Artsiom Sanakoyeu
Token-Shuffle: Towards High-Resolution Image Generation with Autoregressive Models
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) models, long dominant in language generation, are increasingly applied to image synthesis but are often considered less competitive than Diffusion-based models. A primary limitation is the substantial number of image tokens required for AR models, which constrains both training and inference efficiency, as well as image resolution. To address this, we present Token-Shuffle, a novel yet simple method that reduces the number of image tokens in Transformer. Our key insight is the dimensional redundancy of visual vocabularies in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), where low-dimensional visual codes from visual encoder are directly mapped to high-dimensional language vocabularies. Leveraging this, we consider two key operations: token-shuffle, which merges spatially local tokens along channel dimension to decrease the input token number, and token-unshuffle, which untangles the inferred tokens after Transformer blocks to restore the spatial arrangement for output. Jointly training with textual prompts, our strategy requires no additional pretrained text-encoder and enables MLLMs to support extremely high-resolution image synthesis in a unified next-token prediction way while maintaining efficient training and inference. For the first time, we push the boundary of AR text-to-image generation to a resolution of 2048x2048 with gratifying generation performance. In GenAI-benchmark, our 2.7B model achieves 0.77 overall score on hard prompts, outperforming AR models LlamaGen by 0.18 and diffusion models LDM by 0.15. Exhaustive large-scale human evaluations also demonstrate our prominent image generation ability in terms of text-alignment, visual flaw, and visual appearance. We hope that Token-Shuffle can serve as a foundational design for efficient high-resolution image generation within MLLMs.
Autoregressive Distillation of Diffusion Transformers
Apr 15, 2025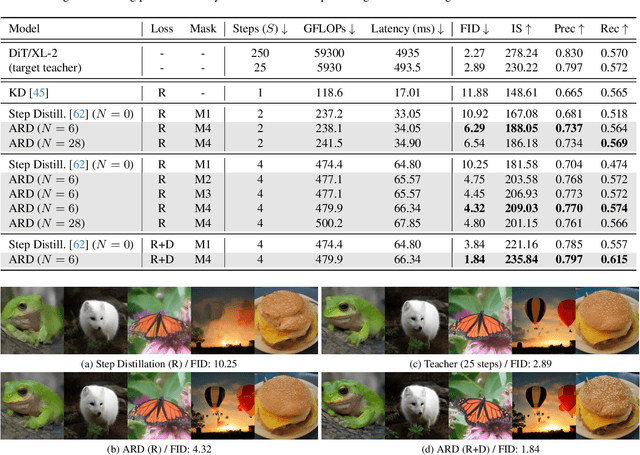
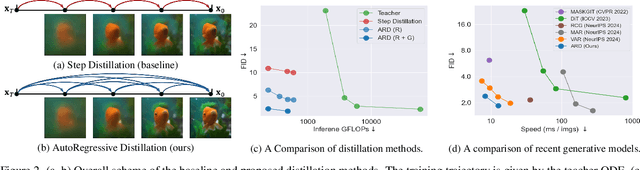
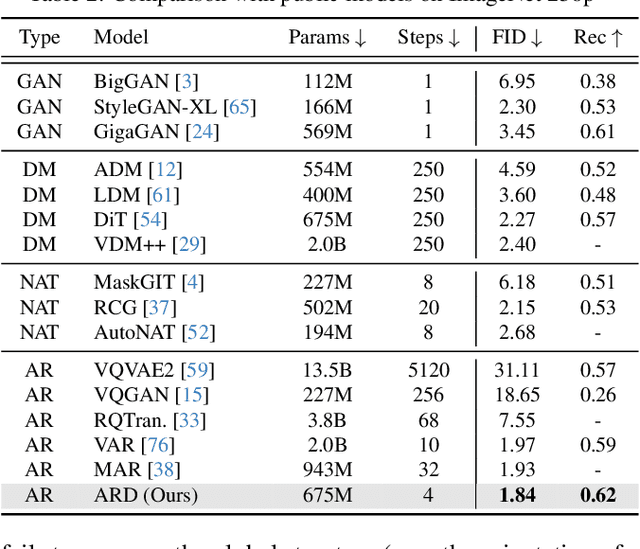
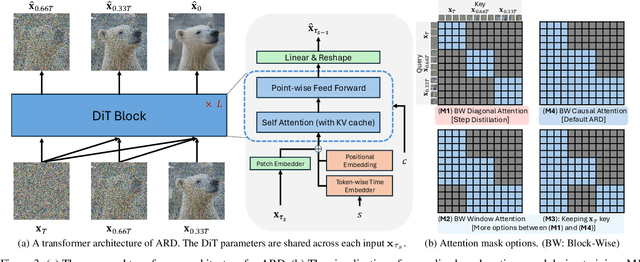
Abstract:Diffusion models with transformer architectures have demonstrated promising capabilities in generating high-fidelity images and scalability for high resolution. However, iterative sampling process required for synthesis is very resource-intensive. A line of work has focused on distilling solutions to probability flow ODEs into few-step student models. Nevertheless, existing methods have been limited by their reliance on the most recent denoised samples as input, rendering them susceptible to exposure bias. To address this limitation, we propose AutoRegressive Distillation (ARD), a novel approach that leverages the historical trajectory of the ODE to predict future steps. ARD offers two key benefits: 1) it mitigates exposure bias by utilizing a predicted historical trajectory that is less susceptible to accumulated errors, and 2) it leverages the previous history of the ODE trajectory as a more effective source of coarse-grained information. ARD modifies the teacher transformer architecture by adding token-wise time embedding to mark each input from the trajectory history and employs a block-wise causal attention mask for training. Furthermore, incorporating historical inputs only in lower transformer layers enhances performance and efficiency. We validate the effectiveness of ARD in a class-conditioned generation on ImageNet and T2I synthesis. Our model achieves a $5\times$ reduction in FID degradation compared to the baseline methods while requiring only 1.1\% extra FLOPs on ImageNet-256. Moreover, ARD reaches FID of 1.84 on ImageNet-256 in merely 4 steps and outperforms the publicly available 1024p text-to-image distilled models in prompt adherence score with a minimal drop in FID compared to the teacher. Project page: https://github.com/alsdudrla10/ARD.
FlexiDiT: Your Diffusion Transformer Can Easily Generate High-Quality Samples with Less Compute
Feb 27, 2025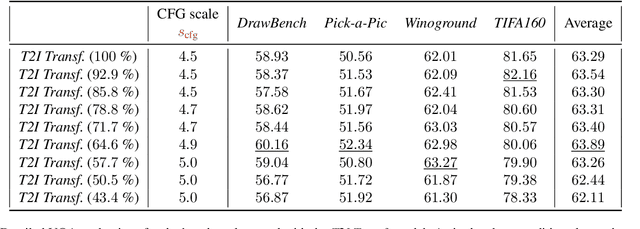

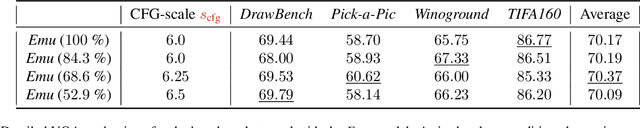

Abstract:Despite their remarkable performance, modern Diffusion Transformers are hindered by substantial resource requirements during inference, stemming from the fixed and large amount of compute needed for each denoising step. In this work, we revisit the conventional static paradigm that allocates a fixed compute budget per denoising iteration and propose a dynamic strategy instead. Our simple and sample-efficient framework enables pre-trained DiT models to be converted into \emph{flexible} ones -- dubbed FlexiDiT -- allowing them to process inputs at varying compute budgets. We demonstrate how a single \emph{flexible} model can generate images without any drop in quality, while reducing the required FLOPs by more than $40$\% compared to their static counterparts, for both class-conditioned and text-conditioned image generation. Our method is general and agnostic to input and conditioning modalities. We show how our approach can be readily extended for video generation, where FlexiDiT models generate samples with up to $75$\% less compute without compromising performance.
Judge Decoding: Faster Speculative Sampling Requires Going Beyond Model Alignment
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:The performance of large language models (LLMs) is closely linked to their underlying size, leading to ever-growing networks and hence slower inference. Speculative decoding has been proposed as a technique to accelerate autoregressive generation, leveraging a fast draft model to propose candidate tokens, which are then verified in parallel based on their likelihood under the target model. While this approach guarantees to reproduce the target output, it incurs a substantial penalty: many high-quality draft tokens are rejected, even when they represent objectively valid continuations. Indeed, we show that even powerful draft models such as GPT-4o, as well as human text cannot achieve high acceptance rates under the standard verification scheme. This severely limits the speedup potential of current speculative decoding methods, as an early rejection becomes overwhelmingly likely when solely relying on alignment of draft and target. We thus ask the following question: Can we adapt verification to recognize correct, but non-aligned replies? To this end, we draw inspiration from the LLM-as-a-judge framework, which demonstrated that LLMs are able to rate answers in a versatile way. We carefully design a dataset to elicit the same capability in the target model by training a compact module on top of the embeddings to produce ``judgements" of the current continuation. We showcase our strategy on the Llama-3.1 family, where our 8b/405B-Judge achieves a speedup of 9x over Llama-405B, while maintaining its quality on a large range of benchmarks. These benefits remain present even in optimized inference frameworks, where our method reaches up to 141 tokens/s for 8B/70B-Judge and 129 tokens/s for 8B/405B on 2 and 8 H100s respectively.
XR-MBT: Multi-modal Full Body Tracking for XR through Self-Supervision with Learned Depth Point Cloud Registration
Nov 27, 2024
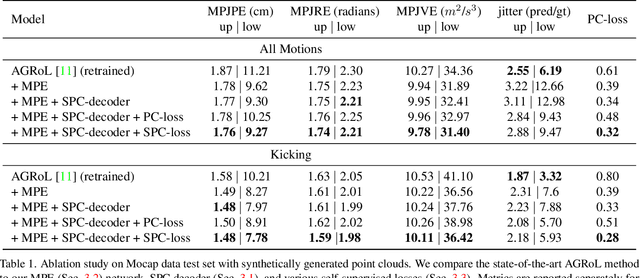
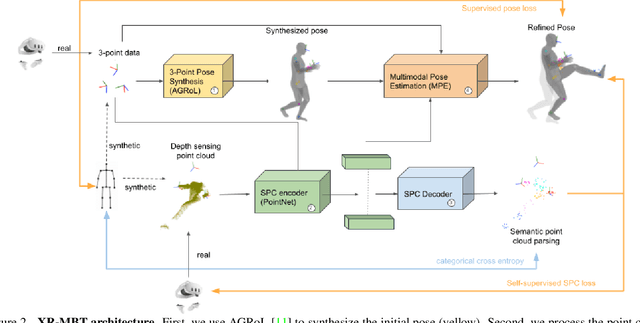

Abstract:Tracking the full body motions of users in XR (AR/VR) devices is a fundamental challenge to bring a sense of authentic social presence. Due to the absence of dedicated leg sensors, currently available body tracking methods adopt a synthesis approach to generate plausible motions given a 3-point signal from the head and controller tracking. In order to enable mixed reality features, modern XR devices are capable of estimating depth information of the headset surroundings using available sensors combined with dedicated machine learning models. Such egocentric depth sensing cannot drive the body directly, as it is not registered and is incomplete due to limited field-of-view and body self-occlusions. For the first time, we propose to leverage the available depth sensing signal combined with self-supervision to learn a multi-modal pose estimation model capable of tracking full body motions in real time on XR devices. We demonstrate how current 3-point motion synthesis models can be extended to point cloud modalities using a semantic point cloud encoder network combined with a residual network for multi-modal pose estimation. These modules are trained jointly in a self-supervised way, leveraging a combination of real unregistered point clouds and simulated data obtained from motion capture. We compare our approach against several state-of-the-art systems for XR body tracking and show that our method accurately tracks a diverse range of body motions. XR-MBT tracks legs in XR for the first time, whereas traditional synthesis approaches based on partial body tracking are blind.
Movie Gen: A Cast of Media Foundation Models
Oct 17, 2024
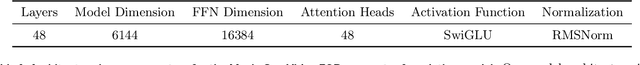
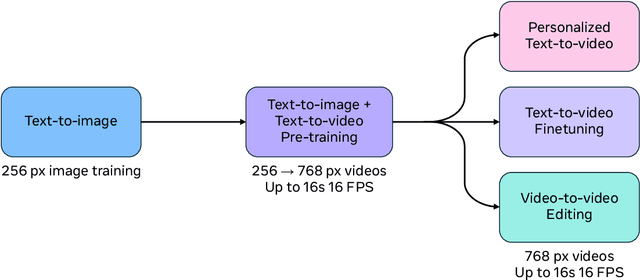
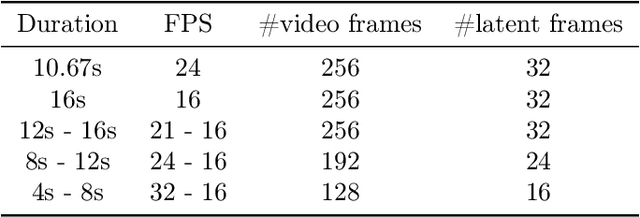
Abstract:We present Movie Gen, a cast of foundation models that generates high-quality, 1080p HD videos with different aspect ratios and synchronized audio. We also show additional capabilities such as precise instruction-based video editing and generation of personalized videos based on a user's image. Our models set a new state-of-the-art on multiple tasks: text-to-video synthesis, video personalization, video editing, video-to-audio generation, and text-to-audio generation. Our largest video generation model is a 30B parameter transformer trained with a maximum context length of 73K video tokens, corresponding to a generated video of 16 seconds at 16 frames-per-second. We show multiple technical innovations and simplifications on the architecture, latent spaces, training objectives and recipes, data curation, evaluation protocols, parallelization techniques, and inference optimizations that allow us to reap the benefits of scaling pre-training data, model size, and training compute for training large scale media generation models. We hope this paper helps the research community to accelerate progress and innovation in media generation models. All videos from this paper are available at https://go.fb.me/MovieGenResearchVideos.
Imagine Flash: Accelerating Emu Diffusion Models with Backward Distillation
May 08, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models are a powerful generative framework, but come with expensive inference. Existing acceleration methods often compromise image quality or fail under complex conditioning when operating in an extremely low-step regime. In this work, we propose a novel distillation framework tailored to enable high-fidelity, diverse sample generation using just one to three steps. Our approach comprises three key components: (i) Backward Distillation, which mitigates training-inference discrepancies by calibrating the student on its own backward trajectory; (ii) Shifted Reconstruction Loss that dynamically adapts knowledge transfer based on the current time step; and (iii) Noise Correction, an inference-time technique that enhances sample quality by addressing singularities in noise prediction. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our method outperforms existing competitors in quantitative metrics and human evaluations. Remarkably, it achieves performance comparable to the teacher model using only three denoising steps, enabling efficient high-quality generation.
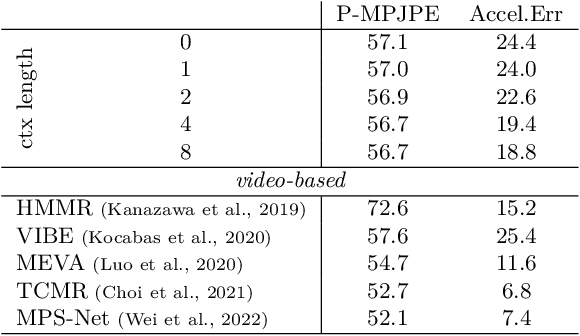
Using Motion Cues to Supervise Single-Frame Body Pose and Shape Estimation in Low Data Regimes
Feb 05, 2024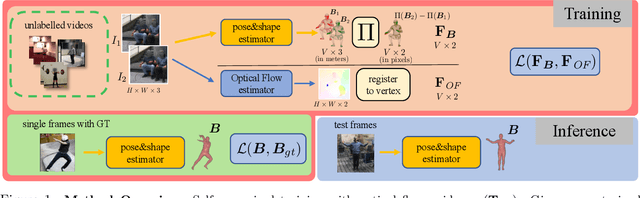
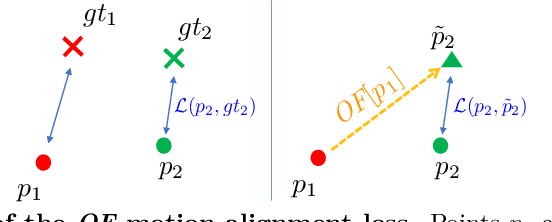
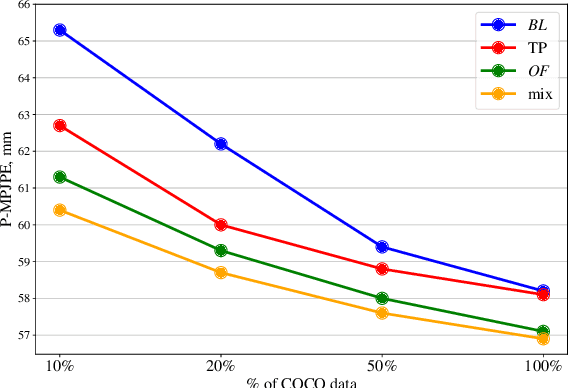
Abstract:When enough annotated training data is available, supervised deep-learning algorithms excel at estimating human body pose and shape using a single camera. The effects of too little such data being available can be mitigated by using other information sources, such as databases of body shapes, to learn priors. Unfortunately, such sources are not always available either. We show that, in such cases, easy-to-obtain unannotated videos can be used instead to provide the required supervisory signals. Given a trained model using too little annotated data, we compute poses in consecutive frames along with the optical flow between them. We then enforce consistency between the image optical flow and the one that can be inferred from the change in pose from one frame to the next. This provides enough additional supervision to effectively refine the network weights and to perform on par with methods trained using far more annotated data.
Cache Me if You Can: Accelerating Diffusion Models through Block Caching
Dec 06, 2023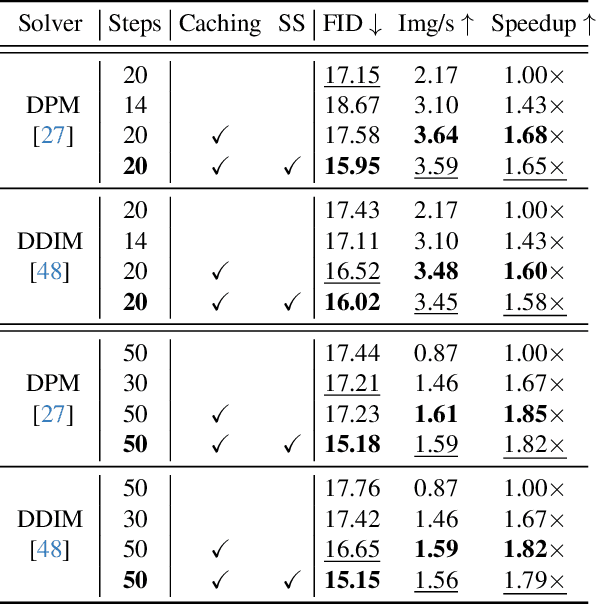

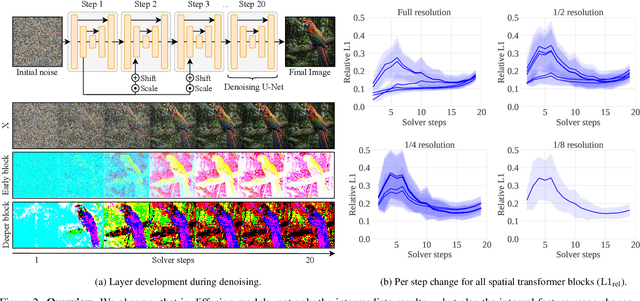
Abstract:Diffusion models have recently revolutionized the field of image synthesis due to their ability to generate photorealistic images. However, one of the major drawbacks of diffusion models is that the image generation process is costly. A large image-to-image network has to be applied many times to iteratively refine an image from random noise. While many recent works propose techniques to reduce the number of required steps, they generally treat the underlying denoising network as a black box. In this work, we investigate the behavior of the layers within the network and find that 1) the layers' output changes smoothly over time, 2) the layers show distinct patterns of change, and 3) the change from step to step is often very small. We hypothesize that many layer computations in the denoising network are redundant. Leveraging this, we introduce block caching, in which we reuse outputs from layer blocks of previous steps to speed up inference. Furthermore, we propose a technique to automatically determine caching schedules based on each block's changes over timesteps. In our experiments, we show through FID, human evaluation and qualitative analysis that Block Caching allows to generate images with higher visual quality at the same computational cost. We demonstrate this for different state-of-the-art models (LDM and EMU) and solvers (DDIM and DPM).
BoDiffusion: Diffusing Sparse Observations for Full-Body Human Motion Synthesis
Apr 21, 2023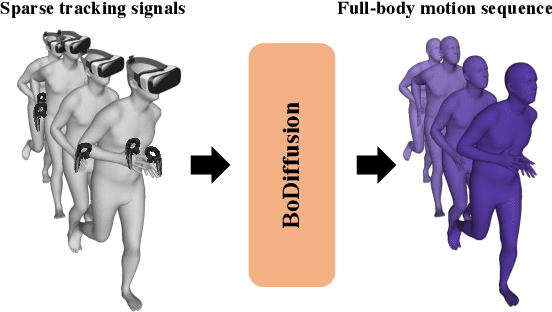
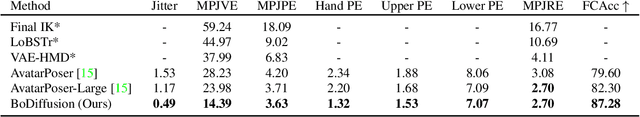
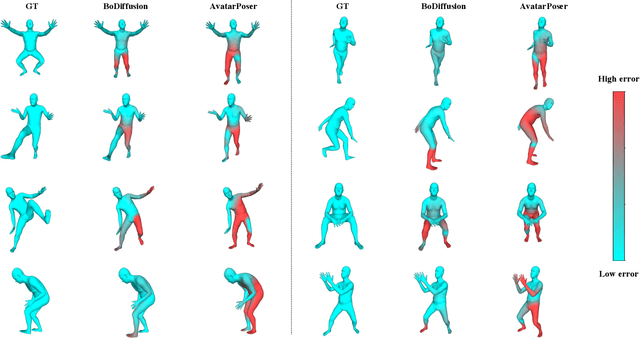
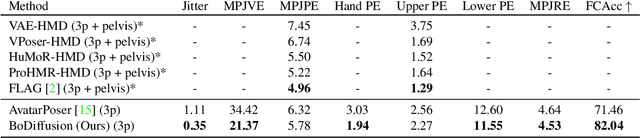
Abstract:Mixed reality applications require tracking the user's full-body motion to enable an immersive experience. However, typical head-mounted devices can only track head and hand movements, leading to a limited reconstruction of full-body motion due to variability in lower body configurations. We propose BoDiffusion -- a generative diffusion model for motion synthesis to tackle this under-constrained reconstruction problem. We present a time and space conditioning scheme that allows BoDiffusion to leverage sparse tracking inputs while generating smooth and realistic full-body motion sequences. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach that uses the reverse diffusion process to model full-body tracking as a conditional sequence generation task. We conduct experiments on the large-scale motion-capture dataset AMASS and show that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches by a significant margin in terms of full-body motion realism and joint reconstruction error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge