Zhebin Zhang
DCUDF2: Improving Efficiency and Accuracy in Extracting Zero Level Sets from Unsigned Distance Fields
Aug 30, 2024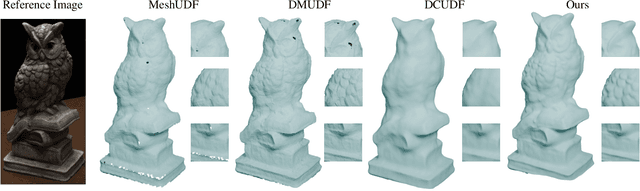
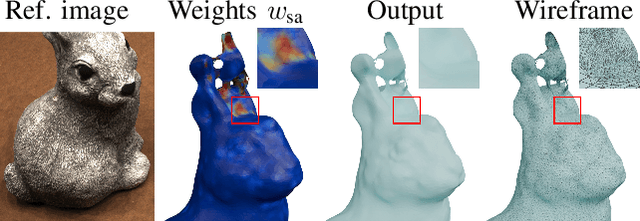
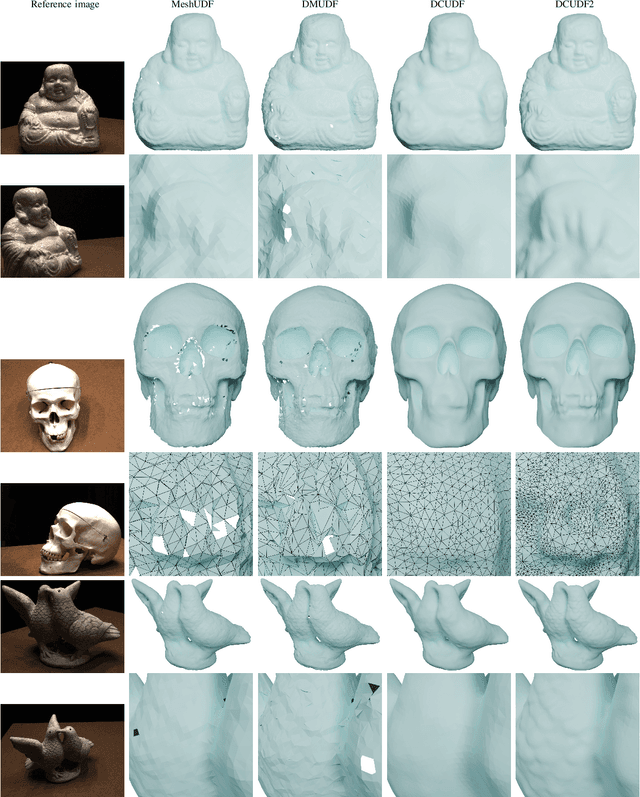
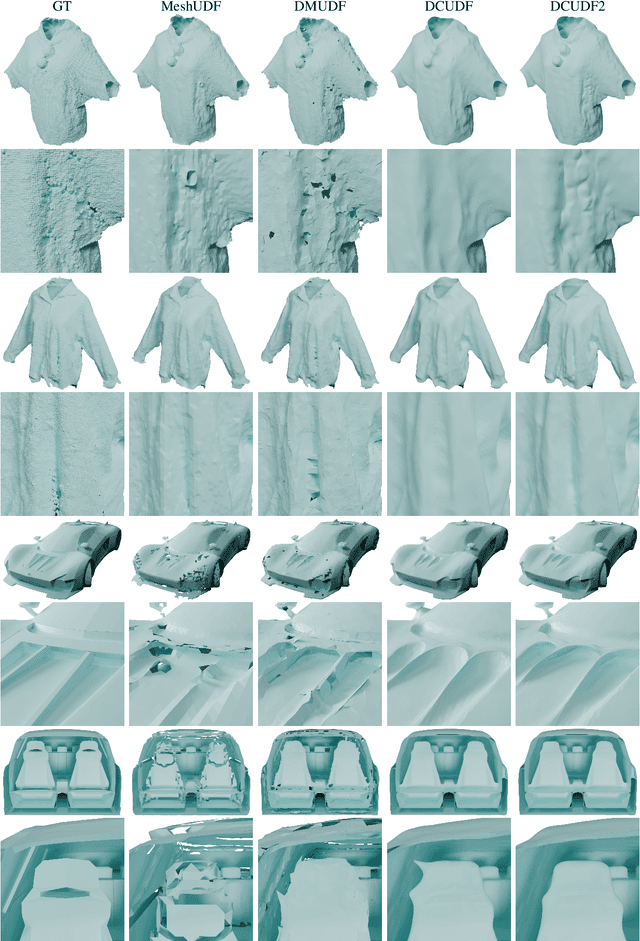
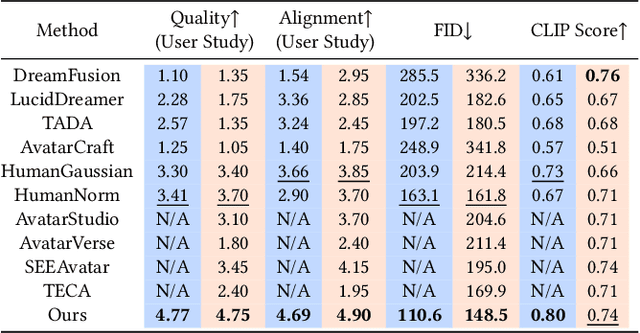
Abstract:Unsigned distance fields (UDFs) allow for the representation of models with complex topologies, but extracting accurate zero level sets from these fields poses significant challenges, particularly in preserving topological accuracy and capturing fine geometric details. To overcome these issues, we introduce DCUDF2, an enhancement over DCUDF--the current state-of-the-art method--for extracting zero level sets from UDFs. Our approach utilizes an accuracy-aware loss function, enhanced with self-adaptive weights, to improve geometric quality significantly. We also propose a topology correction strategy that reduces the dependence on hyper-parameter, increasing the robustness of our method. Furthermore, we develop new operations leveraging self-adaptive weights to boost runtime efficiency. Extensive experiments on surface extraction across diverse datasets demonstrate that DCUDF2 outperforms DCUDF and existing methods in both geometric fidelity and topological accuracy. We will make the source code publicly available.
Learning Unsigned Distance Fields from Local Shape Functions for 3D Surface Reconstruction
Jul 01, 2024



Abstract:Unsigned distance fields (UDFs) provide a versatile framework for representing a diverse array of 3D shapes, encompassing both watertight and non-watertight geometries. Traditional UDF learning methods typically require extensive training on large datasets of 3D shapes, which is costly and often necessitates hyperparameter adjustments for new datasets. This paper presents a novel neural framework, LoSF-UDF, for reconstructing surfaces from 3D point clouds by leveraging local shape functions to learn UDFs. We observe that 3D shapes manifest simple patterns within localized areas, prompting us to create a training dataset of point cloud patches characterized by mathematical functions that represent a continuum from smooth surfaces to sharp edges and corners. Our approach learns features within a specific radius around each query point and utilizes an attention mechanism to focus on the crucial features for UDF estimation. This method enables efficient and robust surface reconstruction from point clouds without the need for shape-specific training. Additionally, our method exhibits enhanced resilience to noise and outliers in point clouds compared to existing methods. We present comprehensive experiments and comparisons across various datasets, including synthetic and real-scanned point clouds, to validate our method's efficacy.
GS-Octree: Octree-based 3D Gaussian Splatting for Robust Object-level 3D Reconstruction Under Strong Lighting
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:The 3D Gaussian Splatting technique has significantly advanced the construction of radiance fields from multi-view images, enabling real-time rendering. While point-based rasterization effectively reduces computational demands for rendering, it often struggles to accurately reconstruct the geometry of the target object, especially under strong lighting. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel approach that combines octree-based implicit surface representations with Gaussian splatting. Our method consists of four stages. Initially, it reconstructs a signed distance field (SDF) and a radiance field through volume rendering, encoding them in a low-resolution octree. The initial SDF represents the coarse geometry of the target object. Subsequently, it introduces 3D Gaussians as additional degrees of freedom, which are guided by the SDF. In the third stage, the optimized Gaussians further improve the accuracy of the SDF, allowing it to recover finer geometric details compared to the initial SDF obtained in the first stage. Finally, it adopts the refined SDF to further optimize the 3D Gaussians via splatting, eliminating those that contribute little to visual appearance. Experimental results show that our method, which leverages the distribution of 3D Gaussians with SDFs, reconstructs more accurate geometry, particularly in images with specular highlights caused by strong lighting.
Details Enhancement in Unsigned Distance Field Learning for High-fidelity 3D Surface Reconstruction
Jun 01, 2024



Abstract:While Signed Distance Fields (SDF) are well-established for modeling watertight surfaces, Unsigned Distance Fields (UDF) broaden the scope to include open surfaces and models with complex inner structures. Despite their flexibility, UDFs encounter significant challenges in high-fidelity 3D reconstruction, such as non-differentiability at the zero level set, difficulty in achieving the exact zero value, numerous local minima, vanishing gradients, and oscillating gradient directions near the zero level set. To address these challenges, we propose Details Enhanced UDF (DEUDF) learning that integrates normal alignment and the SIREN network for capturing fine geometric details, adaptively weighted Eikonal constraints to address vanishing gradients near the target surface, unconditioned MLP-based UDF representation to relax non-negativity constraints, and a UDF-tailored method for extracting iso-surface with non-constant iso-values. These strategies collectively stabilize the learning process from unoriented point clouds and enhance the accuracy of UDFs. Our computational results demonstrate that DEUDF outperforms existing UDF learning methods in both accuracy and the quality of reconstructed surfaces. We will make the source code publicly available.
Multi-View Attentive Contextualization for Multi-View 3D Object Detection
May 20, 2024



Abstract:We present Multi-View Attentive Contextualization (MvACon), a simple yet effective method for improving 2D-to-3D feature lifting in query-based multi-view 3D (MV3D) object detection. Despite remarkable progress witnessed in the field of query-based MV3D object detection, prior art often suffers from either the lack of exploiting high-resolution 2D features in dense attention-based lifting, due to high computational costs, or from insufficiently dense grounding of 3D queries to multi-scale 2D features in sparse attention-based lifting. Our proposed MvACon hits the two birds with one stone using a representationally dense yet computationally sparse attentive feature contextualization scheme that is agnostic to specific 2D-to-3D feature lifting approaches. In experiments, the proposed MvACon is thoroughly tested on the nuScenes benchmark, using both the BEVFormer and its recent 3D deformable attention (DFA3D) variant, as well as the PETR, showing consistent detection performance improvement, especially in enhancing performance in location, orientation, and velocity prediction. It is also tested on the Waymo-mini benchmark using BEVFormer with similar improvement. We qualitatively and quantitatively show that global cluster-based contexts effectively encode dense scene-level contexts for MV3D object detection. The promising results of our proposed MvACon reinforces the adage in computer vision -- ``(contextualized) feature matters".
Portrait3D: Text-Guided High-Quality 3D Portrait Generation Using Pyramid Representation and GANs Prior
Apr 16, 2024
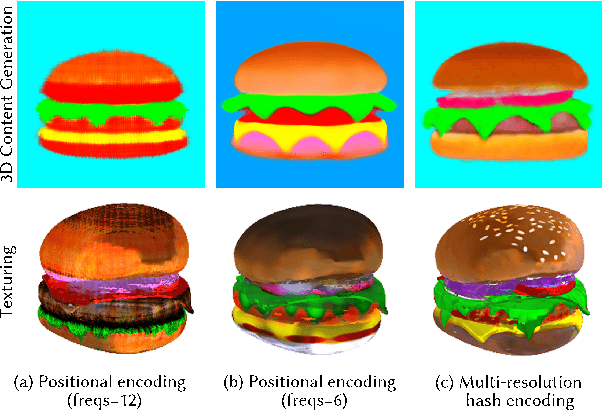
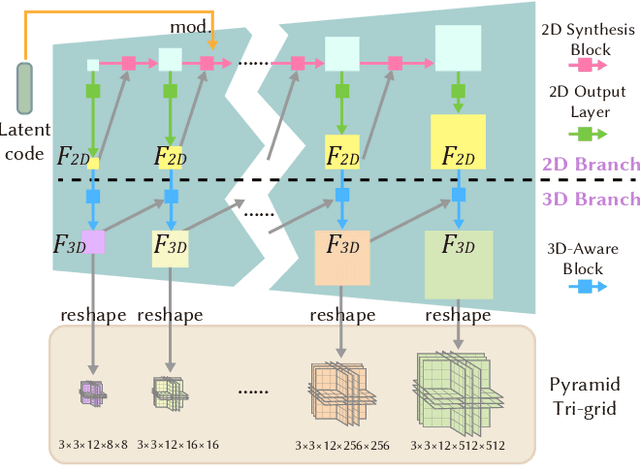
Abstract:Existing neural rendering-based text-to-3D-portrait generation methods typically make use of human geometry prior and diffusion models to obtain guidance. However, relying solely on geometry information introduces issues such as the Janus problem, over-saturation, and over-smoothing. We present Portrait3D, a novel neural rendering-based framework with a novel joint geometry-appearance prior to achieve text-to-3D-portrait generation that overcomes the aforementioned issues. To accomplish this, we train a 3D portrait generator, 3DPortraitGAN-Pyramid, as a robust prior. This generator is capable of producing 360{\deg} canonical 3D portraits, serving as a starting point for the subsequent diffusion-based generation process. To mitigate the "grid-like" artifact caused by the high-frequency information in the feature-map-based 3D representation commonly used by most 3D-aware GANs, we integrate a novel pyramid tri-grid 3D representation into 3DPortraitGAN-Pyramid. To generate 3D portraits from text, we first project a randomly generated image aligned with the given prompt into the pre-trained 3DPortraitGAN-Pyramid's latent space. The resulting latent code is then used to synthesize a pyramid tri-grid. Beginning with the obtained pyramid tri-grid, we use score distillation sampling to distill the diffusion model's knowledge into the pyramid tri-grid. Following that, we utilize the diffusion model to refine the rendered images of the 3D portrait and then use these refined images as training data to further optimize the pyramid tri-grid, effectively eliminating issues with unrealistic color and unnatural artifacts. Our experimental results show that Portrait3D can produce realistic, high-quality, and canonical 3D portraits that align with the prompt.
IAG: Induction-Augmented Generation Framework for Answering Reasoning Questions
Nov 30, 2023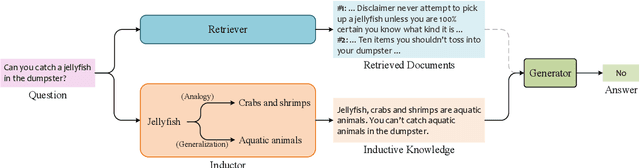
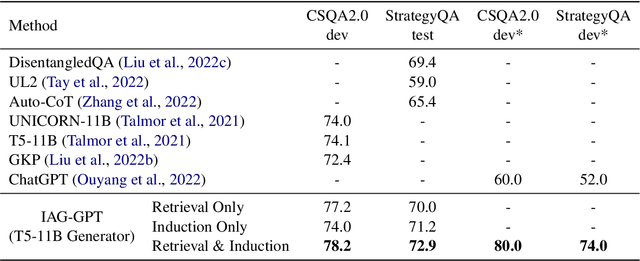
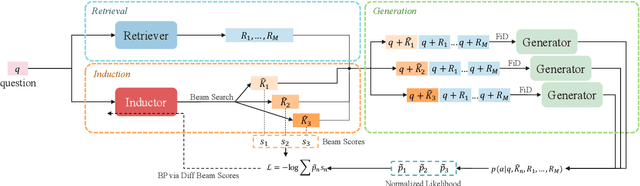
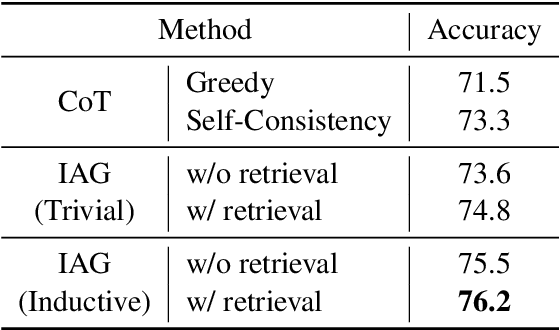
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), by incorporating external knowledge with parametric memory of language models, has become the state-of-the-art architecture for open-domain QA tasks. However, common knowledge bases are inherently constrained by limited coverage and noisy information, making retrieval-based approaches inadequate to answer implicit reasoning questions. In this paper, we propose an Induction-Augmented Generation (IAG) framework that utilizes inductive knowledge along with the retrieved documents for implicit reasoning. We leverage large language models (LLMs) for deriving such knowledge via a novel prompting method based on inductive reasoning patterns. On top of this, we implement two versions of IAG named IAG-GPT and IAG-Student, respectively. IAG-GPT directly utilizes the knowledge generated by GPT-3 for answer prediction, while IAG-Student gets rid of dependencies on GPT service at inference time by incorporating a student inductor model. The inductor is firstly trained via knowledge distillation and further optimized by back-propagating the generator feedback via differentiable beam scores. Experimental results show that IAG outperforms RAG baselines as well as ChatGPT on two Open-Domain QA tasks. Notably, our best models have won the first place in the official leaderboards of CSQA2.0 (since Nov 1, 2022) and StrategyQA (since Jan 8, 2023).
BERT-JAM: Boosting BERT-Enhanced Neural Machine Translation with Joint Attention
Nov 09, 2020
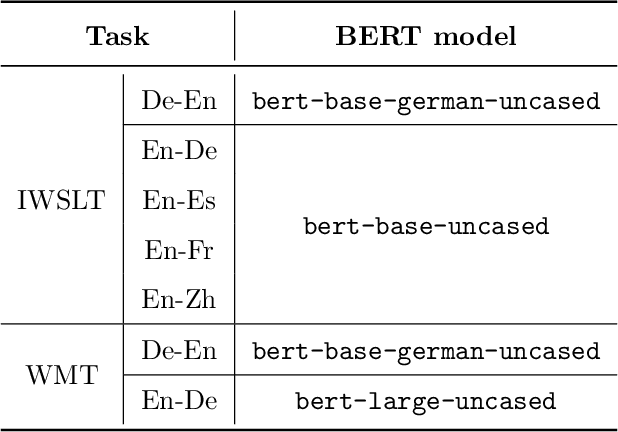
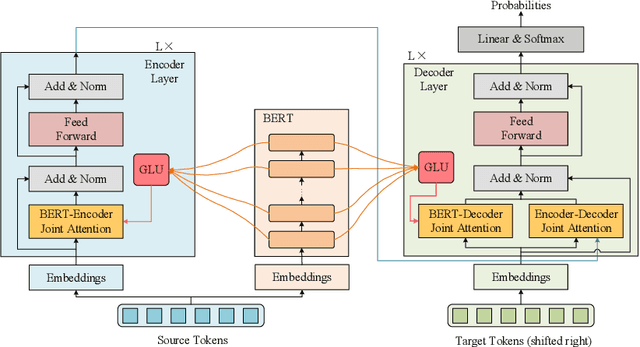
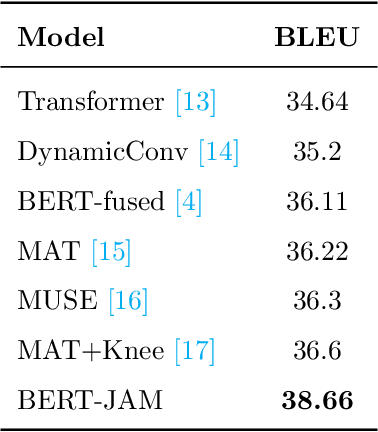
Abstract:BERT-enhanced neural machine translation (NMT) aims at leveraging BERT-encoded representations for translation tasks. A recently proposed approach uses attention mechanisms to fuse Transformer's encoder and decoder layers with BERT's last-layer representation and shows enhanced performance. However, their method doesn't allow for the flexible distribution of attention between the BERT representation and the encoder/decoder representation. In this work, we propose a novel BERT-enhanced NMT model called BERT-JAM which improves upon existing models from two aspects: 1) BERT-JAM uses joint-attention modules to allow the encoder/decoder layers to dynamically allocate attention between different representations, and 2) BERT-JAM allows the encoder/decoder layers to make use of BERT's intermediate representations by composing them using a gated linear unit (GLU). We train BERT-JAM with a novel three-phase optimization strategy that progressively unfreezes different components of BERT-JAM. Our experiments show that BERT-JAM achieves SOTA BLEU scores on multiple translation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge