Xianghua Gan
ProSTformer: Pre-trained Progressive Space-Time Self-attention Model for Traffic Flow Forecasting
Nov 03, 2021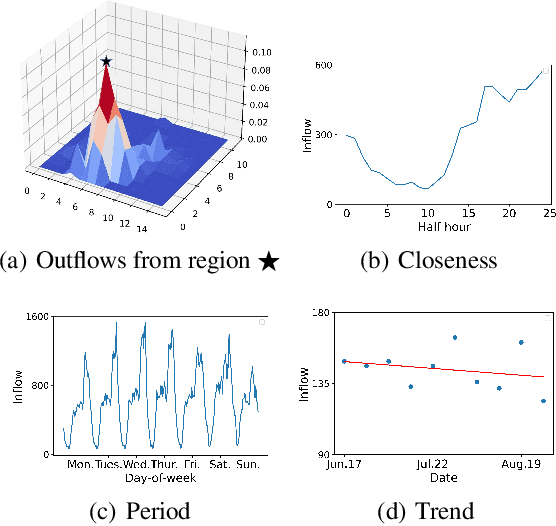
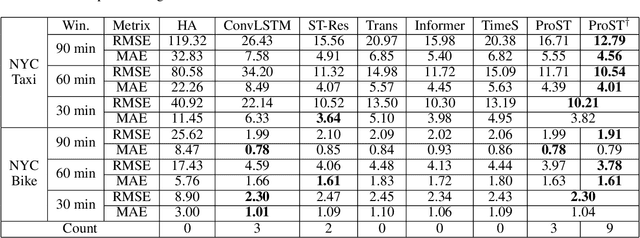
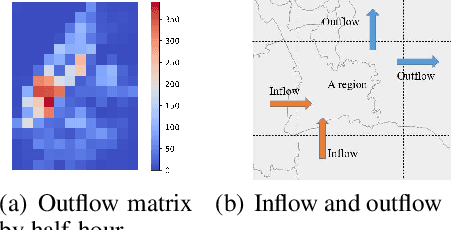
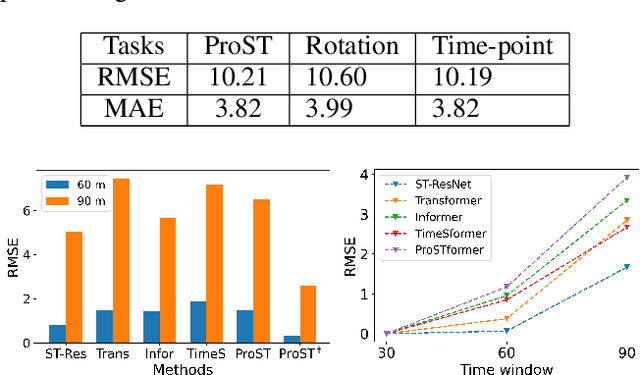
Abstract:Traffic flow forecasting is essential and challenging to intelligent city management and public safety. Recent studies have shown the potential of convolution-free Transformer approach to extract the dynamic dependencies among complex influencing factors. However, two issues prevent the approach from being effectively applied in traffic flow forecasting. First, it ignores the spatiotemporal structure of the traffic flow videos. Second, for a long sequence, it is hard to focus on crucial attention due to the quadratic times dot-product computation. To address the two issues, we first factorize the dependencies and then design a progressive space-time self-attention mechanism named ProSTformer. It has two distinctive characteristics: (1) corresponding to the factorization, the self-attention mechanism progressively focuses on spatial dependence from local to global regions, on temporal dependence from inside to outside fragment (i.e., closeness, period, and trend), and finally on external dependence such as weather, temperature, and day-of-week; (2) by incorporating the spatiotemporal structure into the self-attention mechanism, each block in ProSTformer highlights the unique dependence by aggregating the regions with spatiotemporal positions to significantly decrease the computation. We evaluate ProSTformer on two traffic datasets, and each dataset includes three separate datasets with big, medium, and small scales. Despite the radically different design compared to the convolutional architectures for traffic flow forecasting, ProSTformer performs better or the same on the big scale datasets than six state-of-the-art baseline methods by RMSE. When pre-trained on the big scale datasets and transferred to the medium and small scale datasets, ProSTformer achieves a significant enhancement and behaves best.
Predicting Hourly Demand in Station-free Bike-sharing Systems with Video-level Data
Sep 23, 2020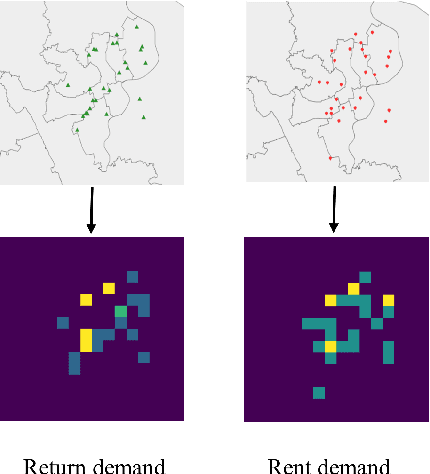
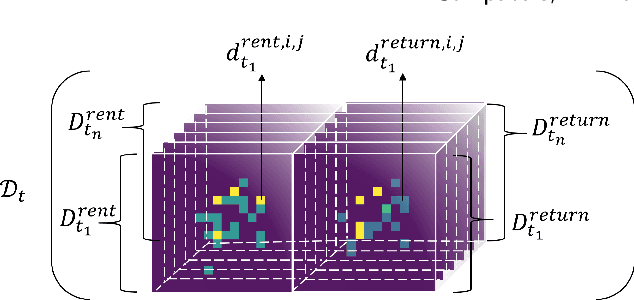
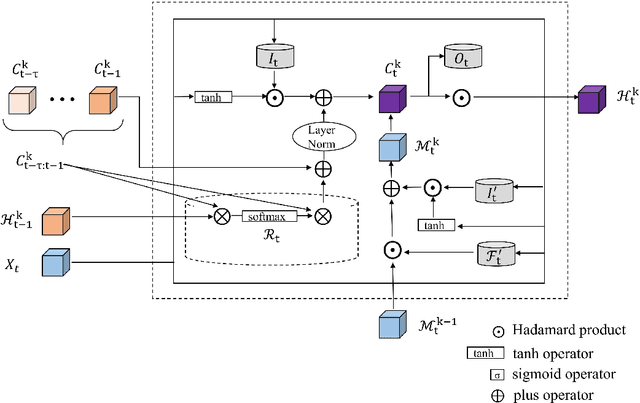
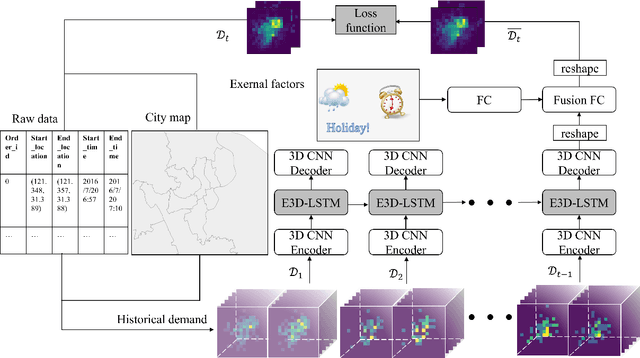
Abstract:Temporal and spatial features are both important for predicting the demands in the bike-sharing systems. Many relevant experiments in the literature support this. Meanwhile, it is observed that the data structure of spatial features with vector form is weaker in space than the videos, which have natural spatial structure. Therefore, to obtain more spatial features, this study introduces city map to generate GPS demand videos while employing a novel algorithm : eidetic 3D convolutional long short-term memory network named E3D-LSTM to process the video-level data in bike-sharing system. The spatio-temporal correlations and feature importance are experimented and visualized to validate the significance of spatial and temporal features. Despite the deep learning model is powerful in non-linear fitting ability, statistic model has better interpretation. This study adopts ensemble learning, which is a popular policy, to improve the performance and decrease variance. In this paper, we propose a novel model stacked by deep learning and statistical models, named the fusion multi-channel eidetic 3D convolutional long short-term memory network(FM-E3DCL-Net), to better process temporal and spatial features on the dataset about 100,000 transactions within one month in Shanghai of Mobike company. Furthermore, other factors like weather, holiday and time intervals are proved useful in addition to historical demand, since they decrease the root mean squared error (RMSE) by 29.4%. On this basis, the ensemble learning further decreases RMSE by 6.6%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge