Songyuan Li
SpaCE-10: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models in Compositional Spatial Intelligence
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in various multimodal tasks. To pursue higher intelligence in space, MLLMs require integrating multiple atomic spatial capabilities to handle complex and dynamic tasks. However, existing benchmarks struggle to comprehensively evaluate the spatial intelligence of common MLLMs from the atomic level to the compositional level. To fill this gap, we present SpaCE-10, a comprehensive benchmark for compositional spatial evaluations. In SpaCE-10, we define 10 atomic spatial capabilities, which are combined to form 8 compositional capabilities. Based on these definitions, we propose a novel hierarchical annotation pipeline to generate high-quality and diverse question-answer (QA) pairs. With over 150+ hours of human expert effort, we obtain over 5k QA pairs for 811 real indoor scenes in SpaCE-10, which covers various evaluation settings like point cloud input and multi-choice QA. We conduct an extensive evaluation of common MLLMs on SpaCE-10 and find that even the most advanced MLLM still lags behind humans by large margins. Through our careful study, we also draw several significant findings that benefit the MLLM community. For example, we reveal that the shortcoming of counting capability greatly limits the compositional spatial capabilities of existing MLLMs. The evaluation code and benchmark datasets are available at https://github.com/Cuzyoung/SpaCE-10.
Incentivizing Multi-Tenant Split Federated Learning for Foundation Models at the Network Edge
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) such as GPT-4 exhibit exceptional generative capabilities across diverse downstream tasks through fine-tuning. Split Federated Learning (SFL) facilitates privacy-preserving FM fine-tuning on resource-constrained local devices by offloading partial FM computations to edge servers, enabling device-edge synergistic fine-tuning. Practical edge networks often host multiple SFL tenants to support diversified downstream tasks. However, existing research primarily focuses on single-tenant SFL scenarios, and lacks tailored incentive mechanisms for multi-tenant settings, which are essential to effectively coordinate self-interested local devices for participation in various downstream tasks, ensuring that each SFL tenant's distinct FM fine-tuning requirements (e.g., FM types, performance targets, and fine-tuning deadlines) are met. To address this gap, we propose a novel Price-Incentive Mechanism (PRINCE) that guides multiple SFL tenants to offer strategic price incentives, which solicit high-quality device participation for efficient FM fine-tuning. Specifically, we first develop a bias-resilient global SFL model aggregation scheme to eliminate model biases caused by independent device participation. We then derive a rigorous SFL convergence bound to evaluate the contributions of heterogeneous devices to FM performance improvements, guiding the incentive strategies of SFL tenants. Furthermore, we model inter-tenant device competition as a congestion game for Stackelberg equilibrium (SE) analysis, deriving each SFL tenant's optimal incentive strategy. Extensive simulations involving four representative SFL tenant types (ViT, BERT, Whisper, and LLaMA) across diverse data modalities (text, images, and audio) demonstrate that PRINCE accelerates FM fine-tuning by up to 3.07x compared to state-of-the-art approaches, while consistently meeting fine-tuning performance targets.
Dynamic Pricing for On-Demand DNN Inference in the Edge-AI Market
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:The convergence of edge computing and AI gives rise to Edge-AI, which enables the deployment of real-time AI applications and services at the network edge. One of the fundamental research issues in Edge-AI is edge inference acceleration, which aims to realize low-latency high-accuracy DNN inference services by leveraging the fine-grained offloading of partitioned inference tasks from end devices to edge servers. However, existing research has yet to adopt a practical Edge-AI market perspective, which would systematically explore the personalized inference needs of AI users (e.g., inference accuracy, latency, and task complexity), the revenue incentives for AI service providers that offer edge inference services, and multi-stakeholder governance within a market-oriented context. To bridge this gap, we propose an Auction-based Edge Inference Pricing Mechanism (AERIA) for revenue maximization to tackle the multi-dimensional optimization problem of DNN model partition, edge inference pricing, and resource allocation. We investigate the multi-exit device-edge synergistic inference scheme for on-demand DNN inference acceleration, and analyse the auction dynamics amongst the AI service providers, AI users and edge infrastructure provider. Owing to the strategic mechanism design via randomized consensus estimate and cost sharing techniques, the Edge-AI market attains several desirable properties, including competitiveness in revenue maximization, incentive compatibility, and envy-freeness, which are crucial to maintain the effectiveness, truthfulness, and fairness of our auction outcomes. The extensive simulation experiments based on four representative DNN inference workloads demonstrate that our AERIA mechanism significantly outperforms several state-of-the-art approaches in revenue maximization, demonstrating the efficacy of AERIA for on-demand DNN inference in the Edge-AI market.
F3A-GAN: Facial Flow for Face Animation with Generative Adversarial Networks
May 13, 2022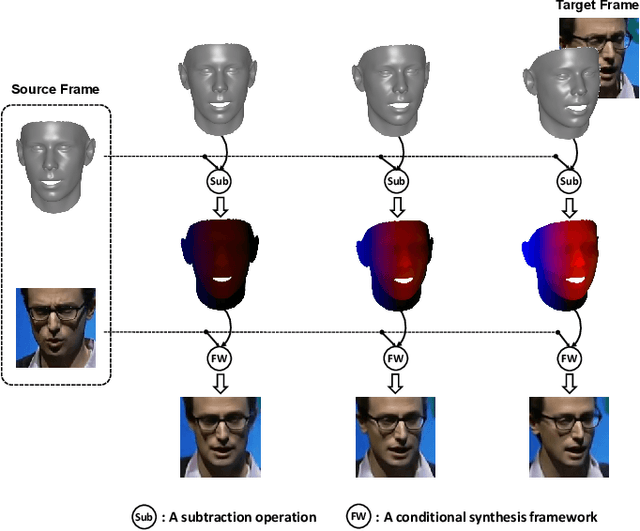



Abstract:Formulated as a conditional generation problem, face animation aims at synthesizing continuous face images from a single source image driven by a set of conditional face motion. Previous works mainly model the face motion as conditions with 1D or 2D representation (e.g., action units, emotion codes, landmark), which often leads to low-quality results in some complicated scenarios such as continuous generation and largepose transformation. To tackle this problem, the conditions are supposed to meet two requirements, i.e., motion information preserving and geometric continuity. To this end, we propose a novel representation based on a 3D geometric flow, termed facial flow, to represent the natural motion of the human face at any pose. Compared with other previous conditions, the proposed facial flow well controls the continuous changes to the face. After that, in order to utilize the facial flow for face editing, we build a synthesis framework generating continuous images with conditional facial flows. To fully take advantage of the motion information of facial flows, a hierarchical conditional framework is designed to combine the extracted multi-scale appearance features from images and motion features from flows in a hierarchical manner. The framework then decodes multiple fused features back to images progressively. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
Multitask Identity-Aware Image Steganography via Minimax Optimization
Jul 13, 2021



Abstract:High-capacity image steganography, aimed at concealing a secret image in a cover image, is a technique to preserve sensitive data, e.g., faces and fingerprints. Previous methods focus on the security during transmission and subsequently run a risk of privacy leakage after the restoration of secret images at the receiving end. To address this issue, we propose a framework, called Multitask Identity-Aware Image Steganography (MIAIS), to achieve direct recognition on container images without restoring secret images. The key issue of the direct recognition is to preserve identity information of secret images into container images and make container images look similar to cover images at the same time. Thus, we introduce a simple content loss to preserve the identity information, and design a minimax optimization to deal with the contradictory aspects. We demonstrate that the robustness results can be transferred across different cover datasets. In order to be flexible for the secret image restoration in some cases, we incorporate an optional restoration network into our method, providing a multitask framework. The experiments under the multitask scenario show the effectiveness of our framework compared with other visual information hiding methods and state-of-the-art high-capacity image steganography methods.
VersatileGait: A Large-Scale Synthetic Gait Dataset Towards in-the-Wild Simulation
Jun 01, 2021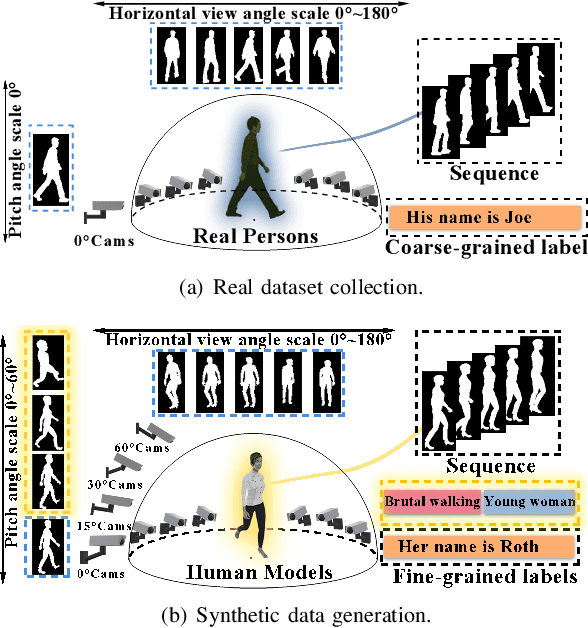
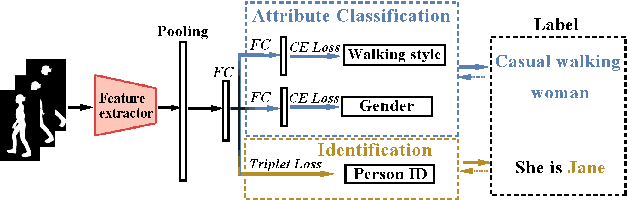
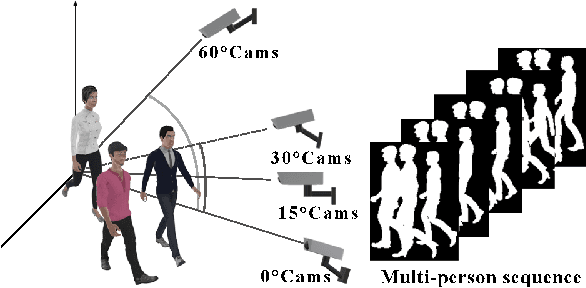
Abstract:Gait recognition has a rapid development in recent years. However, gait recognition in the wild is not well explored yet. An obvious reason could be ascribed to the lack of diverse training data from the perspective of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. To remedy this problem, we propose to construct a large-scale gait dataset with the help of controllable computer simulation. In detail, to diversify the intrinsic factors of gait, we generate numerous characters with diverse attributes and empower them with various types of walking styles. To diversify the extrinsic factors of gait, we build a complicated scene with a dense camera layout. Finally, we design an automated generation toolkit under Unity3D for simulating the walking scenario and capturing the gait data automatically. As a result, we obtain an in-the-wild gait dataset, called VersatileGait, which has more than one million silhouette sequences of 10,000 subjects with diverse scenarios. VersatileGait possesses several nice properties, including huge dataset size, diverse pedestrian attributes, complicated camera layout, high-quality annotations, small domain gap with the real one, good scalability for new demands, and no privacy issues. Based on VersatileGait, we propose series of experiments and applications for both research exploration of gait in the wild and practical applications. Our dataset and its corresponding generation toolkit will be publicly available for further studies.
Recent Advances and Trends in Multimodal Deep Learning: A Review
May 24, 2021



Abstract:Deep Learning has implemented a wide range of applications and has become increasingly popular in recent years. The goal of multimodal deep learning is to create models that can process and link information using various modalities. Despite the extensive development made for unimodal learning, it still cannot cover all the aspects of human learning. Multimodal learning helps to understand and analyze better when various senses are engaged in the processing of information. This paper focuses on multiple types of modalities, i.e., image, video, text, audio, body gestures, facial expressions, and physiological signals. Detailed analysis of past and current baseline approaches and an in-depth study of recent advancements in multimodal deep learning applications has been provided. A fine-grained taxonomy of various multimodal deep learning applications is proposed, elaborating on different applications in more depth. Architectures and datasets used in these applications are also discussed, along with their evaluation metrics. Last, main issues are highlighted separately for each domain along with their possible future research directions.
Deep RGB-D Saliency Detection with Depth-Sensitive Attention and Automatic Multi-Modal Fusion
Mar 22, 2021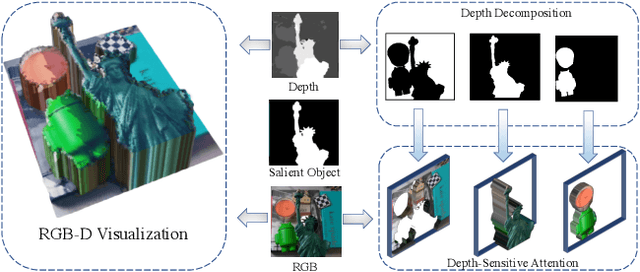
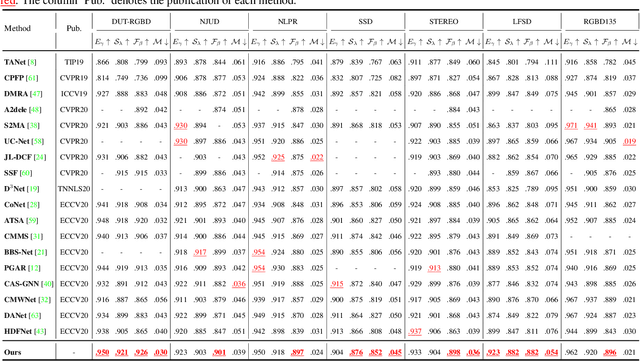
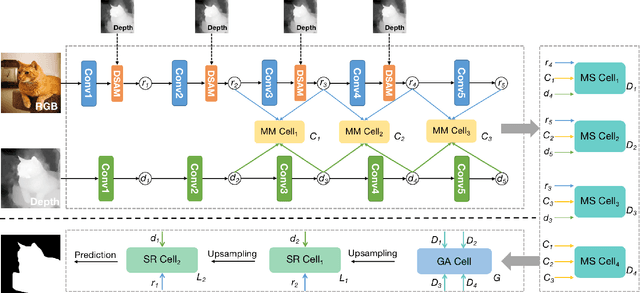
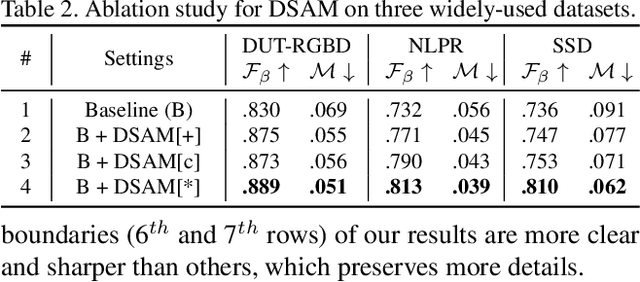
Abstract:RGB-D salient object detection (SOD) is usually formulated as a problem of classification or regression over two modalities, i.e., RGB and depth. Hence, effective RGBD feature modeling and multi-modal feature fusion both play a vital role in RGB-D SOD. In this paper, we propose a depth-sensitive RGB feature modeling scheme using the depth-wise geometric prior of salient objects. In principle, the feature modeling scheme is carried out in a depth-sensitive attention module, which leads to the RGB feature enhancement as well as the background distraction reduction by capturing the depth geometry prior. Moreover, to perform effective multi-modal feature fusion, we further present an automatic architecture search approach for RGB-D SOD, which does well in finding out a feasible architecture from our specially designed multi-modal multi-scale search space. Extensive experiments on seven standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach against the state-of-the-art.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Image Classification via Structure-Conditioned Adversarial Learning
Mar 04, 2021



Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) typically carries out knowledge transfer from a label-rich source domain to an unlabeled target domain by adversarial learning. In principle, existing UDA approaches mainly focus on the global distribution alignment between domains while ignoring the intrinsic local distribution properties. Motivated by this observation, we propose an end-to-end structure-conditioned adversarial learning scheme (SCAL) that is able to preserve the intra-class compactness during domain distribution alignment. By using local structures as structure-aware conditions, the proposed scheme is implemented in a structure-conditioned adversarial learning pipeline. The above learning procedure is iteratively performed by alternating between local structures establishment and structure-conditioned adversarial learning. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme in UDA scenarios.
VersatileGait: A Large-Scale Synthetic Gait Dataset with Fine-GrainedAttributes and Complicated Scenarios
Jan 05, 2021
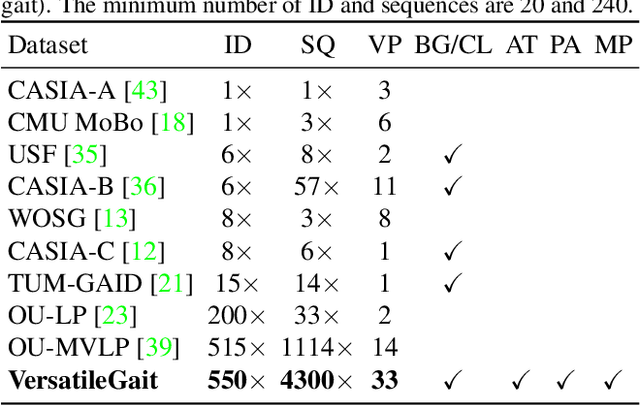
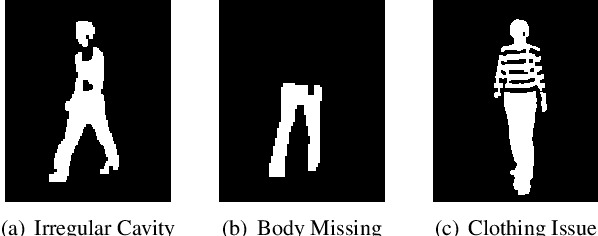
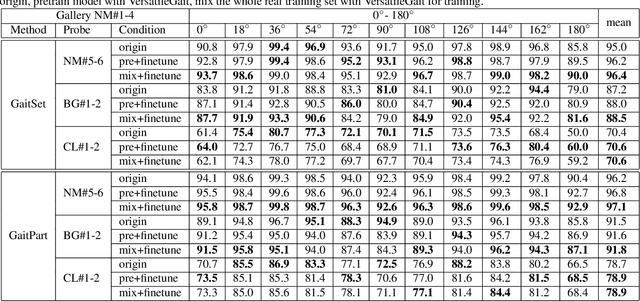
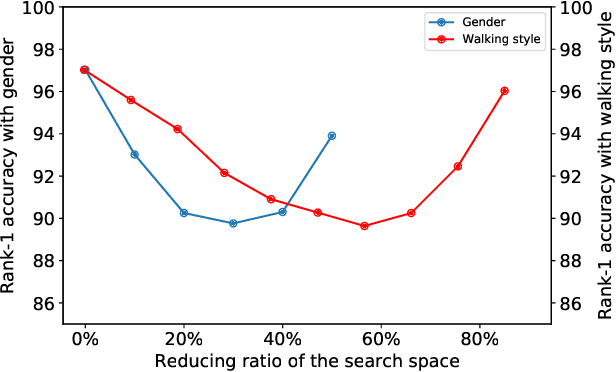
Abstract:With the motivation of practical gait recognition applications, we propose to automatically create a large-scale synthetic gait dataset (called VersatileGait) by a game engine, which consists of around one million silhouette sequences of 11,000 subjects with fine-grained attributes in various complicated scenarios. Compared with existing real gait datasets with limited samples and simple scenarios, the proposed VersatileGait dataset possesses several nice properties, including huge dataset size, high sample diversity, high-quality annotations, multi-pitch angles, small domain gap with the real one, etc. Furthermore, we investigate the effectiveness of our dataset (e.g., domain transfer after pretraining). Then, we use the fine-grained attributes from VersatileGait to promote gait recognition in both accuracy and speed, and meanwhile justify the gait recognition performance under multi-pitch angle settings. Additionally, we explore a variety of potential applications for research.Extensive experiments demonstrate the value and effective-ness of the proposed VersatileGait in gait recognition along with its associated applications. We will release both VersatileGait and its corresponding data generation toolkit for further studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge