a gap in terms of training paradigm, online detection paradigm, and evaluation criteria when compared to the actual needs of real-world industrial systems. Firstly, current algorithms typically train a specific model for each individual time series. In a large-scale online system with tens of thousands of curves, maintaining such a multitude of models is impractical. The performance of using merely one single unified model to detect anomalies remains unknown. Secondly, most TSAD models are trained on the historical part of a time series and are tested on its future segment. In distributed systems, however, there are frequent system deployments and upgrades, with new, previously unseen time series emerging daily. The performance of testing newly incoming unseen time series on current TSAD algorithms remains unknown. Lastly, although some papers have conducted detailed surveys, the absence of an online evaluation platform prevents answering questions like "Who is the best at anomaly detection at the current stage?" In this paper, we propose TimeSeriesBench, an industrial-grade benchmark that we continuously maintain as a leaderboard. On this leaderboard, we assess the performance of existing algorithms across more than 168 evaluation settings combining different training and testing paradigms, evaluation metrics and datasets. Through our comprehensive analysis of the results, we provide recommendations for the future design of anomaly detection algorithms. To address known issues with existing public datasets, we release an industrial dataset to the public together with TimeSeriesBench. All code, data, and the online leaderboard have been made publicly available.
Sim-on-Wheels: Physical World in the Loop Simulation for Self-Driving
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:We present Sim-on-Wheels, a safe, realistic, and vehicle-in-loop framework to test autonomous vehicles' performance in the real world under safety-critical scenarios. Sim-on-wheels runs on a self-driving vehicle operating in the physical world. It creates virtual traffic participants with risky behaviors and seamlessly inserts the virtual events into images perceived from the physical world in real-time. The manipulated images are fed into autonomy, allowing the self-driving vehicle to react to such virtual events. The full pipeline runs on the actual vehicle and interacts with the physical world, but the safety-critical events it sees are virtual. Sim-on-Wheels is safe, interactive, realistic, and easy to use. The experiments demonstrate the potential of Sim-on-Wheels to facilitate the process of testing autonomous driving in challenging real-world scenes with high fidelity and low risk.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge