Xingyu Wan
StrucTexTv3: An Efficient Vision-Language Model for Text-rich Image Perception, Comprehension, and Beyond
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Text-rich images have significant and extensive value, deeply integrated into various aspects of human life. Notably, both visual cues and linguistic symbols in text-rich images play crucial roles in information transmission but are accompanied by diverse challenges. Therefore, the efficient and effective understanding of text-rich images is a crucial litmus test for the capability of Vision-Language Models. We have crafted an efficient vision-language model, StrucTexTv3, tailored to tackle various intelligent tasks for text-rich images. The significant design of StrucTexTv3 is presented in the following aspects: Firstly, we adopt a combination of an effective multi-scale reduced visual transformer and a multi-granularity token sampler (MG-Sampler) as a visual token generator, successfully solving the challenges of high-resolution input and complex representation learning for text-rich images. Secondly, we enhance the perception and comprehension abilities of StrucTexTv3 through instruction learning, seamlessly integrating various text-oriented tasks into a unified framework. Thirdly, we have curated a comprehensive collection of high-quality text-rich images, abbreviated as TIM-30M, encompassing diverse scenarios like incidental scenes, office documents, web pages, and screenshots, thereby improving the robustness of our model. Our method achieved SOTA results in text-rich image perception tasks, and significantly improved performance in comprehension tasks. Among multimodal models with LLM decoder of approximately 1.8B parameters, it stands out as a leader, which also makes the deployment of edge devices feasible. In summary, the StrucTexTv3 model, featuring efficient structural design, outstanding performance, and broad adaptability, offers robust support for diverse intelligent application tasks involving text-rich images, thus exhibiting immense potential for widespread application.
Towards Unified Multi-granularity Text Detection with Interactive Attention
May 30, 2024



Abstract:Existing OCR engines or document image analysis systems typically rely on training separate models for text detection in varying scenarios and granularities, leading to significant computational complexity and resource demands. In this paper, we introduce "Detect Any Text" (DAT), an advanced paradigm that seamlessly unifies scene text detection, layout analysis, and document page detection into a cohesive, end-to-end model. This design enables DAT to efficiently manage text instances at different granularities, including *word*, *line*, *paragraph* and *page*. A pivotal innovation in DAT is the across-granularity interactive attention module, which significantly enhances the representation learning of text instances at varying granularities by correlating structural information across different text queries. As a result, it enables the model to achieve mutually beneficial detection performances across multiple text granularities. Additionally, a prompt-based segmentation module refines detection outcomes for texts of arbitrary curvature and complex layouts, thereby improving DAT's accuracy and expanding its real-world applicability. Experimental results demonstrate that DAT achieves state-of-the-art performances across a variety of text-related benchmarks, including multi-oriented/arbitrarily-shaped scene text detection, document layout analysis and page detection tasks.
Auxiliary Loss Adaptation for Image Inpainting
Nov 22, 2021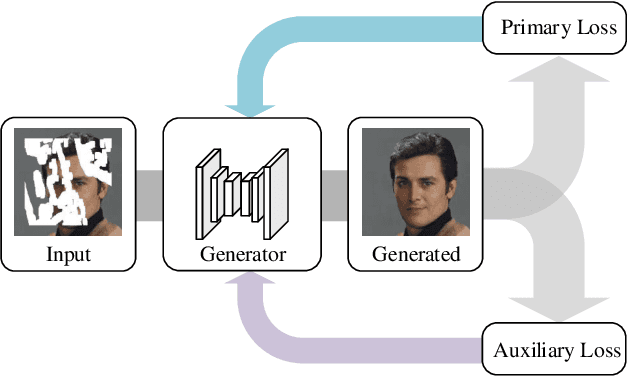
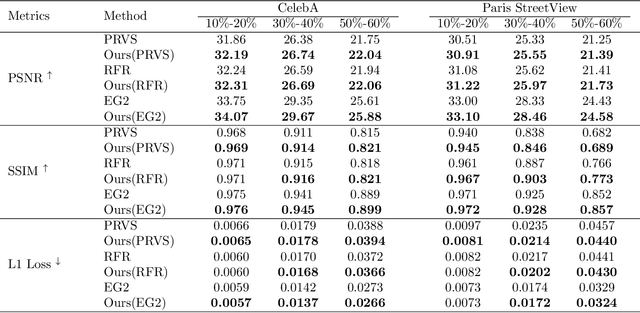
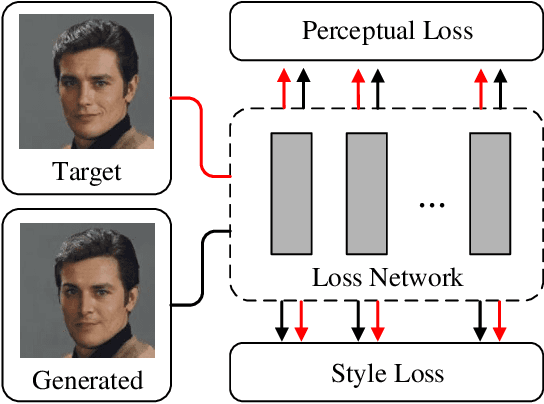
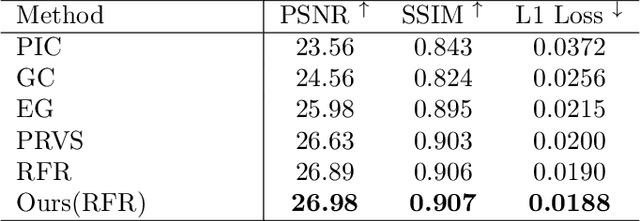
Abstract:Auxiliary losses commonly used in image inpainting lead to better reconstruction performance by incorporating prior knowledge of missing regions. However, it usually requires a lot of effort to fully exploit the potential of auxiliary losses, or otherwise, improperly weighted auxiliary losses would distract the model from the inpainting task, and the effectiveness of an auxiliary loss might vary during the training process. Hence the design of auxiliary losses takes strong domain expertise. To mitigate the problem, in this work, we introduce the Auxiliary Loss Adaptation for Image Inpainting (ALA) algorithm to dynamically adjust the parameters of the auxiliary loss. Our method is based on the principle that the best auxiliary loss is the one that helps increase the performance of the main loss most through several steps of gradient descent. We then examined two commonly used auxiliary losses in inpainting and used ALA to adapt their parameters. Experimental results show that ALA induces more competitive inpainting results than fixed auxiliary losses. In particular, simply combining auxiliary loss with ALA, existing inpainting methods can achieve increased performances without explicitly incorporating delicate network design or structure knowledge prior.
Teacher-Student Asynchronous Learning with Multi-Source Consistency for Facial Landmark Detection
Dec 12, 2020



Abstract:Due to the high annotation cost of large-scale facial landmark detection tasks in videos, a semi-supervised paradigm that uses self-training for mining high-quality pseudo-labels to participate in training has been proposed by researchers. However, self-training based methods often train with a gradually increasing number of samples, whose performances vary a lot depending on the number of pseudo-labeled samples added. In this paper, we propose a teacher-student asynchronous learning~(TSAL) framework based on the multi-source supervision signal consistency criterion, which implicitly mines pseudo-labels through consistency constraints. Specifically, the TSAL framework contains two models with exactly the same structure. The radical student uses multi-source supervision signals from the same task to update parameters, while the calm teacher uses a single-source supervision signal to update parameters. In order to reasonably absorb student's suggestions, teacher's parameters are updated again through recursive average filtering. The experimental results prove that asynchronous-learning framework can effectively filter noise in multi-source supervision signals, thereby mining the pseudo-labels which are more significant for network parameter updating. And extensive experiments on 300W, AFLW, and 300VW benchmarks show that the TSAL framework achieves state-of-the-art performance.
End-to-End Multi-Object Tracking with Global Response Map
Jul 13, 2020



Abstract:Most existing Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) approaches follow the Tracking-by-Detection paradigm and the data association framework where objects are firstly detected and then associated. Although deep-learning based method can noticeably improve the object detection performance and also provide good appearance features for cross-frame association, the framework is not completely end-to-end, and therefore the computation is huge while the performance is limited. To address the problem, we present a completely end-to-end approach that takes image-sequence/video as input and outputs directly the located and tracked objects of learned types. Specifically, with our introduced multi-object representation strategy, a global response map can be accurately generated over frames, from which the trajectory of each tracked object can be easily picked up, just like how a detector inputs an image and outputs the bounding boxes of each detected object. The proposed model is fast and accurate. Experimental results based on the MOT16 and MOT17 benchmarks show that our proposed on-line tracker achieved state-of-the-art performance on several tracking metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge