Yiqian Wu
EgoM2P: Egocentric Multimodal Multitask Pretraining
Jun 09, 2025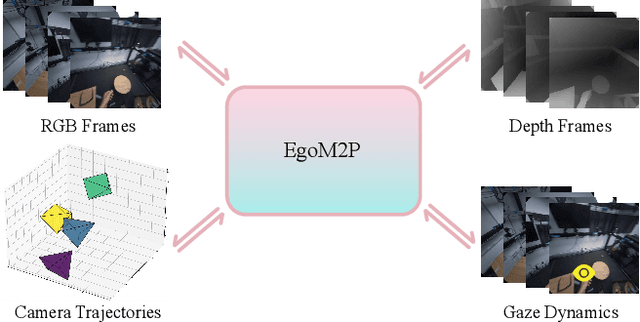
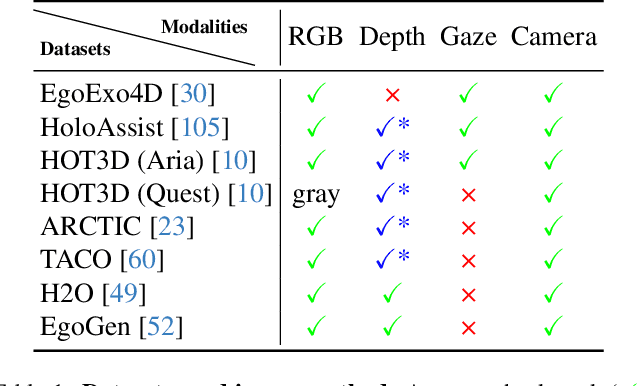
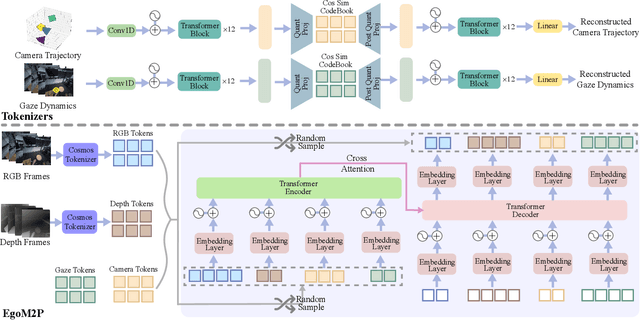
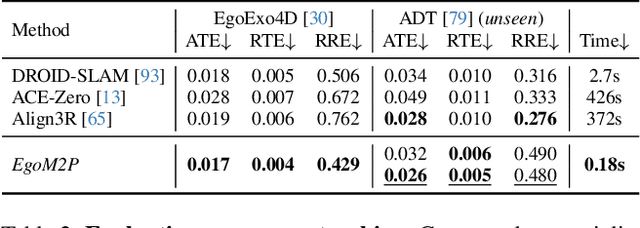
Abstract:Understanding multimodal signals in egocentric vision, such as RGB video, depth, camera poses, and gaze, is essential for applications in augmented reality, robotics, and human-computer interaction. These capabilities enable systems to better interpret the camera wearer's actions, intentions, and surrounding environment. However, building large-scale egocentric multimodal and multitask models presents unique challenges. Egocentric data are inherently heterogeneous, with large variations in modality coverage across devices and settings. Generating pseudo-labels for missing modalities, such as gaze or head-mounted camera trajectories, is often infeasible, making standard supervised learning approaches difficult to scale. Furthermore, dynamic camera motion and the complex temporal and spatial structure of first-person video pose additional challenges for the direct application of existing multimodal foundation models. To address these challenges, we introduce a set of efficient temporal tokenizers and propose EgoM2P, a masked modeling framework that learns from temporally aware multimodal tokens to train a large, general-purpose model for egocentric 4D understanding. This unified design supports multitasking across diverse egocentric perception and synthesis tasks, including gaze prediction, egocentric camera tracking, and monocular depth estimation from egocentric video. EgoM2P also serves as a generative model for conditional egocentric video synthesis. Across these tasks, EgoM2P matches or outperforms specialist models while being an order of magnitude faster. We will fully open-source EgoM2P to support the community and advance egocentric vision research. Project page: https://egom2p.github.io/
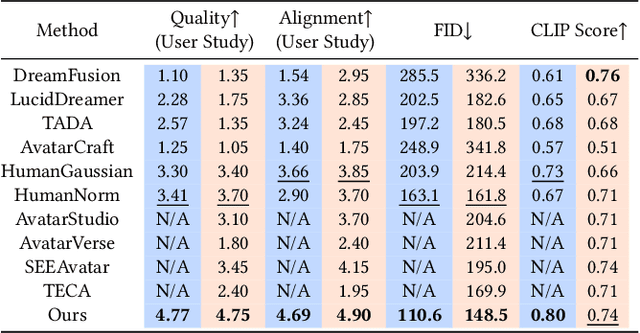
Text-based Animatable 3D Avatars with Morphable Model Alignment
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:The generation of high-quality, animatable 3D head avatars from text has enormous potential in content creation applications such as games, movies, and embodied virtual assistants. Current text-to-3D generation methods typically combine parametric head models with 2D diffusion models using score distillation sampling to produce 3D-consistent results. However, they struggle to synthesize realistic details and suffer from misalignments between the appearance and the driving parametric model, resulting in unnatural animation results. We discovered that these limitations stem from ambiguities in the 2D diffusion predictions during 3D avatar distillation, specifically: i) the avatar's appearance and geometry is underconstrained by the text input, and ii) the semantic alignment between the predictions and the parametric head model is insufficient because the diffusion model alone cannot incorporate information from the parametric model. In this work, we propose a novel framework, AnimPortrait3D, for text-based realistic animatable 3DGS avatar generation with morphable model alignment, and introduce two key strategies to address these challenges. First, we tackle appearance and geometry ambiguities by utilizing prior information from a pretrained text-to-3D model to initialize a 3D avatar with robust appearance, geometry, and rigging relationships to the morphable model. Second, we refine the initial 3D avatar for dynamic expressions using a ControlNet that is conditioned on semantic and normal maps of the morphable model to ensure accurate alignment. As a result, our method outperforms existing approaches in terms of synthesis quality, alignment, and animation fidelity. Our experiments show that the proposed method advances the state of the art in text-based, animatable 3D head avatar generation.
StyleTex: Style Image-Guided Texture Generation for 3D Models
Nov 01, 2024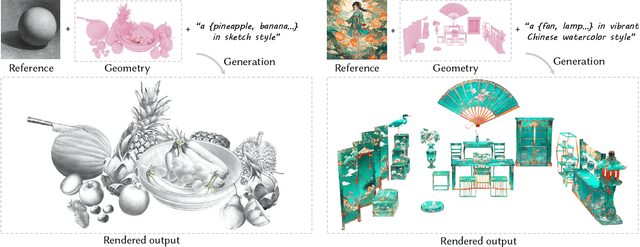
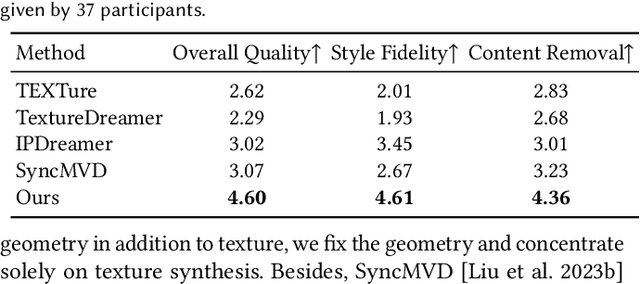
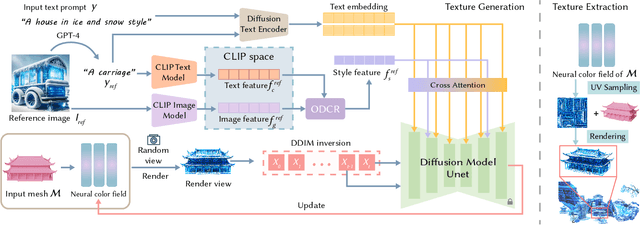
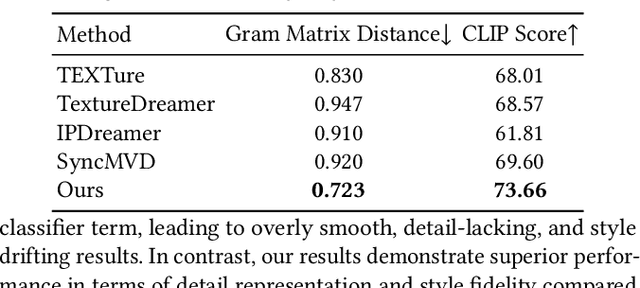
Abstract:Style-guided texture generation aims to generate a texture that is harmonious with both the style of the reference image and the geometry of the input mesh, given a reference style image and a 3D mesh with its text description. Although diffusion-based 3D texture generation methods, such as distillation sampling, have numerous promising applications in stylized games and films, it requires addressing two challenges: 1) decouple style and content completely from the reference image for 3D models, and 2) align the generated texture with the color tone, style of the reference image, and the given text prompt. To this end, we introduce StyleTex, an innovative diffusion-model-based framework for creating stylized textures for 3D models. Our key insight is to decouple style information from the reference image while disregarding content in diffusion-based distillation sampling. Specifically, given a reference image, we first decompose its style feature from the image CLIP embedding by subtracting the embedding's orthogonal projection in the direction of the content feature, which is represented by a text CLIP embedding. Our novel approach to disentangling the reference image's style and content information allows us to generate distinct style and content features. We then inject the style feature into the cross-attention mechanism to incorporate it into the generation process, while utilizing the content feature as a negative prompt to further dissociate content information. Finally, we incorporate these strategies into StyleTex to obtain stylized textures. The resulting textures generated by StyleTex retain the style of the reference image, while also aligning with the text prompts and intrinsic details of the given 3D mesh. Quantitative and qualitative experiments show that our method outperforms existing baseline methods by a significant margin.
Decoupling Contact for Fine-Grained Motion Style Transfer
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:Motion style transfer changes the style of a motion while retaining its content and is useful in computer animations and games. Contact is an essential component of motion style transfer that should be controlled explicitly in order to express the style vividly while enhancing motion naturalness and quality. However, it is unknown how to decouple and control contact to achieve fine-grained control in motion style transfer. In this paper, we present a novel style transfer method for fine-grained control over contacts while achieving both motion naturalness and spatial-temporal variations of style. Based on our empirical evidence, we propose controlling contact indirectly through the hip velocity, which can be further decomposed into the trajectory and contact timing, respectively. To this end, we propose a new model that explicitly models the correlations between motions and trajectory/contact timing/style, allowing us to decouple and control each separately. Our approach is built around a motion manifold, where hip controls can be easily integrated into a Transformer-based decoder. It is versatile in that it can generate motions directly as well as be used as post-processing for existing methods to improve quality and contact controllability. In addition, we propose a new metric that measures a correlation pattern of motions based on our empirical evidence, aligning well with human perception in terms of motion naturalness. Based on extensive evaluation, our method outperforms existing methods in terms of style expressivity and motion quality.
Portrait3D: Text-Guided High-Quality 3D Portrait Generation Using Pyramid Representation and GANs Prior
Apr 16, 2024
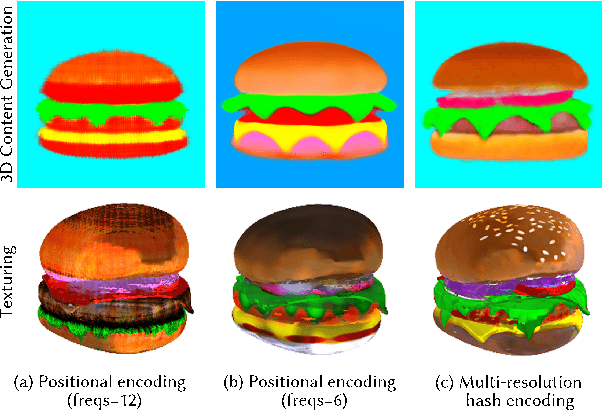
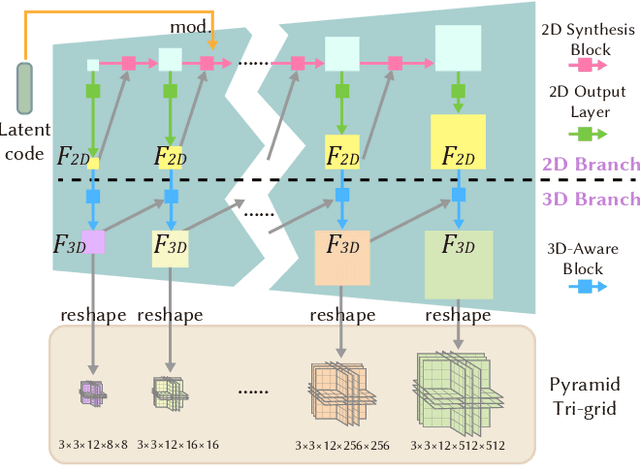
Abstract:Existing neural rendering-based text-to-3D-portrait generation methods typically make use of human geometry prior and diffusion models to obtain guidance. However, relying solely on geometry information introduces issues such as the Janus problem, over-saturation, and over-smoothing. We present Portrait3D, a novel neural rendering-based framework with a novel joint geometry-appearance prior to achieve text-to-3D-portrait generation that overcomes the aforementioned issues. To accomplish this, we train a 3D portrait generator, 3DPortraitGAN-Pyramid, as a robust prior. This generator is capable of producing 360{\deg} canonical 3D portraits, serving as a starting point for the subsequent diffusion-based generation process. To mitigate the "grid-like" artifact caused by the high-frequency information in the feature-map-based 3D representation commonly used by most 3D-aware GANs, we integrate a novel pyramid tri-grid 3D representation into 3DPortraitGAN-Pyramid. To generate 3D portraits from text, we first project a randomly generated image aligned with the given prompt into the pre-trained 3DPortraitGAN-Pyramid's latent space. The resulting latent code is then used to synthesize a pyramid tri-grid. Beginning with the obtained pyramid tri-grid, we use score distillation sampling to distill the diffusion model's knowledge into the pyramid tri-grid. Following that, we utilize the diffusion model to refine the rendered images of the 3D portrait and then use these refined images as training data to further optimize the pyramid tri-grid, effectively eliminating issues with unrealistic color and unnatural artifacts. Our experimental results show that Portrait3D can produce realistic, high-quality, and canonical 3D portraits that align with the prompt.
Enhancing the Authenticity of Rendered Portraits with Identity-Consistent Transfer Learning
Oct 06, 2023
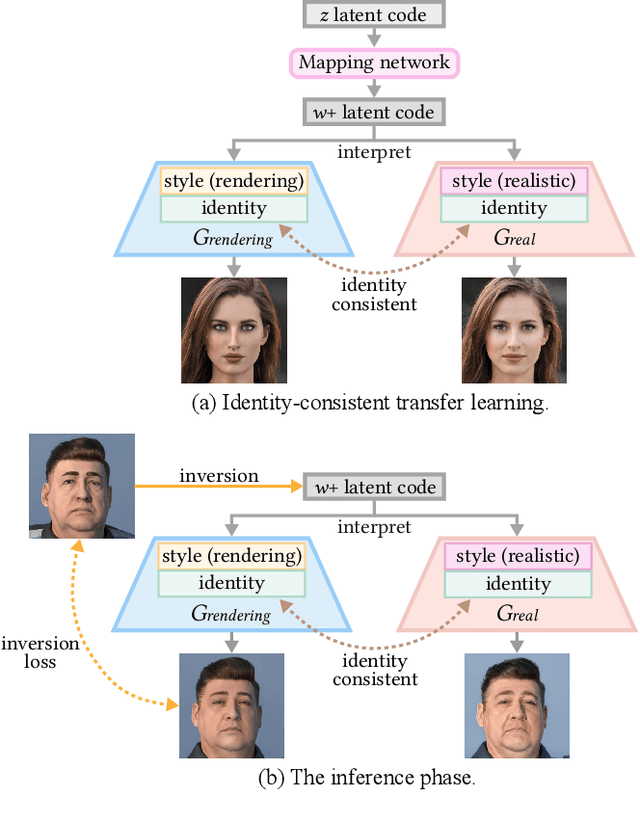

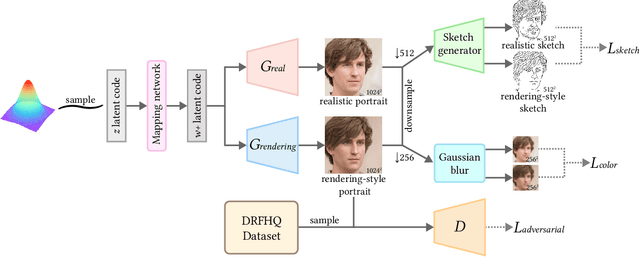
Abstract:Despite rapid advances in computer graphics, creating high-quality photo-realistic virtual portraits is prohibitively expensive. Furthermore, the well-know ''uncanny valley'' effect in rendered portraits has a significant impact on the user experience, especially when the depiction closely resembles a human likeness, where any minor artifacts can evoke feelings of eeriness and repulsiveness. In this paper, we present a novel photo-realistic portrait generation framework that can effectively mitigate the ''uncanny valley'' effect and improve the overall authenticity of rendered portraits. Our key idea is to employ transfer learning to learn an identity-consistent mapping from the latent space of rendered portraits to that of real portraits. During the inference stage, the input portrait of an avatar can be directly transferred to a realistic portrait by changing its appearance style while maintaining the facial identity. To this end, we collect a new dataset, Daz-Rendered-Faces-HQ (DRFHQ), that is specifically designed for rendering-style portraits. We leverage this dataset to fine-tune the StyleGAN2 generator, using our carefully crafted framework, which helps to preserve the geometric and color features relevant to facial identity. We evaluate our framework using portraits with diverse gender, age, and race variations. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations and ablation studies show the advantages of our method compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
Learning Full-Head 3D GANs from a Single-View Portrait Dataset
Jul 27, 2023
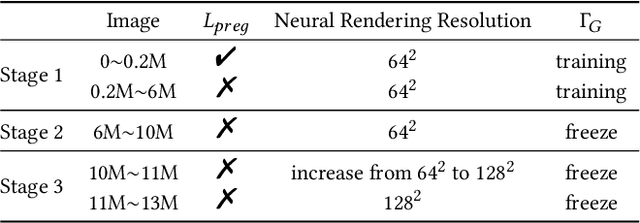

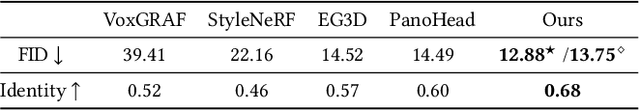
Abstract:33D-aware face generators are commonly trained on 2D real-life face image datasets. Nevertheless, existing facial recognition methods often struggle to extract face data captured from various camera angles. Furthermore, in-the-wild images with diverse body poses introduce a high-dimensional challenge for 3D-aware generators, making it difficult to utilize data that contains complete neck and shoulder regions. Consequently, these face image datasets often contain only near-frontal face data, which poses challenges for 3D-aware face generators to construct \textit{full-head} 3D portraits. To this end, we first create the dataset {$\it{360}^{\circ}$}-\textit{Portrait}-\textit{HQ} (\textit{$\it{360}^{\circ}$PHQ}), which consists of high-quality single-view real portraits annotated with a variety of camera parameters {(the yaw angles span the entire $360^{\circ}$ range)} and body poses. We then propose \textit{3DPortraitGAN}, the first 3D-aware full-head portrait generator that learns a canonical 3D avatar distribution from the body-pose-various \textit{$\it{360}^{\circ}$PHQ} dataset with body pose self-learning. Our model can generate view-consistent portrait images from all camera angles (${360}^{\circ}$) with a full-head 3D representation. We incorporate a mesh-guided deformation field into volumetric rendering to produce deformed results to generate portrait images that conform to the body pose distribution of the dataset using our canonical generator. We integrate two pose predictors into our framework to predict more accurate body poses to address the issue of inaccurately estimated body poses in our dataset. Our experiments show that the proposed framework can generate view-consistent, realistic portrait images with complete geometry from all camera angles and accurately predict portrait body pose.
LPFF: A Portrait Dataset for Face Generators Across Large Poses
Mar 25, 2023



Abstract:The creation of 2D realistic facial images and 3D face shapes using generative networks has been a hot topic in recent years. Existing face generators exhibit exceptional performance on faces in small to medium poses (with respect to frontal faces) but struggle to produce realistic results for large poses. The distorted rendering results on large poses in 3D-aware generators further show that the generated 3D face shapes are far from the distribution of 3D faces in reality. We find that the above issues are caused by the training dataset's pose imbalance. In this paper, we present LPFF, a large-pose Flickr face dataset comprised of 19,590 high-quality real large-pose portrait images. We utilize our dataset to train a 2D face generator that can process large-pose face images, as well as a 3D-aware generator that can generate realistic human face geometry. To better validate our pose-conditional 3D-aware generators, we develop a new FID measure to evaluate the 3D-level performance. Through this novel FID measure and other experiments, we show that LPFF can help 2D face generators extend their latent space and better manipulate the large-pose data, and help 3D-aware face generators achieve better view consistency and more realistic 3D reconstruction results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge