Zhenlong Yuan
EMPOWER: Evolutionary Medical Prompt Optimization With Reinforcement Learning
Aug 25, 2025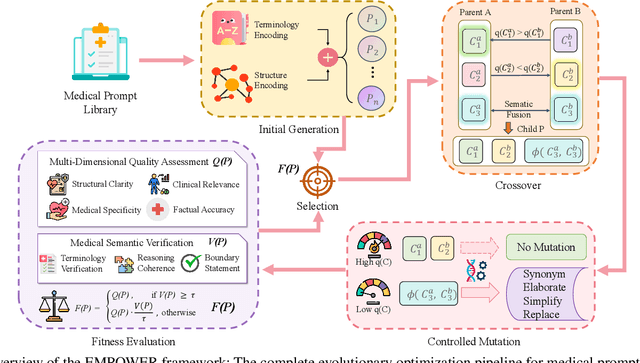
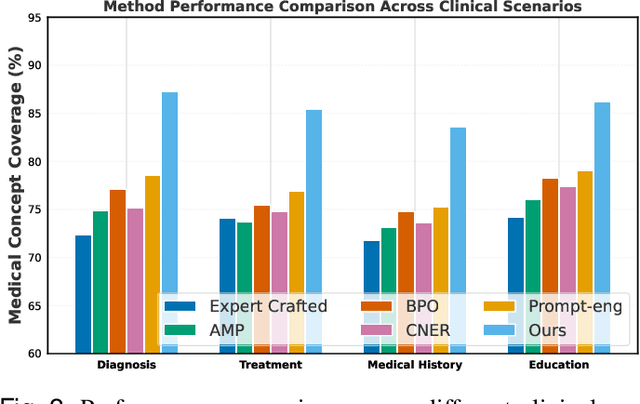
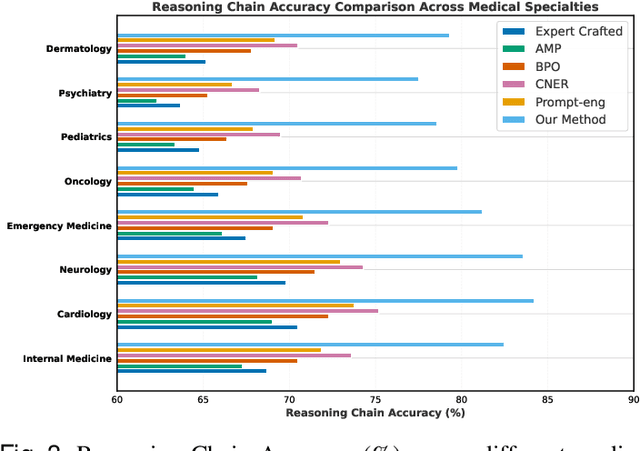
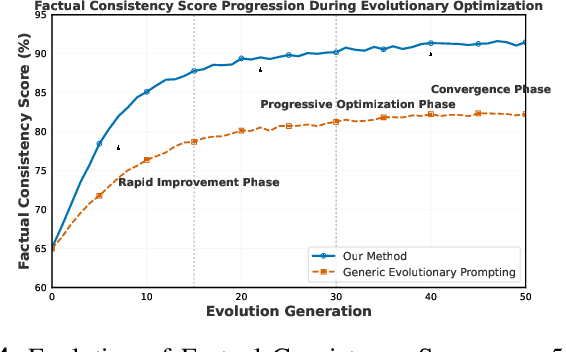
Abstract:Prompt engineering significantly influences the reliability and clinical utility of Large Language Models (LLMs) in medical applications. Current optimization approaches inadequately address domain-specific medical knowledge and safety requirements. This paper introduces EMPOWER, a novel evolutionary framework that enhances medical prompt quality through specialized representation learning, multi-dimensional evaluation, and structure-preserving algorithms. Our methodology incorporates: (1) a medical terminology attention mechanism, (2) a comprehensive assessment architecture evaluating clarity, specificity, clinical relevance, and factual accuracy, (3) a component-level evolutionary algorithm preserving clinical reasoning integrity, and (4) a semantic verification module ensuring adherence to medical knowledge. Evaluation across diagnostic, therapeutic, and educational tasks demonstrates significant improvements: 24.7% reduction in factually incorrect content, 19.6% enhancement in domain specificity, and 15.3% higher clinician preference in blinded evaluations. The framework addresses critical challenges in developing clinically appropriate prompts, facilitating more responsible integration of LLMs into healthcare settings.
DVP-MVS++: Synergize Depth-Normal-Edge and Harmonized Visibility Prior for Multi-View Stereo
Jun 16, 2025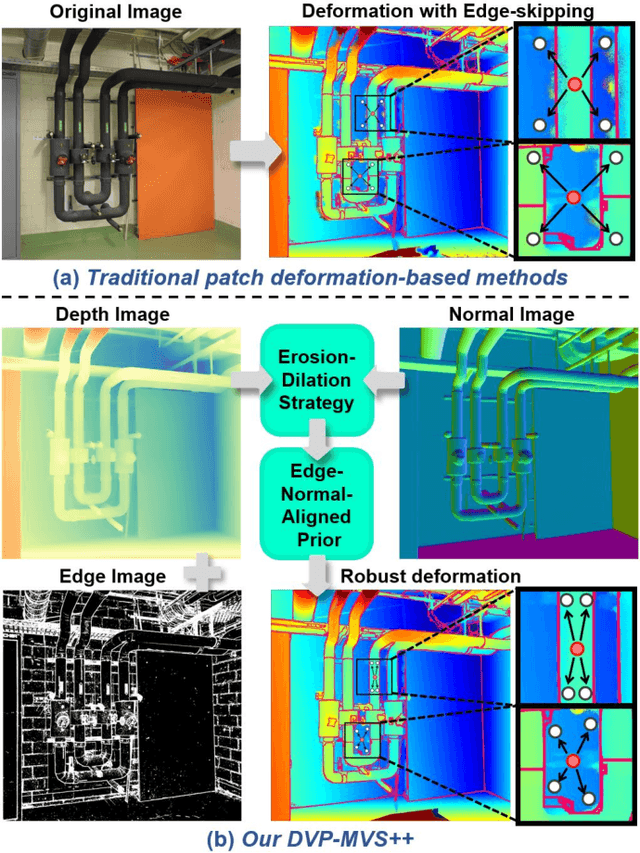
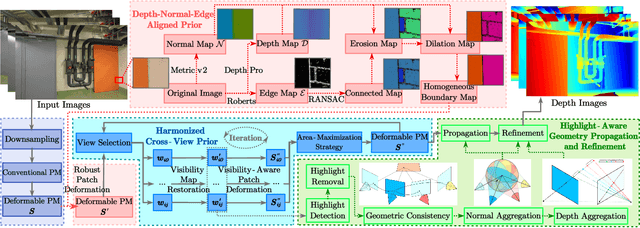
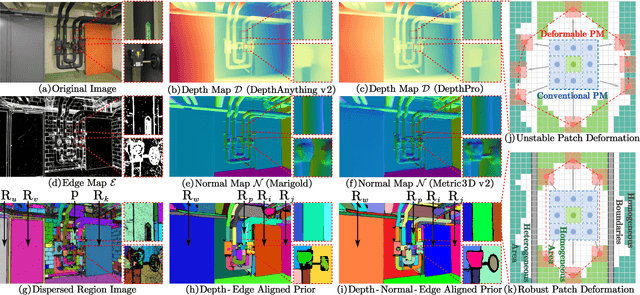
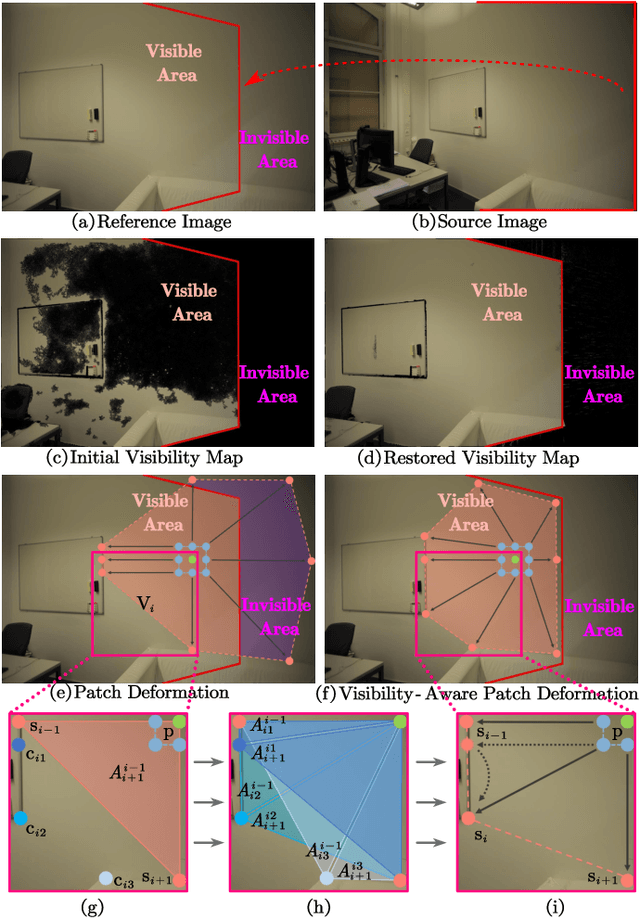
Abstract:Recently, patch deformation-based methods have demonstrated significant effectiveness in multi-view stereo due to their incorporation of deformable and expandable perception for reconstructing textureless areas. However, these methods generally focus on identifying reliable pixel correlations to mitigate matching ambiguity of patch deformation, while neglecting the deformation instability caused by edge-skipping and visibility occlusions, which may cause potential estimation deviations. To address these issues, we propose DVP-MVS++, an innovative approach that synergizes both depth-normal-edge aligned and harmonized cross-view priors for robust and visibility-aware patch deformation. Specifically, to avoid edge-skipping, we first apply DepthPro, Metric3Dv2 and Roberts operator to generate coarse depth maps, normal maps and edge maps, respectively. These maps are then aligned via an erosion-dilation strategy to produce fine-grained homogeneous boundaries for facilitating robust patch deformation. Moreover, we reformulate view selection weights as visibility maps, and then implement both an enhanced cross-view depth reprojection and an area-maximization strategy to help reliably restore visible areas and effectively balance deformed patch, thus acquiring harmonized cross-view priors for visibility-aware patch deformation. Additionally, we obtain geometry consistency by adopting both aggregated normals via view selection and projection depth differences via epipolar lines, and then employ SHIQ for highlight correction to enable geometry consistency with highlight-aware perception, thus improving reconstruction quality during propagation and refinement stage. Evaluation results on ETH3D, Tanks & Temples and Strecha datasets exhibit the state-of-the-art performance and robust generalization capability of our proposed method.
Light4GS: Lightweight Compact 4D Gaussian Splatting Generation via Context Model
Mar 18, 2025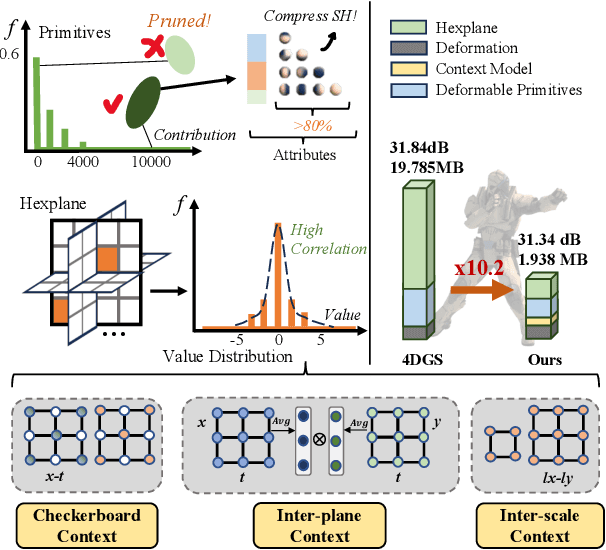



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as an efficient and high-fidelity paradigm for novel view synthesis. To adapt 3DGS for dynamic content, deformable 3DGS incorporates temporally deformable primitives with learnable latent embeddings to capture complex motions. Despite its impressive performance, the high-dimensional embeddings and vast number of primitives lead to substantial storage requirements. In this paper, we introduce a \textbf{Light}weight \textbf{4}D\textbf{GS} framework, called Light4GS, that employs significance pruning with a deep context model to provide a lightweight storage-efficient dynamic 3DGS representation. The proposed Light4GS is based on 4DGS that is a typical representation of deformable 3DGS. Specifically, our framework is built upon two core components: (1) a spatio-temporal significance pruning strategy that eliminates over 64\% of the deformable primitives, followed by an entropy-constrained spherical harmonics compression applied to the remainder; and (2) a deep context model that integrates intra- and inter-prediction with hyperprior into a coarse-to-fine context structure to enable efficient multiscale latent embedding compression. Our approach achieves over 120x compression and increases rendering FPS up to 20\% compared to the baseline 4DGS, and also superior to frame-wise state-of-the-art 3DGS compression methods, revealing the effectiveness of our Light4GS in terms of both intra- and inter-prediction methods without sacrificing rendering quality.
SED-MVS: Segmentation-Driven and Edge-Aligned Deformation Multi-View Stereo with Depth Restoration and Occlusion Constraint
Mar 17, 2025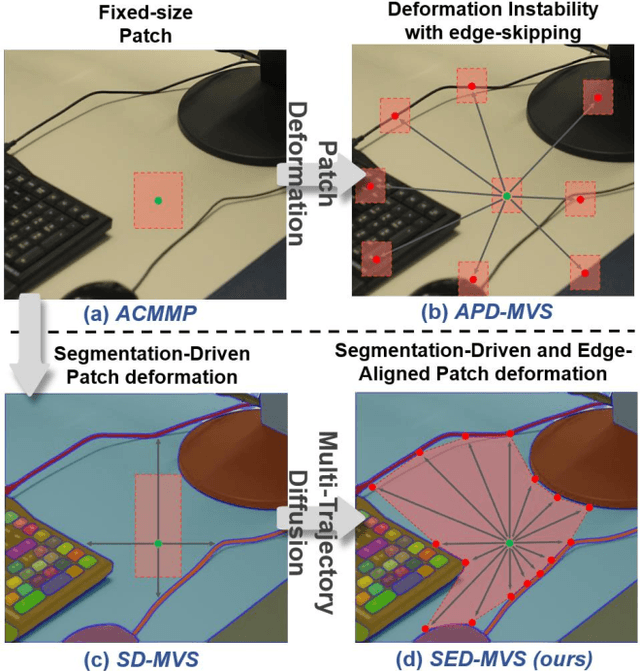
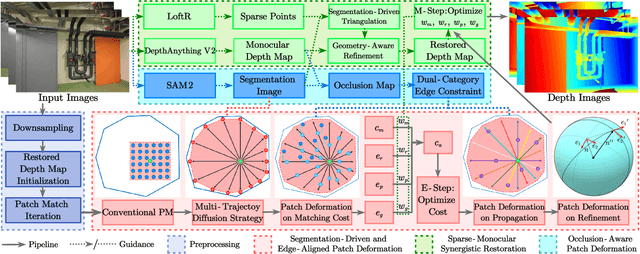
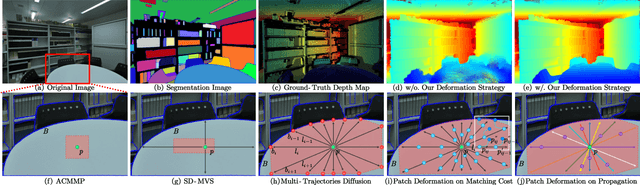
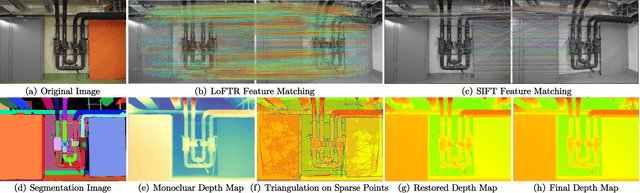
Abstract:Recently, patch-deformation methods have exhibited significant effectiveness in multi-view stereo owing to the deformable and expandable patches in reconstructing textureless areas. However, such methods primarily emphasize broadening the receptive field in textureless areas, while neglecting deformation instability caused by easily overlooked edge-skipping, potentially leading to matching distortions. To address this, we propose SED-MVS, which adopts panoptic segmentation and multi-trajectory diffusion strategy for segmentation-driven and edge-aligned patch deformation. Specifically, to prevent unanticipated edge-skipping, we first employ SAM2 for panoptic segmentation as depth-edge guidance to guide patch deformation, followed by multi-trajectory diffusion strategy to ensure patches are comprehensively aligned with depth edges. Moreover, to avoid potential inaccuracy of random initialization, we combine both sparse points from LoFTR and monocular depth map from DepthAnything V2 to restore reliable and realistic depth map for initialization and supervised guidance. Finally, we integrate segmentation image with monocular depth map to exploit inter-instance occlusion relationship, then further regard them as occlusion map to implement two distinct edge constraint, thereby facilitating occlusion-aware patch deformation. Extensive results on ETH3D, Tanks & Temples, BlendedMVS and Strecha datasets validate the state-of-the-art performance and robust generalization capability of our proposed method.
Adaptive Label Correction for Robust Medical Image Segmentation with Noisy Labels
Mar 15, 2025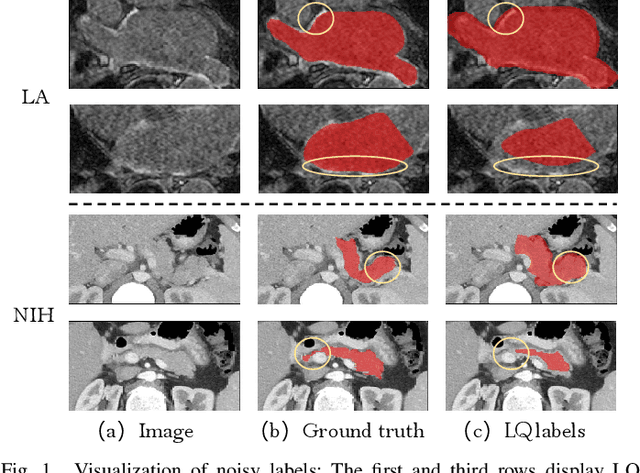
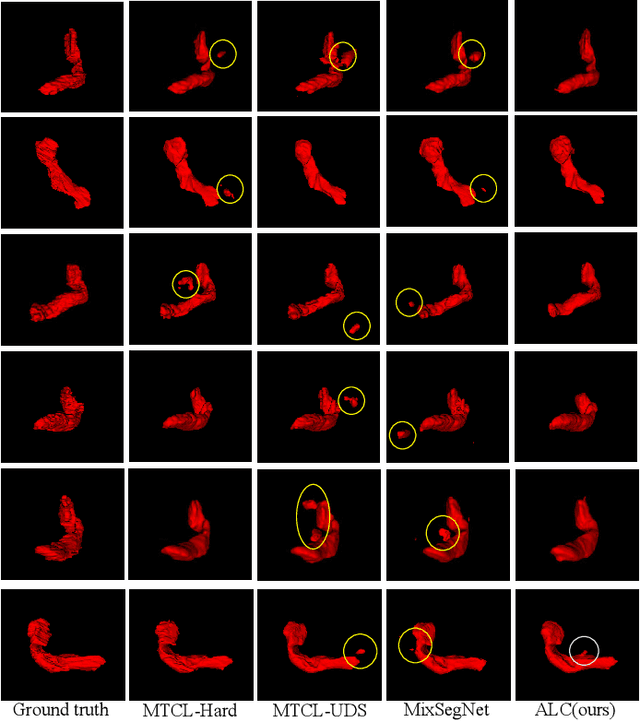
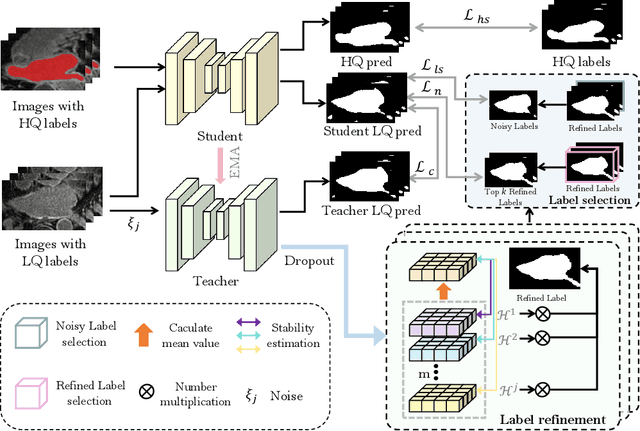
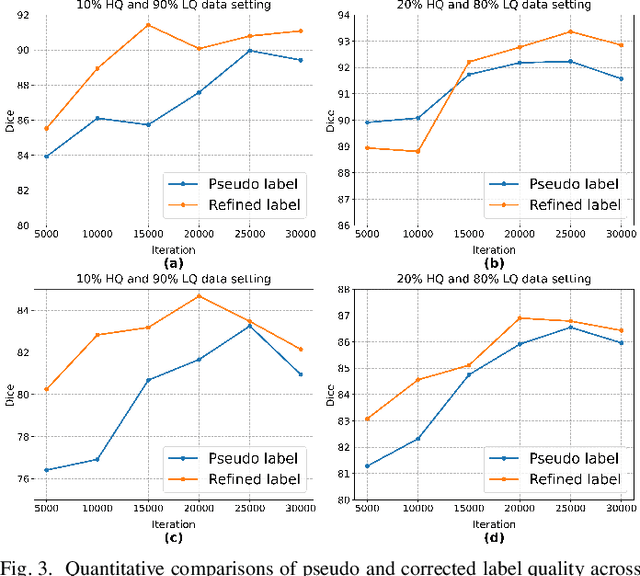

Abstract:Deep learning has shown remarkable success in medical image analysis, but its reliance on large volumes of high-quality labeled data limits its applicability. While noisy labeled data are easier to obtain, directly incorporating them into training can degrade model performance. To address this challenge, we propose a Mean Teacher-based Adaptive Label Correction (ALC) self-ensemble framework for robust medical image segmentation with noisy labels. The framework leverages the Mean Teacher architecture to ensure consistent learning under noise perturbations. It includes an adaptive label refinement mechanism that dynamically captures and weights differences across multiple disturbance versions to enhance the quality of noisy labels. Additionally, a sample-level uncertainty-based label selection algorithm is introduced to prioritize high-confidence samples for network updates, mitigating the impact of noisy annotations. Consistency learning is integrated to align the predictions of the student and teacher networks, further enhancing model robustness. Extensive experiments on two public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, showing significant improvements in segmentation performance. By fully exploiting the strengths of the Mean Teacher structure, the ALC framework effectively processes noisy labels, adapts to challenging scenarios, and achieves competitive results compared to state-of-the-art methods.
DynCIM: Dynamic Curriculum for Imbalanced Multimodal Learning
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Multimodal learning integrates complementary information from diverse modalities to enhance the decision-making process. However, the potential of multimodal collaboration remains under-exploited due to disparities in data quality and modality representation capabilities. To address this, we introduce DynCIM, a novel dynamic curriculum learning framework designed to quantify the inherent imbalances from both sample and modality perspectives. DynCIM employs a sample-level curriculum to dynamically assess each sample's difficulty according to prediction deviation, consistency, and stability, while a modality-level curriculum measures modality contributions from global and local. Furthermore, a gating-based dynamic fusion mechanism is introduced to adaptively adjust modality contributions, minimizing redundancy and optimizing fusion effectiveness. Extensive experiments on six multimodal benchmarking datasets, spanning both bimodal and trimodal scenarios, demonstrate that DynCIM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Our approach effectively mitigates modality and sample imbalances while enhancing adaptability and robustness in multimodal learning tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/Raymond-Qiancx/DynCIM.
Dual-Level Precision Edges Guided Multi-View Stereo with Accurate Planarization
Dec 29, 2024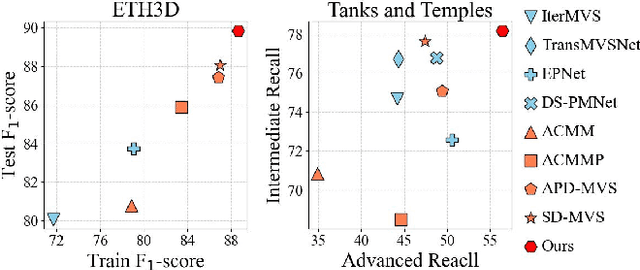
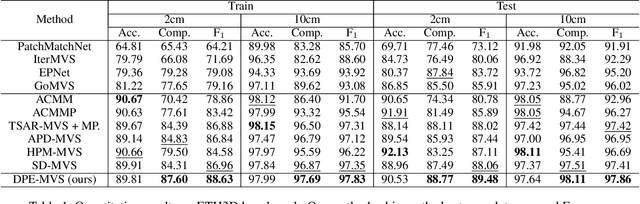
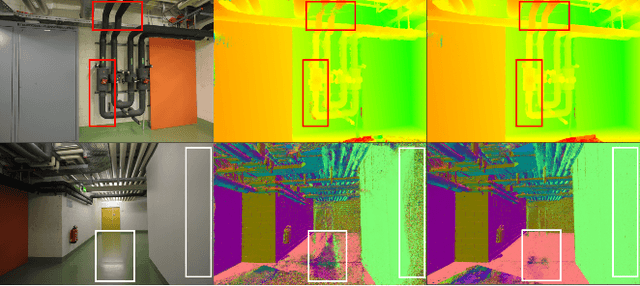
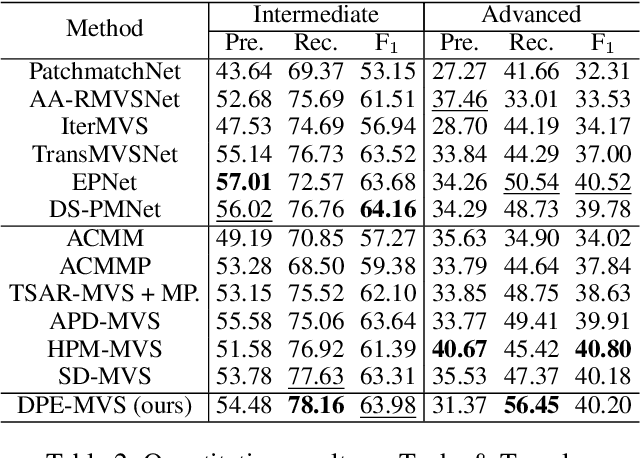
Abstract:The reconstruction of low-textured areas is a prominent research focus in multi-view stereo (MVS). In recent years, traditional MVS methods have performed exceptionally well in reconstructing low-textured areas by constructing plane models. However, these methods often encounter issues such as crossing object boundaries and limited perception ranges, which undermine the robustness of plane model construction. Building on previous work (APD-MVS), we propose the DPE-MVS method. By introducing dual-level precision edge information, including fine and coarse edges, we enhance the robustness of plane model construction, thereby improving reconstruction accuracy in low-textured areas. Furthermore, by leveraging edge information, we refine the sampling strategy in conventional PatchMatch MVS and propose an adaptive patch size adjustment approach to optimize matching cost calculation in both stochastic and low-textured areas. This additional use of edge information allows for more precise and robust matching. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ETH3D and Tanks & Temples benchmarks. Notably, our method outperforms all published methods on the ETH3D benchmark.
MapExpert: Online HD Map Construction with Simple and Efficient Sparse Map Element Expert
Dec 17, 2024
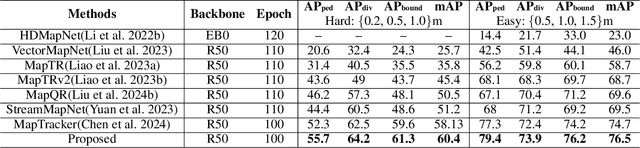

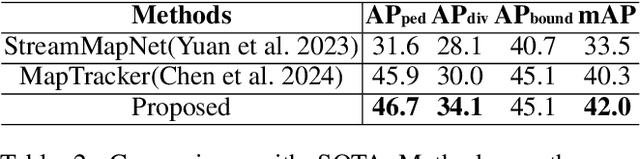
Abstract:Constructing online High-Definition (HD) maps is crucial for the static environment perception of autonomous driving systems (ADS). Existing solutions typically attempt to detect vectorized HD map elements with unified models; however, these methods often overlook the distinct characteristics of different non-cubic map elements, making accurate distinction challenging. To address these issues, we introduce an expert-based online HD map method, termed MapExpert. MapExpert utilizes sparse experts, distributed by our routers, to describe various non-cubic map elements accurately. Additionally, we propose an auxiliary balance loss function to distribute the load evenly across experts. Furthermore, we theoretically analyze the limitations of prevalent bird's-eye view (BEV) feature temporal fusion methods and introduce an efficient temporal fusion module called Learnable Weighted Moving Descentage. This module effectively integrates relevant historical information into the final BEV features. Combined with an enhanced slice head branch, the proposed MapExpert achieves state-of-the-art performance and maintains good efficiency on both nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets.
DVP-MVS: Synergize Depth-Edge and Visibility Prior for Multi-View Stereo
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Patch deformation-based methods have recently exhibited substantial effectiveness in multi-view stereo, due to the incorporation of deformable and expandable perception to reconstruct textureless areas. However, such approaches typically focus on exploring correlative reliable pixels to alleviate match ambiguity during patch deformation, but ignore the deformation instability caused by mistaken edge-skipping and visibility occlusion, leading to potential estimation deviation. To remedy the above issues, we propose DVP-MVS, which innovatively synergizes depth-edge aligned and cross-view prior for robust and visibility-aware patch deformation. Specifically, to avoid unexpected edge-skipping, we first utilize Depth Anything V2 followed by the Roberts operator to initialize coarse depth and edge maps respectively, both of which are further aligned through an erosion-dilation strategy to generate fine-grained homogeneous boundaries for guiding patch deformation. In addition, we reform view selection weights as visibility maps and restore visible areas by cross-view depth reprojection, then regard them as cross-view prior to facilitate visibility-aware patch deformation. Finally, we improve propagation and refinement with multi-view geometry consistency by introducing aggregated visible hemispherical normals based on view selection and local projection depth differences based on epipolar lines, respectively. Extensive evaluations on ETH3D and Tanks & Temples benchmarks demonstrate that our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance with excellent robustness and generalization.
MSP-MVS: Multi-granularity Segmentation Prior Guided Multi-View Stereo
Jul 27, 2024Abstract:Reconstructing textureless areas in MVS poses challenges due to the absence of reliable pixel correspondences within fixed patch. Although certain methods employ patch deformation to expand the receptive field, their patches mistakenly skip depth edges to calculate areas with depth discontinuity, thereby causing ambiguity. Consequently, we introduce Multi-granularity Segmentation Prior Multi-View Stereo (MSP-MVS). Specifically, we first propose multi-granularity segmentation prior by integrating multi-granularity depth edges to restrict patch deformation within homogeneous areas. Moreover, we present anchor equidistribution that bring deformed patches with more uniformly distributed anchors to ensure an adequate coverage of their own homogeneous areas. Furthermore, we introduce iterative local search optimization to represent larger patch with sparse representative candidates, significantly boosting the expressive capacity for each patch. The state-of-the-art results on ETH3D and Tanks & Temples benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and robust generalization ability of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge