Zexin Wang
ViTs: Teaching Machines to See Time Series Anomalies Like Human Experts
Oct 06, 2025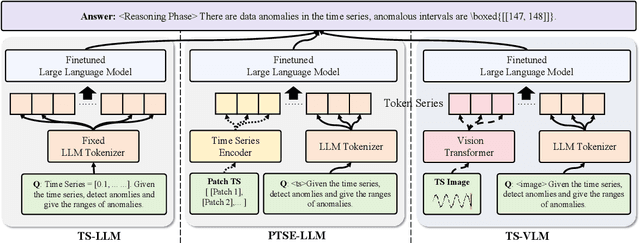
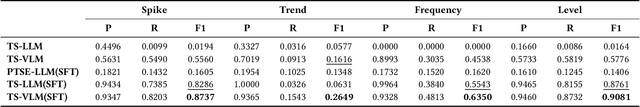
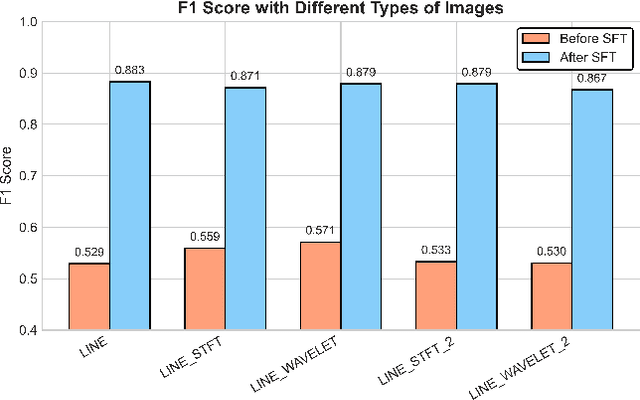
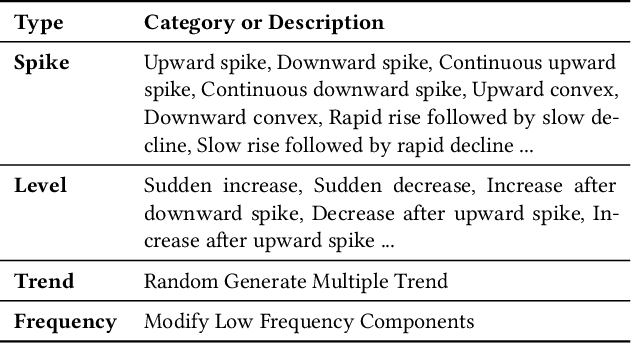
Abstract:Web service administrators must ensure the stability of multiple systems by promptly detecting anomalies in Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Achieving the goal of "train once, infer across scenarios" remains a fundamental challenge for time series anomaly detection models. Beyond improving zero-shot generalization, such models must also flexibly handle sequences of varying lengths during inference, ranging from one hour to one week, without retraining. Conventional approaches rely on sliding-window encoding and self-supervised learning, which restrict inference to fixed-length inputs. Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable zero-shot capabilities across general domains. However, when applied to time series data, they face inherent limitations due to context length. To address this issue, we propose ViTs, a Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based framework that converts time series curves into visual representations. By rescaling time series images, temporal dependencies are preserved while maintaining a consistent input size, thereby enabling efficient processing of arbitrarily long sequences without context constraints. Training VLMs for this purpose introduces unique challenges, primarily due to the scarcity of aligned time series image-text data. To overcome this, we employ an evolutionary algorithm to automatically generate thousands of high-quality image-text pairs and design a three-stage training pipeline consisting of: (1) time series knowledge injection, (2) anomaly detection enhancement, and (3) anomaly reasoning refinement. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ViTs substantially enhance the ability of VLMs to understand and detect anomalies in time series data. All datasets and code will be publicly released at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ViTs-C484/.
Revisiting VAE for Unsupervised Time Series Anomaly Detection: A Frequency Perspective
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Time series Anomaly Detection (AD) plays a crucial role for web systems. Various web systems rely on time series data to monitor and identify anomalies in real time, as well as to initiate diagnosis and remediation procedures. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) have gained popularity in recent decades due to their superior de-noising capabilities, which are useful for anomaly detection. However, our study reveals that VAE-based methods face challenges in capturing long-periodic heterogeneous patterns and detailed short-periodic trends simultaneously. To address these challenges, we propose Frequency-enhanced Conditional Variational Autoencoder (FCVAE), a novel unsupervised AD method for univariate time series. To ensure an accurate AD, FCVAE exploits an innovative approach to concurrently integrate both the global and local frequency features into the condition of Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) to significantly increase the accuracy of reconstructing the normal data. Together with a carefully designed "target attention" mechanism, our approach allows the model to pick the most useful information from the frequency domain for better short-periodic trend construction. Our FCVAE has been evaluated on public datasets and a large-scale cloud system, and the results demonstrate that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods. This confirms the practical applicability of our approach in addressing the limitations of current VAE-based anomaly detection models.
Tight Regret Bounds for Noisy Optimization of a Brownian Motion
Jan 25, 2020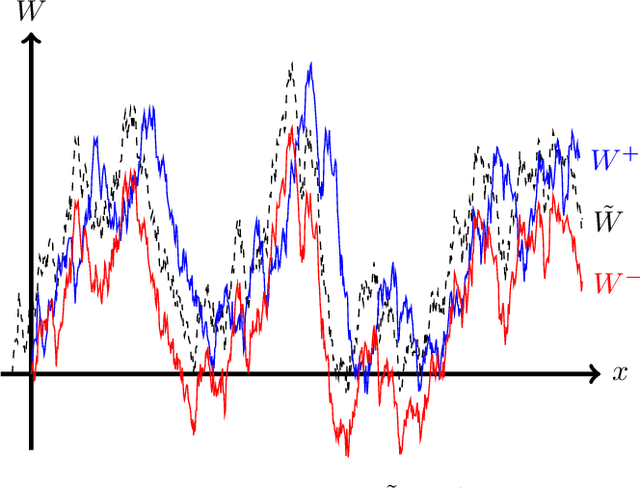
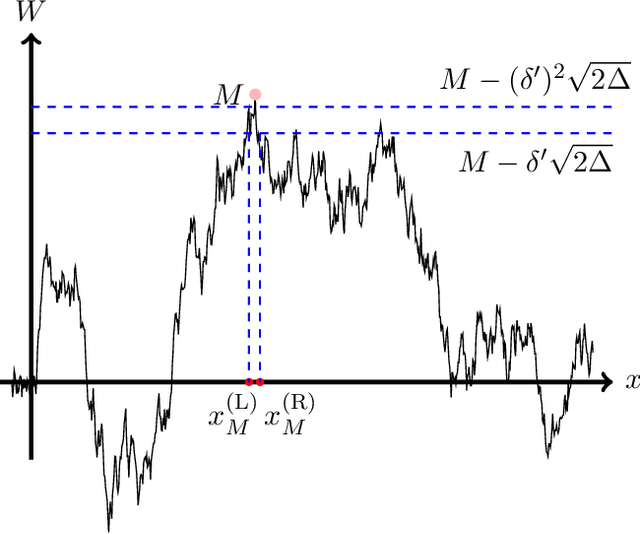
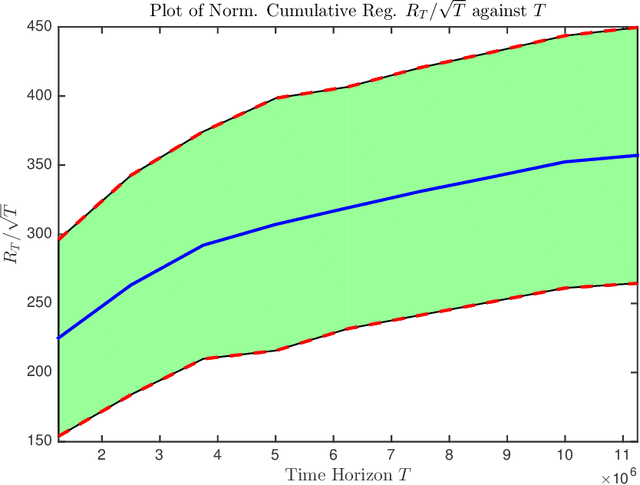
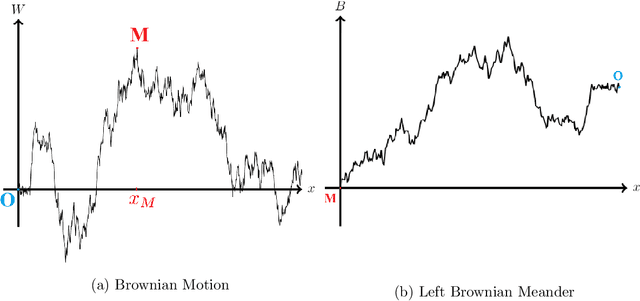
Abstract:We consider the problem of Bayesian optimization of a one-dimensional Brownian motion in which the $T$ adaptively chosen observations are corrupted by Gaussian noise. We show that as the smallest possible expected simple regret and the smallest possible expected cumulative regret scale as $\Omega(1 / \sqrt{T \log (T)}) \cap \mathcal{O}(\log T / \sqrt{T})$ and $\Omega(\sqrt{T / \log (T)}) \cap \mathcal{O}(\sqrt{T} \cdot \log T)$ respectively. Thus, our upper and lower bounds are tight up to a factor of $\mathcal{O}( (\log T)^{1.5} )$. The upper bound uses an algorithm based on confidence bounds and the Markov property of Brownian motion, and the lower bound is based on a reduction to binary hypothesis testing.
Parameter-Free Spatial Attention Network for Person Re-Identification
Nov 29, 2018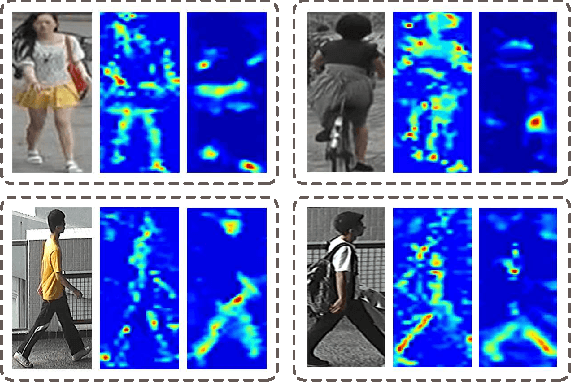
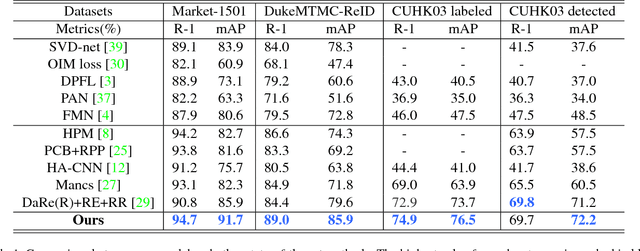
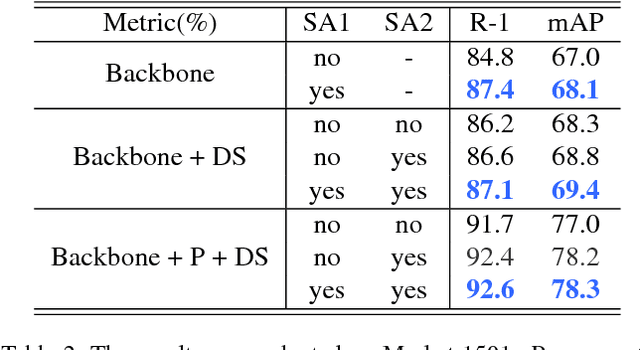
Abstract:Global average pooling (GAP) allows to localize discriminative information for recognition [40]. While GAP helps the convolution neural network to attend to the most discriminative features of an object, it may suffer if that information is missing e.g. due to camera viewpoint changes. To circumvent this issue, we argue that it is advantageous to attend to the global configuration of the object by modeling spatial relations among high-level features. We propose a novel architecture for Person Re-Identification, based on a novel parameter-free spatial attention layer introducing spatial relations among the feature map activations back to the model. Our spatial attention layer consistently improves the performance over the model without it. Results on four benchmarks demonstrate a superiority of our model over the state-of-the-art achieving rank-1 accuracy of 94.7% on Market-1501, 89.0% on DukeMTMC-ReID, 74.9% on CUHK03-labeled and 69.7% on CUHK03-detected.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge