Yizhe Zhu
Wedge Sampling: Efficient Tensor Completion with Nearly-Linear Sample Complexity
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:We introduce Wedge Sampling, a new non-adaptive sampling scheme for low-rank tensor completion. We study recovery of an order-$k$ low-rank tensor of dimension $n \times \cdots \times n$ from a subset of its entries. Unlike the standard uniform entry model (i.e., i.i.d. samples from $[n]^k$), wedge sampling allocates observations to structured length-two patterns (wedges) in an associated bipartite sampling graph. By directly promoting these length-two connections, the sampling design strengthens the spectral signal that underlies efficient initialization, in regimes where uniform sampling is too sparse to generate enough informative correlations. Our main result shows that this change in sampling paradigm enables polynomial-time algorithms to achieve both weak and exact recovery with nearly linear sample complexity in $n$. The approach is also plug-and-play: wedge-sampling-based spectral initialization can be combined with existing refinement procedures (e.g., spectral or gradient-based methods) using only an additional $\tilde{O}(n)$ uniformly sampled entries, substantially improving over the $\tilde{O}(n^{k/2})$ sample complexity typically required under uniform entry sampling for efficient methods. Overall, our results suggest that the statistical-to-computational gap highlighted in Barak and Moitra (2022) is, to a large extent, a consequence of the uniform entry sampling model for tensor completion, and that alternative non-adaptive measurement designs that guarantee a strong initialization can overcome this barrier.
Minimax optimal differentially private synthetic data for smooth queries
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Differentially private synthetic data enables the sharing and analysis of sensitive datasets while providing rigorous privacy guarantees for individual contributors. A central challenge is to achieve strong utility guarantees for meaningful downstream analysis. Many existing methods ensure uniform accuracy over broad query classes, such as all Lipschitz functions, but this level of generality often leads to suboptimal rates for statistics of practical interest. Since many common data analysis queries exhibit smoothness beyond what worst-case Lipschitz bounds capture, we ask whether exploiting this additional structure can yield improved utility. We study the problem of generating $(\varepsilon,δ)$-differentially private synthetic data from a dataset of size $n$ supported on the hypercube $[-1,1]^d$, with utility guarantees uniformly for all smooth queries having bounded derivatives up to order $k$. We propose a polynomial-time algorithm that achieves a minimax error rate of $n^{-\min \{1, \frac{k}{d}\}}$, up to a $\log(n)$ factor. This characterization uncovers a phase transition at $k=d$. Our results generalize the Chebyshev moment matching framework of (Musco et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2016) and strictly improve the error rates for $k$-smooth queries established in (Wang et al., 2016). Moreover, we establish the first minimax lower bound for the utility of $(\varepsilon,δ)$-differentially private synthetic data with respect to $k$-smooth queries, extending the Wasserstein lower bound for $\varepsilon$-differential privacy in (Boedihardjo et al., 2024).
Residual Rotation Correction using Tactile Equivariance
Nov 11, 2025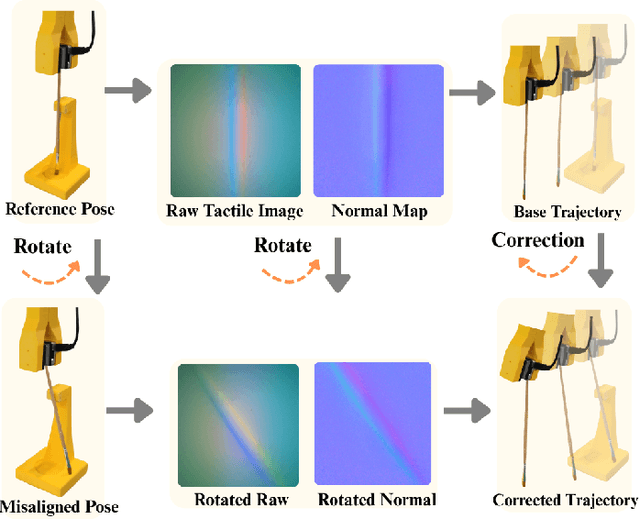
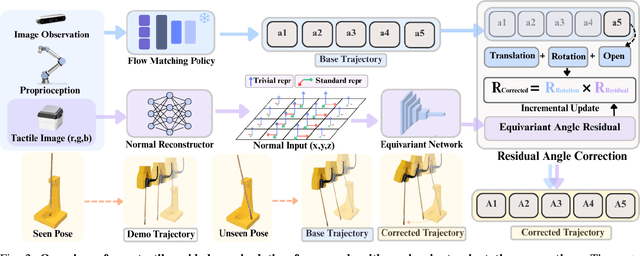
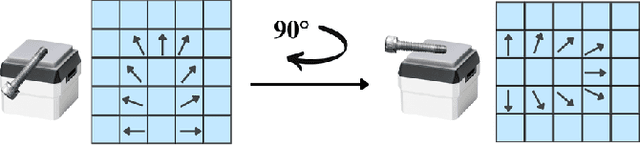
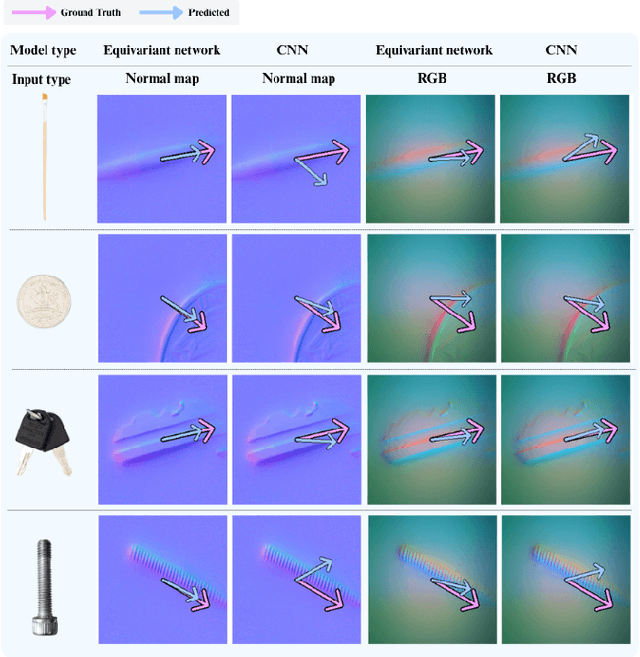
Abstract:Visuotactile policy learning augments vision-only policies with tactile input, facilitating contact-rich manipulation. However, the high cost of tactile data collection makes sample efficiency the key requirement for developing visuotactile policies. We present EquiTac, a framework that exploits the inherent SO(2) symmetry of in-hand object rotation to improve sample efficiency and generalization for visuotactile policy learning. EquiTac first reconstructs surface normals from raw RGB inputs of vision-based tactile sensors, so rotations of the normal vector field correspond to in-hand object rotations. An SO(2)-equivariant network then predicts a residual rotation action that augments a base visuomotor policy at test time, enabling real-time rotation correction without additional reorientation demonstrations. On a real robot, EquiTac accurately achieves robust zero-shot generalization to unseen in-hand orientations with very few training samples, where baselines fail even with more training data. To our knowledge, this is the first tactile learning method to explicitly encode tactile equivariance for policy learning, yielding a lightweight, symmetry-aware module that improves reliability in contact-rich tasks.
EquAct: An SE(3)-Equivariant Multi-Task Transformer for Open-Loop Robotic Manipulation
May 27, 2025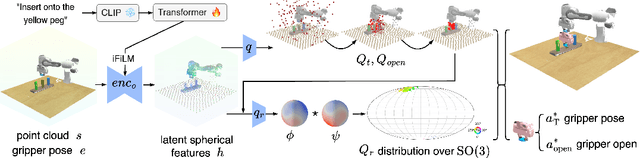
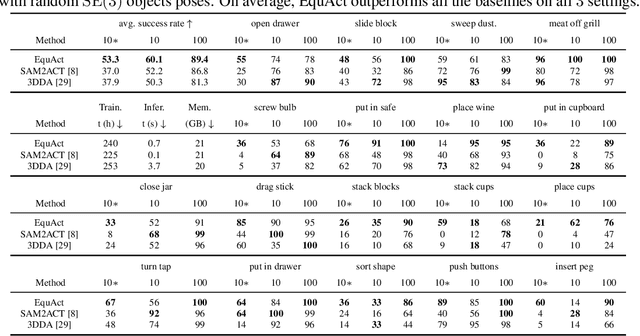
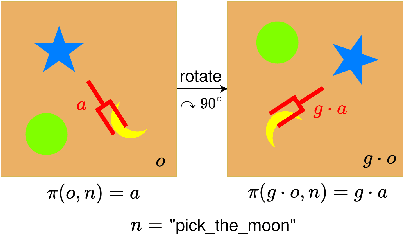
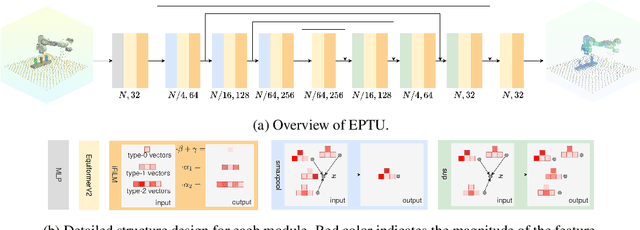
Abstract:Transformer architectures can effectively learn language-conditioned, multi-task 3D open-loop manipulation policies from demonstrations by jointly processing natural language instructions and 3D observations. However, although both the robot policy and language instructions inherently encode rich 3D geometric structures, standard transformers lack built-in guarantees of geometric consistency, often resulting in unpredictable behavior under SE(3) transformations of the scene. In this paper, we leverage SE(3) equivariance as a key structural property shared by both policy and language, and propose EquAct-a novel SE(3)-equivariant multi-task transformer. EquAct is theoretically guaranteed to be SE(3) equivariant and consists of two key components: (1) an efficient SE(3)-equivariant point cloud-based U-net with spherical Fourier features for policy reasoning, and (2) SE(3)-invariant Feature-wise Linear Modulation (iFiLM) layers for language conditioning. To evaluate its spatial generalization ability, we benchmark EquAct on 18 RLBench simulation tasks with both SE(3) and SE(2) scene perturbations, and on 4 physical tasks. EquAct performs state-of-the-art across these simulation and physical tasks.
Hierarchical Equivariant Policy via Frame Transf
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in hierarchical policy learning highlight the advantages of decomposing systems into high-level and low-level agents, enabling efficient long-horizon reasoning and precise fine-grained control. However, the interface between these hierarchy levels remains underexplored, and existing hierarchical methods often ignore domain symmetry, resulting in the need for extensive demonstrations to achieve robust performance. To address these issues, we propose Hierarchical Equivariant Policy (HEP), a novel hierarchical policy framework. We propose a frame transfer interface for hierarchical policy learning, which uses the high-level agent's output as a coordinate frame for the low-level agent, providing a strong inductive bias while retaining flexibility. Additionally, we integrate domain symmetries into both levels and theoretically demonstrate the system's overall equivariance. HEP achieves state-of-the-art performance in complex robotic manipulation tasks, demonstrating significant improvements in both simulation and real-world settings.
Community detection with the Bethe-Hessian
Nov 05, 2024
Abstract:The Bethe-Hessian matrix, introduced by Saade, Krzakala, and Zdeborov\'a (2014), is a Hermitian matrix designed for applying spectral clustering algorithms to sparse networks. Rather than employing a non-symmetric and high-dimensional non-backtracking operator, a spectral method based on the Bethe-Hessian matrix is conjectured to also reach the Kesten-Stigum detection threshold in the sparse stochastic block model (SBM). We provide the first rigorous analysis of the Bethe-Hessian spectral method in the SBM under both the bounded expected degree and the growing degree regimes. Specifically, we demonstrate that: (i) When the expected degree $d\geq 2$, the number of negative outliers of the Bethe-Hessian matrix can consistently estimate the number of blocks above the Kesten-Stigum threshold, thus confirming a conjecture from Saade, Krzakala, and Zdeborov\'a (2014) for $d\geq 2$. (ii) For sufficiently large $d$, its eigenvectors can be used to achieve weak recovery. (iii) As $d\to\infty$, we establish the concentration of the locations of its negative outlier eigenvalues, and weak consistency can be achieved via a spectral method based on the Bethe-Hessian matrix.
Non-convex matrix sensing: Breaking the quadratic rank barrier in the sample complexity
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:For the problem of reconstructing a low-rank matrix from a few linear measurements, two classes of algorithms have been widely studied in the literature: convex approaches based on nuclear norm minimization, and non-convex approaches that use factorized gradient descent. Under certain statistical model assumptions, it is known that nuclear norm minimization recovers the ground truth as soon as the number of samples scales linearly with the number of degrees of freedom of the ground-truth. In contrast, while non-convex approaches are computationally less expensive, existing recovery guarantees assume that the number of samples scales at least quadratically with the rank $r$ of the ground-truth matrix. In this paper, we close this gap by showing that the non-convex approaches can be as efficient as nuclear norm minimization in terms of sample complexity. Namely, we consider the problem of reconstructing a positive semidefinite matrix from a few Gaussian measurements. We show that factorized gradient descent with spectral initialization converges to the ground truth with a linear rate as soon as the number of samples scales with $ \Omega (rd\kappa^2)$, where $d$ is the dimension, and $\kappa$ is the condition number of the ground truth matrix. This improves the previous rank-dependence from quadratic to linear. Our proof relies on a probabilistic decoupling argument, where we show that the gradient descent iterates are only weakly dependent on the individual entries of the measurement matrices. We expect that our proof technique is of independent interest for other non-convex problems.
Universality of kernel random matrices and kernel regression in the quadratic regime
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Kernel ridge regression (KRR) is a popular class of machine learning models that has become an important tool for understanding deep learning. Much of the focus has been on studying the proportional asymptotic regime, $n \asymp d$, where $n$ is the number of training samples and $d$ is the dimension of the dataset. In this regime, under certain conditions on the data distribution, the kernel random matrix involved in KRR exhibits behavior akin to that of a linear kernel. In this work, we extend the study of kernel regression to the quadratic asymptotic regime, where $n \asymp d^2$. In this regime, we demonstrate that a broad class of inner-product kernels exhibit behavior similar to a quadratic kernel. Specifically, we establish an operator norm approximation bound for the difference between the original kernel random matrix and a quadratic kernel random matrix with additional correction terms compared to the Taylor expansion of the kernel functions. The approximation works for general data distributions under a Gaussian-moment-matching assumption with a covariance structure. This new approximation is utilized to obtain a limiting spectral distribution of the original kernel matrix and characterize the precise asymptotic training and generalization errors for KRR in the quadratic regime when $n/d^2$ converges to a non-zero constant. The generalization errors are obtained for both deterministic and random teacher models. Our proof techniques combine moment methods, Wick's formula, orthogonal polynomials, and resolvent analysis of random matrices with correlated entries.
MoMA: Multimodal LLM Adapter for Fast Personalized Image Generation
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present MoMA: an open-vocabulary, training-free personalized image model that boasts flexible zero-shot capabilities. As foundational text-to-image models rapidly evolve, the demand for robust image-to-image translation grows. Addressing this need, MoMA specializes in subject-driven personalized image generation. Utilizing an open-source, Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM), we train MoMA to serve a dual role as both a feature extractor and a generator. This approach effectively synergizes reference image and text prompt information to produce valuable image features, facilitating an image diffusion model. To better leverage the generated features, we further introduce a novel self-attention shortcut method that efficiently transfers image features to an image diffusion model, improving the resemblance of the target object in generated images. Remarkably, as a tuning-free plug-and-play module, our model requires only a single reference image and outperforms existing methods in generating images with high detail fidelity, enhanced identity-preservation and prompt faithfulness. Our work is open-source, thereby providing universal access to these advancements.
Online Differentially Private Synthetic Data Generation
Feb 12, 2024Abstract:We present a polynomial-time algorithm for online differentially private synthetic data generation. For a data stream within the hypercube $[0,1]^d$ and an infinite time horizon, we develop an online algorithm that generates a differentially private synthetic dataset at each time $t$. This algorithm achieves a near-optimal accuracy bound of $O(t^{-1/d}\log(t))$ for $d\geq 2$ and $O(t^{-1}\log^{4.5}(t))$ for $d=1$ in the 1-Wasserstein distance. This result generalizes the previous work on the continual release model for counting queries to include Lipschitz queries. Compared to the offline case, where the entire dataset is available at once, our approach requires only an extra polylog factor in the accuracy bound.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge