Rohit Girdhar
Jack
Human detectors are surprisingly powerful reward models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Video generation models have recently achieved impressive visual fidelity and temporal coherence. Yet, they continue to struggle with complex, non-rigid motions, especially when synthesizing humans performing dynamic actions such as sports, dance, etc. Generated videos often exhibit missing or extra limbs, distorted poses, or physically implausible actions. In this work, we propose a remarkably simple reward model, HuDA, to quantify and improve the human motion in generated videos. HuDA integrates human detection confidence for appearance quality, and a temporal prompt alignment score to capture motion realism. We show this simple reward function that leverages off-the-shelf models without any additional training, outperforms specialized models finetuned with manually annotated data. Using HuDA for Group Reward Policy Optimization (GRPO) post-training of video models, we significantly enhance video generation, especially when generating complex human motions, outperforming state-of-the-art models like Wan 2.1, with win-rate of 73%. Finally, we demonstrate that HuDA improves generation quality beyond just humans, for instance, significantly improving generation of animal videos and human-object interactions.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Diffusion Autoencoders are Scalable Image Tokenizers
Jan 30, 2025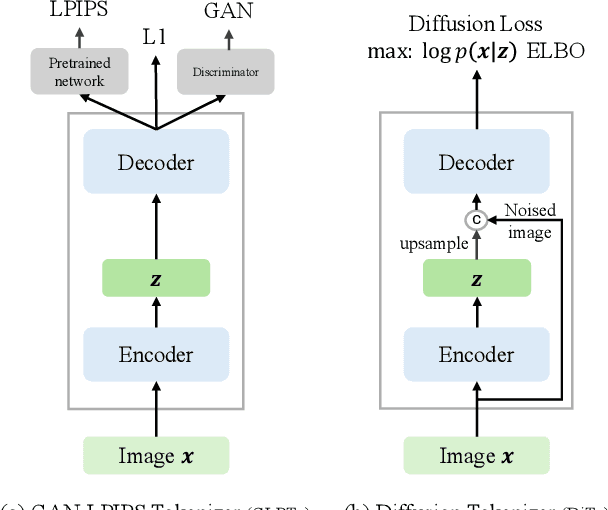
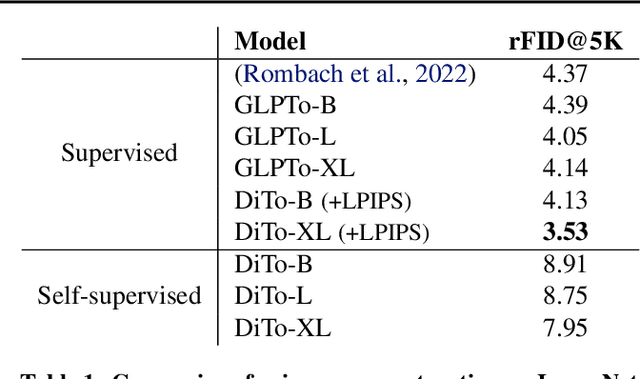


Abstract:Tokenizing images into compact visual representations is a key step in learning efficient and high-quality image generative models. We present a simple diffusion tokenizer (DiTo) that learns compact visual representations for image generation models. Our key insight is that a single learning objective, diffusion L2 loss, can be used for training scalable image tokenizers. Since diffusion is already widely used for image generation, our insight greatly simplifies training such tokenizers. In contrast, current state-of-the-art tokenizers rely on an empirically found combination of heuristics and losses, thus requiring a complex training recipe that relies on non-trivially balancing different losses and pretrained supervised models. We show design decisions, along with theoretical grounding, that enable us to scale DiTo for learning competitive image representations. Our results show that DiTo is a simpler, scalable, and self-supervised alternative to the current state-of-the-art image tokenizer which is supervised. DiTo achieves competitive or better quality than state-of-the-art in image reconstruction and downstream image generation tasks.
LLMs can see and hear without any training
Jan 30, 2025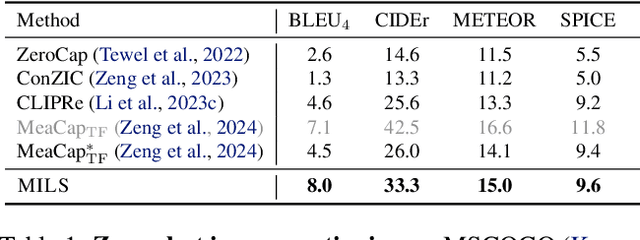
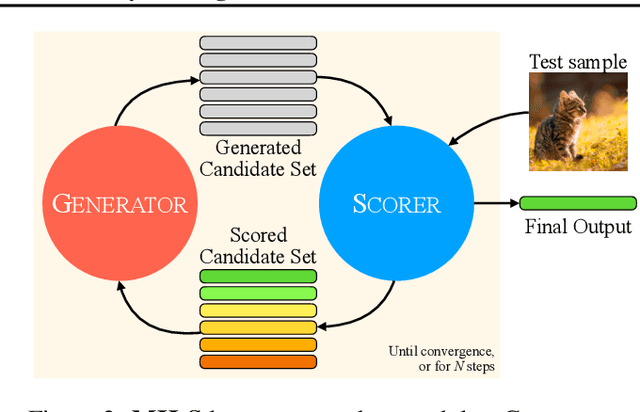

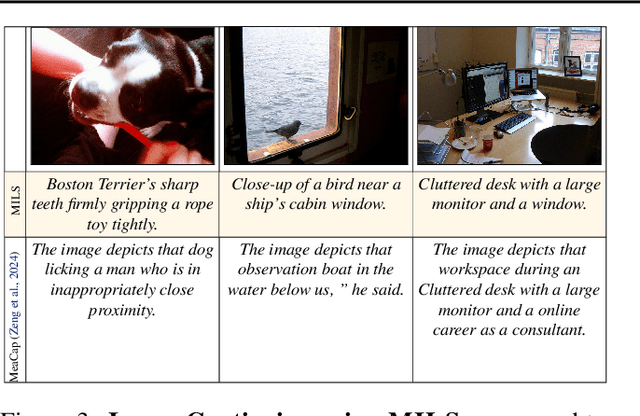
Abstract:We present MILS: Multimodal Iterative LLM Solver, a surprisingly simple, training-free approach, to imbue multimodal capabilities into your favorite LLM. Leveraging their innate ability to perform multi-step reasoning, MILS prompts the LLM to generate candidate outputs, each of which are scored and fed back iteratively, eventually generating a solution to the task. This enables various applications that typically require training specialized models on task-specific data. In particular, we establish a new state-of-the-art on emergent zero-shot image, video and audio captioning. MILS seamlessly applies to media generation as well, discovering prompt rewrites to improve text-to-image generation, and even edit prompts for style transfer! Finally, being a gradient-free optimization approach, MILS can invert multimodal embeddings into text, enabling applications like cross-modal arithmetic.
MotiF: Making Text Count in Image Animation with Motion Focal Loss
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Text-Image-to-Video (TI2V) generation aims to generate a video from an image following a text description, which is also referred to as text-guided image animation. Most existing methods struggle to generate videos that align well with the text prompts, particularly when motion is specified. To overcome this limitation, we introduce MotiF, a simple yet effective approach that directs the model's learning to the regions with more motion, thereby improving the text alignment and motion generation. We use optical flow to generate a motion heatmap and weight the loss according to the intensity of the motion. This modified objective leads to noticeable improvements and complements existing methods that utilize motion priors as model inputs. Additionally, due to the lack of a diverse benchmark for evaluating TI2V generation, we propose TI2V Bench, a dataset consists of 320 image-text pairs for robust evaluation. We present a human evaluation protocol that asks the annotators to select an overall preference between two videos followed by their justifications. Through a comprehensive evaluation on TI2V Bench, MotiF outperforms nine open-sourced models, achieving an average preference of 72%. The TI2V Bench is released in https://wang-sj16.github.io/motif/.
Movie Gen: A Cast of Media Foundation Models
Oct 17, 2024
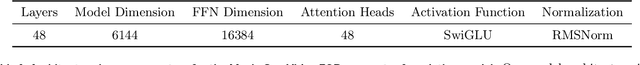
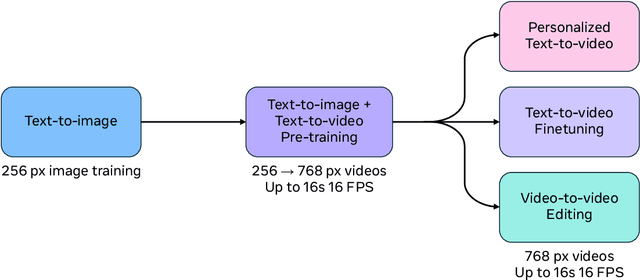
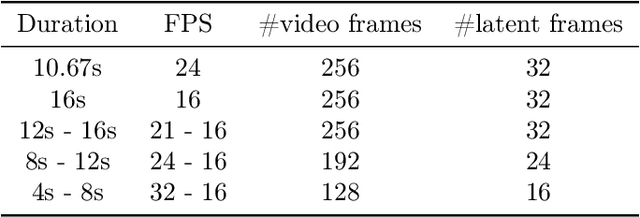
Abstract:We present Movie Gen, a cast of foundation models that generates high-quality, 1080p HD videos with different aspect ratios and synchronized audio. We also show additional capabilities such as precise instruction-based video editing and generation of personalized videos based on a user's image. Our models set a new state-of-the-art on multiple tasks: text-to-video synthesis, video personalization, video editing, video-to-audio generation, and text-to-audio generation. Our largest video generation model is a 30B parameter transformer trained with a maximum context length of 73K video tokens, corresponding to a generated video of 16 seconds at 16 frames-per-second. We show multiple technical innovations and simplifications on the architecture, latent spaces, training objectives and recipes, data curation, evaluation protocols, parallelization techniques, and inference optimizations that allow us to reap the benefits of scaling pre-training data, model size, and training compute for training large scale media generation models. We hope this paper helps the research community to accelerate progress and innovation in media generation models. All videos from this paper are available at https://go.fb.me/MovieGenResearchVideos.
Human Action Anticipation: A Survey
Oct 17, 2024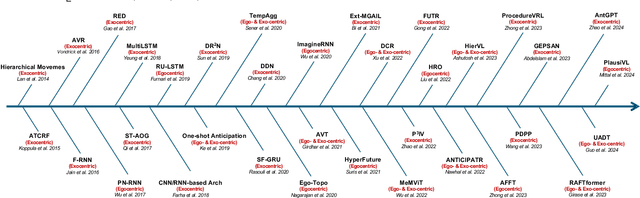
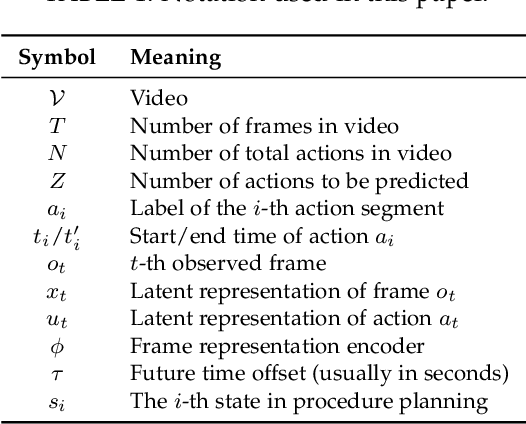
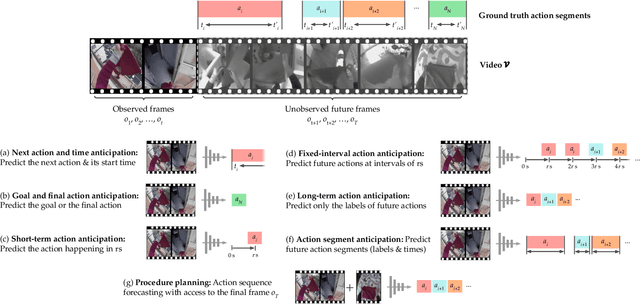
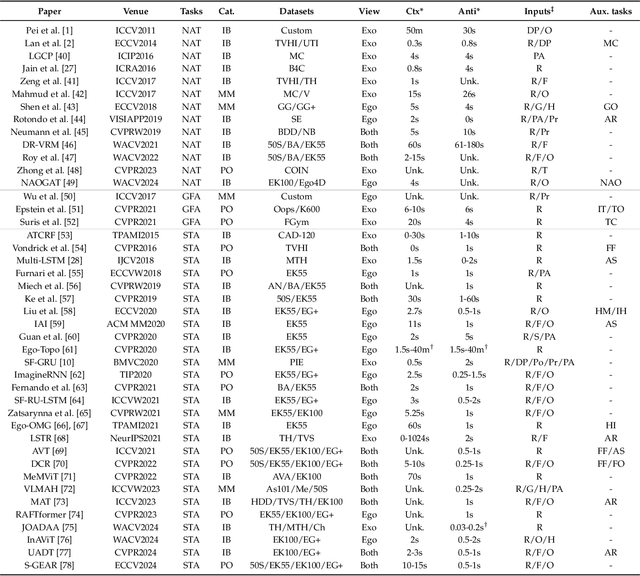
Abstract:Predicting future human behavior is an increasingly popular topic in computer vision, driven by the interest in applications such as autonomous vehicles, digital assistants and human-robot interactions. The literature on behavior prediction spans various tasks, including action anticipation, activity forecasting, intent prediction, goal prediction, and so on. Our survey aims to tie together this fragmented literature, covering recent technical innovations as well as the development of new large-scale datasets for model training and evaluation. We also summarize the widely-used metrics for different tasks and provide a comprehensive performance comparison of existing approaches on eleven action anticipation datasets. This survey serves as not only a reference for contemporary methodologies in action anticipation, but also a guideline for future research direction of this evolving landscape.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
SoundingActions: Learning How Actions Sound from Narrated Egocentric Videos
Apr 08, 2024
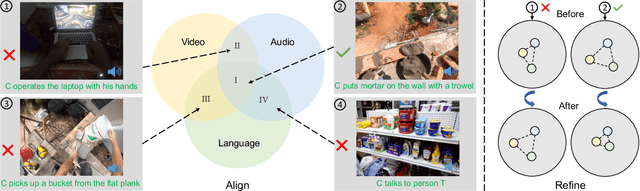
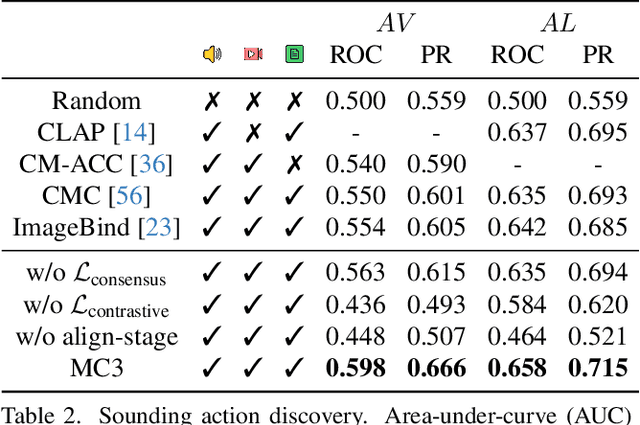
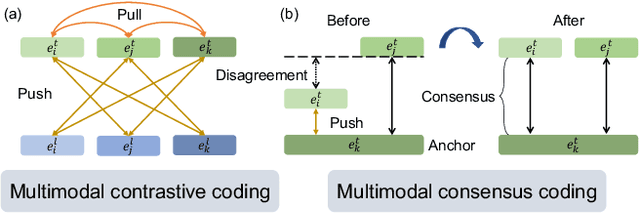
Abstract:We propose a novel self-supervised embedding to learn how actions sound from narrated in-the-wild egocentric videos. Whereas existing methods rely on curated data with known audio-visual correspondence, our multimodal contrastive-consensus coding (MC3) embedding reinforces the associations between audio, language, and vision when all modality pairs agree, while diminishing those associations when any one pair does not. We show our approach can successfully discover how the long tail of human actions sound from egocentric video, outperforming an array of recent multimodal embedding techniques on two datasets (Ego4D and EPIC-Sounds) and multiple cross-modal tasks.
InstanceDiffusion: Instance-level Control for Image Generation
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models produce high quality images but do not offer control over individual instances in the image. We introduce InstanceDiffusion that adds precise instance-level control to text-to-image diffusion models. InstanceDiffusion supports free-form language conditions per instance and allows flexible ways to specify instance locations such as simple single points, scribbles, bounding boxes or intricate instance segmentation masks, and combinations thereof. We propose three major changes to text-to-image models that enable precise instance-level control. Our UniFusion block enables instance-level conditions for text-to-image models, the ScaleU block improves image fidelity, and our Multi-instance Sampler improves generations for multiple instances. InstanceDiffusion significantly surpasses specialized state-of-the-art models for each location condition. Notably, on the COCO dataset, we outperform previous state-of-the-art by 20.4% AP$_{50}^\text{box}$ for box inputs, and 25.4% IoU for mask inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge