Heesung Kwon
Coarse-to-Fine Hierarchical Alignment for UAV-based Human Detection using Diffusion Models
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Training object detectors demands extensive, task-specific annotations, yet this requirement becomes impractical in UAV-based human detection due to constantly shifting target distributions and the scarcity of labeled images. As a remedy, synthetic simulators are adopted to generate annotated data, with a low annotation cost. However, the domain gap between synthetic and real images hinders the model from being effectively applied to the target domain. Accordingly, we introduce Coarse-to-Fine Hierarchical Alignment (CFHA), a three-stage diffusion-based framework designed to transform synthetic data for UAV-based human detection, narrowing the domain gap while preserving the original synthetic labels. CFHA explicitly decouples global style and local content domain discrepancies and bridges those gaps using three modules: (1) Global Style Transfer -- a diffusion model aligns color, illumination, and texture statistics of synthetic images to the realistic style, using only a small real reference set; (2) Local Refinement -- a super-resolution diffusion model is used to facilitate fine-grained and photorealistic details for the small objects, such as human instances, preserving shape and boundary integrity; (3) Hallucination Removal -- a module that filters out human instances whose visual attributes do not align with real-world data to make the human appearance closer to the target distribution. Extensive experiments on public UAV Sim2Real detection benchmarks demonstrate that our methods significantly improve the detection accuracy compared to the non-transformed baselines. Specifically, our method achieves up to $+14.1$ improvement of mAP50 on Semantic-Drone benchmark. Ablation studies confirm the complementary roles of the global and local stages and highlight the importance of hierarchical alignment. The code is released at \href{https://github.com/liwd190019/CFHA}{this url}.
Generative Spatiotemporal Data Augmentation
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:We explore spatiotemporal data augmentation using video foundation models to diversify both camera viewpoints and scene dynamics. Unlike existing approaches based on simple geometric transforms or appearance perturbations, our method leverages off-the-shelf video diffusion models to generate realistic 3D spatial and temporal variations from a given image dataset. Incorporating these synthesized video clips as supplemental training data yields consistent performance gains in low-data settings, such as UAV-captured imagery where annotations are scarce. Beyond empirical improvements, we provide practical guidelines for (i) choosing an appropriate spatiotemporal generative setup, (ii) transferring annotations to synthetic frames, and (iii) addressing disocclusion - regions newly revealed and unlabeled in generated views. Experiments on COCO subsets and UAV-captured datasets show that, when applied judiciously, spatiotemporal augmentation broadens the data distribution along axes underrepresented by traditional and prior generative methods, offering an effective lever for improving model performance in data-scarce regimes.
MoRe: Monocular Geometry Refinement via Graph Optimization for Cross-View Consistency
Oct 08, 2025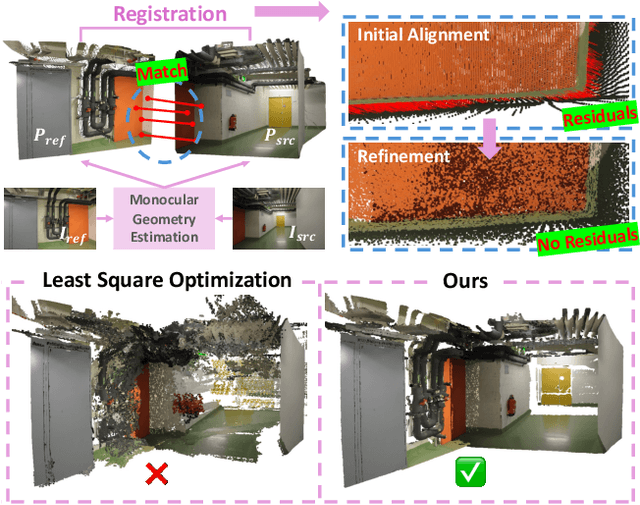
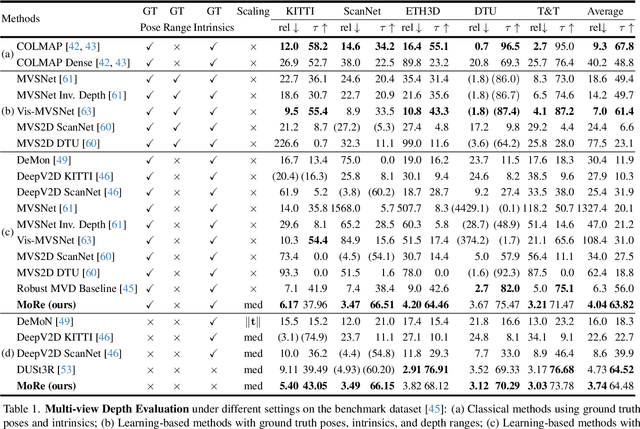
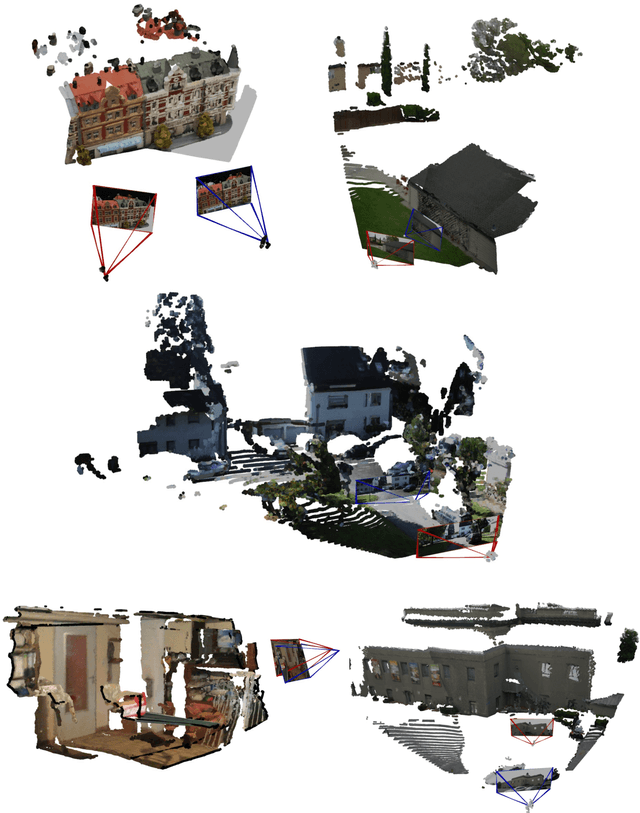
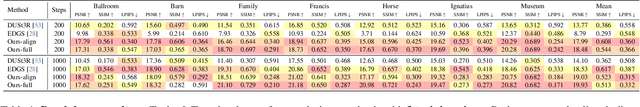
Abstract:Monocular 3D foundation models offer an extensible solution for perception tasks, making them attractive for broader 3D vision applications. In this paper, we propose MoRe, a training-free Monocular Geometry Refinement method designed to improve cross-view consistency and achieve scale alignment. To induce inter-frame relationships, our method employs feature matching between frames to establish correspondences. Rather than applying simple least squares optimization on these matched points, we formulate a graph-based optimization framework that performs local planar approximation using the estimated 3D points and surface normals estimated by monocular foundation models. This formulation addresses the scale ambiguity inherent in monocular geometric priors while preserving the underlying 3D structure. We further demonstrate that MoRe not only enhances 3D reconstruction but also improves novel view synthesis, particularly in sparse view rendering scenarios.
UAV4D: Dynamic Neural Rendering of Human-Centric UAV Imagery using Gaussian Splatting
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Despite significant advancements in dynamic neural rendering, existing methods fail to address the unique challenges posed by UAV-captured scenarios, particularly those involving monocular camera setups, top-down perspective, and multiple small, moving humans, which are not adequately represented in existing datasets. In this work, we introduce UAV4D, a framework for enabling photorealistic rendering for dynamic real-world scenes captured by UAVs. Specifically, we address the challenge of reconstructing dynamic scenes with multiple moving pedestrians from monocular video data without the need for additional sensors. We use a combination of a 3D foundation model and a human mesh reconstruction model to reconstruct both the scene background and humans. We propose a novel approach to resolve the scene scale ambiguity and place both humans and the scene in world coordinates by identifying human-scene contact points. Additionally, we exploit the SMPL model and background mesh to initialize Gaussian splats, enabling holistic scene rendering. We evaluated our method on three complex UAV-captured datasets: VisDrone, Manipal-UAV, and Okutama-Action, each with distinct characteristics and 10~50 humans. Our results demonstrate the benefits of our approach over existing methods in novel view synthesis, achieving a 1.5 dB PSNR improvement and superior visual sharpness.
UAVTwin: Neural Digital Twins for UAVs using Gaussian Splatting
Apr 02, 2025



Abstract:We present UAVTwin, a method for creating digital twins from real-world environments and facilitating data augmentation for training downstream models embedded in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Specifically, our approach focuses on synthesizing foreground components, such as various human instances in motion within complex scene backgrounds, from UAV perspectives. This is achieved by integrating 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) for reconstructing backgrounds along with controllable synthetic human models that display diverse appearances and actions in multiple poses. To the best of our knowledge, UAVTwin is the first approach for UAV-based perception that is capable of generating high-fidelity digital twins based on 3DGS. The proposed work significantly enhances downstream models through data augmentation for real-world environments with multiple dynamic objects and significant appearance variations-both of which typically introduce artifacts in 3DGS-based modeling. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel appearance modeling strategy and a mask refinement module to enhance the training of 3D Gaussian Splatting. We demonstrate the high quality of neural rendering by achieving a 1.23 dB improvement in PSNR compared to recent methods. Furthermore, we validate the effectiveness of data augmentation by showing a 2.5% to 13.7% improvement in mAP for the human detection task.
AutoComPose: Automatic Generation of Pose Transition Descriptions for Composed Pose Retrieval Using Multimodal LLMs
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:Composed pose retrieval (CPR) enables users to search for human poses by specifying a reference pose and a transition description, but progress in this field is hindered by the scarcity and inconsistency of annotated pose transitions. Existing CPR datasets rely on costly human annotations or heuristic-based rule generation, both of which limit scalability and diversity. In this work, we introduce AutoComPose, the first framework that leverages multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to automatically generate rich and structured pose transition descriptions. Our method enhances annotation quality by structuring transitions into fine-grained body part movements and introducing mirrored/swapped variations, while a cyclic consistency constraint ensures logical coherence between forward and reverse transitions. To advance CPR research, we construct and release two dedicated benchmarks, AIST-CPR and PoseFixCPR, supplementing prior datasets with enhanced attributes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that training retrieval models with AutoComPose yields superior performance over human-annotated and heuristic-based methods, significantly reducing annotation costs while improving retrieval quality. Our work pioneers the automatic annotation of pose transitions, establishing a scalable foundation for future CPR research.
MeshGS: Adaptive Mesh-Aligned Gaussian Splatting for High-Quality Rendering
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Recently, 3D Gaussian splatting has gained attention for its capability to generate high-fidelity rendering results. At the same time, most applications such as games, animation, and AR/VR use mesh-based representations to represent and render 3D scenes. We propose a novel approach that integrates mesh representation with 3D Gaussian splats to perform high-quality rendering of reconstructed real-world scenes. In particular, we introduce a distance-based Gaussian splatting technique to align the Gaussian splats with the mesh surface and remove redundant Gaussian splats that do not contribute to the rendering. We consider the distance between each Gaussian splat and the mesh surface to distinguish between tightly-bound and loosely-bound Gaussian splats. The tightly-bound splats are flattened and aligned well with the mesh geometry. The loosely-bound Gaussian splats are used to account for the artifacts in reconstructed 3D meshes in terms of rendering. We present a training strategy of binding Gaussian splats to the mesh geometry, and take into account both types of splats. In this context, we introduce several regularization techniques aimed at precisely aligning tightly-bound Gaussian splats with the mesh surface during the training process. We validate the effectiveness of our method on large and unbounded scene from mip-NeRF 360 and Deep Blending datasets. Our method surpasses recent mesh-based neural rendering techniques by achieving a 2dB higher PSNR, and outperforms mesh-based Gaussian splatting methods by 1.3 dB PSNR, particularly on the outdoor mip-NeRF 360 dataset, demonstrating better rendering quality. We provide analyses for each type of Gaussian splat and achieve a reduction in the number of Gaussian splats by 30% compared to the original 3D Gaussian splatting.
Exploring the Potential of Synthetic Data to Replace Real Data
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:The potential of synthetic data to replace real data creates a huge demand for synthetic data in data-hungry AI. This potential is even greater when synthetic data is used for training along with a small number of real images from domains other than the test domain. We find that this potential varies depending on (i) the number of cross-domain real images and (ii) the test set on which the trained model is evaluated. We introduce two new metrics, the train2test distance and $\text{AP}_\text{t2t}$, to evaluate the ability of a cross-domain training set using synthetic data to represent the characteristics of test instances in relation to training performance. Using these metrics, we delve deeper into the factors that influence the potential of synthetic data and uncover some interesting dynamics about how synthetic data impacts training performance. We hope these discoveries will encourage more widespread use of synthetic data.
SynPlay: Importing Real-world Diversity for a Synthetic Human Dataset
Aug 21, 2024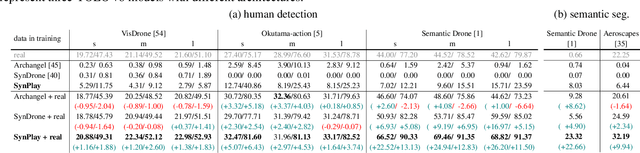

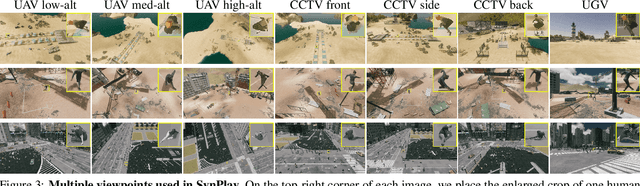
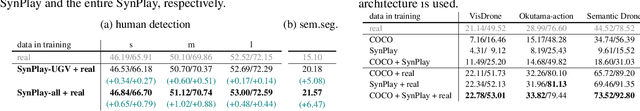
Abstract:We introduce Synthetic Playground (SynPlay), a new synthetic human dataset that aims to bring out the diversity of human appearance in the real world. We focus on two factors to achieve a level of diversity that has not yet been seen in previous works: i) realistic human motions and poses and ii) multiple camera viewpoints towards human instances. We first use a game engine and its library-provided elementary motions to create games where virtual players can take less-constrained and natural movements while following the game rules (i.e., rule-guided motion design as opposed to detail-guided design). We then augment the elementary motions with real human motions captured with a motion capture device. To render various human appearances in the games from multiple viewpoints, we use seven virtual cameras encompassing the ground and aerial views, capturing abundant aerial-vs-ground and dynamic-vs-static attributes of the scene. Through extensive and carefully-designed experiments, we show that using SynPlay in model training leads to enhanced accuracy over existing synthetic datasets for human detection and segmentation. The benefit of SynPlay becomes even greater for tasks in the data-scarce regime, such as few-shot and cross-domain learning tasks. These results clearly demonstrate that SynPlay can be used as an essential dataset with rich attributes of complex human appearances and poses suitable for model pretraining. SynPlay dataset comprising over 73k images and 6.5M human instances, is available for download at https://synplaydataset.github.io/.
Exploring the Impact of Synthetic Data for Aerial-view Human Detection
May 27, 2024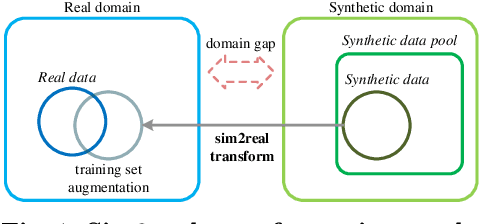

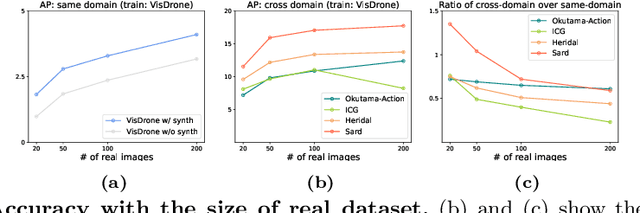
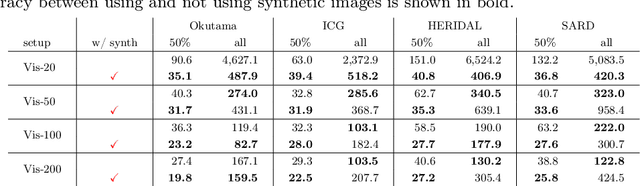
Abstract:Aerial-view human detection has a large demand for large-scale data to capture more diverse human appearances compared to ground-view human detection. Therefore, synthetic data can be a good resource to expand data, but the domain gap with real-world data is the biggest obstacle to its use in training. As a common solution to deal with the domain gap, the sim2real transformation is used, and its quality is affected by three factors: i) the real data serving as a reference when calculating the domain gap, ii) the synthetic data chosen to avoid the transformation quality degradation, and iii) the synthetic data pool from which the synthetic data is selected. In this paper, we investigate the impact of these factors on maximizing the effectiveness of synthetic data in training in terms of improving learning performance and acquiring domain generalization ability--two main benefits expected of using synthetic data. As an evaluation metric for the second benefit, we introduce a method for measuring the distribution gap between two datasets, which is derived as the normalized sum of the Mahalanobis distances of all test data. As a result, we have discovered several important findings that have never been investigated or have been used previously without accurate understanding. We expect that these findings can break the current trend of either naively using or being hesitant to use synthetic data in machine learning due to the lack of understanding, leading to more appropriate use in future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge