Qunyi Xie
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
On Data Synthesis and Post-training for Visual Abstract Reasoning
Apr 02, 2025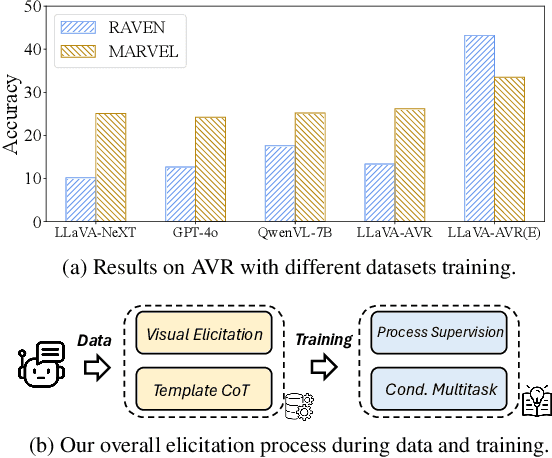

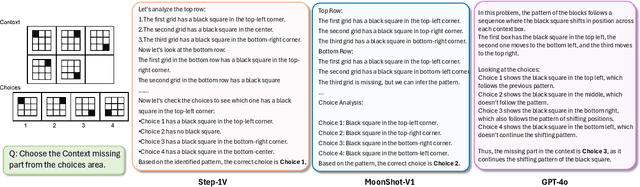

Abstract:This paper is a pioneering work attempting to address abstract visual reasoning (AVR) problems for large vision-language models (VLMs). We make a common LLaVA-NeXT 7B model capable of perceiving and reasoning about specific AVR problems, surpassing both open-sourced (e.g., Qwen-2-VL-72B) and closed-sourced powerful VLMs (e.g., GPT-4o) with significant margin. This is a great breakthrough since almost all previous VLMs fail or show nearly random performance on representative AVR benchmarks. Our key success is our innovative data synthesis and post-training process, aiming to fully relieve the task difficulty and elicit the model to learn, step by step. Our 7B model is also shown to be behave well on AVR without sacrificing common multimodal comprehension abilities. We hope our paper could serve as an early effort in this area and would inspire further research in abstract visual reasoning.
StrucTexTv3: An Efficient Vision-Language Model for Text-rich Image Perception, Comprehension, and Beyond
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Text-rich images have significant and extensive value, deeply integrated into various aspects of human life. Notably, both visual cues and linguistic symbols in text-rich images play crucial roles in information transmission but are accompanied by diverse challenges. Therefore, the efficient and effective understanding of text-rich images is a crucial litmus test for the capability of Vision-Language Models. We have crafted an efficient vision-language model, StrucTexTv3, tailored to tackle various intelligent tasks for text-rich images. The significant design of StrucTexTv3 is presented in the following aspects: Firstly, we adopt a combination of an effective multi-scale reduced visual transformer and a multi-granularity token sampler (MG-Sampler) as a visual token generator, successfully solving the challenges of high-resolution input and complex representation learning for text-rich images. Secondly, we enhance the perception and comprehension abilities of StrucTexTv3 through instruction learning, seamlessly integrating various text-oriented tasks into a unified framework. Thirdly, we have curated a comprehensive collection of high-quality text-rich images, abbreviated as TIM-30M, encompassing diverse scenarios like incidental scenes, office documents, web pages, and screenshots, thereby improving the robustness of our model. Our method achieved SOTA results in text-rich image perception tasks, and significantly improved performance in comprehension tasks. Among multimodal models with LLM decoder of approximately 1.8B parameters, it stands out as a leader, which also makes the deployment of edge devices feasible. In summary, the StrucTexTv3 model, featuring efficient structural design, outstanding performance, and broad adaptability, offers robust support for diverse intelligent application tasks involving text-rich images, thus exhibiting immense potential for widespread application.
MataDoc: Margin and Text Aware Document Dewarping for Arbitrary Boundary
Jul 24, 2023Abstract:Document dewarping from a distorted camera-captured image is of great value for OCR and document understanding. The document boundary plays an important role which is more evident than the inner region in document dewarping. Current learning-based methods mainly focus on complete boundary cases, leading to poor document correction performance of documents with incomplete boundaries. In contrast to these methods, this paper proposes MataDoc, the first method focusing on arbitrary boundary document dewarping with margin and text aware regularizations. Specifically, we design the margin regularization by explicitly considering background consistency to enhance boundary perception. Moreover, we introduce word position consistency to keep text lines straight in rectified document images. To produce a comprehensive evaluation of MataDoc, we propose a novel benchmark ArbDoc, mainly consisting of document images with arbitrary boundaries in four typical scenarios. Extensive experiments confirm the superiority of MataDoc with consideration for the incomplete boundary on ArbDoc and also demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method on DocUNet, DIR300, and WarpDoc datasets.
Fast-StrucTexT: An Efficient Hourglass Transformer with Modality-guided Dynamic Token Merge for Document Understanding
May 19, 2023Abstract:Transformers achieve promising performance in document understanding because of their high effectiveness and still suffer from quadratic computational complexity dependency on the sequence length. General efficient transformers are challenging to be directly adapted to model document. They are unable to handle the layout representation in documents, e.g. word, line and paragraph, on different granularity levels and seem hard to achieve a good trade-off between efficiency and performance. To tackle the concerns, we propose Fast-StrucTexT, an efficient multi-modal framework based on the StrucTexT algorithm with an hourglass transformer architecture, for visual document understanding. Specifically, we design a modality-guided dynamic token merging block to make the model learn multi-granularity representation and prunes redundant tokens. Additionally, we present a multi-modal interaction module called Symmetry Cross Attention (SCA) to consider multi-modal fusion and efficiently guide the token mergence. The SCA allows one modality input as query to calculate cross attention with another modality in a dual phase. Extensive experiments on FUNSD, SROIE, and CORD datasets demonstrate that our model achieves the state-of-the-art performance and almost 1.9X faster inference time than the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge