Linjun Wu
Decoupling Contact for Fine-Grained Motion Style Transfer
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:Motion style transfer changes the style of a motion while retaining its content and is useful in computer animations and games. Contact is an essential component of motion style transfer that should be controlled explicitly in order to express the style vividly while enhancing motion naturalness and quality. However, it is unknown how to decouple and control contact to achieve fine-grained control in motion style transfer. In this paper, we present a novel style transfer method for fine-grained control over contacts while achieving both motion naturalness and spatial-temporal variations of style. Based on our empirical evidence, we propose controlling contact indirectly through the hip velocity, which can be further decomposed into the trajectory and contact timing, respectively. To this end, we propose a new model that explicitly models the correlations between motions and trajectory/contact timing/style, allowing us to decouple and control each separately. Our approach is built around a motion manifold, where hip controls can be easily integrated into a Transformer-based decoder. It is versatile in that it can generate motions directly as well as be used as post-processing for existing methods to improve quality and contact controllability. In addition, we propose a new metric that measures a correlation pattern of motions based on our empirical evidence, aligning well with human perception in terms of motion naturalness. Based on extensive evaluation, our method outperforms existing methods in terms of style expressivity and motion quality.
RSMT: Real-time Stylized Motion Transition for Characters
Jun 21, 2023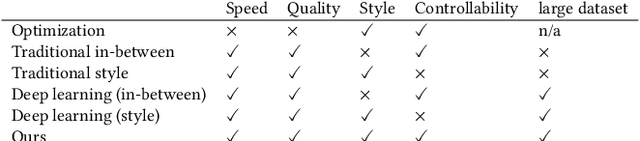
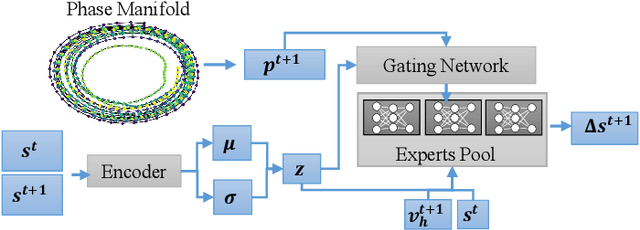
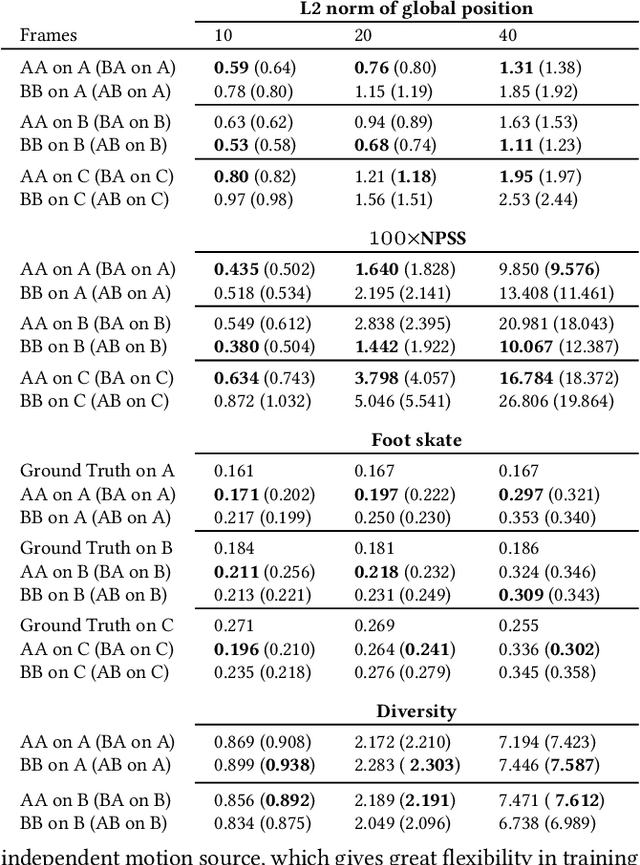
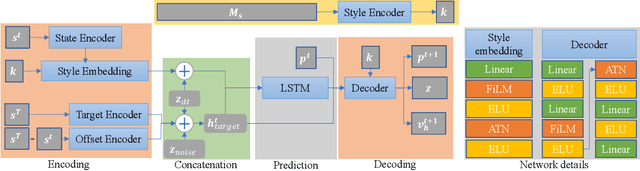
Abstract:Styled online in-between motion generation has important application scenarios in computer animation and games. Its core challenge lies in the need to satisfy four critical requirements simultaneously: generation speed, motion quality, style diversity, and synthesis controllability. While the first two challenges demand a delicate balance between simple fast models and learning capacity for generation quality, the latter two are rarely investigated together in existing methods, which largely focus on either control without style or uncontrolled stylized motions. To this end, we propose a Real-time Stylized Motion Transition method (RSMT) to achieve all aforementioned goals. Our method consists of two critical, independent components: a general motion manifold model and a style motion sampler. The former acts as a high-quality motion source and the latter synthesizes styled motions on the fly under control signals. Since both components can be trained separately on different datasets, our method provides great flexibility, requires less data, and generalizes well when no/few samples are available for unseen styles. Through exhaustive evaluation, our method proves to be fast, high-quality, versatile, and controllable. The code and data are available at {https://github.com/yuyujunjun/RSMT-Realtime-Stylized-Motion-Transition.}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge