Jiakai Cao
SD-MVS: Segmentation-Driven Deformation Multi-View Stereo with Spherical Refinement and EM optimization
Jan 12, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Segmentation-Driven Deformation Multi-View Stereo (SD-MVS), a method that can effectively tackle challenges in 3D reconstruction of textureless areas. We are the first to adopt the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to distinguish semantic instances in scenes and further leverage these constraints for pixelwise patch deformation on both matching cost and propagation. Concurrently, we propose a unique refinement strategy that combines spherical coordinates and gradient descent on normals and pixelwise search interval on depths, significantly improving the completeness of reconstructed 3D model. Furthermore, we adopt the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm to alternately optimize the aggregate matching cost and hyperparameters, effectively mitigating the problem of parameters being excessively dependent on empirical tuning. Evaluations on the ETH3D high-resolution multi-view stereo benchmark and the Tanks and Temples dataset demonstrate that our method can achieve state-of-the-art results with less time consumption.
ASSIST: Interactive Scene Nodes for Scalable and Realistic Indoor Simulation
Nov 10, 2023


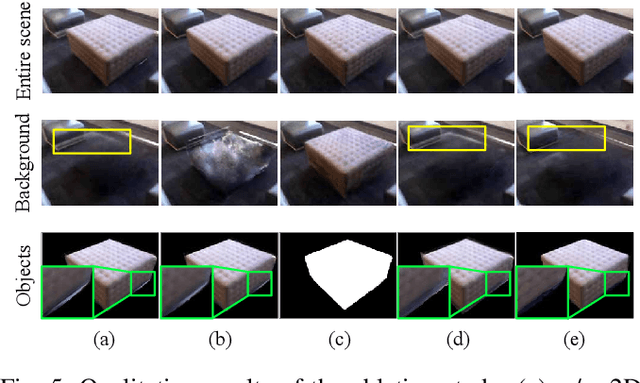
Abstract:We present ASSIST, an object-wise neural radiance field as a panoptic representation for compositional and realistic simulation. Central to our approach is a novel scene node data structure that stores the information of each object in a unified fashion, allowing online interaction in both intra- and cross-scene settings. By incorporating a differentiable neural network along with the associated bounding box and semantic features, the proposed structure guarantees user-friendly interaction on independent objects to scale up novel view simulation. Objects in the scene can be queried, added, duplicated, deleted, transformed, or swapped simply through mouse/keyboard controls or language instructions. Experiments demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method, where scaled realistic simulation can be achieved through interactive editing and compositional rendering, with color images, depth images, and panoptic segmentation masks generated in a 3D consistent manner.
TSAR-MVS: Textureless-aware Segmentation and Correlative Refinement Guided Multi-View Stereo
Aug 19, 2023Abstract:The reconstruction of textureless areas has long been a challenging problem in MVS due to lack of reliable pixel correspondences between images. In this paper, we propose the Textureless-aware Segmentation And Correlative Refinement guided Multi-View Stereo (TSAR-MVS), a novel method that effectively tackles challenges posed by textureless areas in 3D reconstruction through filtering, refinement and segmentation. First, we implement joint hypothesis filtering, a technique that merges a confidence estimator with a disparity discontinuity detector to eliminate incorrect depth estimations. Second, to spread the pixels with confident depth, we introduce a iterative correlation refinement strategy that leverages RANSAC to generate superpixels, succeeded by a median filter for broadening the influence of accurately determined pixels.Finally, we present a textureless-aware segmentation method that leverages edge detection and line detection for accurately identify large textureless regions to be fitted using 3D planes. Experiments on extensive datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms most non-learning methods and exhibits robustness to textureless areas while preserving fine details.
End-to-End Multi-Object Tracking with Global Response Map
Jul 13, 2020



Abstract:Most existing Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) approaches follow the Tracking-by-Detection paradigm and the data association framework where objects are firstly detected and then associated. Although deep-learning based method can noticeably improve the object detection performance and also provide good appearance features for cross-frame association, the framework is not completely end-to-end, and therefore the computation is huge while the performance is limited. To address the problem, we present a completely end-to-end approach that takes image-sequence/video as input and outputs directly the located and tracked objects of learned types. Specifically, with our introduced multi-object representation strategy, a global response map can be accurately generated over frames, from which the trajectory of each tracked object can be easily picked up, just like how a detector inputs an image and outputs the bounding boxes of each detected object. The proposed model is fast and accurate. Experimental results based on the MOT16 and MOT17 benchmarks show that our proposed on-line tracker achieved state-of-the-art performance on several tracking metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge