Yuqing Zhang
Making Machines Sound Sarcastic: LLM-Enhanced and Retrieval-Guided Sarcastic Speech Synthesis
Oct 08, 2025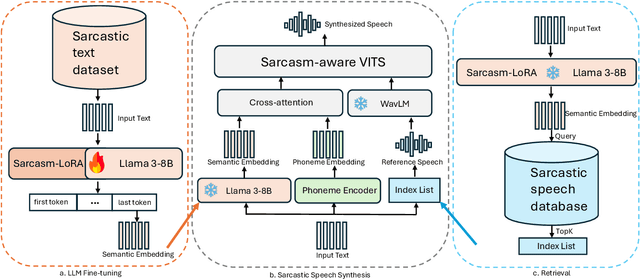
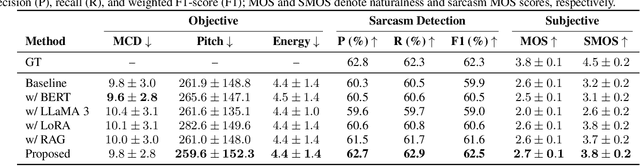
Abstract:Sarcasm is a subtle form of non-literal language that poses significant challenges for speech synthesis due to its reliance on nuanced semantic, contextual, and prosodic cues. While existing speech synthesis research has focused primarily on broad emotional categories, sarcasm remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose a Large Language Model (LLM)-enhanced Retrieval-Augmented framework for sarcasm-aware speech synthesis. Our approach combines (1) semantic embeddings from a LoRA-fine-tuned LLaMA 3, which capture pragmatic incongruity and discourse-level cues of sarcasm, and (2) prosodic exemplars retrieved via a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) module, which provide expressive reference patterns of sarcastic delivery. Integrated within a VITS backbone, this dual conditioning enables more natural and contextually appropriate sarcastic speech. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms baselines in both objective measures and subjective evaluations, yielding improvements in speech naturalness, sarcastic expressivity, and downstream sarcasm detection.
NeLLCom-Lex: A Neural-agent Framework to Study the Interplay between Lexical Systems and Language Use
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Lexical semantic change has primarily been investigated with observational and experimental methods; however, observational methods (corpus analysis, distributional semantic modeling) cannot get at causal mechanisms, and experimental paradigms with humans are hard to apply to semantic change due to the extended diachronic processes involved. This work introduces NeLLCom-Lex, a neural-agent framework designed to simulate semantic change by first grounding agents in a real lexical system (e.g. English) and then systematically manipulating their communicative needs. Using a well-established color naming task, we simulate the evolution of a lexical system within a single generation, and study which factors lead agents to: (i) develop human-like naming behavior and lexicons, and (ii) change their behavior and lexicons according to their communicative needs. Our experiments with different supervised and reinforcement learning pipelines show that neural agents trained to 'speak' an existing language can reproduce human-like patterns in color naming to a remarkable extent, supporting the further use of NeLLCom-Lex to elucidate the mechanisms of semantic change.
NAMO-LLM: Efficient Navigation Among Movable Obstacles with Large Language Model Guidance
May 07, 2025Abstract:Several planners have been proposed to compute robot paths that reach desired goal regions while avoiding obstacles. However, these methods fail when all pathways to the goal are blocked. In such cases, the robot must reason about how to reconfigure the environment to access task-relevant regions - a problem known as Navigation Among Movable Objects (NAMO). While various solutions to this problem have been developed, they often struggle to scale to highly cluttered environments. To address this, we propose NAMO-LLM, a sampling-based planner that searches over robot and obstacle configurations to compute feasible plans specifying which obstacles to move, where, and in what order. Its key novelty is a non-uniform sampling strategy guided by Large Language Models (LLMs) biasing the tree construction toward directions more likely to yield a solution. We show that NAMO-LLM is probabilistically complete and demonstrate through experiments that it efficiently scales to cluttered environments, outperforming related works in both runtime and plan quality.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Single-Image Efficient Super-Resolution (ESR). The challenge aimed to advance the development of deep models that optimize key computational metrics, i.e., runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while achieving a PSNR of at least 26.90 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_valid}$ dataset and 26.99 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_test}$ dataset. A robust participation saw \textbf{244} registered entrants, with \textbf{43} teams submitting valid entries. This report meticulously analyzes these methods and results, emphasizing groundbreaking advancements in state-of-the-art single-image ESR techniques. The analysis highlights innovative approaches and establishes benchmarks for future research in the field.
KSHSeek: Data-Driven Approaches to Mitigating and Detecting Knowledge-Shortcut Hallucinations in Generative Models
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:The emergence of large language models (LLMs) has significantly advanced the development of natural language processing (NLP), especially in text generation tasks like question answering. However, model hallucinations remain a major challenge in natural language generation (NLG) tasks due to their complex causes. We systematically expand on the causes of factual hallucinations from the perspective of knowledge shortcuts, analyzing hallucinations arising from correct and defect-free data and demonstrating that knowledge-shortcut hallucinations are prevalent in generative models. To mitigate this issue, we propose a high similarity pruning algorithm at the data preprocessing level to reduce spurious correlations in the data. Additionally, we design a specific detection method for knowledge-shortcut hallucinations to evaluate the effectiveness of our mitigation strategy. Experimental results show that our approach effectively reduces knowledge-shortcut hallucinations, particularly in fine-tuning tasks, without negatively impacting model performance in question answering. This work introduces a new paradigm for mitigating specific hallucination issues in generative models, enhancing their robustness and reliability in real-world applications.
Graph-Weighted Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Hyperspectral Image Classification
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Most existing graph-based semi-supervised hyperspectral image classification methods rely on superpixel partitioning techniques. However, they suffer from misclassification of certain pixels due to inaccuracies in superpixel boundaries, \ie, the initial inaccuracies in superpixel partitioning limit overall classification performance. In this paper, we propose a novel graph-weighted contrastive learning approach that avoids the use of superpixel partitioning and directly employs neural networks to learn hyperspectral image representation. Furthermore, while many approaches require all graph nodes to be available during training, our approach supports mini-batch training by processing only a subset of nodes at a time, reducing computational complexity and improving generalization to unseen nodes. Experimental results on three widely-used datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach compared to baselines relying on superpixel partitioning.
FDLLM: A Text Fingerprint Detection Method for LLMs in Multi-Language, Multi-Domain Black-Box Environments
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Using large language models (LLMs) integration platforms without transparency about which LLM is being invoked can lead to potential security risks. Specifically, attackers may exploit this black-box scenario to deploy malicious models and embed viruses in the code provided to users. In this context, it is increasingly urgent for users to clearly identify the LLM they are interacting with, in order to avoid unknowingly becoming victims of malicious models. However, existing studies primarily focus on mixed classification of human and machine-generated text, with limited attention to classifying texts generated solely by different models. Current research also faces dual bottlenecks: poor quality of LLM-generated text (LLMGT) datasets and limited coverage of detectable LLMs, resulting in poor detection performance for various LLMGT in black-box scenarios. We propose the first LLMGT fingerprint detection model, \textbf{FDLLM}, based on Qwen2.5-7B and fine-tuned using LoRA to address these challenges. FDLLM can more efficiently handle detection tasks across multilingual and multi-domain scenarios. Furthermore, we constructed a dataset named \textbf{FD-Datasets}, consisting of 90,000 samples that span multiple languages and domains, covering 20 different LLMs. Experimental results demonstrate that FDLLM achieves a macro F1 score 16.7\% higher than the best baseline method, LM-D.
StyleTex: Style Image-Guided Texture Generation for 3D Models
Nov 01, 2024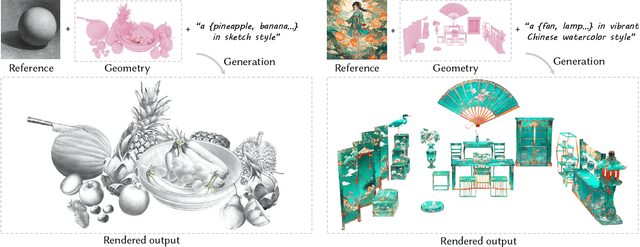
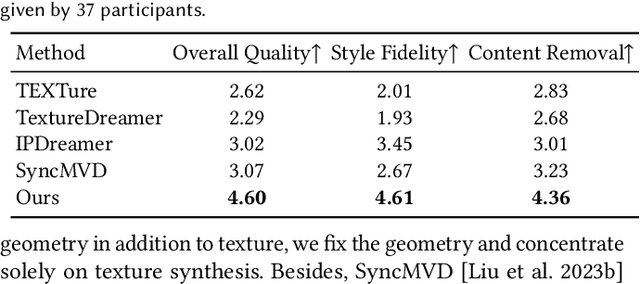
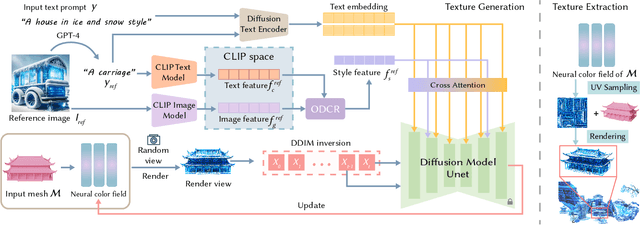
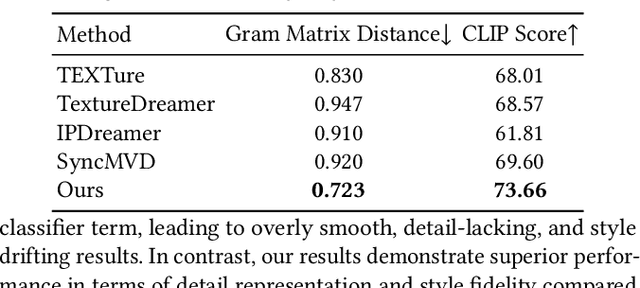
Abstract:Style-guided texture generation aims to generate a texture that is harmonious with both the style of the reference image and the geometry of the input mesh, given a reference style image and a 3D mesh with its text description. Although diffusion-based 3D texture generation methods, such as distillation sampling, have numerous promising applications in stylized games and films, it requires addressing two challenges: 1) decouple style and content completely from the reference image for 3D models, and 2) align the generated texture with the color tone, style of the reference image, and the given text prompt. To this end, we introduce StyleTex, an innovative diffusion-model-based framework for creating stylized textures for 3D models. Our key insight is to decouple style information from the reference image while disregarding content in diffusion-based distillation sampling. Specifically, given a reference image, we first decompose its style feature from the image CLIP embedding by subtracting the embedding's orthogonal projection in the direction of the content feature, which is represented by a text CLIP embedding. Our novel approach to disentangling the reference image's style and content information allows us to generate distinct style and content features. We then inject the style feature into the cross-attention mechanism to incorporate it into the generation process, while utilizing the content feature as a negative prompt to further dissociate content information. Finally, we incorporate these strategies into StyleTex to obtain stylized textures. The resulting textures generated by StyleTex retain the style of the reference image, while also aligning with the text prompts and intrinsic details of the given 3D mesh. Quantitative and qualitative experiments show that our method outperforms existing baseline methods by a significant margin.
Memory Matching is not Enough: Jointly Improving Memory Matching and Decoding for Video Object Segmentation
Sep 22, 2024Abstract:Memory-based video object segmentation methods model multiple objects over long temporal-spatial spans by establishing memory bank, which achieve the remarkable performance. However, they struggle to overcome the false matching and are prone to lose critical information, resulting in confusion among different objects. In this paper, we propose an effective approach which jointly improving the matching and decoding stages to alleviate the false matching issue.For the memory matching stage, we present a cost aware mechanism that suppresses the slight errors for short-term memory and a shunted cross-scale matching for long-term memory which establish a wide filed matching spaces for various object scales. For the readout decoding stage, we implement a compensatory mechanism aims at recovering the essential information where missing at the matching stage. Our approach achieves the outstanding performance in several popular benchmarks (i.e., DAVIS 2016&2017 Val (92.4%&88.1%), and DAVIS 2017 Test (83.9%)), and achieves 84.8%&84.6% on YouTubeVOS 2018&2019 Val.
A Functional Trade-off between Prosodic and Semantic Cues in Conveying Sarcasm
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:This study investigates the acoustic features of sarcasm and disentangles the interplay between the propensity of an utterance being used sarcastically and the presence of prosodic cues signaling sarcasm. Using a dataset of sarcastic utterances compiled from television shows, we analyze the prosodic features within utterances and key phrases belonging to three distinct sarcasm categories (embedded, propositional, and illocutionary), which vary in the degree of semantic cues present, and compare them to neutral expressions. Results show that in phrases where the sarcastic meaning is salient from the semantics, the prosodic cues are less relevant than when the sarcastic meaning is not evident from the semantics, suggesting a trade-off between prosodic and semantic cues of sarcasm at the phrase level. These findings highlight a lessened reliance on prosodic modulation in semantically dense sarcastic expressions and a nuanced interaction that shapes the communication of sarcastic intent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge