Devi Parikh
Jack
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
Video Editing via Factorized Diffusion Distillation
Mar 24, 2024Abstract:We introduce Emu Video Edit (EVE), a model that establishes a new state-of-the art in video editing without relying on any supervised video editing data. To develop EVE we separately train an image editing adapter and a video generation adapter, and attach both to the same text-to-image model. Then, to align the adapters towards video editing we introduce a new unsupervised distillation procedure, Factorized Diffusion Distillation. This procedure distills knowledge from one or more teachers simultaneously, without any supervised data. We utilize this procedure to teach EVE to edit videos by jointly distilling knowledge to (i) precisely edit each individual frame from the image editing adapter, and (ii) ensure temporal consistency among the edited frames using the video generation adapter. Finally, to demonstrate the potential of our approach in unlocking other capabilities, we align additional combinations of adapters
Emu Video: Factorizing Text-to-Video Generation by Explicit Image Conditioning
Nov 17, 2023Abstract:We present Emu Video, a text-to-video generation model that factorizes the generation into two steps: first generating an image conditioned on the text, and then generating a video conditioned on the text and the generated image. We identify critical design decisions--adjusted noise schedules for diffusion, and multi-stage training--that enable us to directly generate high quality and high resolution videos, without requiring a deep cascade of models as in prior work. In human evaluations, our generated videos are strongly preferred in quality compared to all prior work--81% vs. Google's Imagen Video, 90% vs. Nvidia's PYOCO, and 96% vs. Meta's Make-A-Video. Our model outperforms commercial solutions such as RunwayML's Gen2 and Pika Labs. Finally, our factorizing approach naturally lends itself to animating images based on a user's text prompt, where our generations are preferred 96% over prior work.
Emu Edit: Precise Image Editing via Recognition and Generation Tasks
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:Instruction-based image editing holds immense potential for a variety of applications, as it enables users to perform any editing operation using a natural language instruction. However, current models in this domain often struggle with accurately executing user instructions. We present Emu Edit, a multi-task image editing model which sets state-of-the-art results in instruction-based image editing. To develop Emu Edit we train it to multi-task across an unprecedented range of tasks, such as region-based editing, free-form editing, and Computer Vision tasks, all of which are formulated as generative tasks. Additionally, to enhance Emu Edit's multi-task learning abilities, we provide it with learned task embeddings which guide the generation process towards the correct edit type. Both these elements are essential for Emu Edit's outstanding performance. Furthermore, we show that Emu Edit can generalize to new tasks, such as image inpainting, super-resolution, and compositions of editing tasks, with just a few labeled examples. This capability offers a significant advantage in scenarios where high-quality samples are scarce. Lastly, to facilitate a more rigorous and informed assessment of instructable image editing models, we release a new challenging and versatile benchmark that includes seven different image editing tasks.
Emu: Enhancing Image Generation Models Using Photogenic Needles in a Haystack
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:Training text-to-image models with web scale image-text pairs enables the generation of a wide range of visual concepts from text. However, these pre-trained models often face challenges when it comes to generating highly aesthetic images. This creates the need for aesthetic alignment post pre-training. In this paper, we propose quality-tuning to effectively guide a pre-trained model to exclusively generate highly visually appealing images, while maintaining generality across visual concepts. Our key insight is that supervised fine-tuning with a set of surprisingly small but extremely visually appealing images can significantly improve the generation quality. We pre-train a latent diffusion model on $1.1$ billion image-text pairs and fine-tune it with only a few thousand carefully selected high-quality images. The resulting model, Emu, achieves a win rate of $82.9\%$ compared with its pre-trained only counterpart. Compared to the state-of-the-art SDXLv1.0, Emu is preferred $68.4\%$ and $71.3\%$ of the time on visual appeal on the standard PartiPrompts and our Open User Input benchmark based on the real-world usage of text-to-image models. In addition, we show that quality-tuning is a generic approach that is also effective for other architectures, including pixel diffusion and masked generative transformer models.
Make-An-Animation: Large-Scale Text-conditional 3D Human Motion Generation
May 16, 2023Abstract:Text-guided human motion generation has drawn significant interest because of its impactful applications spanning animation and robotics. Recently, application of diffusion models for motion generation has enabled improvements in the quality of generated motions. However, existing approaches are limited by their reliance on relatively small-scale motion capture data, leading to poor performance on more diverse, in-the-wild prompts. In this paper, we introduce Make-An-Animation, a text-conditioned human motion generation model which learns more diverse poses and prompts from large-scale image-text datasets, enabling significant improvement in performance over prior works. Make-An-Animation is trained in two stages. First, we train on a curated large-scale dataset of (text, static pseudo-pose) pairs extracted from image-text datasets. Second, we fine-tune on motion capture data, adding additional layers to model the temporal dimension. Unlike prior diffusion models for motion generation, Make-An-Animation uses a U-Net architecture similar to recent text-to-video generation models. Human evaluation of motion realism and alignment with input text shows that our model reaches state-of-the-art performance on text-to-motion generation.
Text-Conditional Contextualized Avatars For Zero-Shot Personalization
Apr 14, 2023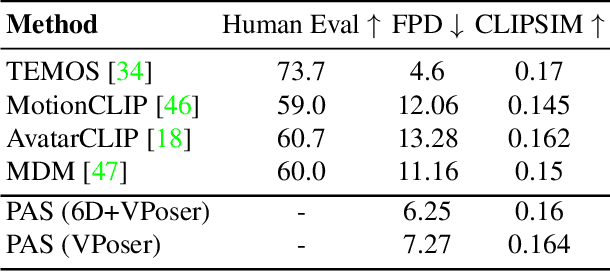
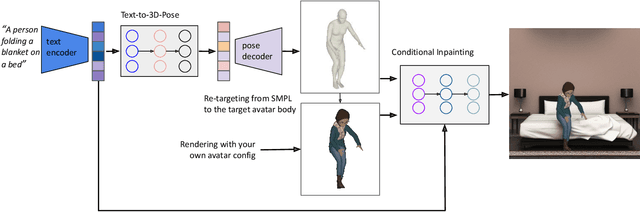
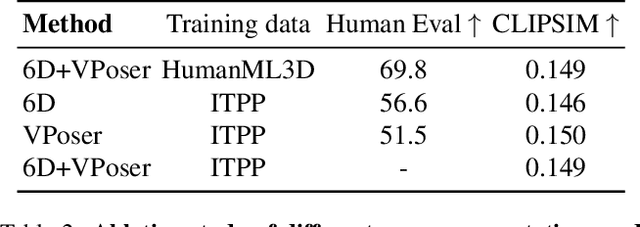
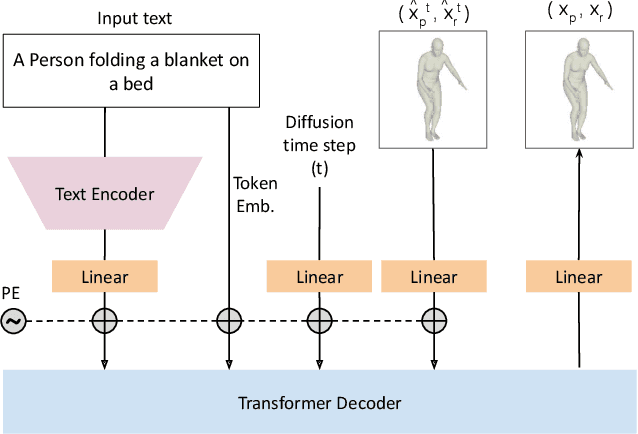
Abstract:Recent large-scale text-to-image generation models have made significant improvements in the quality, realism, and diversity of the synthesized images and enable users to control the created content through language. However, the personalization aspect of these generative models is still challenging and under-explored. In this work, we propose a pipeline that enables personalization of image generation with avatars capturing a user's identity in a delightful way. Our pipeline is zero-shot, avatar texture and style agnostic, and does not require training on the avatar at all - it is scalable to millions of users who can generate a scene with their avatar. To render the avatar in a pose faithful to the given text prompt, we propose a novel text-to-3D pose diffusion model trained on a curated large-scale dataset of in-the-wild human poses improving the performance of the SOTA text-to-motion models significantly. We show, for the first time, how to leverage large-scale image datasets to learn human 3D pose parameters and overcome the limitations of motion capture datasets.
Text-To-4D Dynamic Scene Generation
Jan 26, 2023



Abstract:We present MAV3D (Make-A-Video3D), a method for generating three-dimensional dynamic scenes from text descriptions. Our approach uses a 4D dynamic Neural Radiance Field (NeRF), which is optimized for scene appearance, density, and motion consistency by querying a Text-to-Video (T2V) diffusion-based model. The dynamic video output generated from the provided text can be viewed from any camera location and angle, and can be composited into any 3D environment. MAV3D does not require any 3D or 4D data and the T2V model is trained only on Text-Image pairs and unlabeled videos. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach using comprehensive quantitative and qualitative experiments and show an improvement over previously established internal baselines. To the best of our knowledge, our method is the first to generate 3D dynamic scenes given a text description.
SpaText: Spatio-Textual Representation for Controllable Image Generation
Nov 25, 2022Abstract:Recent text-to-image diffusion models are able to generate convincing results of unprecedented quality. However, it is nearly impossible to control the shapes of different regions/objects or their layout in a fine-grained fashion. Previous attempts to provide such controls were hindered by their reliance on a fixed set of labels. To this end, we present SpaText - a new method for text-to-image generation using open-vocabulary scene control. In addition to a global text prompt that describes the entire scene, the user provides a segmentation map where each region of interest is annotated by a free-form natural language description. Due to lack of large-scale datasets that have a detailed textual description for each region in the image, we choose to leverage the current large-scale text-to-image datasets and base our approach on a novel CLIP-based spatio-textual representation, and show its effectiveness on two state-of-the-art diffusion models: pixel-based and latent-based. In addition, we show how to extend the classifier-free guidance method in diffusion models to the multi-conditional case and present an alternative accelerated inference algorithm. Finally, we offer several automatic evaluation metrics and use them, in addition to FID scores and a user study, to evaluate our method and show that it achieves state-of-the-art results on image generation with free-form textual scene control.
AudioGen: Textually Guided Audio Generation
Sep 30, 2022



Abstract:We tackle the problem of generating audio samples conditioned on descriptive text captions. In this work, we propose AaudioGen, an auto-regressive generative model that generates audio samples conditioned on text inputs. AudioGen operates on a learnt discrete audio representation. The task of text-to-audio generation poses multiple challenges. Due to the way audio travels through a medium, differentiating ``objects'' can be a difficult task (e.g., separating multiple people simultaneously speaking). This is further complicated by real-world recording conditions (e.g., background noise, reverberation, etc.). Scarce text annotations impose another constraint, limiting the ability to scale models. Finally, modeling high-fidelity audio requires encoding audio at high sampling rate, leading to extremely long sequences. To alleviate the aforementioned challenges we propose an augmentation technique that mixes different audio samples, driving the model to internally learn to separate multiple sources. We curated 10 datasets containing different types of audio and text annotations to handle the scarcity of text-audio data points. For faster inference, we explore the use of multi-stream modeling, allowing the use of shorter sequences while maintaining a similar bitrate and perceptual quality. We apply classifier-free guidance to improve adherence to text. Comparing to the evaluated baselines, AudioGen outperforms over both objective and subjective metrics. Finally, we explore the ability of the proposed method to generate audio continuation conditionally and unconditionally. Samples: https://tinyurl.com/audiogen-text2audio
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge