Zhu Li
HPC: Hierarchical Point-based Latent Representation for Streaming Dynamic Gaussian Splatting Compression
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:While dynamic Gaussian Splatting has driven significant advances in free-viewpoint video, maintaining its rendering quality with a small memory footprint for efficient streaming transmission still presents an ongoing challenge. Existing streaming dynamic Gaussian Splatting compression methods typically leverage a latent representation to drive the neural network for predicting Gaussian residuals between frames. Their core latent representations can be categorized into structured grid-based and unstructured point-based paradigms. However, the former incurs significant parameter redundancy by inevitably modeling unoccupied space, while the latter suffers from limited compactness as it fails to exploit local correlations. To relieve these limitations, we propose HPC, a novel streaming dynamic Gaussian Splatting compression framework. It employs a hierarchical point-based latent representation that operates on a per-Gaussian basis to avoid parameter redundancy in unoccupied space. Guided by a tailored aggregation scheme, these latent points achieve high compactness with low spatial redundancy. To improve compression efficiency, we further undertake the first investigation to compress neural networks for streaming dynamic Gaussian Splatting through mining and exploiting the inter-frame correlation of parameters. Combined with latent compression, this forms a fully end-to-end compression framework. Comprehensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that HPC substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods. It achieves a storage reduction of 67% against its baseline while maintaining high reconstruction fidelity.
DALD-PCAC: Density-Adaptive Learning Descriptor for Point Cloud Lossless Attribute Compression
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Recently, deep learning has significantly advanced the performance of point cloud geometry compression. However, the learning-based lossless attribute compression of point clouds with varying densities is under-explored. In this paper, we develop a learning-based framework, namely DALD-PCAC that leverages Levels of Detail (LoD) to tailor for point cloud lossless attribute compression. We develop a point-wise attention model using a permutation-invariant Transformer to tackle the challenges of sparsity and irregularity of point clouds during context modeling. We also propose a Density-Adaptive Learning Descriptor (DALD) capable of capturing structure and correlations among points across a large range of neighbors. In addition, we develop a prior-guided block partitioning to reduce the attribute variance within blocks and enhance the performance. Experiments on LiDAR and object point clouds show that DALD-PCAC achieves the state-of-the-art performance on most data. Our method boosts the compression performance and is robust to the varying densities of point clouds. Moreover, it guarantees a good trade-off between performance and complexity, exhibiting great potential in real-world applications. The source code is available at https://github.com/zb12138/DALD_PCAC.
DeepRAHT: Learning Predictive RAHT for Point Cloud Attribute Compression
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Regional Adaptive Hierarchical Transform (RAHT) is an effective point cloud attribute compression (PCAC) method. However, its application in deep learning lacks research. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end RAHT framework for lossy PCAC based on the sparse tensor, called DeepRAHT. The RAHT transform is performed within the learning reconstruction process, without requiring manual RAHT for preprocessing. We also introduce the predictive RAHT to reduce bitrates and design a learning-based prediction model to enhance performance. Moreover, we devise a bitrate proxy that applies run-length coding to entropy model, achieving seamless variable-rate coding and improving robustness. DeepRAHT is a reversible and distortion-controllable framework, ensuring its lower bound performance and offering significant application potential. The experiments demonstrate that DeepRAHT is a high-performance, faster, and more robust solution than the baseline methods. Project Page: https://github.com/zb12138/DeepRAHT.
Lightweight 3D Gaussian Splatting Compression via Video Codec
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Current video-based GS compression methods rely on using Parallel Linear Assignment Sorting (PLAS) to convert 3D GS into smooth 2D maps, which are computationally expensive and time-consuming, limiting the application of GS on lightweight devices. In this paper, we propose a Lightweight 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS) Compression method based on Video codec (LGSCV). First, a two-stage Morton scan is proposed to generate blockwise 2D maps that are friendly for canonical video codecs in which the coding units (CU) are square blocks. A 3D Morton scan is used to permute GS primitives, followed by a 2D Morton scan to map the ordered GS primitives to 2D maps in a blockwise style. However, although the blockwise 2D maps report close performance to the PLAS map in high-bitrate regions, they show a quality collapse at medium-to-low bitrates. Therefore, a principal component analysis (PCA) is used to reduce the dimensionality of spherical harmonics (SH), and a MiniPLAS, which is flexible and fast, is designed to permute the primitives within certain block sizes. Incorporating SH PCA and MiniPLAS leads to a significant gain in rate-distortion (RD) performance, especially at medium and low bitrates. MiniPLAS can also guide the setting of the codec CU size configuration and significantly reduce encoding time. Experimental results on the MPEG dataset demonstrate that the proposed LGSCV achieves over 20% RD gain compared with state-of-the-art methods, while reducing 2D map generation time to approximately 1 second and cutting encoding time by 50%. The code is available at https://github.com/Qi-Yangsjtu/LGSCV .
J-SGFT: Joint Spatial and Graph Fourier Domain Learning for Point Cloud Attribute Deblocking
Nov 07, 2025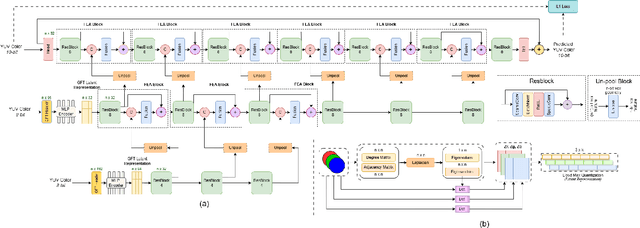
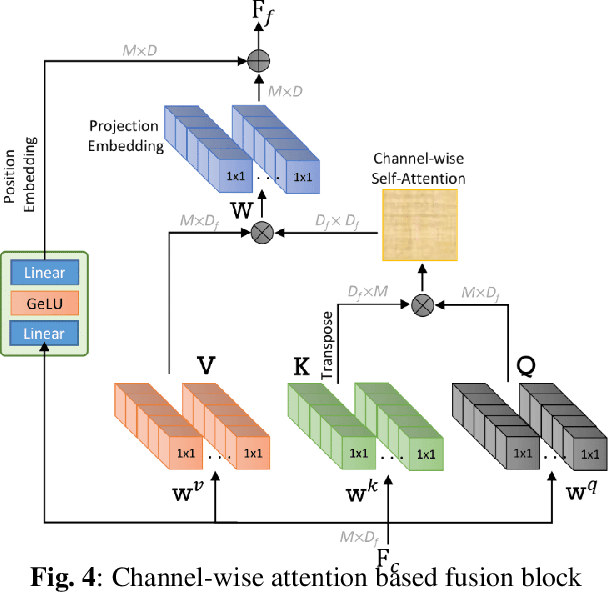
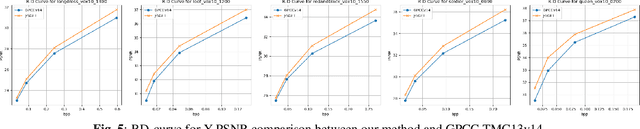
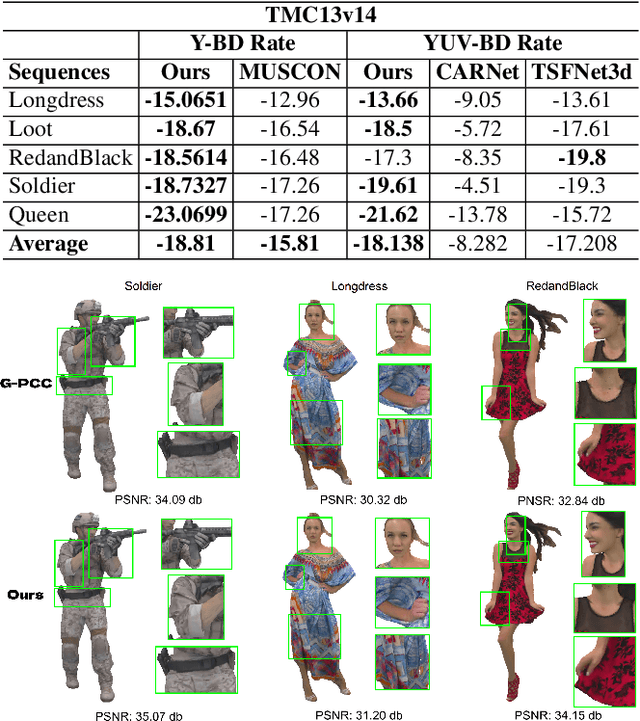
Abstract:Point clouds (PC) are essential for AR/VR and autonomous driving but challenge compression schemes with their size, irregular sampling, and sparsity. MPEG's Geometry-based Point Cloud Compression (GPCC) methods successfully reduce bitrate; however, they introduce significant blocky artifacts in the reconstructed point cloud. We introduce a novel multi-scale postprocessing framework that fuses graph-Fourier latent attribute representations with sparse convolutions and channel-wise attention to efficiently deblock reconstructed point clouds. Against the GPCC TMC13v14 baseline, our approach achieves BD-rate reduction of 18.81\% in the Y channel and 18.14\% in the joint YUV on the 8iVFBv2 dataset, delivering markedly improved visual fidelity with minimal overhead.
TVMC: Time-Varying Mesh Compression via Multi-Stage Anchor Mesh Generation
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Time-varying meshes, characterized by dynamic connectivity and varying vertex counts, hold significant promise for applications such as augmented reality. However, their practical utilization remains challenging due to the substantial data volume required for high-fidelity representation. While various compression methods attempt to leverage temporal redundancy between consecutive mesh frames, most struggle with topological inconsistency and motion-induced artifacts. To address these issues, we propose Time-Varying Mesh Compression (TVMC), a novel framework built on multi-stage coarse-to-fine anchor mesh generation for inter-frame prediction. Specifically, the anchor mesh is progressively constructed in three stages: initial, coarse, and fine. The initial anchor mesh is obtained through fast topology alignment to exploit temporal coherence. A Kalman filter-based motion estimation module then generates a coarse anchor mesh by accurately compensating inter-frame motions. Subsequently, a Quadric Error Metric-based refinement step optimizes vertex positions to form a fine anchor mesh with improved geometric fidelity. Based on the refined anchor mesh, the inter-frame motions relative to the reference base mesh are encoded, while the residual displacements between the subdivided fine anchor mesh and the input mesh are adaptively quantized and compressed. This hierarchical strategy preserves consistent connectivity and high-quality surface approximation, while achieving an efficient and compact representation of dynamic geometry. Extensive experiments on standard MPEG dynamic mesh sequences demonstrate that TVMC achieves state-of-the-art compression performance. Compared to the latest V-DMC standard, it delivers a significant BD-rate gain of 10.2% ~ 16.9%, while preserving high reconstruction quality. The code is available at https://github.com/H-Huang774/TVMC.
Making Machines Sound Sarcastic: LLM-Enhanced and Retrieval-Guided Sarcastic Speech Synthesis
Oct 08, 2025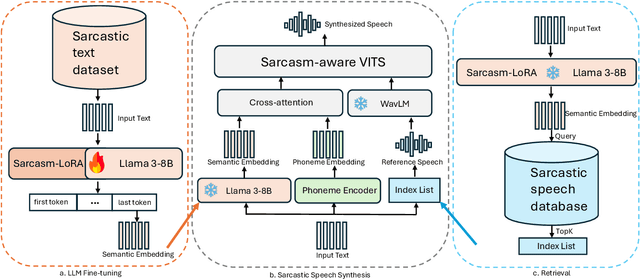
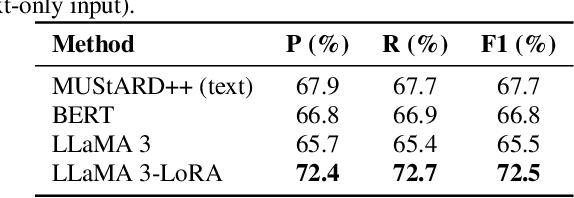
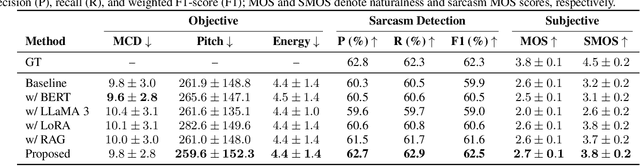
Abstract:Sarcasm is a subtle form of non-literal language that poses significant challenges for speech synthesis due to its reliance on nuanced semantic, contextual, and prosodic cues. While existing speech synthesis research has focused primarily on broad emotional categories, sarcasm remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose a Large Language Model (LLM)-enhanced Retrieval-Augmented framework for sarcasm-aware speech synthesis. Our approach combines (1) semantic embeddings from a LoRA-fine-tuned LLaMA 3, which capture pragmatic incongruity and discourse-level cues of sarcasm, and (2) prosodic exemplars retrieved via a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) module, which provide expressive reference patterns of sarcastic delivery. Integrated within a VITS backbone, this dual conditioning enables more natural and contextually appropriate sarcastic speech. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms baselines in both objective measures and subjective evaluations, yielding improvements in speech naturalness, sarcastic expressivity, and downstream sarcasm detection.
DPCD: A Quality Assessment Database for Dynamic Point Clouds
May 18, 2025
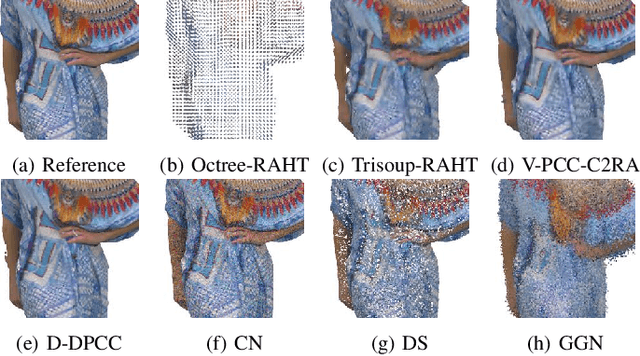
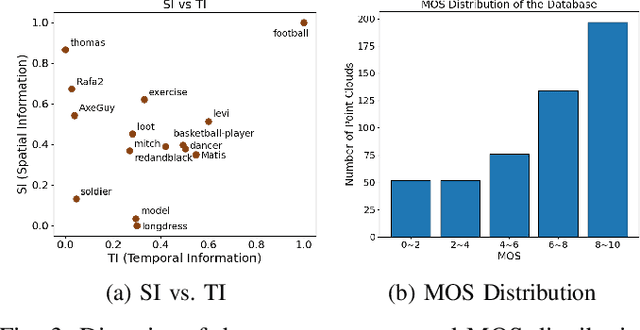
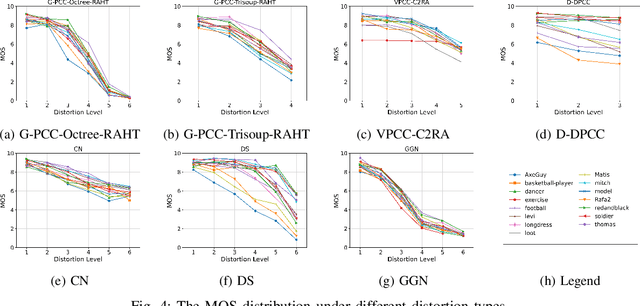
Abstract:Recently, the advancements in Virtual/Augmented Reality (VR/AR) have driven the demand for Dynamic Point Clouds (DPC). Unlike static point clouds, DPCs are capable of capturing temporal changes within objects or scenes, offering a more accurate simulation of the real world. While significant progress has been made in the quality assessment research of static point cloud, little study has been done on Dynamic Point Cloud Quality Assessment (DPCQA), which hinders the development of quality-oriented applications, such as interframe compression and transmission in practical scenarios. In this paper, we introduce a large-scale DPCQA database, named DPCD, which includes 15 reference DPCs and 525 distorted DPCs from seven types of lossy compression and noise distortion. By rendering these samples to Processed Video Sequences (PVS), a comprehensive subjective experiment is conducted to obtain Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) from 21 viewers for analysis. The characteristic of contents, impact of various distortions, and accuracy of MOSs are presented to validate the heterogeneity and reliability of the proposed database. Furthermore, we evaluate the performance of several objective metrics on DPCD. The experiment results show that DPCQA is more challenge than that of static point cloud. The DPCD, which serves as a catalyst for new research endeavors on DPCQA, is publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/Olivialyt/DPCD.
Textured mesh Quality Assessment using Geometry and Color Field Similarity
May 16, 2025Abstract:Textured mesh quality assessment (TMQA) is critical for various 3D mesh applications. However, existing TMQA methods often struggle to provide accurate and robust evaluations. Motivated by the effectiveness of fields in representing both 3D geometry and color information, we propose a novel point-based TMQA method called field mesh quality metric (FMQM). FMQM utilizes signed distance fields and a newly proposed color field named nearest surface point color field to realize effective mesh feature description. Four features related to visual perception are extracted from the geometry and color fields: geometry similarity, geometry gradient similarity, space color distribution similarity, and space color gradient similarity. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that FMQM outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) TMQA metrics. Furthermore, FMQM exhibits low computational complexity, making it a practical and efficient solution for real-world applications in 3D graphics and visualization. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/yyyykf/FMQM.
ADC-GS: Anchor-Driven Deformable and Compressed Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
May 13, 2025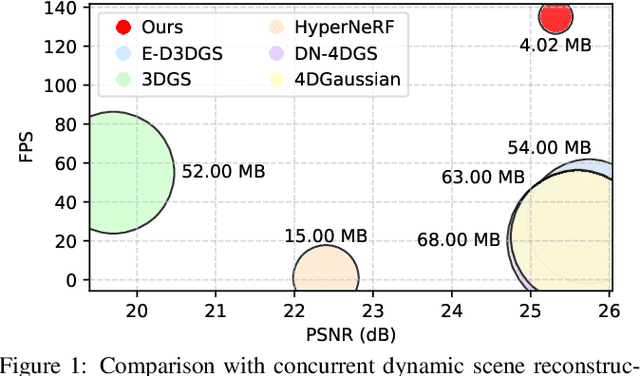


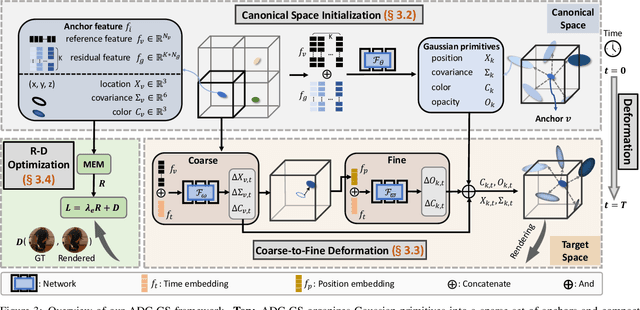
Abstract:Existing 4D Gaussian Splatting methods rely on per-Gaussian deformation from a canonical space to target frames, which overlooks redundancy among adjacent Gaussian primitives and results in suboptimal performance. To address this limitation, we propose Anchor-Driven Deformable and Compressed Gaussian Splatting (ADC-GS), a compact and efficient representation for dynamic scene reconstruction. Specifically, ADC-GS organizes Gaussian primitives into an anchor-based structure within the canonical space, enhanced by a temporal significance-based anchor refinement strategy. To reduce deformation redundancy, ADC-GS introduces a hierarchical coarse-to-fine pipeline that captures motions at varying granularities. Moreover, a rate-distortion optimization is adopted to achieve an optimal balance between bitrate consumption and representation fidelity. Experimental results demonstrate that ADC-GS outperforms the per-Gaussian deformation approaches in rendering speed by 300%-800% while achieving state-of-the-art storage efficiency without compromising rendering quality. The code is released at https://github.com/H-Huang774/ADC-GS.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge