Abhishek Kadian
Jack
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
Emu: Enhancing Image Generation Models Using Photogenic Needles in a Haystack
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:Training text-to-image models with web scale image-text pairs enables the generation of a wide range of visual concepts from text. However, these pre-trained models often face challenges when it comes to generating highly aesthetic images. This creates the need for aesthetic alignment post pre-training. In this paper, we propose quality-tuning to effectively guide a pre-trained model to exclusively generate highly visually appealing images, while maintaining generality across visual concepts. Our key insight is that supervised fine-tuning with a set of surprisingly small but extremely visually appealing images can significantly improve the generation quality. We pre-train a latent diffusion model on $1.1$ billion image-text pairs and fine-tune it with only a few thousand carefully selected high-quality images. The resulting model, Emu, achieves a win rate of $82.9\%$ compared with its pre-trained only counterpart. Compared to the state-of-the-art SDXLv1.0, Emu is preferred $68.4\%$ and $71.3\%$ of the time on visual appeal on the standard PartiPrompts and our Open User Input benchmark based on the real-world usage of text-to-image models. In addition, we show that quality-tuning is a generic approach that is also effective for other architectures, including pixel diffusion and masked generative transformer models.
Filtering, Distillation, and Hard Negatives for Vision-Language Pre-Training
Jan 05, 2023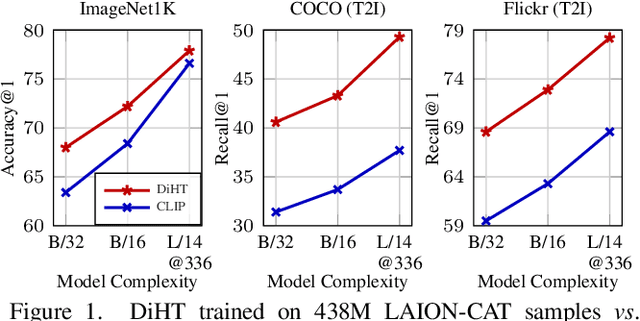
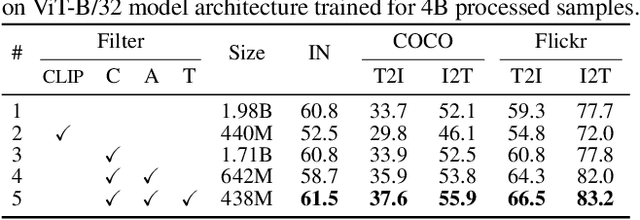
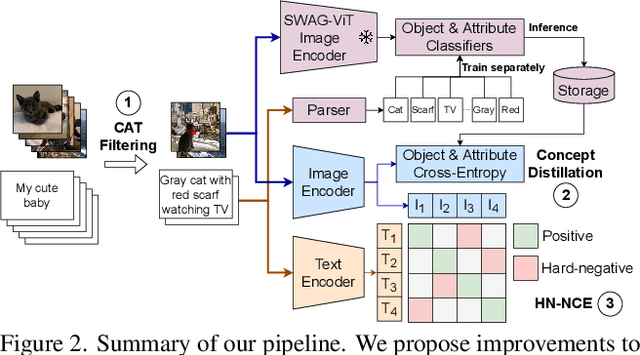
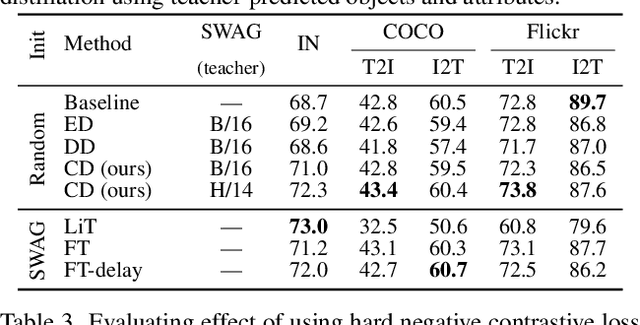
Abstract:Vision-language models trained with contrastive learning on large-scale noisy data are becoming increasingly popular for zero-shot recognition problems. In this paper we improve the following three aspects of the contrastive pre-training pipeline: dataset noise, model initialization and the training objective. First, we propose a straightforward filtering strategy titled Complexity, Action, and Text-spotting (CAT) that significantly reduces dataset size, while achieving improved performance across zero-shot vision-language tasks. Next, we propose an approach titled Concept Distillation to leverage strong unimodal representations for contrastive training that does not increase training complexity while outperforming prior work. Finally, we modify the traditional contrastive alignment objective, and propose an importance-sampling approach to up-sample the importance of hard-negatives without adding additional complexity. On an extensive zero-shot benchmark of 29 tasks, our Distilled and Hard-negative Training (DiHT) approach improves on 20 tasks compared to the baseline. Furthermore, for few-shot linear probing, we propose a novel approach that bridges the gap between zero-shot and few-shot performance, substantially improving over prior work. Models are available at https://github.com/facebookresearch/diht.
PACO: Parts and Attributes of Common Objects
Jan 04, 2023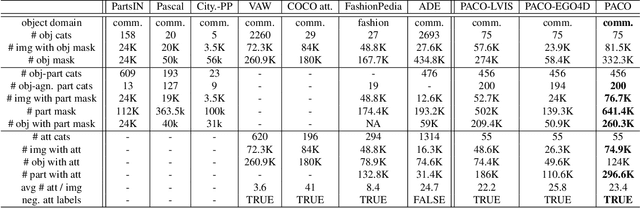
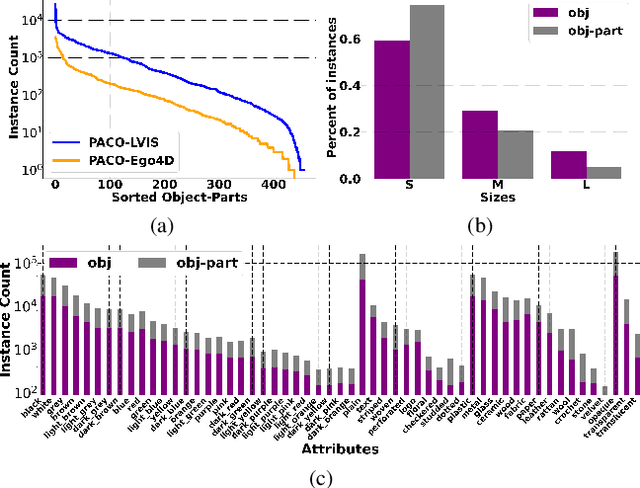
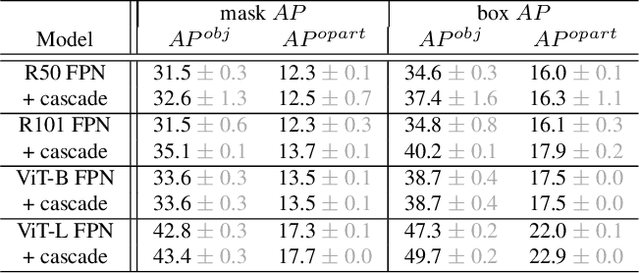
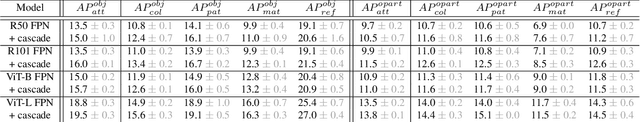
Abstract:Object models are gradually progressing from predicting just category labels to providing detailed descriptions of object instances. This motivates the need for large datasets which go beyond traditional object masks and provide richer annotations such as part masks and attributes. Hence, we introduce PACO: Parts and Attributes of Common Objects. It spans 75 object categories, 456 object-part categories and 55 attributes across image (LVIS) and video (Ego4D) datasets. We provide 641K part masks annotated across 260K object boxes, with roughly half of them exhaustively annotated with attributes as well. We design evaluation metrics and provide benchmark results for three tasks on the dataset: part mask segmentation, object and part attribute prediction and zero-shot instance detection. Dataset, models, and code are open-sourced at https://github.com/facebookresearch/paco.
Visualizing Information Bottleneck through Variational Inference
Dec 24, 2022Abstract:The Information Bottleneck theory provides a theoretical and computational framework for finding approximate minimum sufficient statistics. Analysis of the Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) training of a neural network on a toy problem has shown the existence of two phases, fitting and compression. In this work, we analyze the SGD training process of a Deep Neural Network on MNIST classification and confirm the existence of two phases of SGD training. We also propose a setup for estimating the mutual information for a Deep Neural Network through Variational Inference.
Are We Making Real Progress in Simulated Environments? Measuring the Sim2Real Gap in Embodied Visual Navigation
Dec 13, 2019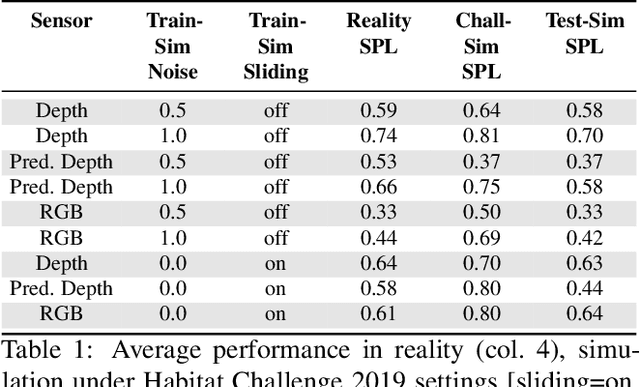

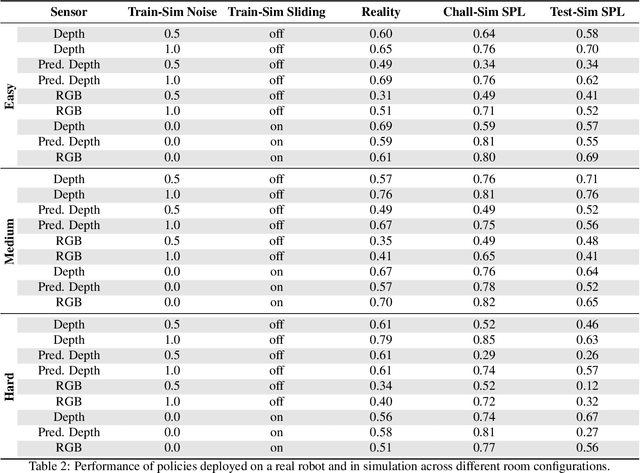
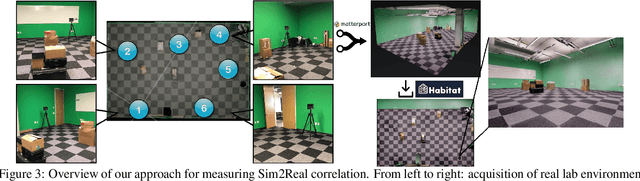
Abstract:Does progress in simulation translate to progress in robotics? Specifically, if method A outperforms method B in simulation, how likely is the trend to hold in reality on a robot? We examine this question for embodied (PointGoal) navigation, developing engineering tools and a research paradigm for evaluating a simulator by its sim2real predictivity, revealing surprising findings about prior work. First, we develop Habitat-PyRobot Bridge (HaPy), a library for seamless execution of identical code on a simulated agent and a physical robot. Habitat-to-Locobot transfer with HaPy involves just one line change in config, essentially treating reality as just another simulator! Second, we investigate sim2real predictivity of Habitat-Sim for PointGoal navigation. We 3D-scan a physical lab space to create a virtualized replica, and run parallel tests of 9 different models in reality and simulation. We present a new metric called Sim-vs-Real Correlation Coefficient (SRCC) to quantify sim2real predictivity. Our analysis reveals several important findings. We find that SRCC for Habitat as used for the CVPR19 challenge is low (0.18 for the success metric), which suggests that performance improvements for this simulator-based challenge would not transfer well to a physical robot. We find that this gap is largely due to AI agents learning to 'cheat' by exploiting simulator imperfections: specifically, the way Habitat allows for 'sliding' along walls on collision. Essentially, the virtual robot is capable of cutting corners, leading to unrealistic shortcuts through non-navigable spaces. Naturally, such exploits do not work in the real world where the robot stops on contact with walls. Our experiments show that it is possible to optimize simulation parameters to enable robots trained in imperfect simulators to generalize learned skills to reality (e.g. improving $SRCC_{Succ}$ from 0.18 to 0.844).
Decentralized Distributed PPO: Solving PointGoal Navigation
Nov 01, 2019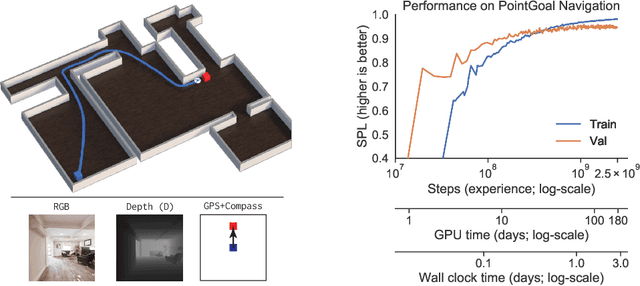
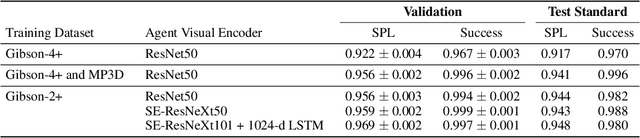
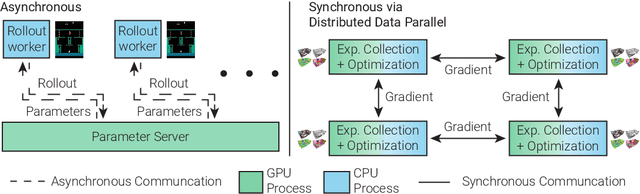
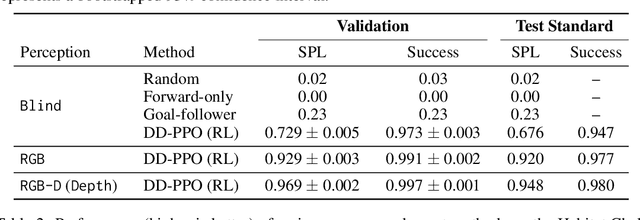
Abstract:We present Decentralized Distributed Proximal Policy Optimization (DD-PPO), a method for distributed reinforcement learning in resource-intensive simulated environments. DD-PPO is distributed (uses multiple machines), decentralized (lacks a centralized server), and synchronous (no computation is ever "stale"), making it conceptually simple and easy to implement. In our experiments on training virtual robots to navigate in Habitat-Sim, DD-PPO exhibits near-linear scaling -- achieving a speedup of 107x on 128 GPUs over a serial implementation. We leverage this scaling to train an agent for 2.5 Billion steps of experience (the equivalent of 80 years of human experience) -- over 6 months of GPU-time training in under 3 days of wall-clock time with 64 GPUs. This massive-scale training not only sets the state of art on Habitat Autonomous Navigation Challenge 2019, but essentially "solves" the task -- near-perfect autonomous navigation in an unseen environment without access to a map, directly from an RGB-D camera and a GPS+Compass sensor. Fortuitously, error vs computation exhibits a power-law-like distribution; thus, 90% of peak performance is obtained relatively early (at 100 million steps) and relatively cheaply (under 1 day with 8 GPUs). Finally, we show that the scene understanding and navigation policies learned can be transferred to other navigation tasks -- the analog of "ImageNet pre-training + task-specific fine-tuning" for embodied AI. Our model outperforms ImageNet pre-trained CNNs on these transfer tasks and can serve as a universal resource (all models + code will be publicly available).
SplitNet: Sim2Sim and Task2Task Transfer for Embodied Visual Navigation
May 21, 2019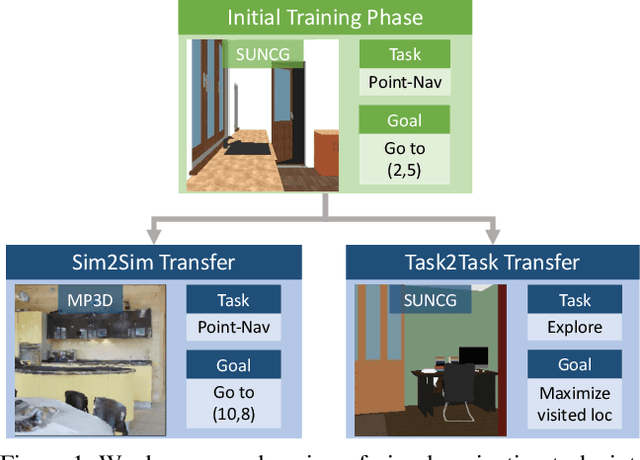
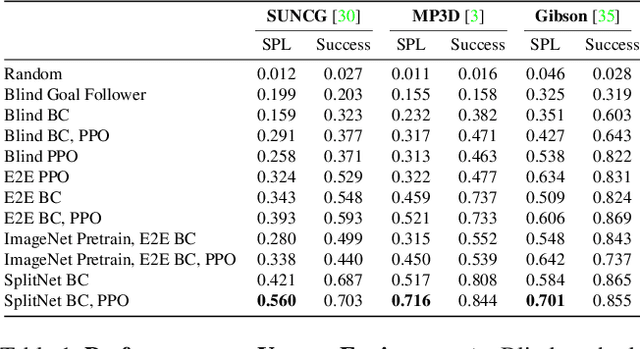
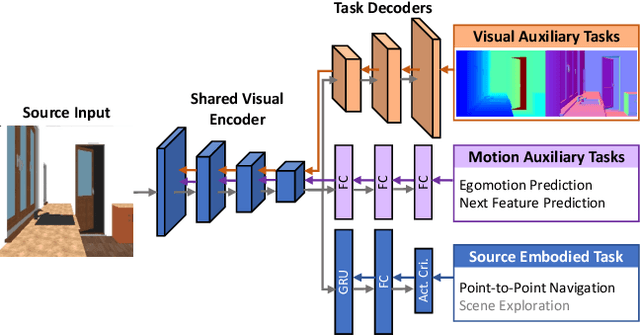
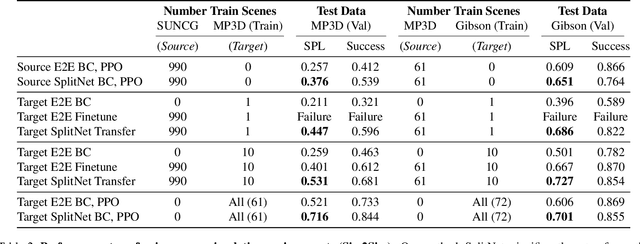
Abstract:We propose SplitNet, a method for decoupling visual perception and policy learning. By incorporating auxiliary tasks and selective learning of portions of the model, we explicitly decompose the learning objectives for visual navigation into perceiving the world and acting on that perception. We show dramatic improvements over baseline models on transferring between simulators, an encouraging step towards Sim2Real. Additionally, SplitNet generalizes better to unseen environments from the same simulator and transfers faster and more effectively to novel embodied navigation tasks. Further, given only a small sample from a target domain, SplitNet can match the performance of traditional end-to-end pipelines which receive the entire dataset. Code and video are available at https://github.com/facebookresearch/splitnet and https://youtu.be/TJkZcsD2vrc
Habitat: A Platform for Embodied AI Research
Apr 02, 2019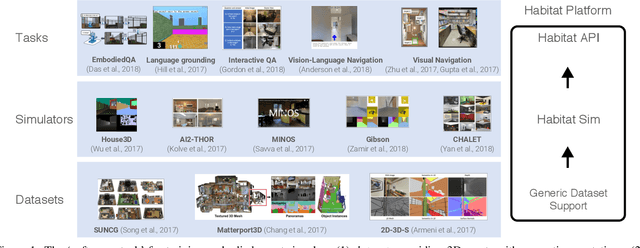
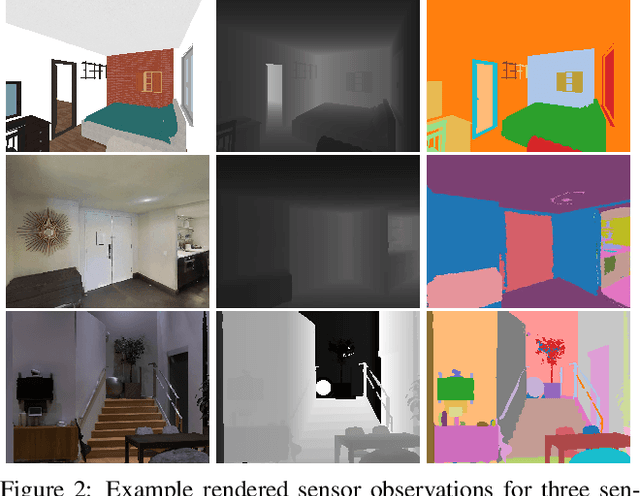
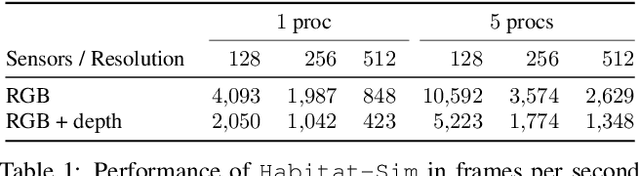

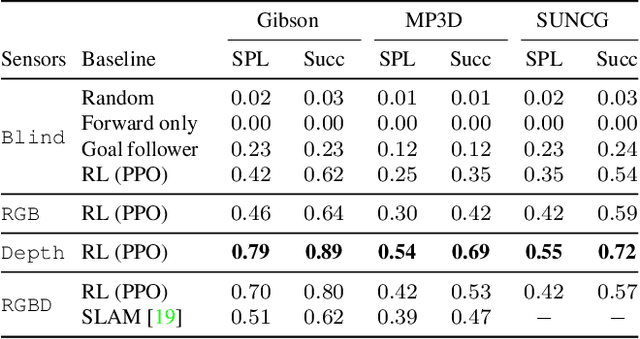
Abstract:We present Habitat, a new platform for research in embodied artificial intelligence (AI). Habitat enables training embodied agents (virtual robots) in highly efficient photorealistic 3D simulation, before transferring the learned skills to reality. Specifically, Habitat consists of the following: 1. Habitat-Sim: a flexible, high-performance 3D simulator with configurable agents, multiple sensors, and generic 3D dataset handling (with built-in support for SUNCG, Matterport3D, Gibson datasets). Habitat-Sim is fast -- when rendering a scene from the Matterport3D dataset, Habitat-Sim achieves several thousand frames per second (fps) running single-threaded, and can reach over 10,000 fps multi-process on a single GPU, which is orders of magnitude faster than the closest simulator. 2. Habitat-API: a modular high-level library for end-to-end development of embodied AI algorithms -- defining embodied AI tasks (e.g. navigation, instruction following, question answering), configuring and training embodied agents (via imitation or reinforcement learning, or via classic SLAM), and benchmarking using standard metrics. These large-scale engineering contributions enable us to answer scientific questions requiring experiments that were till now impracticable or `merely' impractical. Specifically, in the context of point-goal navigation (1) we revisit the comparison between learning and SLAM approaches from two recent works and find evidence for the opposite conclusion -- that learning outperforms SLAM, if scaled to total experience far surpassing that of previous investigations, and (2) we conduct the first cross-dataset generalization experiments {train, test} x {Matterport3D, Gibson} for multiple sensors {blind, RGB, RGBD, D} and find that only agents with depth (D) sensors generalize across datasets. We hope that our open-source platform and these findings will advance research in embodied AI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge