Junjie Fei
MAGNET: A Multi-agent Framework for Finding Audio-Visual Needles by Reasoning over Multi-Video Haystacks
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have shown remarkable progress in audio-visual understanding, yet they struggle with real-world scenarios that require complex reasoning across extensive video collections. Existing benchmarks for video question answering remain limited in scope, typically involving one clip per query, which falls short of representing the challenges of large-scale, audio-visual retrieval and reasoning encountered in practical applications. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel task named AV-HaystacksQA, where the goal is to identify salient segments across different videos in response to a query and link them together to generate the most informative answer. To this end, we present AVHaystacks, an audio-visual benchmark comprising 3100 annotated QA pairs designed to assess the capabilities of LMMs in multi-video retrieval and temporal grounding task. Additionally, we propose a model-agnostic, multi-agent framework MAGNET to address this challenge, achieving up to 89% and 65% relative improvements over baseline methods on BLEU@4 and GPT evaluation scores in QA task on our proposed AVHaystacks. To enable robust evaluation of multi-video retrieval and temporal grounding for optimal response generation, we introduce two new metrics, STEM, which captures alignment errors between a ground truth and a predicted step sequence and MTGS, to facilitate balanced and interpretable evaluation of segment-level grounding performance. Project: https://schowdhury671.github.io/magnet_project/
WikiAutoGen: Towards Multi-Modal Wikipedia-Style Article Generation
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Knowledge discovery and collection are intelligence-intensive tasks that traditionally require significant human effort to ensure high-quality outputs. Recent research has explored multi-agent frameworks for automating Wikipedia-style article generation by retrieving and synthesizing information from the internet. However, these methods primarily focus on text-only generation, overlooking the importance of multimodal content in enhancing informativeness and engagement. In this work, we introduce WikiAutoGen, a novel system for automated multimodal Wikipedia-style article generation. Unlike prior approaches, WikiAutoGen retrieves and integrates relevant images alongside text, enriching both the depth and visual appeal of generated content. To further improve factual accuracy and comprehensiveness, we propose a multi-perspective self-reflection mechanism, which critically assesses retrieved content from diverse viewpoints to enhance reliability, breadth, and coherence, etc. Additionally, we introduce WikiSeek, a benchmark comprising Wikipedia articles with topics paired with both textual and image-based representations, designed to evaluate multimodal knowledge generation on more challenging topics. Experimental results show that WikiAutoGen outperforms previous methods by 8%-29% on our WikiSeek benchmark, producing more accurate, coherent, and visually enriched Wikipedia-style articles. We show some of our generated examples in https://wikiautogen.github.io/ .
Document Haystacks: Vision-Language Reasoning Over Piles of 1000+ Documents
Nov 23, 2024



Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have achieved impressive progress in vision-language understanding, yet they face limitations in real-world applications requiring complex reasoning over a large number of images. Existing benchmarks for multi-image question-answering are limited in scope, each question is paired with only up to 30 images, which does not fully capture the demands of large-scale retrieval tasks encountered in the real-world usages. To reduce these gaps, we introduce two document haystack benchmarks, dubbed DocHaystack and InfoHaystack, designed to evaluate LMM performance on large-scale visual document retrieval and understanding. Additionally, we propose V-RAG, a novel, vision-centric retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework that leverages a suite of multimodal vision encoders, each optimized for specific strengths, and a dedicated question-document relevance module. V-RAG sets a new standard, with a 9% and 11% improvement in Recall@1 on the challenging DocHaystack-1000 and InfoHaystack-1000 benchmarks, respectively, compared to the previous best baseline models. Additionally, integrating V-RAG with LMMs enables them to efficiently operate across thousands of images, yielding significant improvements on our DocHaystack and InfoHaystack benchmarks. Our code and datasets are available at https://github.com/Vision-CAIR/dochaystacks
Kestrel: Point Grounding Multimodal LLM for Part-Aware 3D Vision-Language Understanding
May 29, 2024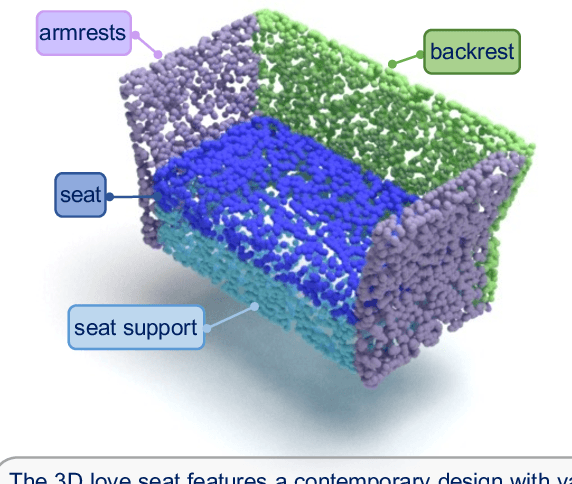
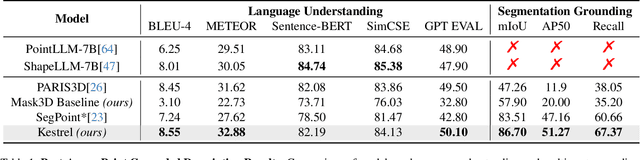
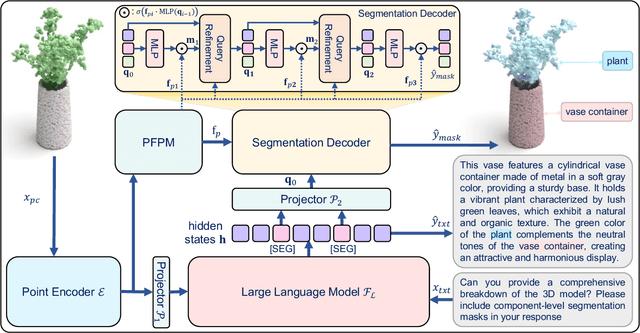
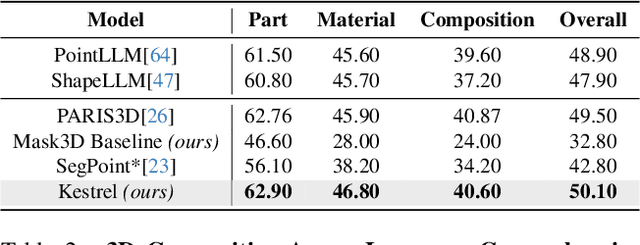
Abstract:While 3D MLLMs have achieved significant progress, they are restricted to object and scene understanding and struggle to understand 3D spatial structures at the part level. In this paper, we introduce Kestrel, representing a novel approach that empowers 3D MLLMs with part-aware understanding, enabling better interpretation and segmentation grounding of 3D objects at the part level. Despite its significance, the current landscape lacks tasks and datasets that endow and assess this capability. Therefore, we propose two novel tasks: (1) Part-Aware Point Grounding, the model is tasked with directly predicting a part-level segmentation mask based on user instructions, and (2) Part-Aware Point Grounded Captioning, the model provides a detailed caption that includes part-level descriptions and their corresponding masks. To support learning and evaluating for these tasks, we introduce 3DCoMPaT Grounded Instructions Dataset (3DCoMPaT-GRIN). 3DCoMPaT-GRIN Vanilla, comprising 789k part-aware point cloud-instruction-segmentation mask triplets, is used to evaluate MLLMs' ability of part-aware segmentation grounding. 3DCoMPaT-GRIN Grounded Caption, containing 107k part-aware point cloud-instruction-grounded caption triplets, assesses both MLLMs' part-aware language comprehension and segmentation grounding capabilities. Our introduced tasks, dataset, and Kestrel represent a preliminary effort to bridge the gap between human cognition and 3D MLLMs, i.e., the ability to perceive and engage with the environment at both global and part levels. Extensive experiments on the 3DCoMPaT-GRIN show that Kestrel can generate user-specified segmentation masks, a capability not present in any existing 3D MLLM. Kestrel thus established a benchmark for evaluating the part-aware language comprehension and segmentation grounding of 3D objects. Project page at https://feielysia.github.io/Kestrel.github.io/
Transferable Decoding with Visual Entities for Zero-Shot Image Captioning
Jul 31, 2023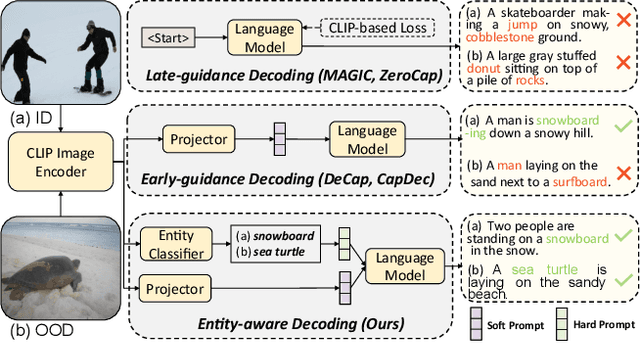
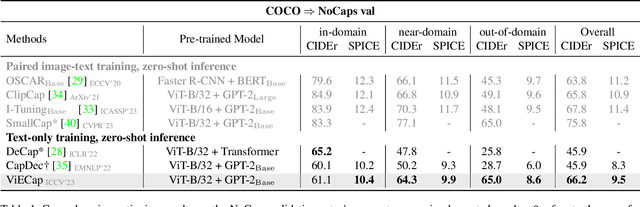
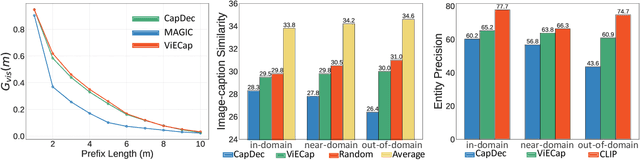
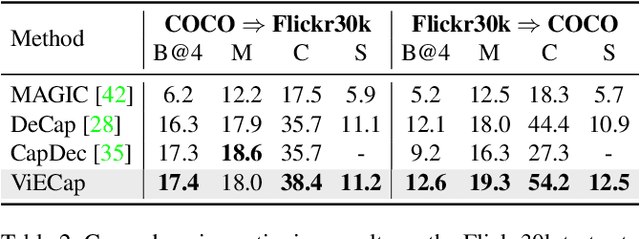
Abstract:Image-to-text generation aims to describe images using natural language. Recently, zero-shot image captioning based on pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) and large language models (LLMs) has made significant progress. However, we have observed and empirically demonstrated that these methods are susceptible to modality bias induced by LLMs and tend to generate descriptions containing objects (entities) that do not actually exist in the image but frequently appear during training (i.e., object hallucination). In this paper, we propose ViECap, a transferable decoding model that leverages entity-aware decoding to generate descriptions in both seen and unseen scenarios. ViECap incorporates entity-aware hard prompts to guide LLMs' attention toward the visual entities present in the image, enabling coherent caption generation across diverse scenes. With entity-aware hard prompts, ViECap is capable of maintaining performance when transferring from in-domain to out-of-domain scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ViECap sets a new state-of-the-art cross-domain (transferable) captioning and performs competitively in-domain captioning compared to previous VLMs-based zero-shot methods. Our code is available at: https://github.com/FeiElysia/ViECap
Caption Anything: Interactive Image Description with Diverse Multimodal Controls
May 08, 2023Abstract:Controllable image captioning is an emerging multimodal topic that aims to describe the image with natural language following human purpose, $\textit{e.g.}$, looking at the specified regions or telling in a particular text style. State-of-the-art methods are trained on annotated pairs of input controls and output captions. However, the scarcity of such well-annotated multimodal data largely limits their usability and scalability for interactive AI systems. Leveraging unimodal instruction-following foundation models is a promising alternative that benefits from broader sources of data. In this paper, we present Caption AnyThing (CAT), a foundation model augmented image captioning framework supporting a wide range of multimodel controls: 1) visual controls, including points, boxes, and trajectories; 2) language controls, such as sentiment, length, language, and factuality. Powered by Segment Anything Model (SAM) and ChatGPT, we unify the visual and language prompts into a modularized framework, enabling the flexible combination between different controls. Extensive case studies demonstrate the user intention alignment capabilities of our framework, shedding light on effective user interaction modeling in vision-language applications. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/ttengwang/Caption-Anything.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge