Pedram Ghamisi
Sabrina
Towards Realistic Remote Sensing Dataset Distillation with Discriminative Prototype-guided Diffusion
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the remarkable success of deep learning in remote sensing image interpretation, driven by the availability of large-scale benchmark datasets. However, this reliance on massive training data also brings two major challenges: (1) high storage and computational costs, and (2) the risk of data leakage, especially when sensitive categories are involved. To address these challenges, this study introduces the concept of dataset distillation into the field of remote sensing image interpretation for the first time. Specifically, we train a text-to-image diffusion model to condense a large-scale remote sensing dataset into a compact and representative distilled dataset. To improve the discriminative quality of the synthesized samples, we propose a classifier-driven guidance by injecting a classification consistency loss from a pre-trained model into the diffusion training process. Besides, considering the rich semantic complexity of remote sensing imagery, we further perform latent space clustering on training samples to select representative and diverse prototypes as visual style guidance, while using a visual language model to provide aggregated text descriptions. Experiments on three high-resolution remote sensing scene classification benchmarks show that the proposed method can distill realistic and diverse samples for downstream model training. Code and pre-trained models are available online (https://github.com/YonghaoXu/DPD).
Automated Road Crack Localization to Guide Highway Maintenance
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Highway networks are crucial for economic prosperity. Climate change-induced temperature fluctuations are exacerbating stress on road pavements, resulting in elevated maintenance costs. This underscores the need for targeted and efficient maintenance strategies. This study investigates the potential of open-source data to guide highway infrastructure maintenance. The proposed framework integrates airborne imagery and OpenStreetMap (OSM) to fine-tune YOLOv11 for highway crack localization. To demonstrate the framework's real-world applicability, a Swiss Relative Highway Crack Density (RHCD) index was calculated to inform nationwide highway maintenance. The crack classification model achieved an F1-score of $0.84$ for the positive class (crack) and $0.97$ for the negative class (no crack). The Swiss RHCD index exhibited weak correlations with Long-term Land Surface Temperature Amplitudes (LT-LST-A) (Pearson's $r\ = -0.05$) and Traffic Volume (TV) (Pearson's $r\ = 0.17$), underlining the added value of this novel index for guiding maintenance over other data. Significantly high RHCD values were observed near urban centers and intersections, providing contextual validation for the predictions. These findings highlight the value of open-source data sharing to drive innovation, ultimately enabling more efficient solutions in the public sector.
CangLing-KnowFlow: A Unified Knowledge-and-Flow-fused Agent for Comprehensive Remote Sensing Applications
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:The automated and intelligent processing of massive remote sensing (RS) datasets is critical in Earth observation (EO). Existing automated systems are normally task-specific, lacking a unified framework to manage diverse, end-to-end workflows--from data preprocessing to advanced interpretation--across diverse RS applications. To address this gap, this paper introduces CangLing-KnowFlow, a unified intelligent agent framework that integrates a Procedural Knowledge Base (PKB), Dynamic Workflow Adjustment, and an Evolutionary Memory Module. The PKB, comprising 1,008 expert-validated workflow cases across 162 practical RS tasks, guides planning and substantially reduces hallucinations common in general-purpose agents. During runtime failures, the Dynamic Workflow Adjustment autonomously diagnoses and replans recovery strategies, while the Evolutionary Memory Module continuously learns from these events, iteratively enhancing the agent's knowledge and performance. This synergy enables CangLing-KnowFlow to adapt, learn, and operate reliably across diverse, complex tasks. We evaluated CangLing-KnowFlow on the KnowFlow-Bench, a novel benchmark of 324 workflows inspired by real-world applications, testing its performance across 13 top Large Language Model (LLM) backbones, from open-source to commercial. Across all complex tasks, CangLing-KnowFlow surpassed the Reflexion baseline by at least 4% in Task Success Rate. As the first most comprehensive validation along this emerging field, this research demonstrates the great potential of CangLing-KnowFlow as a robust, efficient, and scalable automated solution for complex EO challenges by leveraging expert knowledge (Knowledge) into adaptive and verifiable procedures (Flow).
FarSLIP: Discovering Effective CLIP Adaptation for Fine-Grained Remote Sensing Understanding
Nov 18, 2025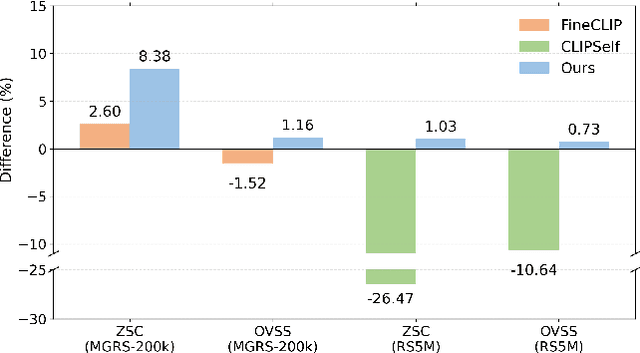
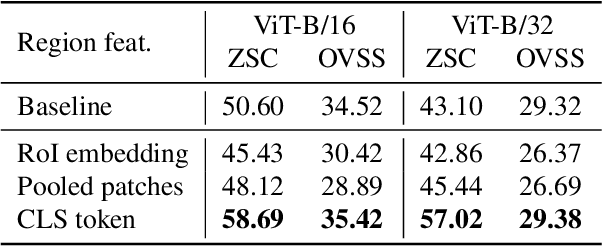
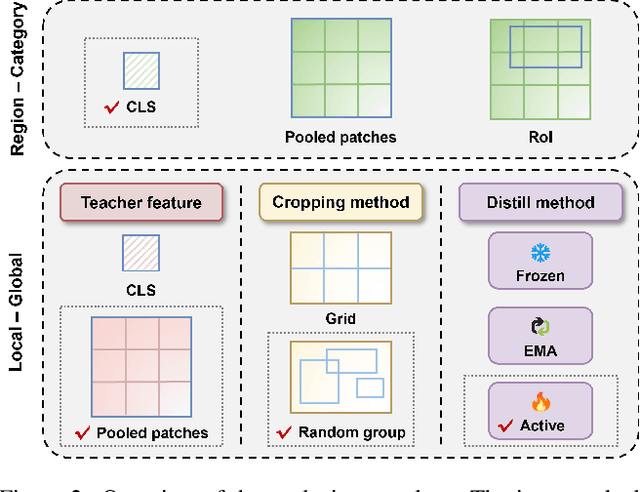
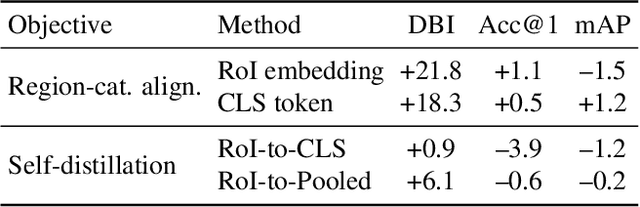
Abstract:As CLIP's global alignment limits its ability to capture fine-grained details, recent efforts have focused on enhancing its region-text alignment. However, current remote sensing (RS)-specific CLIP variants still inherit this limited spatial awareness. We identify two key limitations behind this: (1) current RS image-text datasets generate global captions from object-level labels, leaving the original object-level supervision underutilized; (2) despite the success of region-text alignment methods in general domain, their direct application to RS data often leads to performance degradation. To address these, we construct the first multi-granularity RS image-text dataset, MGRS-200k, featuring rich object-level textual supervision for RS region-category alignment. We further investigate existing fine-grained CLIP tuning strategies and find that current explicit region-text alignment methods, whether in a direct or indirect way, underperform due to severe degradation of CLIP's semantic coherence. Building on these, we propose FarSLIP, a Fine-grained Aligned RS Language-Image Pretraining framework. Rather than the commonly used patch-to-CLS self-distillation, FarSLIP employs patch-to-patch distillation to align local and global visual cues, which improves feature discriminability while preserving semantic coherence. Additionally, to effectively utilize region-text supervision, it employs simple CLS token-based region-category alignment rather than explicit patch-level alignment, further enhancing spatial awareness. FarSLIP features improved fine-grained vision-language alignment in RS domain and sets a new state of the art not only on RS open-vocabulary semantic segmentation, but also on image-level tasks such as zero-shot classification and image-text retrieval. Our dataset, code, and models are available at https://github.com/NJU-LHRS/FarSLIP.
Label-Efficient 3D Forest Mapping: Self-Supervised and Transfer Learning for Individual, Structural, and Species Analysis
Nov 09, 2025



Abstract:Detailed structural and species information on individual tree level is increasingly important to support precision forestry, biodiversity conservation, and provide reference data for biomass and carbon mapping. Point clouds from airborne and ground-based laser scanning are currently the most suitable data source to rapidly derive such information at scale. Recent advancements in deep learning improved segmenting and classifying individual trees and identifying semantic tree components. However, deep learning models typically require large amounts of annotated training data which limits further improvement. Producing dense, high-quality annotations for 3D point clouds, especially in complex forests, is labor-intensive and challenging to scale. We explore strategies to reduce dependence on large annotated datasets using self-supervised and transfer learning architectures. Our objective is to improve performance across three tasks: instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, and tree classification using realistic and operational training sets. Our findings indicate that combining self-supervised learning with domain adaptation significantly enhances instance segmentation compared to training from scratch (AP50 +16.98%), self-supervised learning suffices for semantic segmentation (mIoU +1.79%), and hierarchical transfer learning enables accurate classification of unseen species (Jaccard +6.07%). To simplify use and encourage uptake, we integrated the tasks into a unified framework, streamlining the process from raw point clouds to tree delineation, structural analysis, and species classification. Pretrained models reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions by ~21%. This open-source contribution aims to accelerate operational extraction of individual tree information from laser scanning point clouds to support forestry, biodiversity, and carbon mapping.
Survey of Multimodal Geospatial Foundation Models: Techniques, Applications, and Challenges
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Foundation models have transformed natural language processing and computer vision, and their impact is now reshaping remote sensing image analysis. With powerful generalization and transfer learning capabilities, they align naturally with the multimodal, multi-resolution, and multi-temporal characteristics of remote sensing data. To address unique challenges in the field, multimodal geospatial foundation models (GFMs) have emerged as a dedicated research frontier. This survey delivers a comprehensive review of multimodal GFMs from a modality-driven perspective, covering five core visual and vision-language modalities. We examine how differences in imaging physics and data representation shape interaction design, and we analyze key techniques for alignment, integration, and knowledge transfer to tackle modality heterogeneity, distribution shifts, and semantic gaps. Advances in training paradigms, architectures, and task-specific adaptation strategies are systematically assessed alongside a wealth of emerging benchmarks. Representative multimodal visual and vision-language GFMs are evaluated across ten downstream tasks, with insights into their architectures, performance, and application scenarios. Real-world case studies, spanning land cover mapping, agricultural monitoring, disaster response, climate studies, and geospatial intelligence, demonstrate the practical potential of GFMs. Finally, we outline pressing challenges in domain generalization, interpretability, efficiency, and privacy, and chart promising avenues for future research.
Geospatial Foundation Models to Enable Progress on Sustainable Development Goals
May 30, 2025Abstract:Foundation Models (FMs) are large-scale, pre-trained AI systems that have revolutionized natural language processing and computer vision, and are now advancing geospatial analysis and Earth Observation (EO). They promise improved generalization across tasks, scalability, and efficient adaptation with minimal labeled data. However, despite the rapid proliferation of geospatial FMs, their real-world utility and alignment with global sustainability goals remain underexplored. We introduce SustainFM, a comprehensive benchmarking framework grounded in the 17 Sustainable Development Goals with extremely diverse tasks ranging from asset wealth prediction to environmental hazard detection. This study provides a rigorous, interdisciplinary assessment of geospatial FMs and offers critical insights into their role in attaining sustainability goals. Our findings show: (1) While not universally superior, FMs often outperform traditional approaches across diverse tasks and datasets. (2) Evaluating FMs should go beyond accuracy to include transferability, generalization, and energy efficiency as key criteria for their responsible use. (3) FMs enable scalable, SDG-grounded solutions, offering broad utility for tackling complex sustainability challenges. Critically, we advocate for a paradigm shift from model-centric development to impact-driven deployment, and emphasize metrics such as energy efficiency, robustness to domain shifts, and ethical considerations.
HyperPointFormer: Multimodal Fusion in 3D Space with Dual-Branch Cross-Attention Transformers
May 29, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal remote sensing data, including spectral and lidar or photogrammetry, is crucial for achieving satisfactory land-use / land-cover classification results in urban scenes. So far, most studies have been conducted in a 2D context. When 3D information is available in the dataset, it is typically integrated with the 2D data by rasterizing the 3D data into 2D formats. Although this method yields satisfactory classification results, it falls short in fully exploiting the potential of 3D data by restricting the model's ability to learn 3D spatial features directly from raw point clouds. Additionally, it limits the generation of 3D predictions, as the dimensionality of the input data has been reduced. In this study, we propose a fully 3D-based method that fuses all modalities within the 3D point cloud and employs a dedicated dual-branch Transformer model to simultaneously learn geometric and spectral features. To enhance the fusion process, we introduce a cross-attention-based mechanism that fully operates on 3D points, effectively integrating features from various modalities across multiple scales. The purpose of cross-attention is to allow one modality to assess the importance of another by weighing the relevant features. We evaluated our method by comparing it against both 3D and 2D methods using the 2018 IEEE GRSS Data Fusion Contest (DFC2018) dataset. Our findings indicate that 3D fusion delivers competitive results compared to 2D methods and offers more flexibility by providing 3D predictions. These predictions can be projected onto 2D maps, a capability that is not feasible in reverse. Additionally, we evaluated our method on different datasets, specifically the ISPRS Vaihingen 3D and the IEEE 2019 Data Fusion Contest. Our code will be published here: https://github.com/aldinorizaldy/hyperpointformer.
Electrolyzers-HSI: Close-Range Multi-Scene Hyperspectral Imaging Benchmark Dataset
May 26, 2025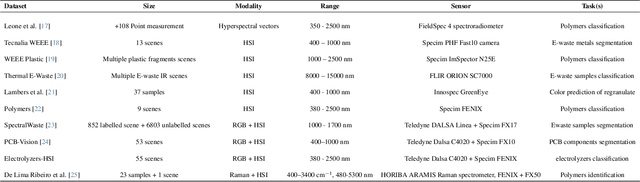
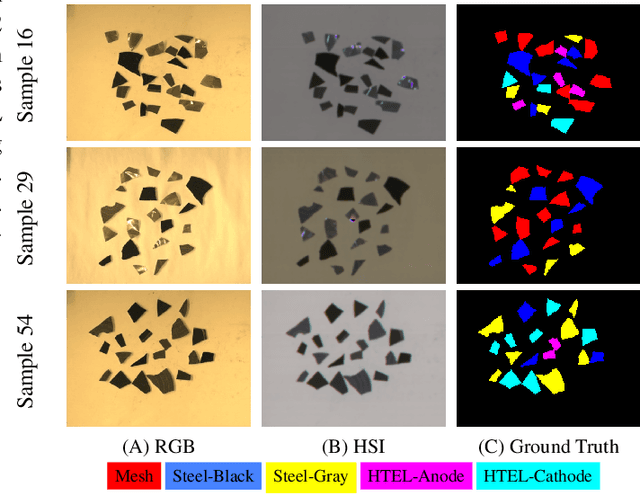
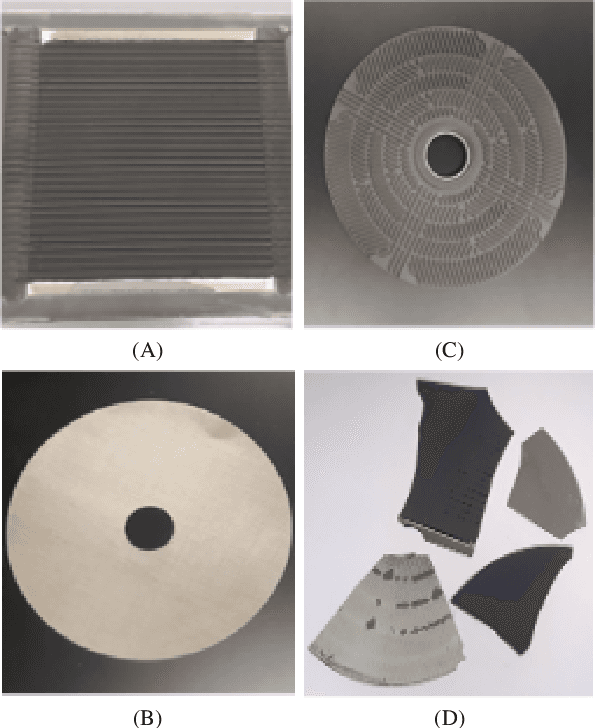
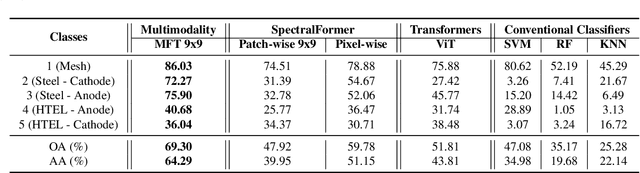

Abstract:The global challenge of sustainable recycling demands automated, fast, and accurate, state-of-the-art (SOTA) material detection systems that act as a bedrock for a circular economy. Democratizing access to these cutting-edge solutions that enable real-time waste analysis is essential for scaling up recycling efforts and fostering the Green Deal. In response, we introduce \textbf{Electrolyzers-HSI}, a novel multimodal benchmark dataset designed to accelerate the recovery of critical raw materials through accurate electrolyzer materials classification. The dataset comprises 55 co-registered high-resolution RGB images and hyperspectral imaging (HSI) data cubes spanning the 400--2500 nm spectral range, yielding over 4.2 million pixel vectors and 424,169 labeled ones. This enables non-invasive spectral analysis of shredded electrolyzer samples, supporting quantitative and qualitative material classification and spectral properties investigation. We evaluate a suite of baseline machine learning (ML) methods alongside SOTA transformer-based deep learning (DL) architectures, including Vision Transformer, SpectralFormer, and the Multimodal Fusion Transformer, to investigate architectural bottlenecks for further efficiency optimisation when deploying transformers in material identification. We implement zero-shot detection techniques and majority voting across pixel-level predictions to establish object-level classification robustness. In adherence to the FAIR data principles, the electrolyzers-HSI dataset and accompanying codebase are openly available at https://github.com/hifexplo/Electrolyzers-HSI and https://rodare.hzdr.de/record/3668, supporting reproducible research and facilitating the broader adoption of smart and sustainable e-waste recycling solutions.
FlexiMo: A Flexible Remote Sensing Foundation Model
Mar 31, 2025
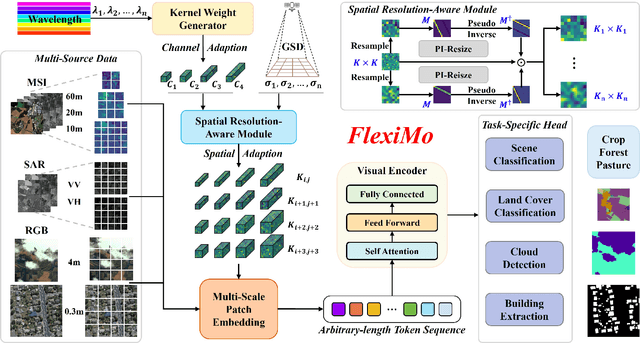
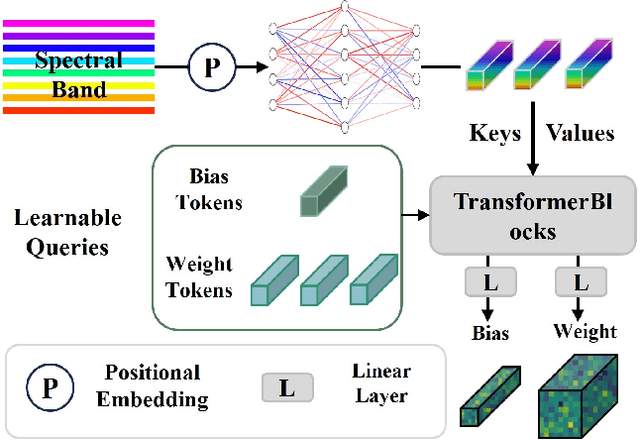

Abstract:The rapid expansion of multi-source satellite imagery drives innovation in Earth observation, opening unprecedented opportunities for Remote Sensing Foundation Models to harness diverse data. However, many existing models remain constrained by fixed spatial resolutions and patch sizes, limiting their ability to fully exploit the heterogeneous spatial characteristics inherent in satellite imagery. To address these challenges, we propose FlexiMo, a flexible remote sensing foundation model that endows the pre-trained model with the flexibility to adapt to arbitrary spatial resolutions. Central to FlexiMo is a spatial resolution-aware module that employs a parameter-free alignment embedding mechanism to dynamically recalibrate patch embeddings based on the input image's resolution and dimensions. This design not only preserves critical token characteristics and ensures multi-scale feature fidelity but also enables efficient feature extraction without requiring modifications to the underlying network architecture. In addition, FlexiMo incorporates a lightweight channel adaptation module that leverages prior spectral information from sensors. This mechanism allows the model to process images with varying numbers of channels while maintaining the data's intrinsic physical properties. Extensive experiments on diverse multimodal, multi-resolution, and multi-scale datasets demonstrate that FlexiMo significantly enhances model generalization and robustness. In particular, our method achieves outstanding performance across a range of downstream tasks, including scene classification, land cover classification, urban building segmentation, and cloud detection. By enabling parameter-efficient and physically consistent adaptation, FlexiMo paves the way for more adaptable and effective foundation models in real-world remote sensing applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge