Pratap Tokekar
University of Maryland, College Park
Active Asymmetric Multi-Agent Multimodal Learning under Uncertainty
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent systems are increasingly equipped with heterogeneous multimodal sensors, enabling richer perception but introducing modality-specific and agent-dependent uncertainty. Existing multi-agent collaboration frameworks typically reason at the agent level, assume homogeneous sensing, and handle uncertainty implicitly, limiting robustness under sensor corruption. We propose Active Asymmetric Multi-Agent Multimodal Learning under Uncertainty (A2MAML), a principled approach for uncertainty-aware, modality-level collaboration. A2MAML models each modality-specific feature as a stochastic estimate with uncertainty prediction, actively selects reliable agent-modality pairs, and aggregates information via Bayesian inverse-variance weighting. This formulation enables fine-grained, modality-level fusion, supports asymmetric modality availability, and provides a principled mechanism to suppress corrupted or noisy modalities. Extensive experiments on connected autonomous driving scenarios for collaborative accident detection demonstrate that A2MAML consistently outperforms both single-agent and collaborative baselines, achieving up to 18.7% higher accident detection rate.
PRISM: Performer RS-IMLE for Single-pass Multisensory Imitation Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Robotic imitation learning typically requires models that capture multimodal action distributions while operating at real-time control rates and accommodating multiple sensing modalities. Although recent generative approaches such as diffusion models, flow matching, and Implicit Maximum Likelihood Estimation (IMLE) have achieved promising results, they often satisfy only a subset of these requirements. To address this, we introduce PRISM, a single-pass policy based on a batch-global rejection-sampling variant of IMLE. PRISM couples a temporal multisensory encoder (integrating RGB, depth, tactile, audio, and proprioception) with a linear-attention generator using a Performer architecture. We demonstrate the efficacy of PRISM on a diverse real-world hardware suite, including loco-manipulation using a Unitree Go2 with a 7-DoF arm D1 and tabletop manipulation with a UR5 manipulator. Across challenging physical tasks such as pre-manipulation parking, high-precision insertion, and multi-object pick-and-place, PRISM outperforms state-of-the-art diffusion policies by 10-25% in success rate while maintaining high-frequency (30-50 Hz) closed-loop control. We further validate our approach on large-scale simulation benchmarks, including CALVIN, MetaWorld, and Robomimic. In CALVIN (10% data split), PRISM improves success rates by approximately 25% over diffusion and approximately 20% over flow matching, while simultaneously reducing trajectory jerk by 20x-50x. These results position PRISM as a fast, accurate, and multisensory imitation policy that retains multimodal action coverage without the latency of iterative sampling.
Stable and Efficient Single-Rollout RL for Multimodal Reasoning
Dec 20, 2025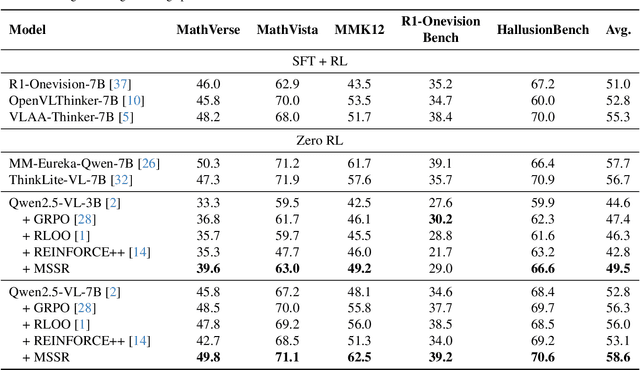
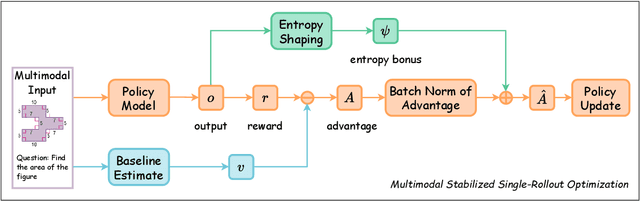

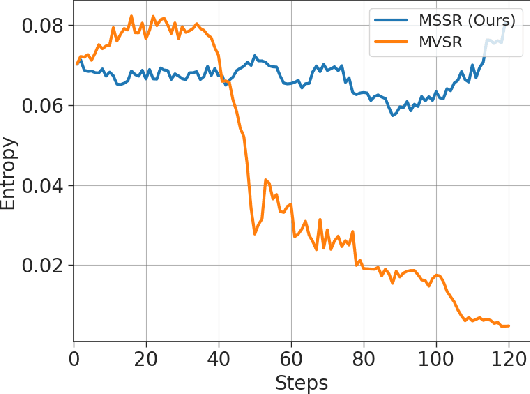
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has become a key paradigm to improve the reasoning capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). However, prevalent group-based algorithms such as GRPO require multi-rollout sampling for each prompt. While more efficient single-rollout variants have recently been explored in text-only settings, we find that they suffer from severe instability in multimodal contexts, often leading to training collapse. To address this training efficiency-stability trade-off, we introduce $\textbf{MSSR}$ (Multimodal Stabilized Single-Rollout), a group-free RLVR framework that achieves both stable optimization and effective multimodal reasoning performance. MSSR achieves this via an entropy-based advantage-shaping mechanism that adaptively regularizes advantage magnitudes, preventing collapse and maintaining training stability. While such mechanisms have been used in group-based RLVR, we show that in the multimodal single-rollout setting they are not merely beneficial but essential for stability. In in-distribution evaluations, MSSR demonstrates superior training compute efficiency, achieving similar validation accuracy to the group-based baseline with half the training steps. When trained for the same number of steps, MSSR's performance surpasses the group-based baseline and shows consistent generalization improvements across five diverse reasoning-intensive benchmarks. Together, these results demonstrate that MSSR enables stable, compute-efficient, and effective RLVR for complex multimodal reasoning tasks.
VOGUE: Guiding Exploration with Visual Uncertainty Improves Multimodal Reasoning
Oct 01, 2025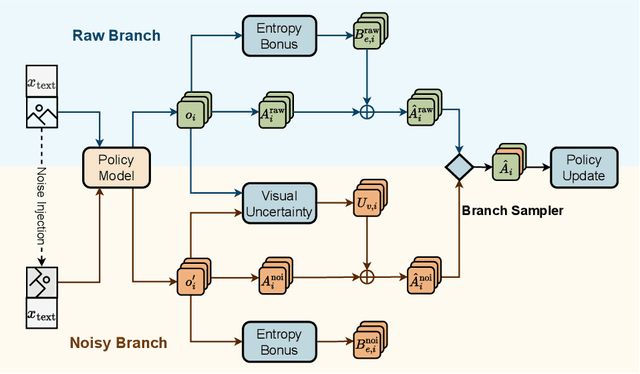
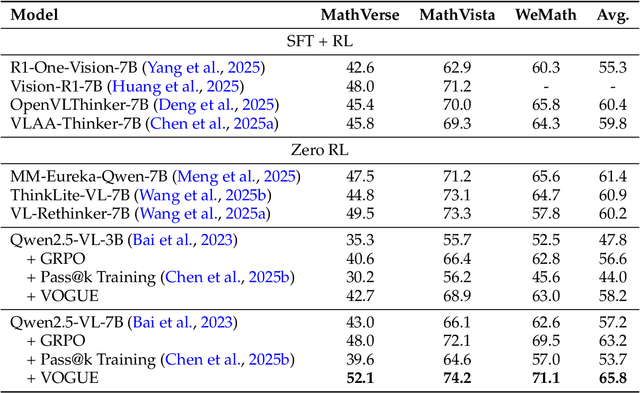
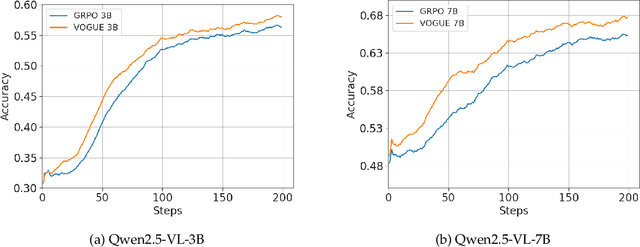
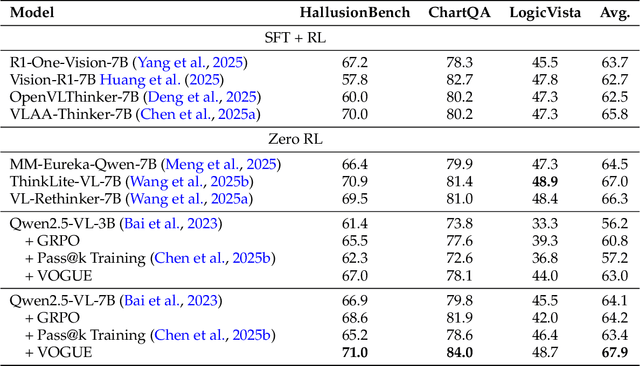
Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) improves reasoning in large language models (LLMs) but struggles with exploration, an issue that still persists for multimodal LLMs (MLLMs). Current methods treat the visual input as a fixed, deterministic condition, overlooking a critical source of ambiguity and struggling to build policies robust to plausible visual variations. We introduce $\textbf{VOGUE (Visual Uncertainty Guided Exploration)}$, a novel method that shifts exploration from the output (text) to the input (visual) space. By treating the image as a stochastic context, VOGUE quantifies the policy's sensitivity to visual perturbations using the symmetric KL divergence between a "raw" and "noisy" branch, creating a direct signal for uncertainty-aware exploration. This signal shapes the learning objective via an uncertainty-proportional bonus, which, combined with a token-entropy bonus and an annealed sampling schedule, effectively balances exploration and exploitation. Implemented within GRPO on two model scales (Qwen2.5-VL-3B/7B), VOGUE boosts pass@1 accuracy by an average of 2.6% on three visual math benchmarks and 3.7% on three general-domain reasoning benchmarks, while simultaneously increasing pass@4 performance and mitigating the exploration decay commonly observed in RL fine-tuning. Our work shows that grounding exploration in the inherent uncertainty of visual inputs is an effective strategy for improving multimodal reasoning.
AFFORD2ACT: Affordance-Guided Automatic Keypoint Selection for Generalizable and Lightweight Robotic Manipulation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Vision-based robot learning often relies on dense image or point-cloud inputs, which are computationally heavy and entangle irrelevant background features. Existing keypoint-based approaches can focus on manipulation-centric features and be lightweight, but either depend on manual heuristics or task-coupled selection, limiting scalability and semantic understanding. To address this, we propose AFFORD2ACT, an affordance-guided framework that distills a minimal set of semantic 2D keypoints from a text prompt and a single image. AFFORD2ACT follows a three-stage pipeline: affordance filtering, category-level keypoint construction, and transformer-based policy learning with embedded gating to reason about the most relevant keypoints, yielding a compact 38-dimensional state policy that can be trained in 15 minutes, which performs well in real-time without proprioception or dense representations. Across diverse real-world manipulation tasks, AFFORD2ACT consistently improves data efficiency, achieving an 82% success rate on unseen objects, novel categories, backgrounds, and distractors.
Multi-Agent Trust Region Policy Optimisation: A Joint Constraint Approach
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) requires coordinated and stable policy updates among interacting agents. Heterogeneous-Agent Trust Region Policy Optimization (HATRPO) enforces per-agent trust region constraints using Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence to stabilize training. However, assigning each agent the same KL threshold can lead to slow and locally optimal updates, especially in heterogeneous settings. To address this limitation, we propose two approaches for allocating the KL divergence threshold across agents: HATRPO-W, a Karush-Kuhn-Tucker-based (KKT-based) method that optimizes threshold assignment under global KL constraints, and HATRPO-G, a greedy algorithm that prioritizes agents based on improvement-to-divergence ratio. By connecting sequential policy optimization with constrained threshold scheduling, our approach enables more flexible and effective learning in heterogeneous-agent settings. Experimental results demonstrate that our methods significantly boost the performance of HATRPO, achieving faster convergence and higher final rewards across diverse MARL benchmarks. Specifically, HATRPO-W and HATRPO-G achieve comparable improvements in final performance, each exceeding 22.5%. Notably, HATRPO-W also demonstrates more stable learning dynamics, as reflected by its lower variance.
Option Discovery Using LLM-guided Semantic Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable promise in reasoning and decision-making, yet their integration with Reinforcement Learning (RL) for complex robotic tasks remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose an LLM-guided hierarchical RL framework, termed LDSC, that leverages LLM-driven subgoal selection and option reuse to enhance sample efficiency, generalization, and multi-task adaptability. Traditional RL methods often suffer from inefficient exploration and high computational cost. Hierarchical RL helps with these challenges, but existing methods often fail to reuse options effectively when faced with new tasks. To address these limitations, we introduce a three-stage framework that uses LLMs for subgoal generation given natural language description of the task, a reusable option learning and selection method, and an action-level policy, enabling more effective decision-making across diverse tasks. By incorporating LLMs for subgoal prediction and policy guidance, our approach improves exploration efficiency and enhances learning performance. On average, LDSC outperforms the baseline by 55.9\% in average reward, demonstrating its effectiveness in complex RL settings. More details and experiment videos could be found in \href{https://raaslab.org/projects/LDSC/}{this link\footnote{https://raaslab.org/projects/LDSC}}.
Learning Multi-Robot Coordination through Locality-Based Factorized Multi-Agent Actor-Critic Algorithm
Mar 24, 2025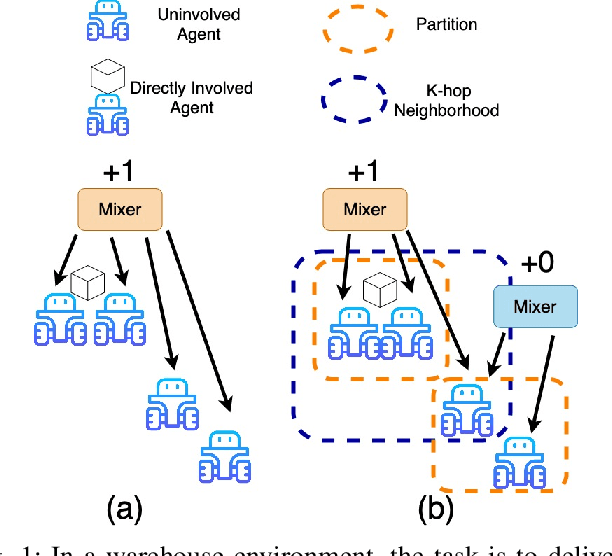
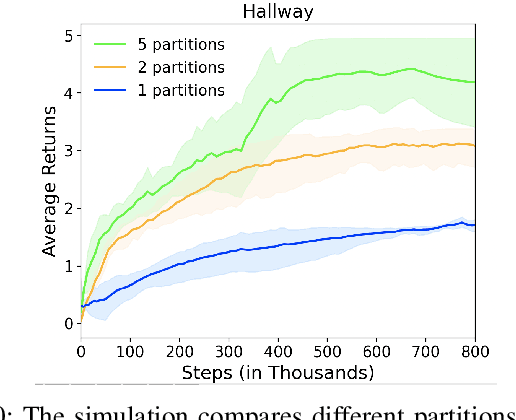
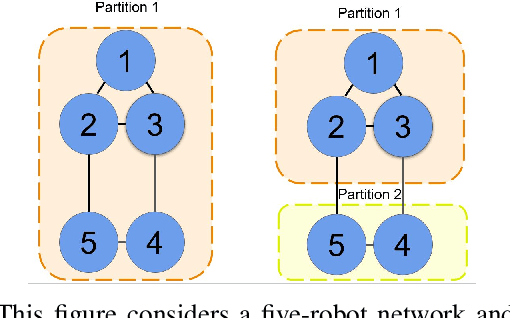
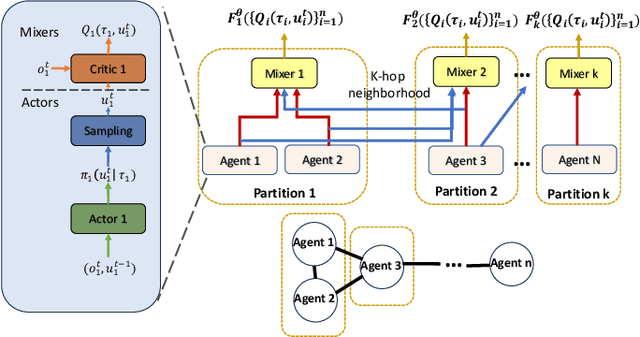
Abstract:In this work, we present a novel cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning method called \textbf{Loc}ality based \textbf{Fac}torized \textbf{M}ulti-Agent \textbf{A}ctor-\textbf{C}ritic (Loc-FACMAC). Existing state-of-the-art algorithms, such as FACMAC, rely on global reward information, which may not accurately reflect the quality of individual robots' actions in decentralized systems. We integrate the concept of locality into critic learning, where strongly related robots form partitions during training. Robots within the same partition have a greater impact on each other, leading to more precise policy evaluation. Additionally, we construct a dependency graph to capture the relationships between robots, facilitating the partitioning process. This approach mitigates the curse of dimensionality and prevents robots from using irrelevant information. Our method improves existing algorithms by focusing on local rewards and leveraging partition-based learning to enhance training efficiency and performance. We evaluate the performance of Loc-FACMAC in three environments: Hallway, Multi-cartpole, and Bounded-Cooperative-Navigation. We explore the impact of partition sizes on the performance and compare the result with baseline MARL algorithms such as LOMAQ, FACMAC, and QMIX. The experiments reveal that, if the locality structure is defined properly, Loc-FACMAC outperforms these baseline algorithms up to 108\%, indicating that exploiting the locality structure in the actor-critic framework improves the MARL performance.
PEnGUiN: Partially Equivariant Graph NeUral Networks for Sample Efficient MARL
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Equivariant Graph Neural Networks (EGNNs) have emerged as a promising approach in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL), leveraging symmetry guarantees to greatly improve sample efficiency and generalization. However, real-world environments often exhibit inherent asymmetries arising from factors such as external forces, measurement inaccuracies, or intrinsic system biases. This paper introduces \textit{Partially Equivariant Graph NeUral Networks (PEnGUiN)}, a novel architecture specifically designed to address these challenges. We formally identify and categorize various types of partial equivariance relevant to MARL, including subgroup equivariance, feature-wise equivariance, regional equivariance, and approximate equivariance. We theoretically demonstrate that PEnGUiN is capable of learning both fully equivariant (EGNN) and non-equivariant (GNN) representations within a unified framework. Through extensive experiments on a range of MARL problems incorporating various asymmetries, we empirically validate the efficacy of PEnGUiN. Our results consistently demonstrate that PEnGUiN outperforms both EGNNs and standard GNNs in asymmetric environments, highlighting their potential to improve the robustness and applicability of graph-based MARL algorithms in real-world scenarios.
VARP: Reinforcement Learning from Vision-Language Model Feedback with Agent Regularized Preferences
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Designing reward functions for continuous-control robotics often leads to subtle misalignments or reward hacking, especially in complex tasks. Preference-based RL mitigates some of these pitfalls by learning rewards from comparative feedback rather than hand-crafted signals, yet scaling human annotations remains challenging. Recent work uses Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to automate preference labeling, but a single final-state image generally fails to capture the agent's full motion. In this paper, we present a two-part solution that both improves feedback accuracy and better aligns reward learning with the agent's policy. First, we overlay trajectory sketches on final observations to reveal the path taken, allowing VLMs to provide more reliable preferences-improving preference accuracy by approximately 15-20% in metaworld tasks. Second, we regularize reward learning by incorporating the agent's performance, ensuring that the reward model is optimized based on data generated by the current policy; this addition boosts episode returns by 20-30% in locomotion tasks. Empirical studies on metaworld demonstrate that our method achieves, for instance, around 70-80% success rate in all tasks, compared to below 50% for standard approaches. These results underscore the efficacy of combining richer visual representations with agent-aware reward regularization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge