Peizhao Zhang
Non-Markov Multi-Round Conversational Image Generation with History-Conditioned MLLMs
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Conversational image generation requires a model to follow user instructions across multiple rounds of interaction, grounded in interleaved text and images that accumulate as chat history. While recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) can generate and edit images, most existing multi-turn benchmarks and training recipes are effectively Markov: the next output depends primarily on the most recent image, enabling shortcut solutions that ignore long-range history. In this work we formalize and target the more challenging non-Markov setting, where a user may refer back to earlier states, undo changes, or reference entities introduced several rounds ago. We present (i) non-Markov multi-round data construction strategies, including rollback-style editing that forces retrieval of earlier visual states and name-based multi-round personalization that binds names to appearances across rounds; (ii) a history-conditioned training and inference framework with token-level caching to prevent multi-round identity drift; and (iii) enabling improvements for high-fidelity image reconstruction and editable personalization, including a reconstruction-based DiT detokenizer and a multi-stage fine-tuning curriculum. We demonstrate that explicitly training for non-Markov interactions yields substantial improvements in multi-round consistency and instruction compliance, while maintaining strong single-round editing and personalization.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
REFA: Real-time Egocentric Facial Animations for Virtual Reality
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:We present a novel system for real-time tracking of facial expressions using egocentric views captured from a set of infrared cameras embedded in a virtual reality (VR) headset. Our technology facilitates any user to accurately drive the facial expressions of virtual characters in a non-intrusive manner and without the need of a lengthy calibration step. At the core of our system is a distillation based approach to train a machine learning model on heterogeneous data and labels coming form multiple sources, \eg synthetic and real images. As part of our dataset, we collected 18k diverse subjects using a lightweight capture setup consisting of a mobile phone and a custom VR headset with extra cameras. To process this data, we developed a robust differentiable rendering pipeline enabling us to automatically extract facial expression labels. Our system opens up new avenues for communication and expression in virtual environments, with applications in video conferencing, gaming, entertainment, and remote collaboration.
Token-Shuffle: Towards High-Resolution Image Generation with Autoregressive Models
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) models, long dominant in language generation, are increasingly applied to image synthesis but are often considered less competitive than Diffusion-based models. A primary limitation is the substantial number of image tokens required for AR models, which constrains both training and inference efficiency, as well as image resolution. To address this, we present Token-Shuffle, a novel yet simple method that reduces the number of image tokens in Transformer. Our key insight is the dimensional redundancy of visual vocabularies in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), where low-dimensional visual codes from visual encoder are directly mapped to high-dimensional language vocabularies. Leveraging this, we consider two key operations: token-shuffle, which merges spatially local tokens along channel dimension to decrease the input token number, and token-unshuffle, which untangles the inferred tokens after Transformer blocks to restore the spatial arrangement for output. Jointly training with textual prompts, our strategy requires no additional pretrained text-encoder and enables MLLMs to support extremely high-resolution image synthesis in a unified next-token prediction way while maintaining efficient training and inference. For the first time, we push the boundary of AR text-to-image generation to a resolution of 2048x2048 with gratifying generation performance. In GenAI-benchmark, our 2.7B model achieves 0.77 overall score on hard prompts, outperforming AR models LlamaGen by 0.18 and diffusion models LDM by 0.15. Exhaustive large-scale human evaluations also demonstrate our prominent image generation ability in terms of text-alignment, visual flaw, and visual appearance. We hope that Token-Shuffle can serve as a foundational design for efficient high-resolution image generation within MLLMs.
DirectorLLM for Human-Centric Video Generation
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce DirectorLLM, a novel video generation model that employs a large language model (LLM) to orchestrate human poses within videos. As foundational text-to-video models rapidly evolve, the demand for high-quality human motion and interaction grows. To address this need and enhance the authenticity of human motions, we extend the LLM from a text generator to a video director and human motion simulator. Utilizing open-source resources from Llama 3, we train the DirectorLLM to generate detailed instructional signals, such as human poses, to guide video generation. This approach offloads the simulation of human motion from the video generator to the LLM, effectively creating informative outlines for human-centric scenes. These signals are used as conditions by the video renderer, facilitating more realistic and prompt-following video generation. As an independent LLM module, it can be applied to different video renderers, including UNet and DiT, with minimal effort. Experiments on automatic evaluation benchmarks and human evaluations show that our model outperforms existing ones in generating videos with higher human motion fidelity, improved prompt faithfulness, and enhanced rendered subject naturalness.
LinGen: Towards High-Resolution Minute-Length Text-to-Video Generation with Linear Computational Complexity
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-video generation enhances content creation but is highly computationally intensive: The computational cost of Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) scales quadratically in the number of pixels. This makes minute-length video generation extremely expensive, limiting most existing models to generating videos of only 10-20 seconds length. We propose a Linear-complexity text-to-video Generation (LinGen) framework whose cost scales linearly in the number of pixels. For the first time, LinGen enables high-resolution minute-length video generation on a single GPU without compromising quality. It replaces the computationally-dominant and quadratic-complexity block, self-attention, with a linear-complexity block called MATE, which consists of an MA-branch and a TE-branch. The MA-branch targets short-to-long-range correlations, combining a bidirectional Mamba2 block with our token rearrangement method, Rotary Major Scan, and our review tokens developed for long video generation. The TE-branch is a novel TEmporal Swin Attention block that focuses on temporal correlations between adjacent tokens and medium-range tokens. The MATE block addresses the adjacency preservation issue of Mamba and improves the consistency of generated videos significantly. Experimental results show that LinGen outperforms DiT (with a 75.6% win rate) in video quality with up to 15$\times$ (11.5$\times$) FLOPs (latency) reduction. Furthermore, both automatic metrics and human evaluation demonstrate our LinGen-4B yields comparable video quality to state-of-the-art models (with a 50.5%, 52.1%, 49.1% win rate with respect to Gen-3, LumaLabs, and Kling, respectively). This paves the way to hour-length movie generation and real-time interactive video generation. We provide 68s video generation results and more examples in our project website: https://lineargen.github.io/.
Movie Gen: A Cast of Media Foundation Models
Oct 17, 2024
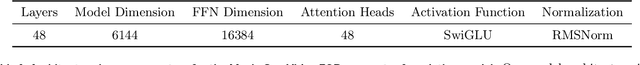
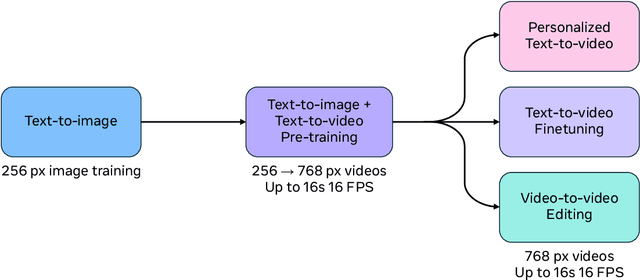
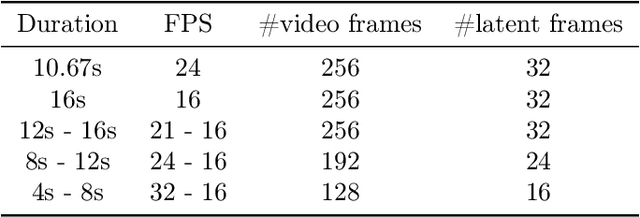
Abstract:We present Movie Gen, a cast of foundation models that generates high-quality, 1080p HD videos with different aspect ratios and synchronized audio. We also show additional capabilities such as precise instruction-based video editing and generation of personalized videos based on a user's image. Our models set a new state-of-the-art on multiple tasks: text-to-video synthesis, video personalization, video editing, video-to-audio generation, and text-to-audio generation. Our largest video generation model is a 30B parameter transformer trained with a maximum context length of 73K video tokens, corresponding to a generated video of 16 seconds at 16 frames-per-second. We show multiple technical innovations and simplifications on the architecture, latent spaces, training objectives and recipes, data curation, evaluation protocols, parallelization techniques, and inference optimizations that allow us to reap the benefits of scaling pre-training data, model size, and training compute for training large scale media generation models. We hope this paper helps the research community to accelerate progress and innovation in media generation models. All videos from this paper are available at https://go.fb.me/MovieGenResearchVideos.
An Analysis on Quantizing Diffusion Transformers
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion Models (DMs) utilize an iterative denoising process to transform random noise into synthetic data. Initally proposed with a UNet structure, DMs excel at producing images that are virtually indistinguishable with or without conditioned text prompts. Later transformer-only structure is composed with DMs to achieve better performance. Though Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) reduce the computational requirement by denoising in a latent space, it is extremely expensive to inference images for any operating devices due to the shear volume of parameters and feature sizes. Post Training Quantization (PTQ) offers an immediate remedy for a smaller storage size and more memory-efficient computation during inferencing. Prior works address PTQ of DMs on UNet structures have addressed the challenges in calibrating parameters for both activations and weights via moderate optimization. In this work, we pioneer an efficient PTQ on transformer-only structure without any optimization. By analysing challenges in quantizing activations and weights for diffusion transformers, we propose a single-step sampling calibration on activations and adapt group-wise quantization on weights for low-bit quantization. We demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of proposed methods with preliminary experiments on conditional image generation.
FlowVid: Taming Imperfect Optical Flows for Consistent Video-to-Video Synthesis
Dec 29, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion models have transformed the image-to-image (I2I) synthesis and are now permeating into videos. However, the advancement of video-to-video (V2V) synthesis has been hampered by the challenge of maintaining temporal consistency across video frames. This paper proposes a consistent V2V synthesis framework by jointly leveraging spatial conditions and temporal optical flow clues within the source video. Contrary to prior methods that strictly adhere to optical flow, our approach harnesses its benefits while handling the imperfection in flow estimation. We encode the optical flow via warping from the first frame and serve it as a supplementary reference in the diffusion model. This enables our model for video synthesis by editing the first frame with any prevalent I2I models and then propagating edits to successive frames. Our V2V model, FlowVid, demonstrates remarkable properties: (1) Flexibility: FlowVid works seamlessly with existing I2I models, facilitating various modifications, including stylization, object swaps, and local edits. (2) Efficiency: Generation of a 4-second video with 30 FPS and 512x512 resolution takes only 1.5 minutes, which is 3.1x, 7.2x, and 10.5x faster than CoDeF, Rerender, and TokenFlow, respectively. (3) High-quality: In user studies, our FlowVid is preferred 45.7% of the time, outperforming CoDeF (3.5%), Rerender (10.2%), and TokenFlow (40.4%).
Efficient Quantization Strategies for Latent Diffusion Models
Dec 09, 2023



Abstract:Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) capture the dynamic evolution of latent variables over time, blending patterns and multimodality in a generative system. Despite the proficiency of LDM in various applications, such as text-to-image generation, facilitated by robust text encoders and a variational autoencoder, the critical need to deploy large generative models on edge devices compels a search for more compact yet effective alternatives. Post Training Quantization (PTQ), a method to compress the operational size of deep learning models, encounters challenges when applied to LDM due to temporal and structural complexities. This study proposes a quantization strategy that efficiently quantize LDMs, leveraging Signal-to-Quantization-Noise Ratio (SQNR) as a pivotal metric for evaluation. By treating the quantization discrepancy as relative noise and identifying sensitive part(s) of a model, we propose an efficient quantization approach encompassing both global and local strategies. The global quantization process mitigates relative quantization noise by initiating higher-precision quantization on sensitive blocks, while local treatments address specific challenges in quantization-sensitive and time-sensitive modules. The outcomes of our experiments reveal that the implementation of both global and local treatments yields a highly efficient and effective Post Training Quantization (PTQ) of LDMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge