Zeke Xie
Optimizing Few-Step Generation with Adaptive Matching Distillation
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) is a powerful acceleration paradigm, yet its stability is often compromised in Forbidden Zone, regions where the real teacher provides unreliable guidance while the fake teacher exerts insufficient repulsive force. In this work, we propose a unified optimization framework that reinterprets prior art as implicit strategies to avoid these corrupted regions. Based on this insight, we introduce Adaptive Matching Distillation (AMD), a self-correcting mechanism that utilizes reward proxies to explicitly detect and escape Forbidden Zones. AMD dynamically prioritizes corrective gradients via structural signal decomposition and introduces Repulsive Landscape Sharpening to enforce steep energy barriers against failure mode collapse. Extensive experiments across image and video generation tasks (e.g., SDXL, Wan2.1) and rigorous benchmarks (e.g., VBench, GenEval) demonstrate that AMD significantly enhances sample fidelity and training robustness. For instance, AMD improves the HPSv2 score on SDXL from 30.64 to 31.25, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. These findings validate that explicitly rectifying optimization trajectories within Forbidden Zones is essential for pushing the performance ceiling of few-step generative models.
Late-to-Early Training: LET LLMs Learn Earlier, So Faster and Better
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve remarkable empirical success through scaling model and data size, pretraining has become increasingly critical yet computationally prohibitive, hindering rapid development. Despite the availability of numerous pretrained LLMs developed at significant computational expense, a fundamental real-world question remains underexplored: \textit{Can we leverage existing small pretrained models to accelerate the training of larger models?} In this paper, we propose a Late-to-Early Training (LET) paradigm that enables LLMs to explicitly learn later knowledge in earlier steps and earlier layers. The core idea is to guide the early layers of an LLM during early training using representations from the late layers of a pretrained (i.e. late training phase) model. We identify two key mechanisms that drive LET's effectiveness: late-to-early-step learning and late-to-early-layer learning. These mechanisms significantly accelerate training convergence while robustly enhancing both language modeling capabilities and downstream task performance, enabling faster training with superior performance. Extensive experiments on 1.4B and 7B parameter models demonstrate LET's efficiency and effectiveness. Notably, when training a 1.4B LLM on the Pile dataset, our method achieves up to 1.6$\times$ speedup with nearly 5\% improvement in downstream task accuracy compared to standard training, even when using a pretrained model with 10$\times$ fewer parameters than the target model.
PISA: Piecewise Sparse Attention Is Wiser for Efficient Diffusion Transformers
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Transformers are fundamental for video and image generation, but their efficiency is bottlenecked by the quadratic complexity of attention. While block sparse attention accelerates computation by attending only critical key-value blocks, it suffers from degradation at high sparsity by discarding context. In this work, we discover that attention scores of non-critical blocks exhibit distributional stability, allowing them to be approximated accurately and efficiently rather than discarded, which is essentially important for sparse attention design. Motivated by this key insight, we propose PISA, a training-free Piecewise Sparse Attention that covers the full attention span with sub-quadratic complexity. Unlike the conventional keep-or-drop paradigm that directly drop the non-critical block information, PISA introduces a novel exact-or-approximate strategy: it maintains exact computation for critical blocks while efficiently approximating the remainder through block-wise Taylor expansion. This design allows PISA to serve as a faithful proxy to full attention, effectively bridging the gap between speed and quality. Experimental results demonstrate that PISA achieves 1.91 times and 2.57 times speedups on Wan2.1-14B and Hunyuan-Video, respectively, while consistently maintaining the highest quality among sparse attention methods. Notably, even for image generation on FLUX, PISA achieves a 1.2 times acceleration without compromising visual quality. Code is available at: https://github.com/xie-lab-ml/piecewise-sparse-attention.
Do All Individual Layers Help? An Empirical Study of Task-Interfering Layers in Vision-Language Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Current VLMs have demonstrated capabilities across a wide range of multimodal tasks. Typically, in a pretrained VLM, all layers are engaged by default to make predictions on downstream tasks. We find that intervening on a single layer, such as by zeroing its parameters, can improve the performance on certain tasks, indicating that some layers hinder rather than help downstream tasks. We systematically investigate how individual layers influence different tasks via layer intervention. Specifically, we measure the change in performance relative to the base model after intervening on each layer and observe improvements when bypassing specific layers. This improvement can be generalizable across models and datasets, indicating the presence of Task-Interfering Layers that harm downstream tasks' performance. We introduce Task-Layer Interaction Vector, which quantifies the effect of intervening on each layer of a VLM given a task. These task-interfering layers exhibit task-specific sensitivity patterns: tasks requiring similar capabilities show consistent response trends under layer interventions, as evidenced by the high similarity in their task-layer interaction vectors. Inspired by these findings, we propose TaLo (Task-Adaptive Layer Knockout), a training-free, test-time adaptation method that dynamically identifies and bypasses the most interfering layer for a given task. Without parameter updates, TaLo improves performance across various models and datasets, including boosting Qwen-VL's accuracy on the Maps task in ScienceQA by up to 16.6%. Our work reveals an unexpected form of modularity in pretrained VLMs and provides a plug-and-play, training-free mechanism to unlock hidden capabilities at inference time. The source code will be publicly available.
Learning to Accelerate Vision-Language-Action Models through Adaptive Visual Token Caching
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated remarkable generalization capabilities in robotic manipulation tasks, yet their substantial computational overhead remains a critical obstacle to real-world deployment. Improving inference efficiency is therefore essential for practical robotic applications. Existing acceleration methods often rely on heuristic or static strategies--such as rule-based token caching or pruning--that are decoupled from task objectives and fail to adapt to dynamic scene changes. In this work, we reformulate inference acceleration as a learnable policy optimization problem and propose a novel framework that integrates a dynamic, task-aware decision-making process directly into the VLA model. At its core are two lightweight, cooperative modules: a Cached Token Selector, which determines which tokens should be reused, and a Cache Ratio Predictor, which controls how many tokens to reuse. Training these modules is non-trivial due to their discrete decisions. We address this by adopting a differentiable relaxation that allows gradient-based end-to-end optimization. Extensive experiments on the LIBERO and SIMPLER benchmarks, as well as real-robot evaluations, show that our method achieves a 1.76x wall-clock inference speedup while simultaneously improving the average success rate by 1.9 percentage points (from 75.0% to 76.9%) on LIBERO and by 5.0 percentage points on real-world tasks, significantly outperforming existing baselines. This work highlights the potential of learning task-aware computational allocation policies, paving the way for VLA models that are both powerful and efficient.
Mano: Restriking Manifold Optimization for LLM Training
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have emerged as a significant advancement in artificial intelligence, the hardware and computational costs for training LLMs are also significantly burdensome. Among the state-of-the-art optimizers, AdamW relies on diagonal curvature estimates and ignores structural properties, while Muon applies global spectral normalization at the expense of losing curvature information. In this study, we restriked manifold optimization methods for training LLMs, which may address both optimizers' limitations, while conventional manifold optimization methods have been largely overlooked due to the poor performance in large-scale model optimization. By innovatively projecting the momentum onto the tangent space of model parameters and constraining it on a rotational Oblique manifold, we propose a novel, powerful, and efficient optimizer **Mano** that is the first to bridge the performance gap between manifold optimization and modern optimizers. Extensive experiments on the LLaMA and Qwen3 models demonstrate that Mano consistently and significantly outperforms AdamW and Muon even with less memory consumption and computational complexity, respectively, suggesting an expanded Pareto frontier in terms of space and time efficiency.
CMPhysBench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models in Condensed Matter Physics
Aug 25, 2025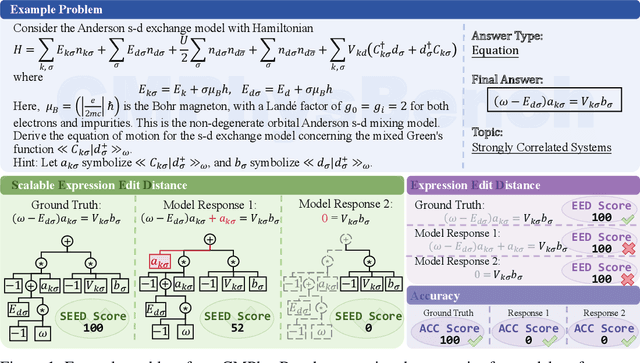
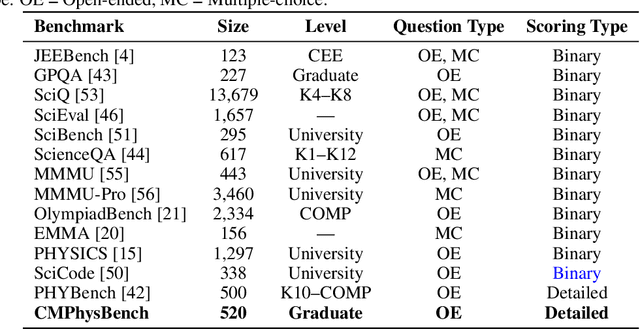
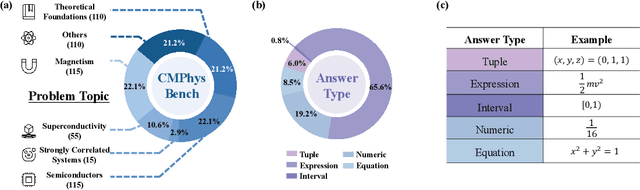
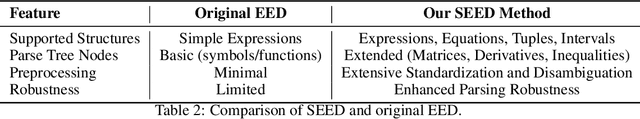
Abstract:We introduce CMPhysBench, designed to assess the proficiency of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Condensed Matter Physics, as a novel Benchmark. CMPhysBench is composed of more than 520 graduate-level meticulously curated questions covering both representative subfields and foundational theoretical frameworks of condensed matter physics, such as magnetism, superconductivity, strongly correlated systems, etc. To ensure a deep understanding of the problem-solving process,we focus exclusively on calculation problems, requiring LLMs to independently generate comprehensive solutions. Meanwhile, leveraging tree-based representations of expressions, we introduce the Scalable Expression Edit Distance (SEED) score, which provides fine-grained (non-binary) partial credit and yields a more accurate assessment of similarity between prediction and ground-truth. Our results show that even the best models, Grok-4, reach only 36 average SEED score and 28% accuracy on CMPhysBench, underscoring a significant capability gap, especially for this practical and frontier domain relative to traditional physics. The code anddataset are publicly available at https://github.com/CMPhysBench/CMPhysBench.
Understanding Data Influence with Differential Approximation
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Data plays a pivotal role in the groundbreaking advancements in artificial intelligence. The quantitative analysis of data significantly contributes to model training, enhancing both the efficiency and quality of data utilization. However, existing data analysis tools often lag in accuracy. For instance, many of these tools even assume that the loss function of neural networks is convex. These limitations make it challenging to implement current methods effectively. In this paper, we introduce a new formulation to approximate a sample's influence by accumulating the differences in influence between consecutive learning steps, which we term Diff-In. Specifically, we formulate the sample-wise influence as the cumulative sum of its changes/differences across successive training iterations. By employing second-order approximations, we approximate these difference terms with high accuracy while eliminating the need for model convexity required by existing methods. Despite being a second-order method, Diff-In maintains computational complexity comparable to that of first-order methods and remains scalable. This efficiency is achieved by computing the product of the Hessian and gradient, which can be efficiently approximated using finite differences of first-order gradients. We assess the approximation accuracy of Diff-In both theoretically and empirically. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates that Diff-In achieves significantly lower approximation error compared to existing influence estimators. Extensive experiments further confirm its superior performance across multiple benchmark datasets in three data-centric tasks: data cleaning, data deletion, and coreset selection. Notably, our experiments on data pruning for large-scale vision-language pre-training show that Diff-In can scale to millions of data points and outperforms strong baselines.
Multiphysics Bench: Benchmarking and Investigating Scientific Machine Learning for Multiphysics PDEs
May 23, 2025



Abstract:Solving partial differential equations (PDEs) with machine learning has recently attracted great attention, as PDEs are fundamental tools for modeling real-world systems that range from fundamental physical science to advanced engineering disciplines. Most real-world physical systems across various disciplines are actually involved in multiple coupled physical fields rather than a single field. However, previous machine learning studies mainly focused on solving single-field problems, but overlooked the importance and characteristics of multiphysics problems in real world. Multiphysics PDEs typically entail multiple strongly coupled variables, thereby introducing additional complexity and challenges, such as inter-field coupling. Both benchmarking and solving multiphysics problems with machine learning remain largely unexamined. To identify and address the emerging challenges in multiphysics problems, we mainly made three contributions in this work. First, we collect the first general multiphysics dataset, the Multiphysics Bench, that focuses on multiphysics PDE solving with machine learning. Multiphysics Bench is also the most comprehensive PDE dataset to date, featuring the broadest range of coupling types, the greatest diversity of PDE formulations, and the largest dataset scale. Second, we conduct the first systematic investigation on multiple representative learning-based PDE solvers, such as PINNs, FNO, DeepONet, and DiffusionPDE solvers, on multiphysics problems. Unfortunately, naively applying these existing solvers usually show very poor performance for solving multiphysics. Third, through extensive experiments and discussions, we report multiple insights and a bag of useful tricks for solving multiphysics with machine learning, motivating future directions in the study and simulation of complex, coupled physical systems.
DSADF: Thinking Fast and Slow for Decision Making
May 13, 2025



Abstract:Although Reinforcement Learning (RL) agents are effective in well-defined environments, they often struggle to generalize their learned policies to dynamic settings due to their reliance on trial-and-error interactions. Recent work has explored applying Large Language Models (LLMs) or Vision Language Models (VLMs) to boost the generalization of RL agents through policy optimization guidance or prior knowledge. However, these approaches often lack seamless coordination between the RL agent and the foundation model, leading to unreasonable decision-making in unfamiliar environments and efficiency bottlenecks. Making full use of the inferential capabilities of foundation models and the rapid response capabilities of RL agents and enhancing the interaction between the two to form a dual system is still a lingering scientific question. To address this problem, we draw inspiration from Kahneman's theory of fast thinking (System 1) and slow thinking (System 2), demonstrating that balancing intuition and deep reasoning can achieve nimble decision-making in a complex world. In this study, we propose a Dual-System Adaptive Decision Framework (DSADF), integrating two complementary modules: System 1, comprising an RL agent and a memory space for fast and intuitive decision making, and System 2, driven by a VLM for deep and analytical reasoning. DSADF facilitates efficient and adaptive decision-making by combining the strengths of both systems. The empirical study in the video game environment: Crafter and Housekeep demonstrates the effectiveness of our proposed method, showing significant improvements in decision abilities for both unseen and known tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge