Kunpeng Song
Creative Image Generation with Diffusion Model
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Creative image generation has emerged as a compelling area of research, driven by the need to produce novel and high-quality images that expand the boundaries of imagination. In this work, we propose a novel framework for creative generation using diffusion models, where creativity is associated with the inverse probability of an image's existence in the CLIP embedding space. Unlike prior approaches that rely on a manual blending of concepts or exclusion of subcategories, our method calculates the probability distribution of generated images and drives it towards low-probability regions to produce rare, imaginative, and visually captivating outputs. We also introduce pullback mechanisms, achieving high creativity without sacrificing visual fidelity. Extensive experiments on text-to-image diffusion models demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our creative generation framework, showcasing its ability to produce unique, novel, and thought-provoking images. This work provides a new perspective on creativity in generative models, offering a principled method to foster innovation in visual content synthesis.
DirectorLLM for Human-Centric Video Generation
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce DirectorLLM, a novel video generation model that employs a large language model (LLM) to orchestrate human poses within videos. As foundational text-to-video models rapidly evolve, the demand for high-quality human motion and interaction grows. To address this need and enhance the authenticity of human motions, we extend the LLM from a text generator to a video director and human motion simulator. Utilizing open-source resources from Llama 3, we train the DirectorLLM to generate detailed instructional signals, such as human poses, to guide video generation. This approach offloads the simulation of human motion from the video generator to the LLM, effectively creating informative outlines for human-centric scenes. These signals are used as conditions by the video renderer, facilitating more realistic and prompt-following video generation. As an independent LLM module, it can be applied to different video renderers, including UNet and DiT, with minimal effort. Experiments on automatic evaluation benchmarks and human evaluations show that our model outperforms existing ones in generating videos with higher human motion fidelity, improved prompt faithfulness, and enhanced rendered subject naturalness.
MoMA: Multimodal LLM Adapter for Fast Personalized Image Generation
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present MoMA: an open-vocabulary, training-free personalized image model that boasts flexible zero-shot capabilities. As foundational text-to-image models rapidly evolve, the demand for robust image-to-image translation grows. Addressing this need, MoMA specializes in subject-driven personalized image generation. Utilizing an open-source, Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM), we train MoMA to serve a dual role as both a feature extractor and a generator. This approach effectively synergizes reference image and text prompt information to produce valuable image features, facilitating an image diffusion model. To better leverage the generated features, we further introduce a novel self-attention shortcut method that efficiently transfers image features to an image diffusion model, improving the resemblance of the target object in generated images. Remarkably, as a tuning-free plug-and-play module, our model requires only a single reference image and outperforms existing methods in generating images with high detail fidelity, enhanced identity-preservation and prompt faithfulness. Our work is open-source, thereby providing universal access to these advancements.
Improving Tuning-Free Real Image Editing with Proximal Guidance
Jun 29, 2023
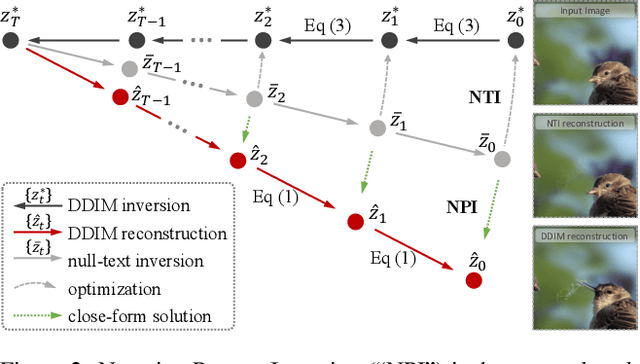
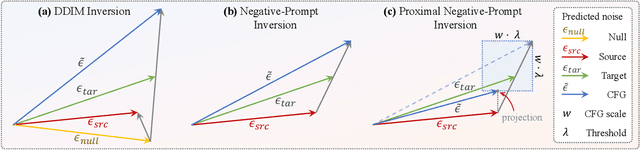

Abstract:DDIM inversion has revealed the remarkable potential of real image editing within diffusion-based methods. However, the accuracy of DDIM reconstruction degrades as larger classifier-free guidance (CFG) scales being used for enhanced editing. Null-text inversion (NTI) optimizes null embeddings to align the reconstruction and inversion trajectories with larger CFG scales, enabling real image editing with cross-attention control. Negative-prompt inversion (NPI) further offers a training-free closed-form solution of NTI. However, it may introduce artifacts and is still constrained by DDIM reconstruction quality. To overcome these limitations, we propose proximal guidance and incorporate it to NPI with cross-attention control. We enhance NPI with a regularization term and reconstruction guidance, which reduces artifacts while capitalizing on its training-free nature. Additionally, we extend the concepts to incorporate mutual self-attention control, enabling geometry and layout alterations in the editing process. Our method provides an efficient and straightforward approach, effectively addressing real image editing tasks with minimal computational overhead.
Diffusion Guided Domain Adaptation of Image Generators
Dec 09, 2022Abstract:Can a text-to-image diffusion model be used as a training objective for adapting a GAN generator to another domain? In this paper, we show that the classifier-free guidance can be leveraged as a critic and enable generators to distill knowledge from large-scale text-to-image diffusion models. Generators can be efficiently shifted into new domains indicated by text prompts without access to groundtruth samples from target domains. We demonstrate the effectiveness and controllability of our method through extensive experiments. Although not trained to minimize CLIP loss, our model achieves equally high CLIP scores and significantly lower FID than prior work on short prompts, and outperforms the baseline qualitatively and quantitatively on long and complicated prompts. To our best knowledge, the proposed method is the first attempt at incorporating large-scale pre-trained diffusion models and distillation sampling for text-driven image generator domain adaptation and gives a quality previously beyond possible. Moreover, we extend our work to 3D-aware style-based generators and DreamBooth guidance.
Towards Faster and Stabilized GAN Training for High-fidelity Few-shot Image Synthesis
Jan 12, 2021
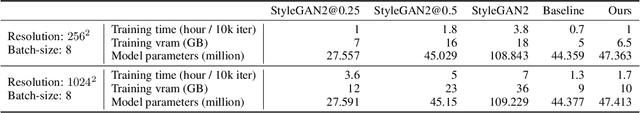
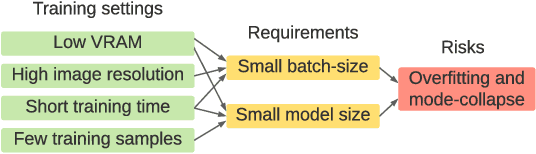
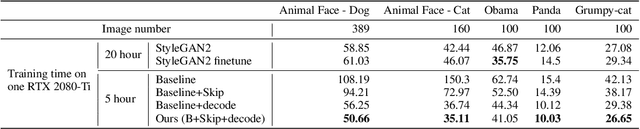
Abstract:Training Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) on high-fidelity images usually requires large-scale GPU-clusters and a vast number of training images. In this paper, we study the few-shot image synthesis task for GAN with minimum computing cost. We propose a light-weight GAN structure that gains superior quality on 1024*1024 resolution. Notably, the model converges from scratch with just a few hours of training on a single RTX-2080 GPU, and has a consistent performance, even with less than 100 training samples. Two technique designs constitute our work, a skip-layer channel-wise excitation module and a self-supervised discriminator trained as a feature-encoder. With thirteen datasets covering a wide variety of image domains (The datasets and code are available at: https://github.com/odegeasslbc/FastGAN-pytorch), we show our model's superior performance compared to the state-of-the-art StyleGAN2, when data and computing budget are limited.
Self-Supervised Sketch-to-Image Synthesis
Dec 22, 2020
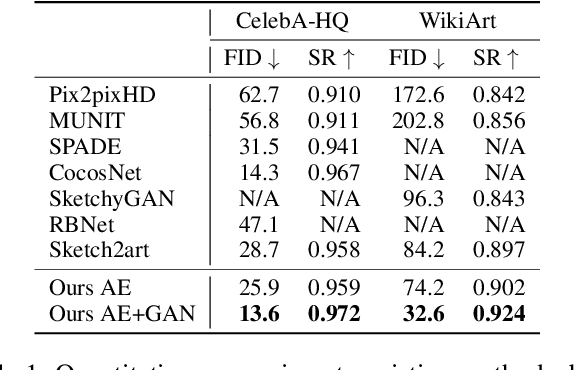
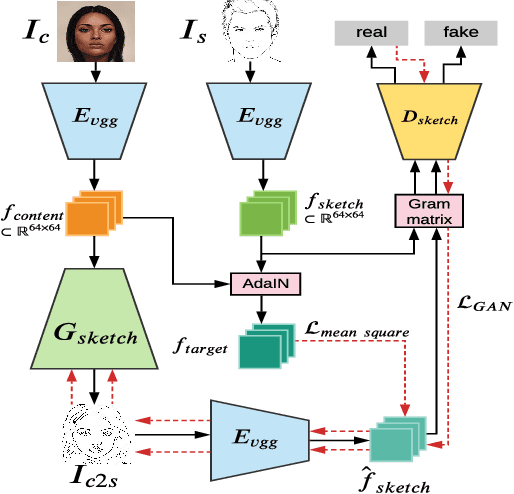
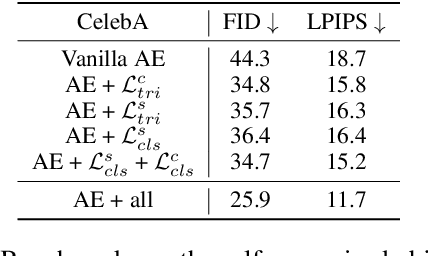
Abstract:Imagining a colored realistic image from an arbitrarily drawn sketch is one of the human capabilities that we eager machines to mimic. Unlike previous methods that either requires the sketch-image pairs or utilize low-quantity detected edges as sketches, we study the exemplar-based sketch-to-image (s2i) synthesis task in a self-supervised learning manner, eliminating the necessity of the paired sketch data. To this end, we first propose an unsupervised method to efficiently synthesize line-sketches for general RGB-only datasets. With the synthetic paired-data, we then present a self-supervised Auto-Encoder (AE) to decouple the content/style features from sketches and RGB-images, and synthesize images that are both content-faithful to the sketches and style-consistent to the RGB-images. While prior works employ either the cycle-consistence loss or dedicated attentional modules to enforce the content/style fidelity, we show AE's superior performance with pure self-supervisions. To further improve the synthesis quality in high resolution, we also leverage an adversarial network to refine the details of synthetic images. Extensive experiments on 1024*1024 resolution demonstrate a new state-of-art-art performance of the proposed model on CelebA-HQ and Wiki-Art datasets. Moreover, with the proposed sketch generator, the model shows a promising performance on style mixing and style transfer, which require synthesized images to be both style-consistent and semantically meaningful. Our code is available on https://github.com/odegeasslbc/Self-Supervised-Sketch-to-Image-Synthesis-PyTorch, and please visit https://create.playform.io/my-projects?mode=sketch for an online demo of our model.
TIME: Text and Image Mutual-Translation Adversarial Networks
May 27, 2020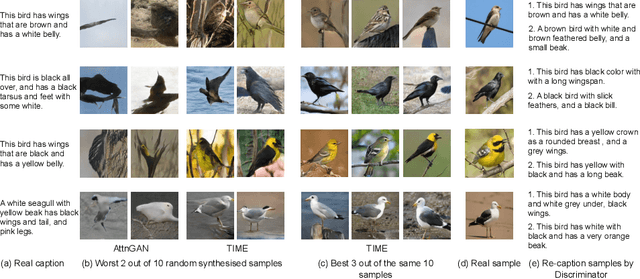

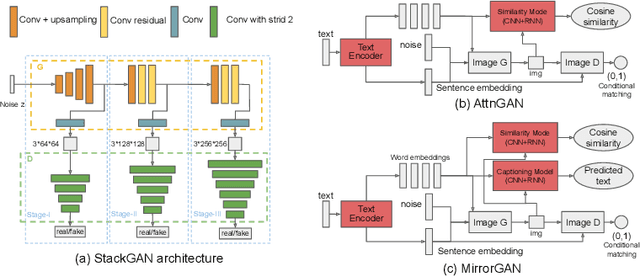

Abstract:Focusing on text-to-image (T2I) generation, we propose Text and Image Mutual-Translation Adversarial Networks (TIME), a lightweight but effective model that jointly learns a T2I generator $G$ and an image captioning discriminator $D$ under the Generative Adversarial Network framework. While previous methods tackle the T2I problem as a uni-directional task and use pre-trained language models to enforce the image-text consistency, TIME requires neither extra modules nor pre-training. We show that the performance of $G$ can be boosted substantially by training it jointly with $D$ as a language model. Specifically, we adopt Transformers to model the cross-modal connections between the image features and word embeddings, and design a hinged and annealing conditional loss that dynamically balances the adversarial learning. In our experiments, TIME establishes the new state-of-the-art Inception Score of 4.88 on the CUB dataset, and shows competitive performance on MS-COCO on both text-to-image and image captioning tasks.
Sketch-to-Art: Synthesizing Stylized Art Images From Sketches
Mar 03, 2020
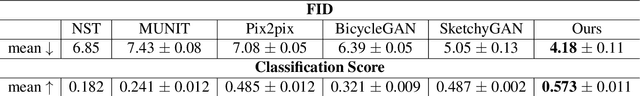

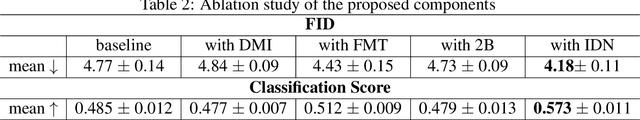
Abstract:We propose a new approach for synthesizing fully detailed art-stylized images from sketches. Given a sketch, with no semantic tagging, and a reference image of a specific style, the model can synthesize meaningful details with colors and textures. The model consists of three modules designed explicitly for better artistic style capturing and generation. Based on a GAN framework, a dual-masked mechanism is introduced to enforce the content constraints (from the sketch), and a feature-map transformation technique is developed to strengthen the style consistency (to the reference image). Finally, an inverse procedure of instance-normalization is proposed to disentangle the style and content information, therefore yields better synthesis performance. Experiments demonstrate a significant qualitative and quantitative boost over baselines based on previous state-of-the-art techniques, adopted for the proposed process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge