Dinesh Manocha
Wid3R: Wide Field-of-View 3D Reconstruction via Camera Model Conditioning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:We present Wid3R, a feed-forward neural network for visual geometry reconstruction that supports wide field-of-view camera models. Prior methods typically assume that input images are rectified or captured with pinhole cameras, since both their architectures and training datasets are tailored to perspective images only. These assumptions limit their applicability in real-world scenarios that use fisheye or panoramic cameras and often require careful calibration and undistortion. In contrast, Wid3R is a generalizable multi-view 3D estimation method that can model wide field-of-view camera types. Our approach leverages a ray representation with spherical harmonics and a novel camera model token within the network, enabling distortion-aware 3D reconstruction. Furthermore, Wid3R is the first multi-view foundation model to support feed-forward 3D reconstruction directly from 360 imagery. It demonstrates strong zero-shot robustness and consistently outperforms prior methods, achieving improvements of up to +77.33 on Stanford2D3D.
MemCtrl: Using MLLMs as Active Memory Controllers on Embodied Agents
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Foundation models rely on in-context learning for personalized decision making. The limited size of this context window necessitates memory compression and retrieval systems like RAG. These systems however often treat memory as large offline storage spaces, which is unfavorable for embodied agents that are expected to operate under strict memory and compute constraints, online. In this work, we propose MemCtrl, a novel framework that uses Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for pruning memory online. MemCtrl augments MLLMs with a trainable memory head μthat acts as a gate to determine which observations or reflections to retain, update, or discard during exploration. We evaluate with training two types of μ, 1) via an offline expert, and 2) via online RL, and observe significant improvement in overall embodied task completion ability on μ-augmented MLLMs. In particular, on augmenting two low performing MLLMs with MemCtrl on multiple subsets of the EmbodiedBench benchmark, we observe that μ-augmented MLLMs show an improvement of around 16% on average, with over 20% on specific instruction subsets. Finally, we present a qualitative analysis on the memory fragments collected by μ, noting the superior performance of μaugmented MLLMs on long and complex instruction types.
AMUSE: Audio-Visual Benchmark and Alignment Framework for Agentic Multi-Speaker Understanding
Dec 18, 2025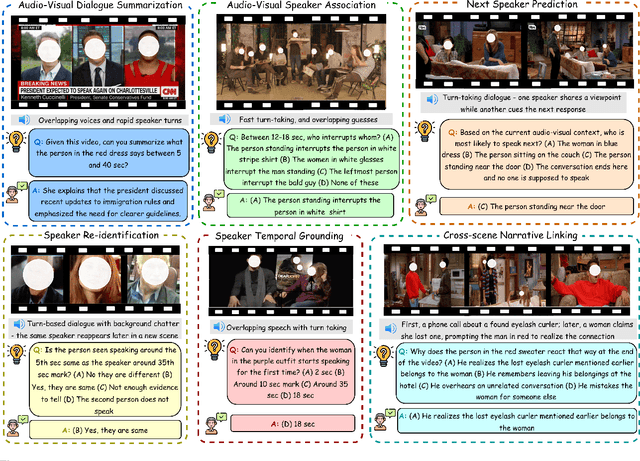
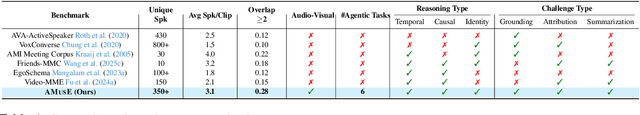
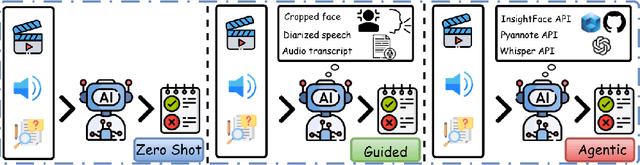
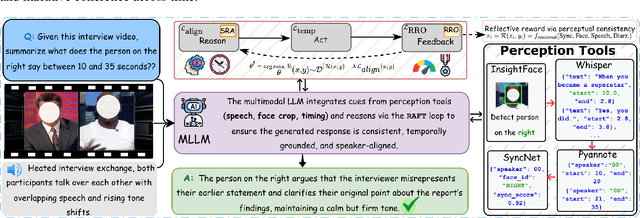
Abstract:Recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) such as GPT-4o and Qwen3-Omni show strong perception but struggle in multi-speaker, dialogue-centric settings that demand agentic reasoning tracking who speaks, maintaining roles, and grounding events across time. These scenarios are central to multimodal audio-video understanding, where models must jointly reason over audio and visual streams in applications such as conversational video assistants and meeting analytics. We introduce AMUSE, a benchmark designed around tasks that are inherently agentic, requiring models to decompose complex audio-visual interactions into planning, grounding, and reflection steps. It evaluates MLLMs across three modes zero-shot, guided, and agentic and six task families, including spatio-temporal speaker grounding and multimodal dialogue summarization. Across all modes, current models exhibit weak multi-speaker reasoning and inconsistent behavior under both non-agentic and agentic evaluation. Motivated by the inherently agentic nature of these tasks and recent advances in LLM agents, we propose RAFT, a data-efficient agentic alignment framework that integrates reward optimization with intrinsic multimodal self-evaluation as reward and selective parameter adaptation for data and parameter efficient updates. Using RAFT, we achieve up to 39.52\% relative improvement in accuracy on our benchmark. Together, AMUSE and RAFT provide a practical platform for examining agentic reasoning in multimodal models and improving their capabilities.
DR. Nav: Semantic-Geometric Representations for Proactive Dead-End Recovery and Navigation
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:We present DR. Nav (Dead-End Recovery-aware Navigation), a novel approach to autonomous navigation in scenarios where dead-end detection and recovery are critical, particularly in unstructured environments where robots must handle corners, vegetation occlusions, and blocked junctions. DR. Nav introduces a proactive strategy for navigation in unmapped environments without prior assumptions. Our method unifies dead-end prediction and recovery by generating a single, continuous, real-time semantic cost map. Specifically, DR. Nav leverages cross-modal RGB-LiDAR fusion with attention-based filtering to estimate per-cell dead-end likelihoods and recovery points, which are continuously updated through Bayesian inference to enhance robustness. Unlike prior mapping methods that only encode traversability, DR. Nav explicitly incorporates recovery-aware risk into the navigation cost map, enabling robots to anticipate unsafe regions and plan safer alternative trajectories. We evaluate DR. Nav across multiple dense indoor and outdoor scenarios and demonstrate an increase of 83.33% in accuracy in detection, a 52.4% reduction in time-to-goal (path efficiency), compared to state-of-the-art planners such as DWA, MPPI, and Nav2 DWB. Furthermore, the dead-end classifier functions
Music Flamingo: Scaling Music Understanding in Audio Language Models
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:We introduce Music Flamingo, a novel large audio-language model designed to advance music (including song) understanding in foundational audio models. While audio-language research has progressed rapidly, music remains challenging due to its dynamic, layered, and information-dense nature. Progress has been further limited by the difficulty of scaling open audio understanding models, primarily because of the scarcity of high-quality music data and annotations. As a result, prior models are restricted to producing short, high-level captions, answering only surface-level questions, and showing limited generalization across diverse musical cultures. To address these challenges, we curate MF-Skills, a large-scale dataset labeled through a multi-stage pipeline that yields rich captions and question-answer pairs covering harmony, structure, timbre, lyrics, and cultural context. We fine-tune an enhanced Audio Flamingo 3 backbone on MF-Skills and further strengthen multiple skills relevant to music understanding. To improve the model's reasoning abilities, we introduce a post-training recipe: we first cold-start with MF-Think, a novel chain-of-thought dataset grounded in music theory, followed by GRPO-based reinforcement learning with custom rewards. Music Flamingo achieves state-of-the-art results across 10+ benchmarks for music understanding and reasoning, establishing itself as a generalist and musically intelligent audio-language model. Beyond strong empirical results, Music Flamingo sets a new standard for advanced music understanding by demonstrating how models can move from surface-level recognition toward layered, human-like perception of songs. We believe this work provides both a benchmark and a foundation for the community to build the next generation of models that engage with music as meaningfully as humans do.
SPUR: A Plug-and-Play Framework for Integrating Spatial Audio Understanding and Reasoning into Large Audio-Language Models
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Spatial perception is central to auditory intelligence, enabling accurate understanding of real-world acoustic scenes and advancing human-level perception of the world around us. While recent large audio-language models (LALMs) show strong reasoning over complex audios, most operate on monaural inputs and lack the ability to capture spatial cues such as direction, elevation, and distance. We introduce SPUR, a lightweight, plug-in approach that equips LALMs with spatial perception through minimal architectural changes. SPUR consists of: (i) a First-Order Ambisonics (FOA) encoder that maps (W, X, Y, Z) channels to rotation-aware, listener-centric spatial features, integrated into target LALMs via a multimodal adapter; and (ii) SPUR-Set, a spatial QA dataset combining open-source FOA recordings with controlled simulations, emphasizing relative direction, elevation, distance, and overlap for supervised spatial reasoning. Fine-tuning our model on the SPUR-Set consistently improves spatial QA and multi-speaker attribution while preserving general audio understanding. SPUR provides a simple recipe that transforms monaural LALMs into spatially aware models. Extensive ablations validate the effectiveness of our approach.
Structured Uncertainty guided Clarification for LLM Agents
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:LLM agents extend large language models with tool-calling capabilities, but ambiguous user instructions often lead to incorrect invocations and task failures. We introduce a principled formulation of structured uncertainty over tool-call parameters, modeling joint tool-argument clarification as a POMDP with Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI) objective for optimal question selection and aspect-based cost modeling to prevent redundancy. Our SAGE-Agent leverages this structured uncertainty to achieve superior efficiency: increasing coverage on ambiguous tasks by 7-39\% while reducing clarification questions by 1.5-2.7$\times$ compared to strong prompting and uncertainty-based baselines. We present ClarifyBench, the first multi-turn tool-augmented disambiguation benchmark with realistic LLM-based user simulation across diverse domains including document editing, vehicle control, and travel booking. Additionally, we demonstrate that structured uncertainty provides effective training signals for reinforcement learning, boosting When2Call accuracy from 36.5\% to 65.2\% (3B model) and 36.7\% to 62.9\% (7B model) through uncertainty-weighted GRPO training. These results establish structured uncertainty as a principled, efficient approach for tool-augmented agents, improving both task success and interaction efficiency in real-world scenarios.
MoRe: Monocular Geometry Refinement via Graph Optimization for Cross-View Consistency
Oct 08, 2025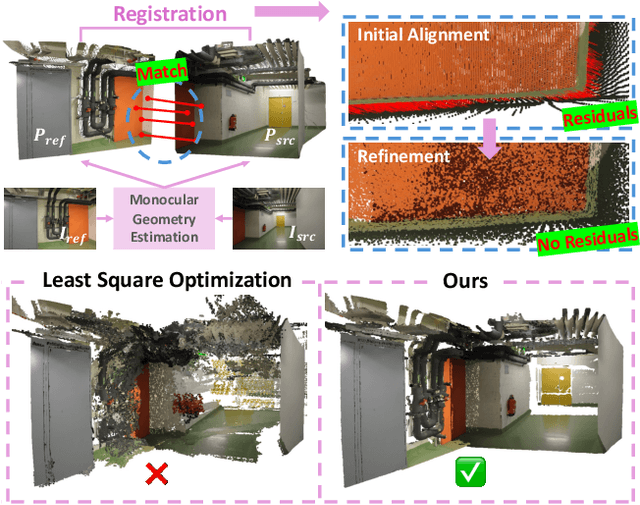
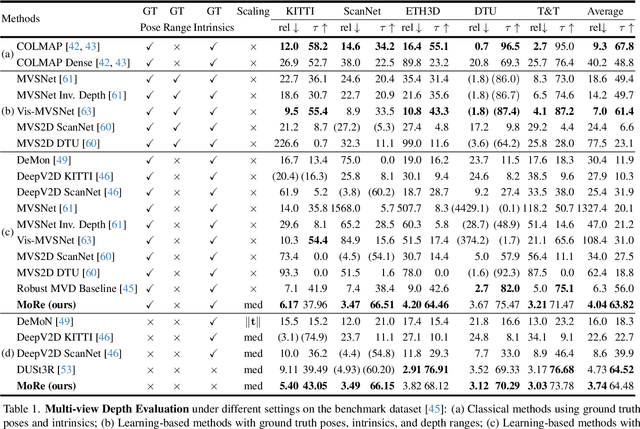
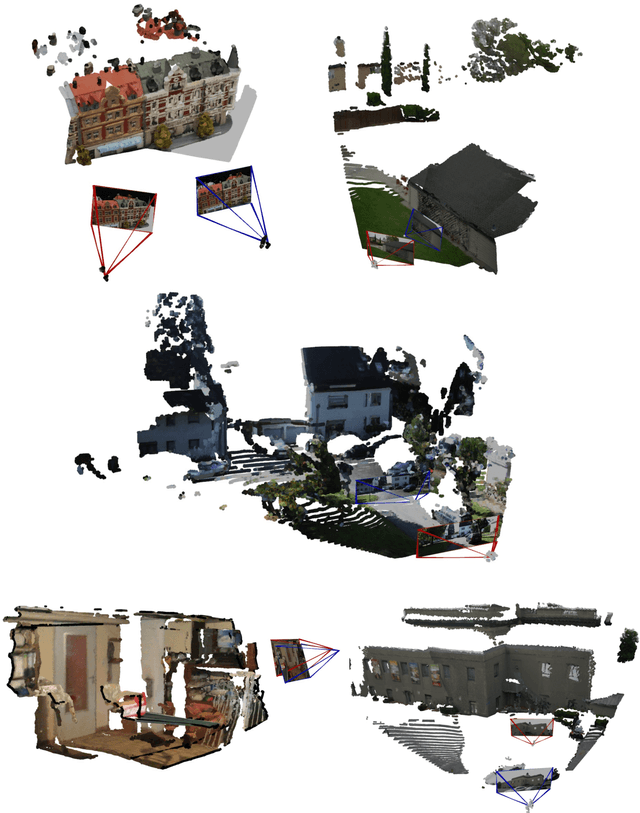
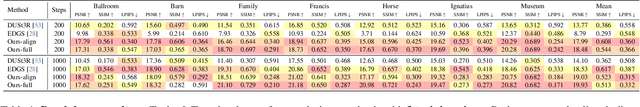
Abstract:Monocular 3D foundation models offer an extensible solution for perception tasks, making them attractive for broader 3D vision applications. In this paper, we propose MoRe, a training-free Monocular Geometry Refinement method designed to improve cross-view consistency and achieve scale alignment. To induce inter-frame relationships, our method employs feature matching between frames to establish correspondences. Rather than applying simple least squares optimization on these matched points, we formulate a graph-based optimization framework that performs local planar approximation using the estimated 3D points and surface normals estimated by monocular foundation models. This formulation addresses the scale ambiguity inherent in monocular geometric priors while preserving the underlying 3D structure. We further demonstrate that MoRe not only enhances 3D reconstruction but also improves novel view synthesis, particularly in sparse view rendering scenarios.
NavMoE: Hybrid Model- and Learning-based Traversability Estimation for Local Navigation via Mixture of Experts
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:This paper explores traversability estimation for robot navigation. A key bottleneck in traversability estimation lies in efficiently achieving reliable and robust predictions while accurately encoding both geometric and semantic information across diverse environments. We introduce Navigation via Mixture of Experts (NAVMOE), a hierarchical and modular approach for traversability estimation and local navigation. NAVMOE combines multiple specialized models for specific terrain types, each of which can be either a classical model-based or a learning-based approach that predicts traversability for specific terrain types. NAVMOE dynamically weights the contributions of different models based on the input environment through a gating network. Overall, our approach offers three advantages: First, NAVMOE enables traversability estimation to adaptively leverage specialized approaches for different terrains, which enhances generalization across diverse and unseen environments. Second, our approach significantly improves efficiency with negligible cost of solution quality by introducing a training-free lazy gating mechanism, which is designed to minimize the number of activated experts during inference. Third, our approach uses a two-stage training strategy that enables the training for the gating networks within the hybrid MoE method that contains nondifferentiable modules. Extensive experiments show that NAVMOE delivers a better efficiency and performance balance than any individual expert or full ensemble across different domains, improving cross- domain generalization and reducing average computational cost by 81.2% via lazy gating, with less than a 2% loss in path quality.
A Survey on Long-Video Storytelling Generation: Architectures, Consistency, and Cinematic Quality
Jul 09, 2025

Abstract:Despite the significant progress that has been made in video generative models, existing state-of-the-art methods can only produce videos lasting 5-16 seconds, often labeled "long-form videos". Furthermore, videos exceeding 16 seconds struggle to maintain consistent character appearances and scene layouts throughout the narrative. In particular, multi-subject long videos still fail to preserve character consistency and motion coherence. While some methods can generate videos up to 150 seconds long, they often suffer from frame redundancy and low temporal diversity. Recent work has attempted to produce long-form videos featuring multiple characters, narrative coherence, and high-fidelity detail. We comprehensively studied 32 papers on video generation to identify key architectural components and training strategies that consistently yield these qualities. We also construct a comprehensive novel taxonomy of existing methods and present comparative tables that categorize papers by their architectural designs and performance characteristics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge