Dapeng Zhang
VLA-R1: Enhancing Reasoning in Vision-Language-Action Models
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models aim to unify perception, language understanding, and action generation, offering strong cross-task and cross-scene generalization with broad impact on embodied AI. However, current VLA models often lack explicit step-by-step reasoning, instead emitting final actions without considering affordance constraints or geometric relations. Their post-training pipelines also rarely reinforce reasoning quality, relying primarily on supervised fine-tuning with weak reward design. To address these challenges, we present VLA-R1, a reasoning-enhanced VLA that integrates Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to systematically optimize both reasoning and execution. Specifically, we design an RLVR-based post-training strategy with verifiable rewards for region alignment, trajectory consistency, and output formatting, thereby strengthening reasoning robustness and execution accuracy. Moreover, we develop VLA-CoT-13K, a high-quality dataset that provides chain-of-thought supervision explicitly aligned with affordance and trajectory annotations. Furthermore, extensive evaluations on in-domain, out-of-domain, simulation, and real-robot platforms demonstrate that VLA-R1 achieves superior generalization and real-world performance compared to prior VLA methods. We plan to release the model, code, and dataset following the publication of this work. Code: https://github.com/GigaAI-research/VLA-R1. Website: https://gigaai-research.github.io/VLA-R1.
EMPOWER: Evolutionary Medical Prompt Optimization With Reinforcement Learning
Aug 25, 2025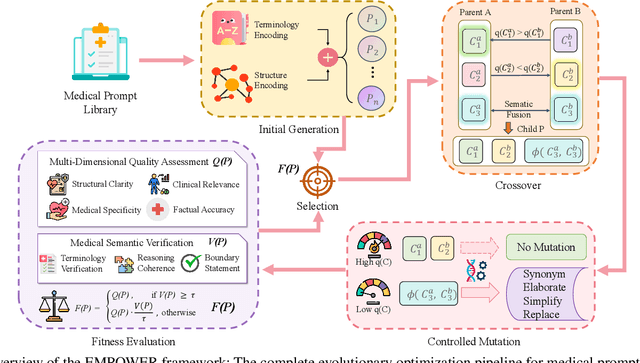
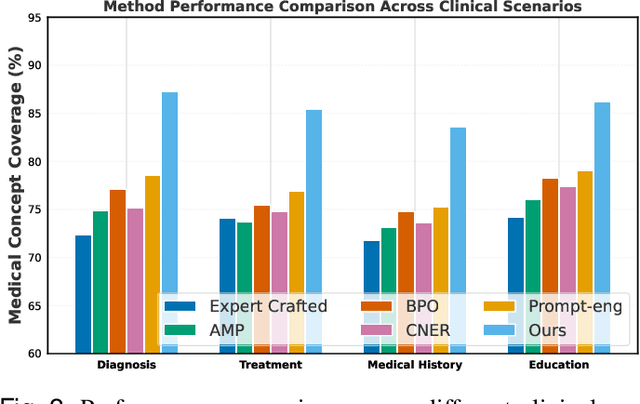
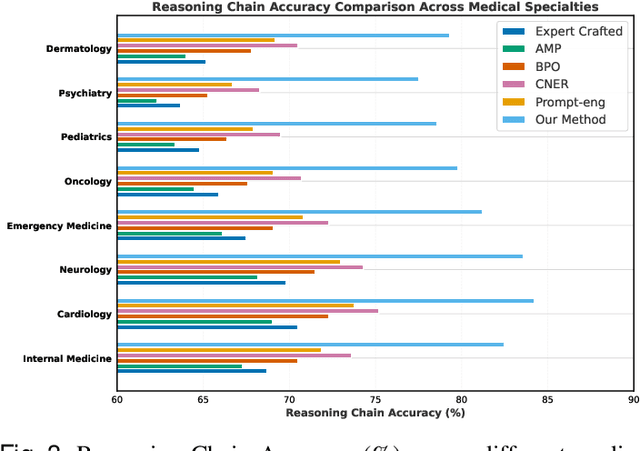
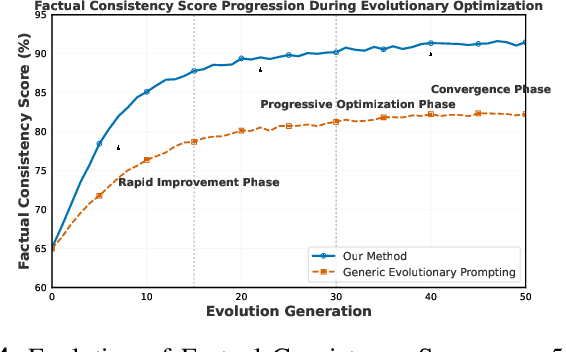
Abstract:Prompt engineering significantly influences the reliability and clinical utility of Large Language Models (LLMs) in medical applications. Current optimization approaches inadequately address domain-specific medical knowledge and safety requirements. This paper introduces EMPOWER, a novel evolutionary framework that enhances medical prompt quality through specialized representation learning, multi-dimensional evaluation, and structure-preserving algorithms. Our methodology incorporates: (1) a medical terminology attention mechanism, (2) a comprehensive assessment architecture evaluating clarity, specificity, clinical relevance, and factual accuracy, (3) a component-level evolutionary algorithm preserving clinical reasoning integrity, and (4) a semantic verification module ensuring adherence to medical knowledge. Evaluation across diagnostic, therapeutic, and educational tasks demonstrates significant improvements: 24.7% reduction in factually incorrect content, 19.6% enhancement in domain specificity, and 15.3% higher clinician preference in blinded evaluations. The framework addresses critical challenges in developing clinically appropriate prompts, facilitating more responsible integration of LLMs into healthcare settings.
Low-Cost Test-Time Adaptation for Robust Video Editing
Jul 29, 2025



Abstract:Video editing is a critical component of content creation that transforms raw footage into coherent works aligned with specific visual and narrative objectives. Existing approaches face two major challenges: temporal inconsistencies due to failure in capturing complex motion patterns, and overfitting to simple prompts arising from limitations in UNet backbone architectures. While learning-based methods can enhance editing quality, they typically demand substantial computational resources and are constrained by the scarcity of high-quality annotated data. In this paper, we present Vid-TTA, a lightweight test-time adaptation framework that personalizes optimization for each test video during inference through self-supervised auxiliary tasks. Our approach incorporates a motion-aware frame reconstruction mechanism that identifies and preserves crucial movement regions, alongside a prompt perturbation and reconstruction strategy that strengthens model robustness to diverse textual descriptions. These innovations are orchestrated by a meta-learning driven dynamic loss balancing mechanism that adaptively adjusts the optimization process based on video characteristics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Vid-TTA significantly improves video temporal consistency and mitigates prompt overfitting while maintaining low computational overhead, offering a plug-and-play performance boost for existing video editing models.
DVP-MVS++: Synergize Depth-Normal-Edge and Harmonized Visibility Prior for Multi-View Stereo
Jun 16, 2025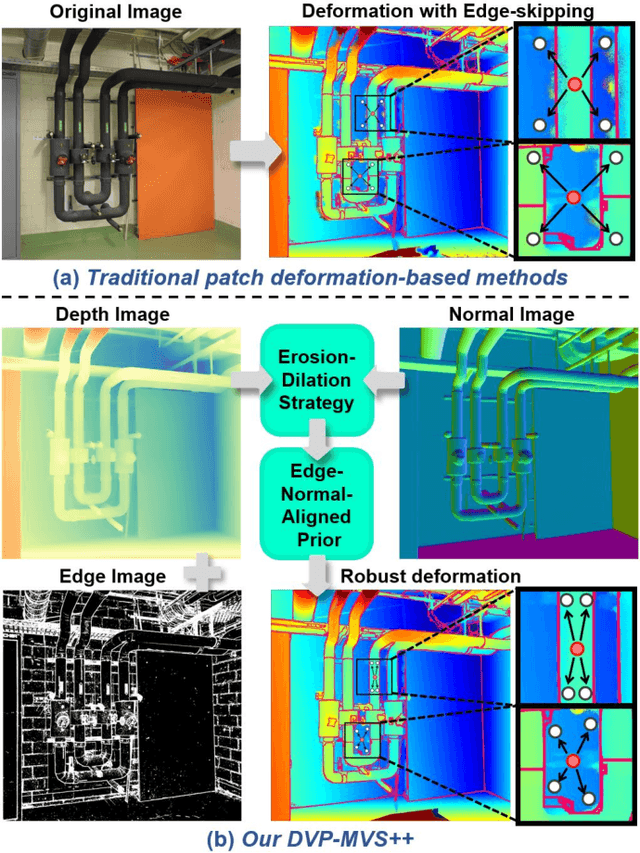
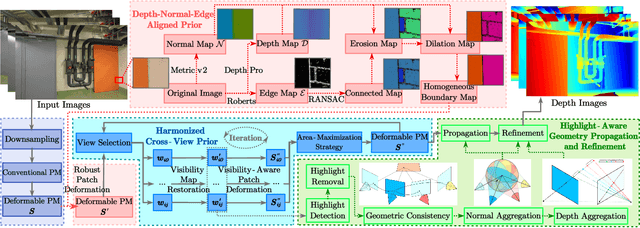
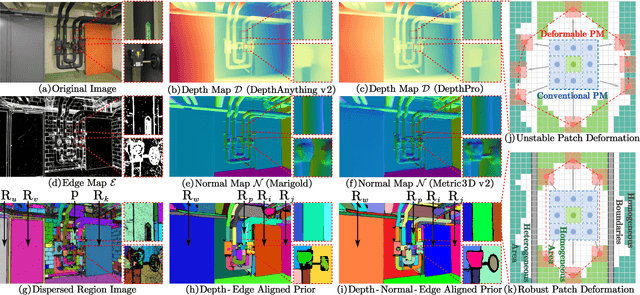
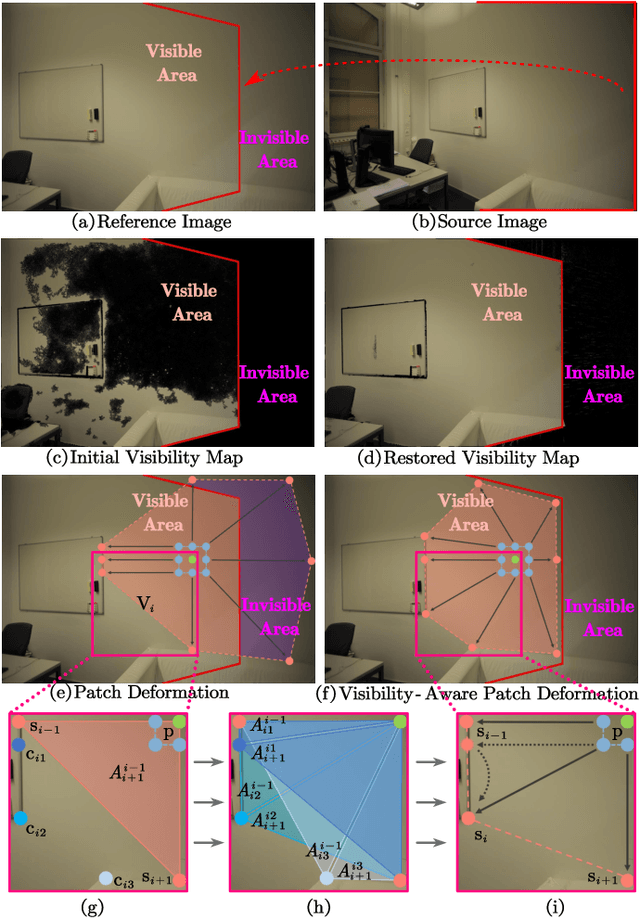
Abstract:Recently, patch deformation-based methods have demonstrated significant effectiveness in multi-view stereo due to their incorporation of deformable and expandable perception for reconstructing textureless areas. However, these methods generally focus on identifying reliable pixel correlations to mitigate matching ambiguity of patch deformation, while neglecting the deformation instability caused by edge-skipping and visibility occlusions, which may cause potential estimation deviations. To address these issues, we propose DVP-MVS++, an innovative approach that synergizes both depth-normal-edge aligned and harmonized cross-view priors for robust and visibility-aware patch deformation. Specifically, to avoid edge-skipping, we first apply DepthPro, Metric3Dv2 and Roberts operator to generate coarse depth maps, normal maps and edge maps, respectively. These maps are then aligned via an erosion-dilation strategy to produce fine-grained homogeneous boundaries for facilitating robust patch deformation. Moreover, we reformulate view selection weights as visibility maps, and then implement both an enhanced cross-view depth reprojection and an area-maximization strategy to help reliably restore visible areas and effectively balance deformed patch, thus acquiring harmonized cross-view priors for visibility-aware patch deformation. Additionally, we obtain geometry consistency by adopting both aggregated normals via view selection and projection depth differences via epipolar lines, and then employ SHIQ for highlight correction to enable geometry consistency with highlight-aware perception, thus improving reconstruction quality during propagation and refinement stage. Evaluation results on ETH3D, Tanks & Temples and Strecha datasets exhibit the state-of-the-art performance and robust generalization capability of our proposed method.
SED-MVS: Segmentation-Driven and Edge-Aligned Deformation Multi-View Stereo with Depth Restoration and Occlusion Constraint
Mar 17, 2025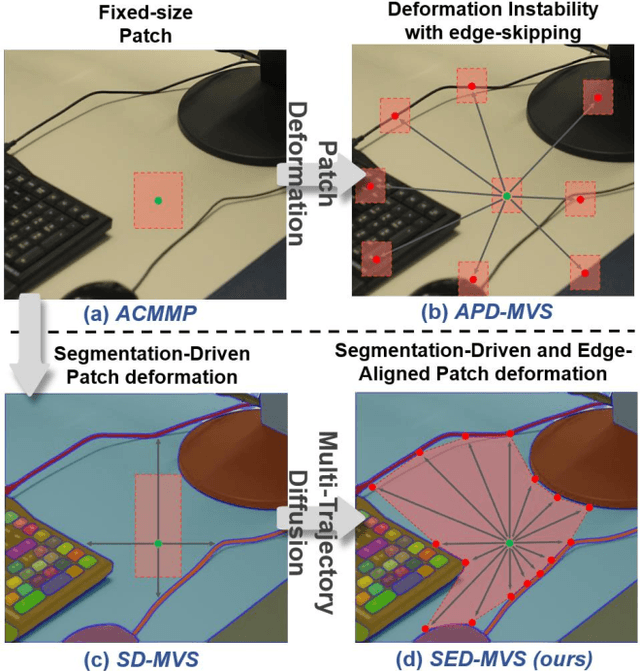
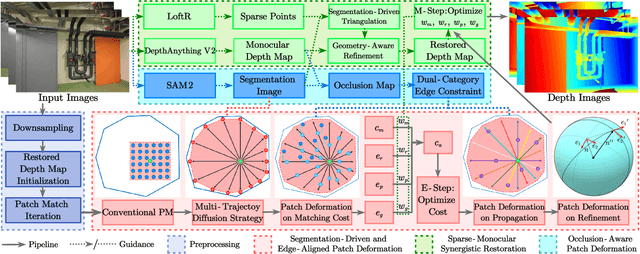
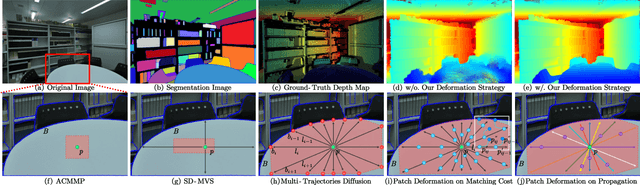
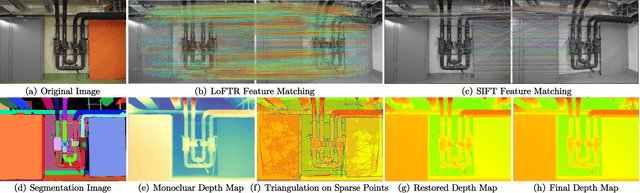
Abstract:Recently, patch-deformation methods have exhibited significant effectiveness in multi-view stereo owing to the deformable and expandable patches in reconstructing textureless areas. However, such methods primarily emphasize broadening the receptive field in textureless areas, while neglecting deformation instability caused by easily overlooked edge-skipping, potentially leading to matching distortions. To address this, we propose SED-MVS, which adopts panoptic segmentation and multi-trajectory diffusion strategy for segmentation-driven and edge-aligned patch deformation. Specifically, to prevent unanticipated edge-skipping, we first employ SAM2 for panoptic segmentation as depth-edge guidance to guide patch deformation, followed by multi-trajectory diffusion strategy to ensure patches are comprehensively aligned with depth edges. Moreover, to avoid potential inaccuracy of random initialization, we combine both sparse points from LoFTR and monocular depth map from DepthAnything V2 to restore reliable and realistic depth map for initialization and supervised guidance. Finally, we integrate segmentation image with monocular depth map to exploit inter-instance occlusion relationship, then further regard them as occlusion map to implement two distinct edge constraint, thereby facilitating occlusion-aware patch deformation. Extensive results on ETH3D, Tanks & Temples, BlendedMVS and Strecha datasets validate the state-of-the-art performance and robust generalization capability of our proposed method.
MapExpert: Online HD Map Construction with Simple and Efficient Sparse Map Element Expert
Dec 17, 2024
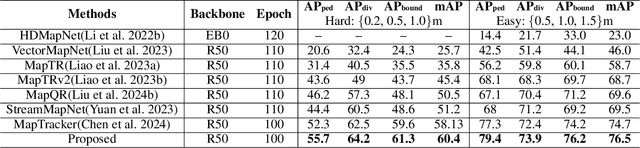

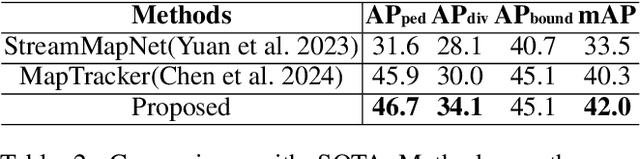
Abstract:Constructing online High-Definition (HD) maps is crucial for the static environment perception of autonomous driving systems (ADS). Existing solutions typically attempt to detect vectorized HD map elements with unified models; however, these methods often overlook the distinct characteristics of different non-cubic map elements, making accurate distinction challenging. To address these issues, we introduce an expert-based online HD map method, termed MapExpert. MapExpert utilizes sparse experts, distributed by our routers, to describe various non-cubic map elements accurately. Additionally, we propose an auxiliary balance loss function to distribute the load evenly across experts. Furthermore, we theoretically analyze the limitations of prevalent bird's-eye view (BEV) feature temporal fusion methods and introduce an efficient temporal fusion module called Learnable Weighted Moving Descentage. This module effectively integrates relevant historical information into the final BEV features. Combined with an enhanced slice head branch, the proposed MapExpert achieves state-of-the-art performance and maintains good efficiency on both nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets.
EFSA: Towards Event-Level Financial Sentiment Analysis
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we extend financial sentiment analysis~(FSA) to event-level since events usually serve as the subject of the sentiment in financial text. Though extracting events from the financial text may be conducive to accurate sentiment predictions, it has specialized challenges due to the lengthy and discontinuity of events in a financial text. To this end, we reconceptualize the event extraction as a classification task by designing a categorization comprising coarse-grained and fine-grained event categories. Under this setting, we formulate the \textbf{E}vent-Level \textbf{F}inancial \textbf{S}entiment \textbf{A}nalysis~(\textbf{EFSA} for short) task that outputs quintuples consisting of (company, industry, coarse-grained event, fine-grained event, sentiment) from financial text. A large-scale Chinese dataset containing $12,160$ news articles and $13,725$ quintuples is publicized as a brand new testbed for our task. A four-hop Chain-of-Thought LLM-based approach is devised for this task. Systematically investigations are conducted on our dataset, and the empirical results demonstrate the benchmarking scores of existing methods and our proposed method can reach the current state-of-the-art. Our dataset and framework implementation are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/EFSA-645E
Predicting Hourly Demand in Station-free Bike-sharing Systems with Video-level Data
Sep 23, 2020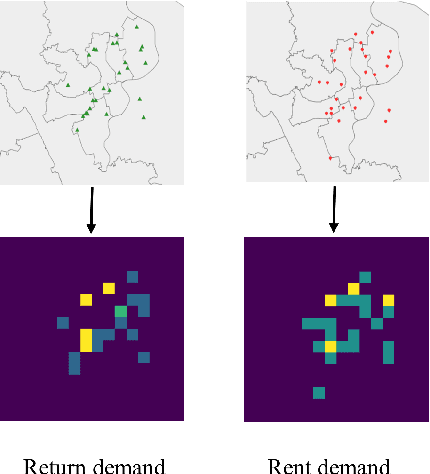
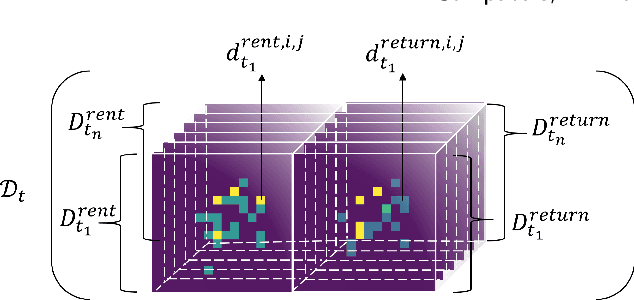
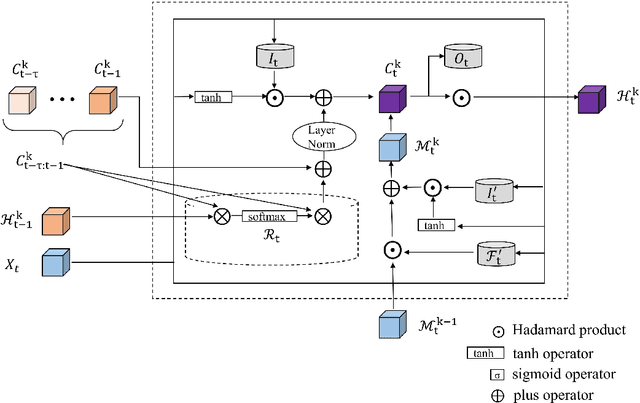
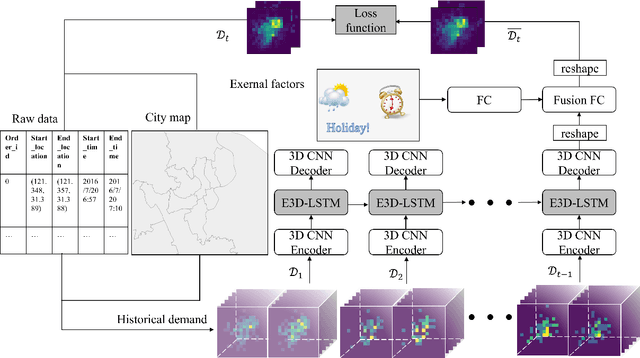
Abstract:Temporal and spatial features are both important for predicting the demands in the bike-sharing systems. Many relevant experiments in the literature support this. Meanwhile, it is observed that the data structure of spatial features with vector form is weaker in space than the videos, which have natural spatial structure. Therefore, to obtain more spatial features, this study introduces city map to generate GPS demand videos while employing a novel algorithm : eidetic 3D convolutional long short-term memory network named E3D-LSTM to process the video-level data in bike-sharing system. The spatio-temporal correlations and feature importance are experimented and visualized to validate the significance of spatial and temporal features. Despite the deep learning model is powerful in non-linear fitting ability, statistic model has better interpretation. This study adopts ensemble learning, which is a popular policy, to improve the performance and decrease variance. In this paper, we propose a novel model stacked by deep learning and statistical models, named the fusion multi-channel eidetic 3D convolutional long short-term memory network(FM-E3DCL-Net), to better process temporal and spatial features on the dataset about 100,000 transactions within one month in Shanghai of Mobike company. Furthermore, other factors like weather, holiday and time intervals are proved useful in addition to historical demand, since they decrease the root mean squared error (RMSE) by 29.4%. On this basis, the ensemble learning further decreases RMSE by 6.6%.
Learning Spatiotemporal Features of Ride-sourcing Services with Fusion Convolutional Network
Apr 15, 2019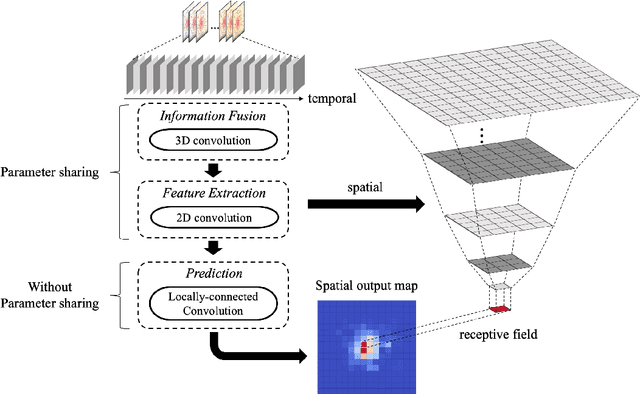
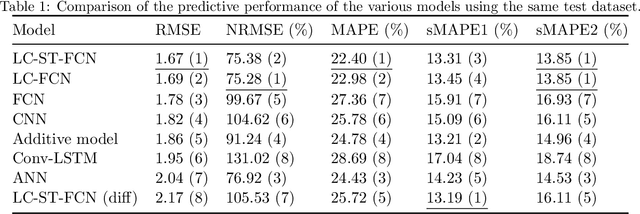
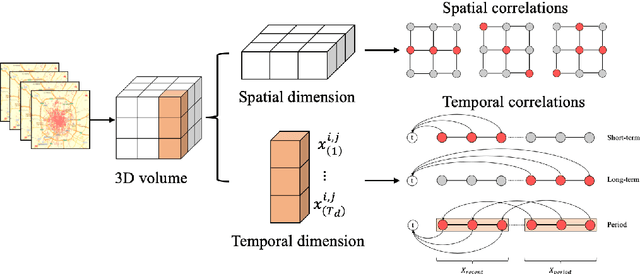
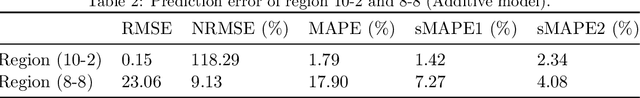
Abstract:In order to collectively forecast the demand of ride-sourcing services in all regions of a city, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been applied with commendable results. However, local statistical differences throughout the geographical layout of the city make the spatial stationarity assumption of the convolution invalid, which limits the performance of CNNs on demand forecasting task. Hence, we propose a novel deep learning framework called LC-ST-FCN (locally-connected spatiotemporal fully-convolutional neural network) that consists of a stack of 3D convolutional layers, 2D (standard) convolutional layers, and locally connected convolutional layers. This fully convolutional architecture maintains the spatial coordinates of the input and no spatial information is lost between layers. Features are fused across layers to define a tunable nonlinear local-to-global-to-local representation, where both global and local statistics can be learned to improve predictive performance. Furthermore, as the local statistics vary from region to region, the arithmetic-mean-based metrics frequently used in spatial stationarity situations cannot effectively evaluate the models. We propose a weighted-arithmetic approach to deal with this situation. In the experiments, a real dataset from a ride-sourcing service platform (DiDiChuxing) is used, which demonstrates the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed model and evaluation method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge