Shuvra S. Bhattacharyya
AutoComPose: Automatic Generation of Pose Transition Descriptions for Composed Pose Retrieval Using Multimodal LLMs
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:Composed pose retrieval (CPR) enables users to search for human poses by specifying a reference pose and a transition description, but progress in this field is hindered by the scarcity and inconsistency of annotated pose transitions. Existing CPR datasets rely on costly human annotations or heuristic-based rule generation, both of which limit scalability and diversity. In this work, we introduce AutoComPose, the first framework that leverages multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to automatically generate rich and structured pose transition descriptions. Our method enhances annotation quality by structuring transitions into fine-grained body part movements and introducing mirrored/swapped variations, while a cyclic consistency constraint ensures logical coherence between forward and reverse transitions. To advance CPR research, we construct and release two dedicated benchmarks, AIST-CPR and PoseFixCPR, supplementing prior datasets with enhanced attributes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that training retrieval models with AutoComPose yields superior performance over human-annotated and heuristic-based methods, significantly reducing annotation costs while improving retrieval quality. Our work pioneers the automatic annotation of pose transitions, establishing a scalable foundation for future CPR research.
SynPlay: Importing Real-world Diversity for a Synthetic Human Dataset
Aug 21, 2024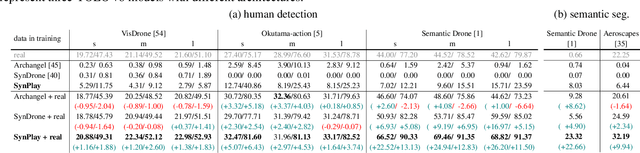

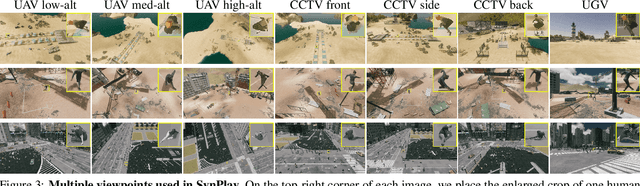
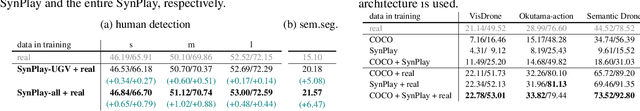
Abstract:We introduce Synthetic Playground (SynPlay), a new synthetic human dataset that aims to bring out the diversity of human appearance in the real world. We focus on two factors to achieve a level of diversity that has not yet been seen in previous works: i) realistic human motions and poses and ii) multiple camera viewpoints towards human instances. We first use a game engine and its library-provided elementary motions to create games where virtual players can take less-constrained and natural movements while following the game rules (i.e., rule-guided motion design as opposed to detail-guided design). We then augment the elementary motions with real human motions captured with a motion capture device. To render various human appearances in the games from multiple viewpoints, we use seven virtual cameras encompassing the ground and aerial views, capturing abundant aerial-vs-ground and dynamic-vs-static attributes of the scene. Through extensive and carefully-designed experiments, we show that using SynPlay in model training leads to enhanced accuracy over existing synthetic datasets for human detection and segmentation. The benefit of SynPlay becomes even greater for tasks in the data-scarce regime, such as few-shot and cross-domain learning tasks. These results clearly demonstrate that SynPlay can be used as an essential dataset with rich attributes of complex human appearances and poses suitable for model pretraining. SynPlay dataset comprising over 73k images and 6.5M human instances, is available for download at https://synplaydataset.github.io/.
Exploring the Impact of Synthetic Data for Aerial-view Human Detection
May 27, 2024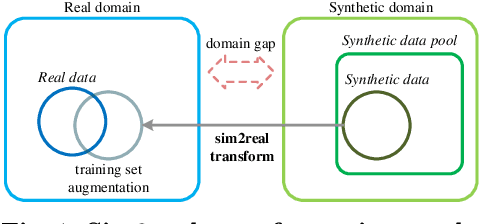

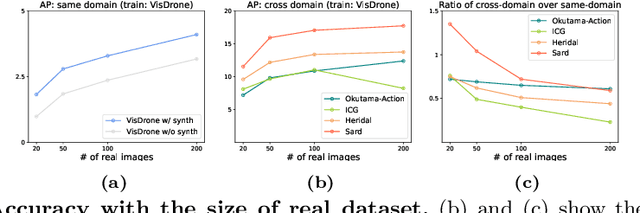
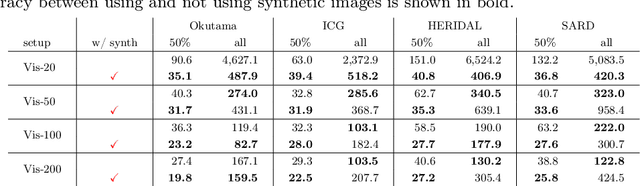
Abstract:Aerial-view human detection has a large demand for large-scale data to capture more diverse human appearances compared to ground-view human detection. Therefore, synthetic data can be a good resource to expand data, but the domain gap with real-world data is the biggest obstacle to its use in training. As a common solution to deal with the domain gap, the sim2real transformation is used, and its quality is affected by three factors: i) the real data serving as a reference when calculating the domain gap, ii) the synthetic data chosen to avoid the transformation quality degradation, and iii) the synthetic data pool from which the synthetic data is selected. In this paper, we investigate the impact of these factors on maximizing the effectiveness of synthetic data in training in terms of improving learning performance and acquiring domain generalization ability--two main benefits expected of using synthetic data. As an evaluation metric for the second benefit, we introduce a method for measuring the distribution gap between two datasets, which is derived as the normalized sum of the Mahalanobis distances of all test data. As a result, we have discovered several important findings that have never been investigated or have been used previously without accurate understanding. We expect that these findings can break the current trend of either naively using or being hesitant to use synthetic data in machine learning due to the lack of understanding, leading to more appropriate use in future research.
Diversifying Human Pose in Synthetic Data for Aerial-view Human Detection
May 24, 2024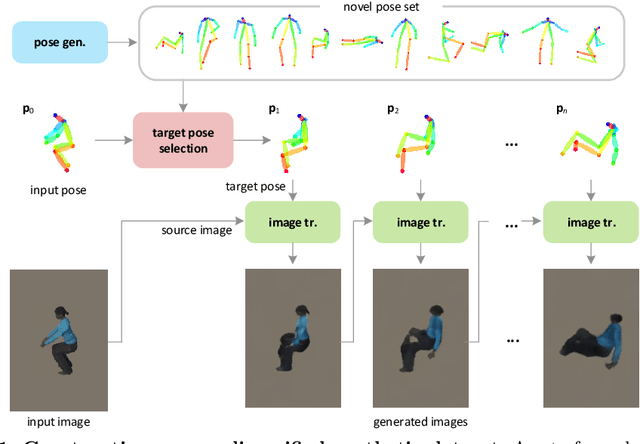
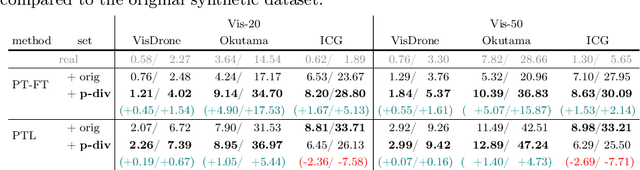
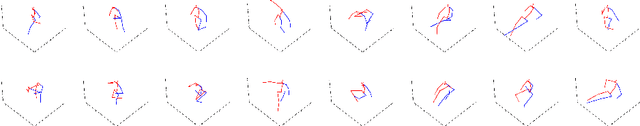

Abstract:We present a framework for diversifying human poses in a synthetic dataset for aerial-view human detection. Our method firstly constructs a set of novel poses using a pose generator and then alters images in the existing synthetic dataset to assume the novel poses while maintaining the original style using an image translator. Since images corresponding to the novel poses are not available in training, the image translator is trained to be applicable only when the input and target poses are similar, thus training does not require the novel poses and their corresponding images. Next, we select a sequence of target novel poses from the novel pose set, using Dijkstra's algorithm to ensure that poses closer to each other are located adjacently in the sequence. Finally, we repeatedly apply the image translator to each target pose in sequence to produce a group of novel pose images representing a variety of different limited body movements from the source pose. Experiments demonstrate that, regardless of how the synthetic data is used for training or the data size, leveraging the pose-diversified synthetic dataset in training generally presents remarkably better accuracy than using the original synthetic dataset on three aerial-view human detection benchmarks (VisDrone, Okutama-Action, and ICG) in the few-shot regime.
HashReID: Dynamic Network with Binary Codes for Efficient Person Re-identification
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:Biometric applications, such as person re-identification (ReID), are often deployed on energy constrained devices. While recent ReID methods prioritize high retrieval performance, they often come with large computational costs and high search time, rendering them less practical in real-world settings. In this work, we propose an input-adaptive network with multiple exit blocks, that can terminate computation early if the retrieval is straightforward or noisy, saving a lot of computation. To assess the complexity of the input, we introduce a temporal-based classifier driven by a new training strategy. Furthermore, we adopt a binary hash code generation approach instead of relying on continuous-valued features, which significantly improves the search process by a factor of 20. To ensure similarity preservation, we utilize a new ranking regularizer that bridges the gap between continuous and binary features. Extensive analysis of our proposed method is conducted on three datasets: Market1501, MSMT17 (Multi-Scene Multi-Time), and the BGC1 (BRIAR Government Collection). Using our approach, more than 70% of the samples with compact hash codes exit early on the Market1501 dataset, saving 80% of the networks computational cost and improving over other hash-based methods by 60%. These results demonstrate a significant improvement over dynamic networks and showcase comparable accuracy performance to conventional ReID methods. Code will be made available.
Hyperspectral Image Classification with Attention Aided CNNs
Jun 12, 2020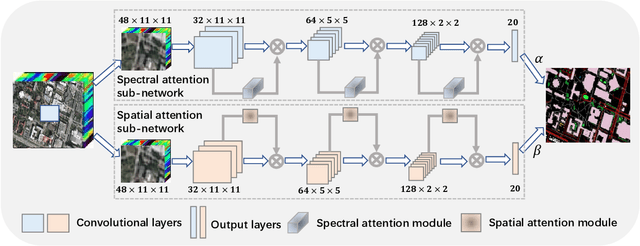
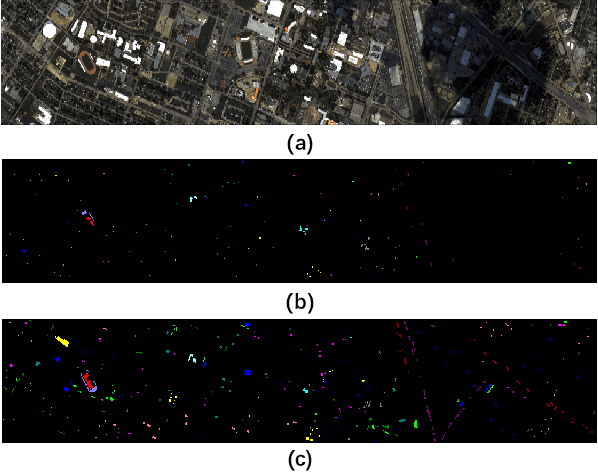
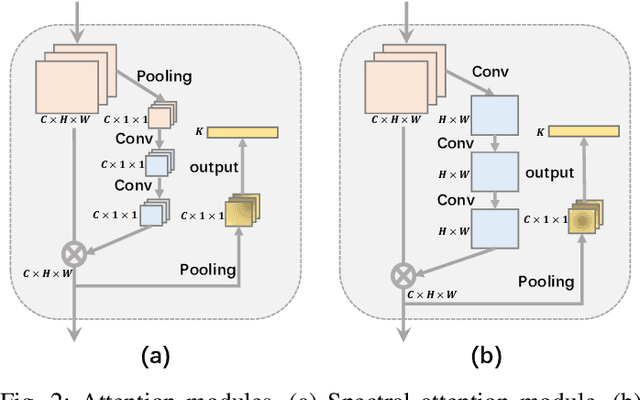

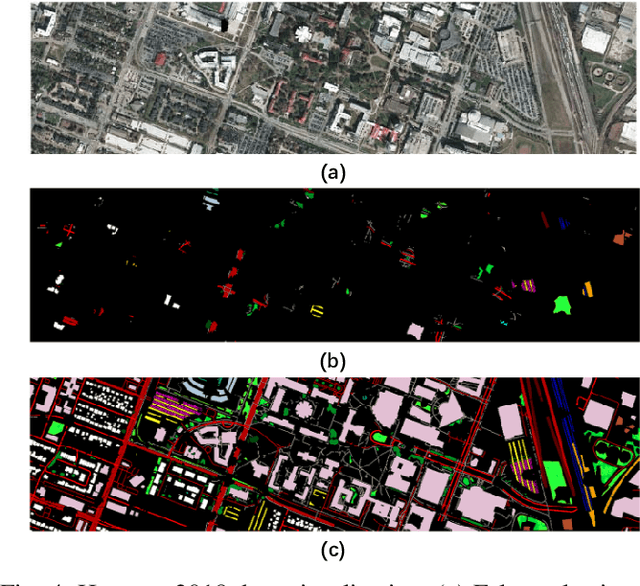
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely used for hyperspectral image classification. As a common process, small cubes are firstly cropped from the hyperspectral image and then fed into CNNs to extract spectral and spatial features. It is well known that different spectral bands and spatial positions in the cubes have different discriminative abilities. If fully explored, this prior information will help improve the learning capacity of CNNs. Along this direction, we propose an attention aided CNN model for spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral images. Specifically, a spectral attention sub-network and a spatial attention sub-network are proposed for spectral and spatial classification, respectively. Both of them are based on the traditional CNN model, and incorporate attention modules to aid networks focus on more discriminative channels or positions. In the final classification phase, the spectral classification result and the spatial classification result are combined together via an adaptively weighted summation method. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed model, we conduct experiments on three standard hyperspectral datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed model can achieve superior performance compared to several state-of-the-art CNN-related models.
Elastic Neural Networks for Classification
Oct 05, 2018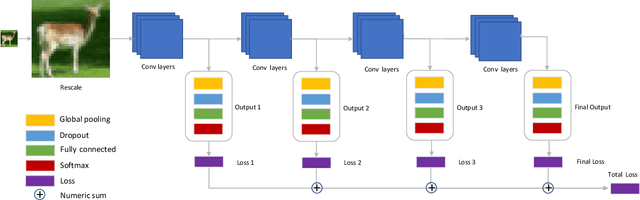
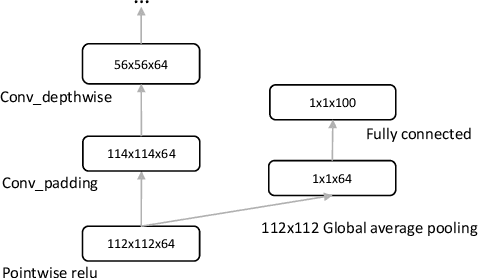
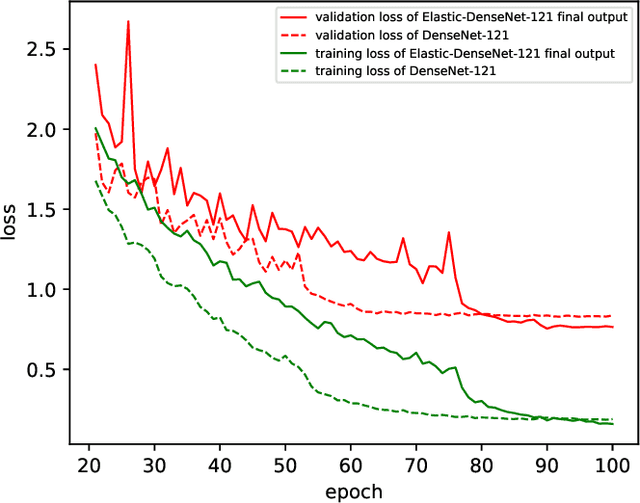
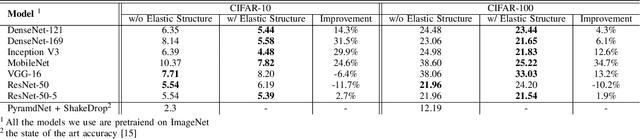
Abstract:In this work we propose a framework for improving the performance of any deep neural network that may suffer from vanishing gradients. To address the vanishing gradient issue, we study a framework, where we insert an intermediate output branch after each layer in the computational graph and use the corresponding prediction loss for feeding the gradient to the early layers. The framework - which we name Elastic network - is tested with several well-known networks on CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 datasets, and the experimental results show that the proposed framework improves the accuracy on both shallow networks (e.g., MobileNet) and deep convolutional neural networks (e.g., DenseNet). We also identify the types of networks where the framework does not improve the performance and discuss the reasons. Finally, as a side product, the computational complexity of the resulting networks can be adjusted in an elastic manner by selecting the output branch according to current computational budget.
Elastic Neural Networks: A Scalable Framework for Embedded Computer Vision
Oct 02, 2018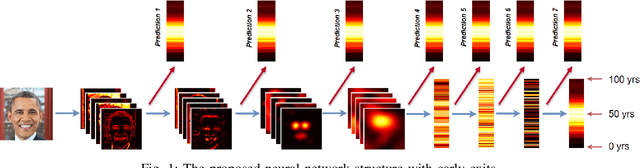
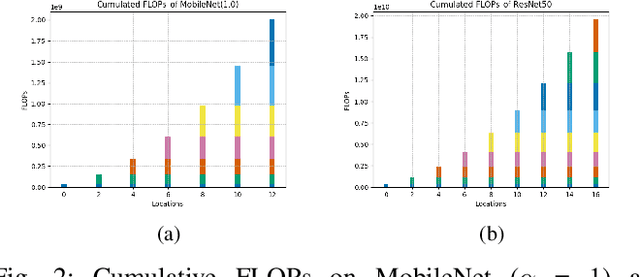
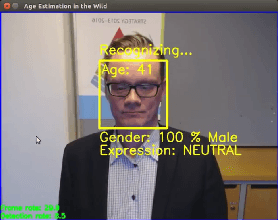

Abstract:We propose a new framework for image classification with deep neural networks. The framework introduces intermediate outputs to the computational graph of a network. This enables flexible control of the computational load and balances the tradeoff between accuracy and execution time. Moreover, we present an interesting finding that the intermediate outputs can act as a regularizer at training time, improving the prediction accuracy. In the experimental section we demonstrate the performance of our proposed framework with various commonly used pretrained deep networks in the use case of apparent age estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge