Zhaoqi Wang
DVP-MVS++: Synergize Depth-Normal-Edge and Harmonized Visibility Prior for Multi-View Stereo
Jun 16, 2025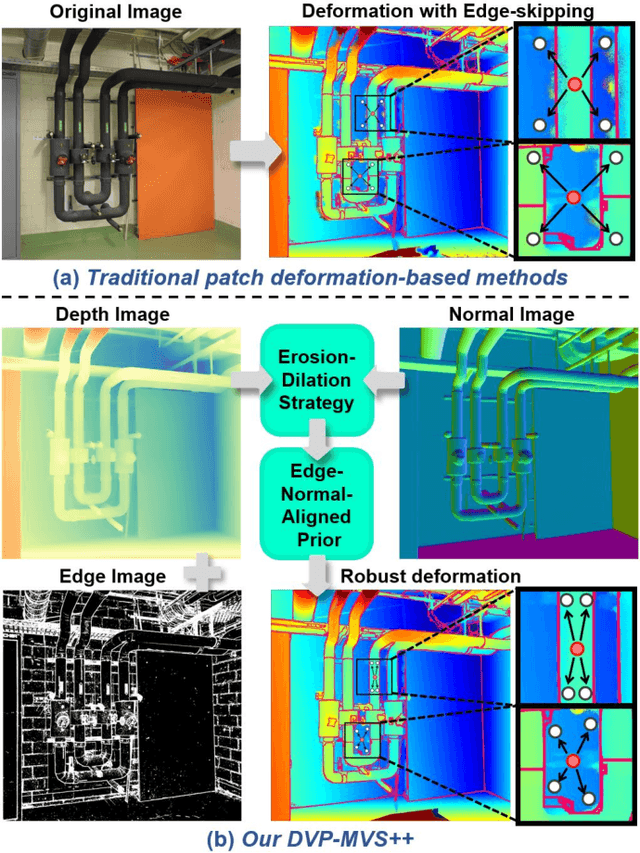
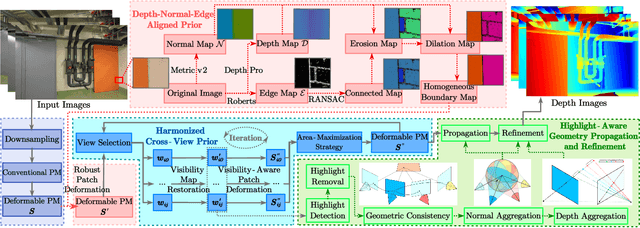
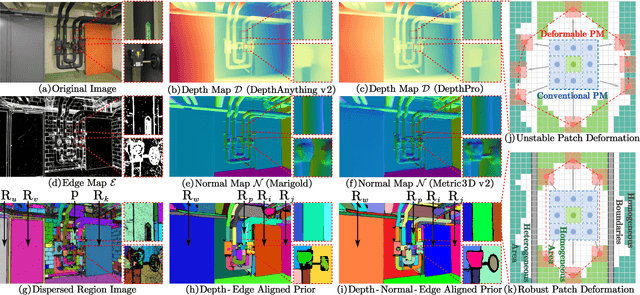
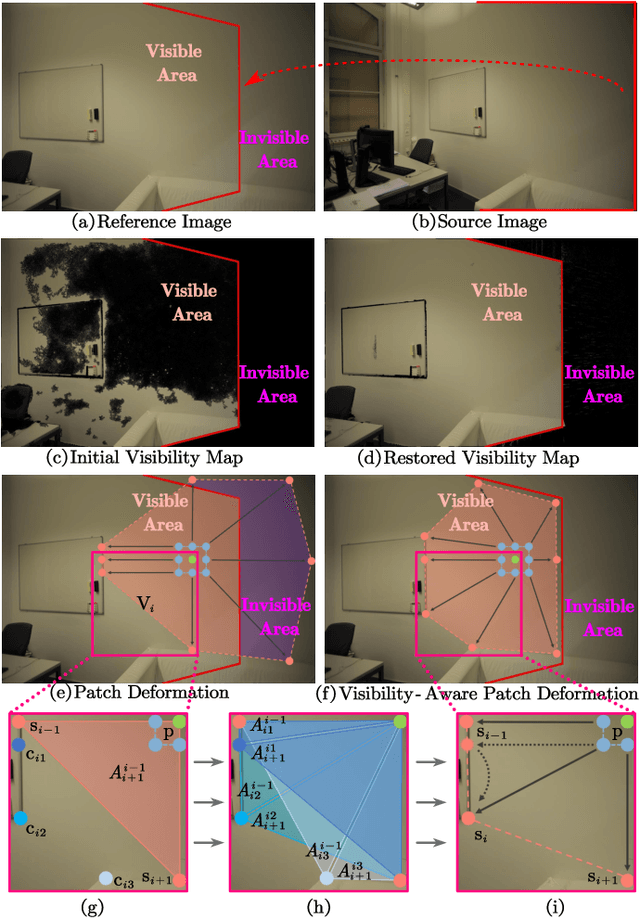
Abstract:Recently, patch deformation-based methods have demonstrated significant effectiveness in multi-view stereo due to their incorporation of deformable and expandable perception for reconstructing textureless areas. However, these methods generally focus on identifying reliable pixel correlations to mitigate matching ambiguity of patch deformation, while neglecting the deformation instability caused by edge-skipping and visibility occlusions, which may cause potential estimation deviations. To address these issues, we propose DVP-MVS++, an innovative approach that synergizes both depth-normal-edge aligned and harmonized cross-view priors for robust and visibility-aware patch deformation. Specifically, to avoid edge-skipping, we first apply DepthPro, Metric3Dv2 and Roberts operator to generate coarse depth maps, normal maps and edge maps, respectively. These maps are then aligned via an erosion-dilation strategy to produce fine-grained homogeneous boundaries for facilitating robust patch deformation. Moreover, we reformulate view selection weights as visibility maps, and then implement both an enhanced cross-view depth reprojection and an area-maximization strategy to help reliably restore visible areas and effectively balance deformed patch, thus acquiring harmonized cross-view priors for visibility-aware patch deformation. Additionally, we obtain geometry consistency by adopting both aggregated normals via view selection and projection depth differences via epipolar lines, and then employ SHIQ for highlight correction to enable geometry consistency with highlight-aware perception, thus improving reconstruction quality during propagation and refinement stage. Evaluation results on ETH3D, Tanks & Temples and Strecha datasets exhibit the state-of-the-art performance and robust generalization capability of our proposed method.
STDR: Spatio-Temporal Decoupling for Real-Time Dynamic Scene Rendering
May 28, 2025Abstract:Although dynamic scene reconstruction has long been a fundamental challenge in 3D vision, the recent emergence of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) offers a promising direction by enabling high-quality, real-time rendering through explicit Gaussian primitives. However, existing 3DGS-based methods for dynamic reconstruction often suffer from \textit{spatio-temporal incoherence} during initialization, where canonical Gaussians are constructed by aggregating observations from multiple frames without temporal distinction. This results in spatio-temporally entangled representations, making it difficult to model dynamic motion accurately. To overcome this limitation, we propose \textbf{STDR} (Spatio-Temporal Decoupling for Real-time rendering), a plug-and-play module that learns spatio-temporal probability distributions for each Gaussian. STDR introduces a spatio-temporal mask, a separated deformation field, and a consistency regularization to jointly disentangle spatial and temporal patterns. Extensive experiments demonstrate that incorporating our module into existing 3DGS-based dynamic scene reconstruction frameworks leads to notable improvements in both reconstruction quality and spatio-temporal consistency across synthetic and real-world benchmarks.
SED-MVS: Segmentation-Driven and Edge-Aligned Deformation Multi-View Stereo with Depth Restoration and Occlusion Constraint
Mar 17, 2025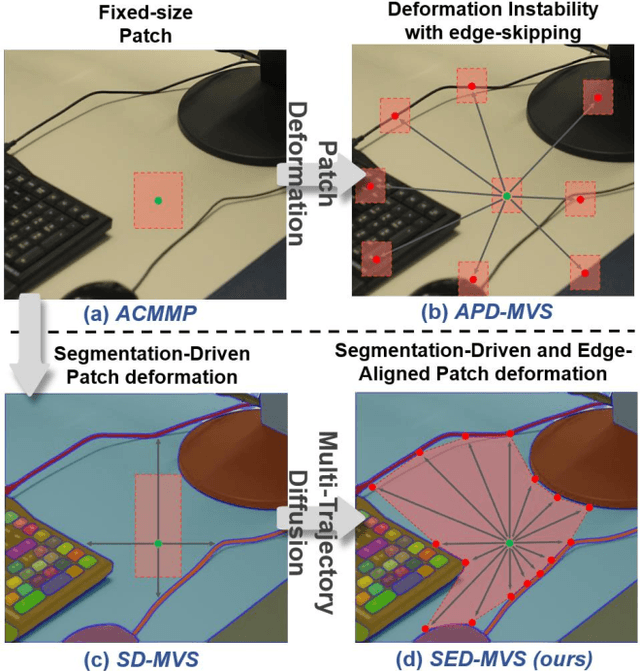
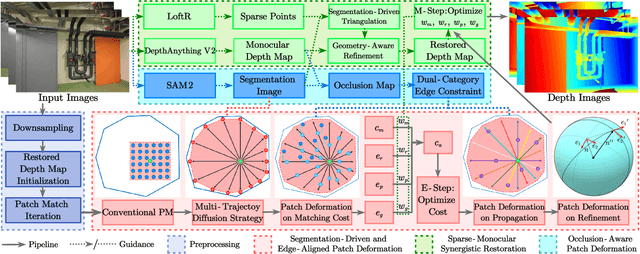
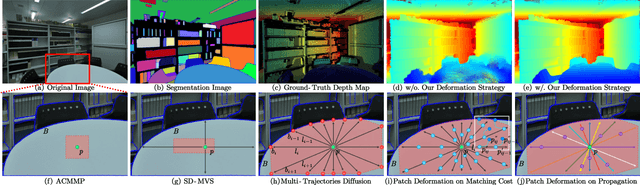
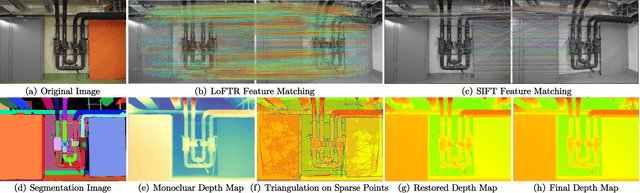
Abstract:Recently, patch-deformation methods have exhibited significant effectiveness in multi-view stereo owing to the deformable and expandable patches in reconstructing textureless areas. However, such methods primarily emphasize broadening the receptive field in textureless areas, while neglecting deformation instability caused by easily overlooked edge-skipping, potentially leading to matching distortions. To address this, we propose SED-MVS, which adopts panoptic segmentation and multi-trajectory diffusion strategy for segmentation-driven and edge-aligned patch deformation. Specifically, to prevent unanticipated edge-skipping, we first employ SAM2 for panoptic segmentation as depth-edge guidance to guide patch deformation, followed by multi-trajectory diffusion strategy to ensure patches are comprehensively aligned with depth edges. Moreover, to avoid potential inaccuracy of random initialization, we combine both sparse points from LoFTR and monocular depth map from DepthAnything V2 to restore reliable and realistic depth map for initialization and supervised guidance. Finally, we integrate segmentation image with monocular depth map to exploit inter-instance occlusion relationship, then further regard them as occlusion map to implement two distinct edge constraint, thereby facilitating occlusion-aware patch deformation. Extensive results on ETH3D, Tanks & Temples, BlendedMVS and Strecha datasets validate the state-of-the-art performance and robust generalization capability of our proposed method.
Dual-Level Precision Edges Guided Multi-View Stereo with Accurate Planarization
Dec 29, 2024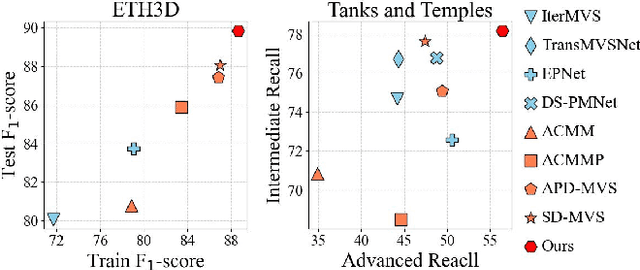
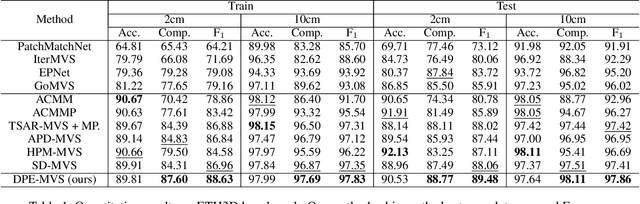
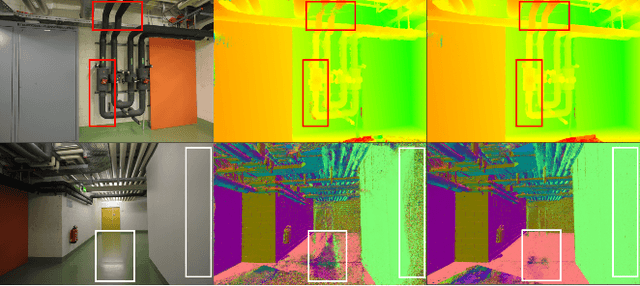
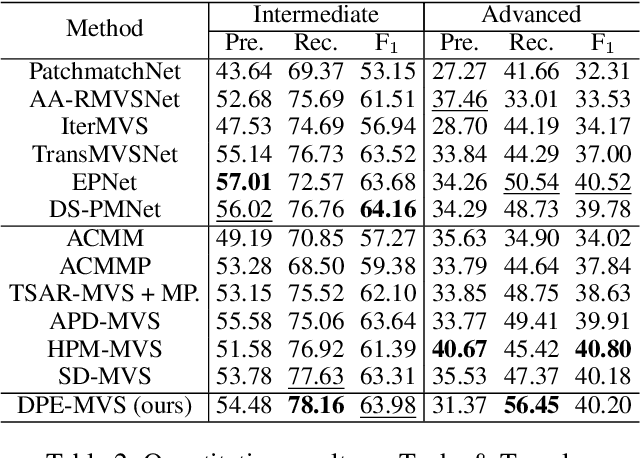
Abstract:The reconstruction of low-textured areas is a prominent research focus in multi-view stereo (MVS). In recent years, traditional MVS methods have performed exceptionally well in reconstructing low-textured areas by constructing plane models. However, these methods often encounter issues such as crossing object boundaries and limited perception ranges, which undermine the robustness of plane model construction. Building on previous work (APD-MVS), we propose the DPE-MVS method. By introducing dual-level precision edge information, including fine and coarse edges, we enhance the robustness of plane model construction, thereby improving reconstruction accuracy in low-textured areas. Furthermore, by leveraging edge information, we refine the sampling strategy in conventional PatchMatch MVS and propose an adaptive patch size adjustment approach to optimize matching cost calculation in both stochastic and low-textured areas. This additional use of edge information allows for more precise and robust matching. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ETH3D and Tanks & Temples benchmarks. Notably, our method outperforms all published methods on the ETH3D benchmark.
DVP-MVS: Synergize Depth-Edge and Visibility Prior for Multi-View Stereo
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Patch deformation-based methods have recently exhibited substantial effectiveness in multi-view stereo, due to the incorporation of deformable and expandable perception to reconstruct textureless areas. However, such approaches typically focus on exploring correlative reliable pixels to alleviate match ambiguity during patch deformation, but ignore the deformation instability caused by mistaken edge-skipping and visibility occlusion, leading to potential estimation deviation. To remedy the above issues, we propose DVP-MVS, which innovatively synergizes depth-edge aligned and cross-view prior for robust and visibility-aware patch deformation. Specifically, to avoid unexpected edge-skipping, we first utilize Depth Anything V2 followed by the Roberts operator to initialize coarse depth and edge maps respectively, both of which are further aligned through an erosion-dilation strategy to generate fine-grained homogeneous boundaries for guiding patch deformation. In addition, we reform view selection weights as visibility maps and restore visible areas by cross-view depth reprojection, then regard them as cross-view prior to facilitate visibility-aware patch deformation. Finally, we improve propagation and refinement with multi-view geometry consistency by introducing aggregated visible hemispherical normals based on view selection and local projection depth differences based on epipolar lines, respectively. Extensive evaluations on ETH3D and Tanks & Temples benchmarks demonstrate that our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance with excellent robustness and generalization.
GradiSeg: Gradient-Guided Gaussian Segmentation with Enhanced 3D Boundary Precision
Nov 30, 2024Abstract:While 3D Gaussian Splatting enables high-quality real-time rendering, existing Gaussian-based frameworks for 3D semantic segmentation still face significant challenges in boundary recognition accuracy. To address this, we propose a novel 3DGS-based framework named GradiSeg, incorporating Identity Encoding to construct a deeper semantic understanding of scenes. Our approach introduces two key modules: Identity Gradient Guided Densification (IGD) and Local Adaptive K-Nearest Neighbors (LA-KNN). The IGD module supervises gradients of Identity Encoding to refine Gaussian distributions along object boundaries, aligning them closely with boundary contours. Meanwhile, the LA-KNN module employs position gradients to adaptively establish locality-aware propagation of Identity Encodings, preventing irregular Gaussian spreads near boundaries. We validate the effectiveness of our method through comprehensive experiments. Results show that GradiSeg effectively addresses boundary-related issues, significantly improving segmentation accuracy without compromising scene reconstruction quality. Furthermore, our method's robust segmentation capability and decoupled Identity Encoding representation make it highly suitable for various downstream scene editing tasks, including 3D object removal, swapping and so on.
MSP-MVS: Multi-granularity Segmentation Prior Guided Multi-View Stereo
Jul 27, 2024Abstract:Reconstructing textureless areas in MVS poses challenges due to the absence of reliable pixel correspondences within fixed patch. Although certain methods employ patch deformation to expand the receptive field, their patches mistakenly skip depth edges to calculate areas with depth discontinuity, thereby causing ambiguity. Consequently, we introduce Multi-granularity Segmentation Prior Multi-View Stereo (MSP-MVS). Specifically, we first propose multi-granularity segmentation prior by integrating multi-granularity depth edges to restrict patch deformation within homogeneous areas. Moreover, we present anchor equidistribution that bring deformed patches with more uniformly distributed anchors to ensure an adequate coverage of their own homogeneous areas. Furthermore, we introduce iterative local search optimization to represent larger patch with sparse representative candidates, significantly boosting the expressive capacity for each patch. The state-of-the-art results on ETH3D and Tanks & Temples benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and robust generalization ability of our proposed method.
Deep Learning-based Anomaly Detection and Log Analysis for Computer Networks
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:Computer network anomaly detection and log analysis, as an important topic in the field of network security, has been a key task to ensure network security and system reliability. First, existing network anomaly detection and log analysis methods are often challenged by high-dimensional data and complex network topologies, resulting in unstable performance and high false-positive rates. In addition, traditional methods are usually difficult to handle time-series data, which is crucial for anomaly detection and log analysis. Therefore, we need a more efficient and accurate method to cope with these problems. To compensate for the shortcomings of current methods, we propose an innovative fusion model that integrates Isolation Forest, GAN (Generative Adversarial Network), and Transformer with each other, and each of them plays a unique role. Isolation Forest is used to quickly identify anomalous data points, and GAN is used to generate synthetic data with the real data distribution characteristics to augment the training dataset, while the Transformer is used for modeling and context extraction on time series data. The synergy of these three components makes our model more accurate and robust in anomaly detection and log analysis tasks. We validate the effectiveness of this fusion model in an extensive experimental evaluation. Experimental results show that our model significantly improves the accuracy of anomaly detection while reducing the false alarm rate, which helps to detect potential network problems in advance. The model also performs well in the log analysis task and is able to quickly identify anomalous behaviors, which helps to improve the stability of the system. The significance of this study is that it introduces advanced deep learning techniques, which work anomaly detection and log analysis.
Image anomaly detection and prediction scheme based on SSA optimized ResNet50-BiGRU model
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Image anomaly detection is a popular research direction, with many methods emerging in recent years due to rapid advancements in computing. The use of artificial intelligence for image anomaly detection has been widely studied. By analyzing images of athlete posture and movement, it is possible to predict injury status and suggest necessary adjustments. Most existing methods rely on convolutional networks to extract information from irrelevant pixel data, limiting model accuracy. This paper introduces a network combining Residual Network (ResNet) and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (BiGRU), which can predict potential injury types and provide early warnings by analyzing changes in muscle and bone poses from video images. To address the high complexity of this network, the Sparrow search algorithm was used for optimization. Experiments conducted on four datasets demonstrated that our model has the smallest error in image anomaly detection compared to other models, showing strong adaptability. This provides a new approach for anomaly detection and predictive analysis in images, contributing to the sustainable development of human health and performance.
SD-MVS: Segmentation-Driven Deformation Multi-View Stereo with Spherical Refinement and EM optimization
Jan 12, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Segmentation-Driven Deformation Multi-View Stereo (SD-MVS), a method that can effectively tackle challenges in 3D reconstruction of textureless areas. We are the first to adopt the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to distinguish semantic instances in scenes and further leverage these constraints for pixelwise patch deformation on both matching cost and propagation. Concurrently, we propose a unique refinement strategy that combines spherical coordinates and gradient descent on normals and pixelwise search interval on depths, significantly improving the completeness of reconstructed 3D model. Furthermore, we adopt the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm to alternately optimize the aggregate matching cost and hyperparameters, effectively mitigating the problem of parameters being excessively dependent on empirical tuning. Evaluations on the ETH3D high-resolution multi-view stereo benchmark and the Tanks and Temples dataset demonstrate that our method can achieve state-of-the-art results with less time consumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge