Bin Wu
NativeTok: Native Visual Tokenization for Improved Image Generation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:VQ-based image generation typically follows a two-stage pipeline: a tokenizer encodes images into discrete tokens, and a generative model learns their dependencies for reconstruction. However, improved tokenization in the first stage does not necessarily enhance the second-stage generation, as existing methods fail to constrain token dependencies. This mismatch forces the generative model to learn from unordered distributions, leading to bias and weak coherence. To address this, we propose native visual tokenization, which enforces causal dependencies during tokenization. Building on this idea, we introduce NativeTok, a framework that achieves efficient reconstruction while embedding relational constraints within token sequences. NativeTok consists of: (1) a Meta Image Transformer (MIT) for latent image modeling, and (2) a Mixture of Causal Expert Transformer (MoCET), where each lightweight expert block generates a single token conditioned on prior tokens and latent features. We further design a Hierarchical Native Training strategy that updates only new expert blocks, ensuring training efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of NativeTok.
MUSE: A Simple Yet Effective Multimodal Search-Based Framework for Lifelong User Interest Modeling
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Lifelong user interest modeling is crucial for industrial recommender systems, yet existing approaches rely predominantly on ID-based features, suffering from poor generalization on long-tail items and limited semantic expressiveness. While recent work explores multimodal representations for behavior retrieval in the General Search Unit (GSU), they often neglect multimodal integration in the fine-grained modeling stage -- the Exact Search Unit (ESU). In this work, we present a systematic analysis of how to effectively leverage multimodal signals across both stages of the two-stage lifelong modeling framework. Our key insight is that simplicity suffices in the GSU: lightweight cosine similarity with high-quality multimodal embeddings outperforms complex retrieval mechanisms. In contrast, the ESU demands richer multimodal sequence modeling and effective ID-multimodal fusion to unlock its full potential. Guided by these principles, we propose MUSE, a simple yet effective multimodal search-based framework. MUSE has been deployed in Taobao display advertising system, enabling 100K-length user behavior sequence modeling and delivering significant gains in top-line metrics with negligible online latency overhead. To foster community research, we share industrial deployment practices and open-source the first large-scale dataset featuring ultra-long behavior sequences paired with high-quality multimodal embeddings. Our code and data is available at https://taobao-mm.github.io.
Unifying and Enhancing Graph Transformers via a Hierarchical Mask Framework
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:Graph Transformers (GTs) have emerged as a powerful paradigm for graph representation learning due to their ability to model diverse node interactions. However, existing GTs often rely on intricate architectural designs tailored to specific interactions, limiting their flexibility. To address this, we propose a unified hierarchical mask framework that reveals an underlying equivalence between model architecture and attention mask construction. This framework enables a consistent modeling paradigm by capturing diverse interactions through carefully designed attention masks. Theoretical analysis under this framework demonstrates that the probability of correct classification positively correlates with the receptive field size and label consistency, leading to a fundamental design principle: an effective attention mask should ensure both a sufficiently large receptive field and a high level of label consistency. While no single existing mask satisfies this principle across all scenarios, our analysis reveals that hierarchical masks offer complementary strengths, motivating their effective integration. Then, we introduce M3Dphormer, a Mixture-of-Experts-based Graph Transformer with Multi-Level Masking and Dual Attention Computation. M3Dphormer incorporates three theoretically grounded hierarchical masks and employs a bi-level expert routing mechanism to adaptively integrate multi-level interaction information. To ensure scalability, we further introduce a dual attention computation scheme that dynamically switches between dense and sparse modes based on local mask sparsity. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that M3Dphormer achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating the effectiveness of our unified framework and model design.
A Trustworthy Method for Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Existing emotion recognition methods mainly focus on enhancing performance by employing complex deep models, typically resulting in significantly higher model complexity. Although effective, it is also crucial to ensure the reliability of the final decision, especially for noisy, corrupted and out-of-distribution data. To this end, we propose a novel emotion recognition method called trusted emotion recognition (TER), which utilizes uncertainty estimation to calculate the confidence value of predictions. TER combines the results from multiple modalities based on their confidence values to output the trusted predictions. We also provide a new evaluation criterion to assess the reliability of predictions. Specifically, we incorporate trusted precision and trusted recall to determine the trusted threshold and formulate the trusted Acc. and trusted F1 score to evaluate the model's trusted performance. The proposed framework combines the confidence module that accordingly endows the model with reliability and robustness against possible noise or corruption. The extensive experimental results validate the effectiveness of our proposed model. The TER achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Music-video, achieving 82.40% Acc. In terms of trusted performance, TER outperforms other methods on the IEMOCAP and Music-video, achieving trusted F1 scores of 0.7511 and 0.9035, respectively.
A Comprehensive Survey of Self-Evolving AI Agents: A New Paradigm Bridging Foundation Models and Lifelong Agentic Systems
Aug 10, 2025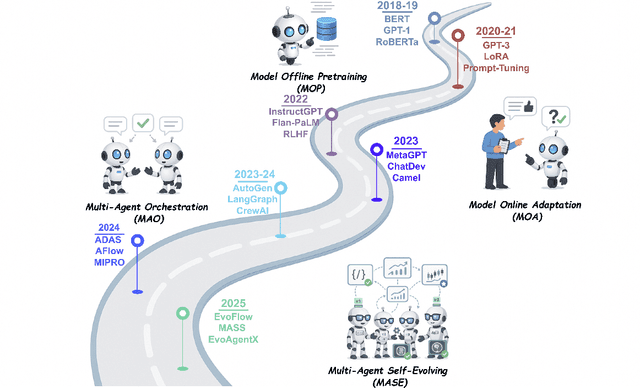
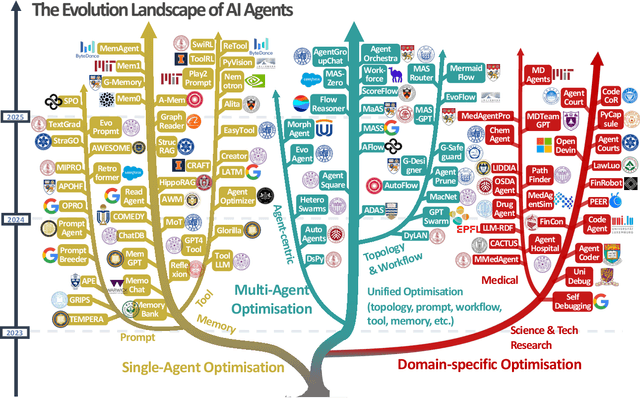
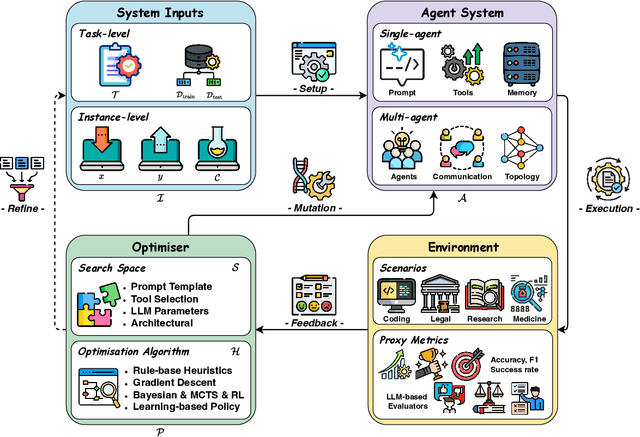
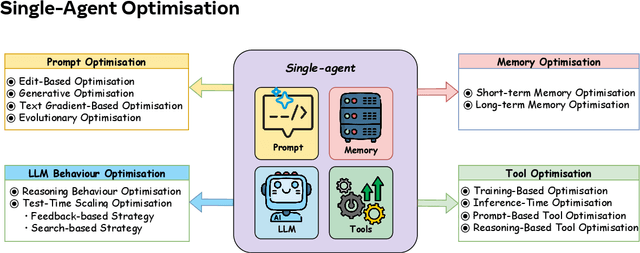
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have sparked growing interest in AI agents capable of solving complex, real-world tasks. However, most existing agent systems rely on manually crafted configurations that remain static after deployment, limiting their ability to adapt to dynamic and evolving environments. To this end, recent research has explored agent evolution techniques that aim to automatically enhance agent systems based on interaction data and environmental feedback. This emerging direction lays the foundation for self-evolving AI agents, which bridge the static capabilities of foundation models with the continuous adaptability required by lifelong agentic systems. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of existing techniques for self-evolving agentic systems. Specifically, we first introduce a unified conceptual framework that abstracts the feedback loop underlying the design of self-evolving agentic systems. The framework highlights four key components: System Inputs, Agent System, Environment, and Optimisers, serving as a foundation for understanding and comparing different strategies. Based on this framework, we systematically review a wide range of self-evolving techniques that target different components of the agent system. We also investigate domain-specific evolution strategies developed for specialised fields such as biomedicine, programming, and finance, where optimisation objectives are tightly coupled with domain constraints. In addition, we provide a dedicated discussion on the evaluation, safety, and ethical considerations for self-evolving agentic systems, which are critical to ensuring their effectiveness and reliability. This survey aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a systematic understanding of self-evolving AI agents, laying the foundation for the development of more adaptive, autonomous, and lifelong agentic systems.
DiffusionReward: Enhancing Blind Face Restoration through Reward Feedback Learning
May 23, 2025Abstract:Reward Feedback Learning (ReFL) has recently shown great potential in aligning model outputs with human preferences across various generative tasks. In this work, we introduce a ReFL framework, named DiffusionReward, to the Blind Face Restoration task for the first time. DiffusionReward effectively overcomes the limitations of diffusion-based methods, which often fail to generate realistic facial details and exhibit poor identity consistency. The core of our framework is the Face Reward Model (FRM), which is trained using carefully annotated data. It provides feedback signals that play a pivotal role in steering the optimization process of the restoration network. In particular, our ReFL framework incorporates a gradient flow into the denoising process of off-the-shelf face restoration methods to guide the update of model parameters. The guiding gradient is collaboratively determined by three aspects: (i) the FRM to ensure the perceptual quality of the restored faces; (ii) a regularization term that functions as a safeguard to preserve generative diversity; and (iii) a structural consistency constraint to maintain facial fidelity. Furthermore, the FRM undergoes dynamic optimization throughout the process. It not only ensures that the restoration network stays precisely aligned with the real face manifold, but also effectively prevents reward hacking. Experiments on synthetic and wild datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods, significantly improving identity consistency and facial details. The source codes, data, and models are available at: https://github.com/01NeuralNinja/DiffusionReward.
LLM-CoT Enhanced Graph Neural Recommendation with Harmonized Group Policy Optimization
May 18, 2025Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have advanced recommender systems by modeling interaction relationships. However, existing graph-based recommenders rely on sparse ID features and do not fully exploit textual information, resulting in low information density within representations. Furthermore, graph contrastive learning faces challenges. Random negative sampling can introduce false negative samples, while fixed temperature coefficients cannot adapt to the heterogeneity of different nodes. In addition, current efforts to enhance recommendations with large language models (LLMs) have not fully utilized their Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning capabilities to guide representation learning. To address these limitations, we introduces LGHRec (LLM-CoT Enhanced Graph Neural Recommendation with Harmonized Group Policy Optimization). This framework leverages the CoT reasoning ability of LLMs to generate semantic IDs, enriching reasoning processes and improving information density and semantic quality of representations. Moreover, we design a reinforcement learning algorithm, Harmonized Group Policy Optimization (HGPO), to optimize negative sampling strategies and temperature coefficients in contrastive learning. This approach enhances long-tail recommendation performance and ensures optimization consistency across different groups. Experimental results on three datasets demonstrate that LGHRec improves representation quality through semantic IDs generated by LLM's CoT reasoning and effectively boosts contrastive learning with HGPO. Our method outperforms several baseline models. The code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LLM-Rec.
Synthetic Data is an Elegant GIFT for Continual Vision-Language Models
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) require Continual Learning (CL) to efficiently update their knowledge and adapt to various downstream tasks without retraining from scratch. However, for VLMs, in addition to the loss of knowledge previously learned from downstream tasks, pre-training knowledge is also corrupted during continual fine-tuning. This issue is exacerbated by the unavailability of original pre-training data, leaving VLM's generalization ability degrading. In this paper, we propose GIFT, a novel continual fine-tuning approach that utilizes synthetic data to overcome catastrophic forgetting in VLMs. Taking advantage of recent advances in text-to-image synthesis, we employ a pre-trained diffusion model to recreate both pre-training and learned downstream task data. In this way, the VLM can revisit previous knowledge through distillation on matching diffusion-generated images and corresponding text prompts. Leveraging the broad distribution and high alignment between synthetic image-text pairs in VLM's feature space, we propose a contrastive distillation loss along with an image-text alignment constraint. To further combat in-distribution overfitting and enhance distillation performance with limited amount of generated data, we incorporate adaptive weight consolidation, utilizing Fisher information from these synthetic image-text pairs and achieving a better stability-plasticity balance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches across various settings.
Graph Foundation Models for Recommendation: A Comprehensive Survey
Feb 12, 2025



Abstract:Recommender systems (RS) serve as a fundamental tool for navigating the vast expanse of online information, with deep learning advancements playing an increasingly important role in improving ranking accuracy. Among these, graph neural networks (GNNs) excel at extracting higher-order structural information, while large language models (LLMs) are designed to process and comprehend natural language, making both approaches highly effective and widely adopted. Recent research has focused on graph foundation models (GFMs), which integrate the strengths of GNNs and LLMs to model complex RS problems more efficiently by leveraging the graph-based structure of user-item relationships alongside textual understanding. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive overview of GFM-based RS technologies by introducing a clear taxonomy of current approaches, diving into methodological details, and highlighting key challenges and future directions. By synthesizing recent advancements, we aim to offer valuable insights into the evolving landscape of GFM-based recommender systems.
A Transformer Framework for Simultaneous Segmentation, Classification, and Caller Identification of Marmoset Vocalization
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:Marmoset, a highly vocalized primate, has become a popular animal model for studying social-communicative behavior and its underlying mechanism comparing with human infant linguistic developments. In the study of vocal communication, it is vital to know the caller identities, call contents, and vocal exchanges. Previous work of a CNN has achieved a joint model for call segmentation, classification, and caller identification for marmoset vocalizations. However, the CNN has limitations in modeling long-range acoustic patterns; the Transformer architecture that has been shown to outperform CNNs, utilizes the self-attention mechanism that efficiently segregates information parallelly over long distances and captures the global structure of marmoset vocalization. We propose using the Transformer to jointly segment and classify the marmoset calls and identify the callers for each vocalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge