Nadine Bertsch
From Sparse Signal to Smooth Motion: Real-Time Motion Generation with Rolling Prediction Models
Apr 07, 2025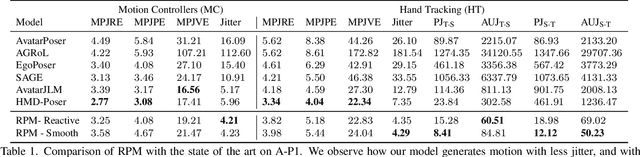
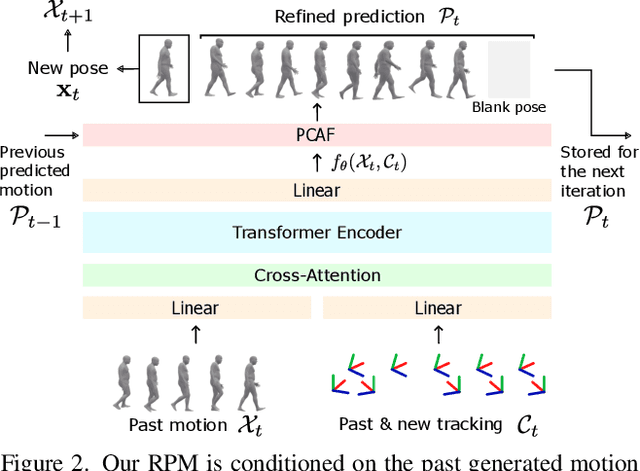
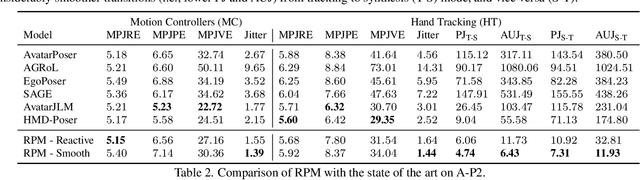
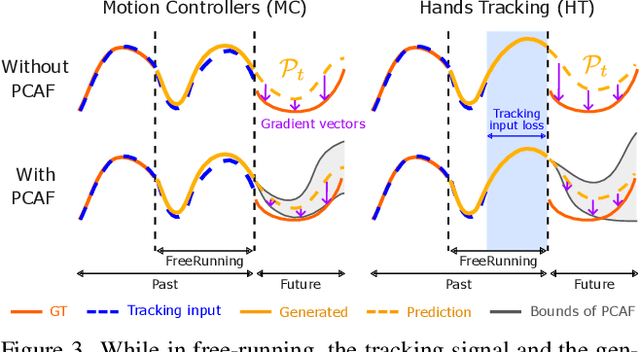
Abstract:In extended reality (XR), generating full-body motion of the users is important to understand their actions, drive their virtual avatars for social interaction, and convey a realistic sense of presence. While prior works focused on spatially sparse and always-on input signals from motion controllers, many XR applications opt for vision-based hand tracking for reduced user friction and better immersion. Compared to controllers, hand tracking signals are less accurate and can even be missing for an extended period of time. To handle such unreliable inputs, we present Rolling Prediction Model (RPM), an online and real-time approach that generates smooth full-body motion from temporally and spatially sparse input signals. Our model generates 1) accurate motion that matches the inputs (i.e., tracking mode) and 2) plausible motion when inputs are missing (i.e., synthesis mode). More importantly, RPM generates seamless transitions from tracking to synthesis, and vice versa. To demonstrate the practical importance of handling noisy and missing inputs, we present GORP, the first dataset of realistic sparse inputs from a commercial virtual reality (VR) headset with paired high quality body motion ground truth. GORP provides >14 hours of VR gameplay data from 28 people using motion controllers (spatially sparse) and hand tracking (spatially and temporally sparse). We benchmark RPM against the state of the art on both synthetic data and GORP to highlight how we can bridge the gap for real-world applications with a realistic dataset and by handling unreliable input signals. Our code, pretrained models, and GORP dataset are available in the project webpage.
XR-MBT: Multi-modal Full Body Tracking for XR through Self-Supervision with Learned Depth Point Cloud Registration
Nov 27, 2024
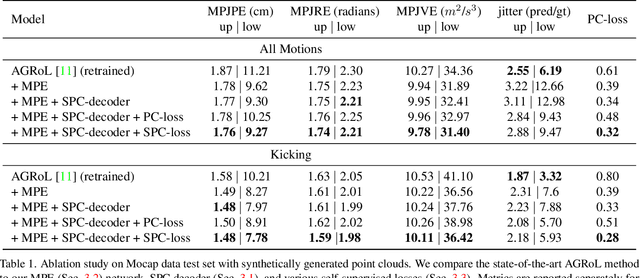
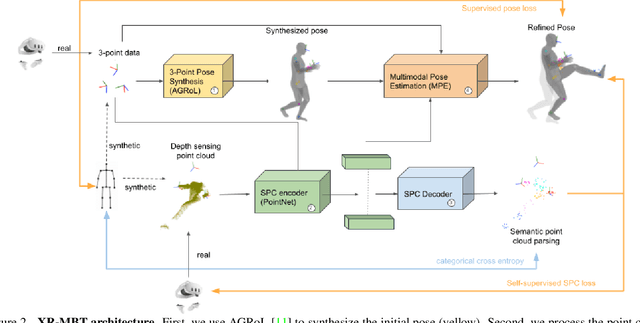

Abstract:Tracking the full body motions of users in XR (AR/VR) devices is a fundamental challenge to bring a sense of authentic social presence. Due to the absence of dedicated leg sensors, currently available body tracking methods adopt a synthesis approach to generate plausible motions given a 3-point signal from the head and controller tracking. In order to enable mixed reality features, modern XR devices are capable of estimating depth information of the headset surroundings using available sensors combined with dedicated machine learning models. Such egocentric depth sensing cannot drive the body directly, as it is not registered and is incomplete due to limited field-of-view and body self-occlusions. For the first time, we propose to leverage the available depth sensing signal combined with self-supervision to learn a multi-modal pose estimation model capable of tracking full body motions in real time on XR devices. We demonstrate how current 3-point motion synthesis models can be extended to point cloud modalities using a semantic point cloud encoder network combined with a residual network for multi-modal pose estimation. These modules are trained jointly in a self-supervised way, leveraging a combination of real unregistered point clouds and simulated data obtained from motion capture. We compare our approach against several state-of-the-art systems for XR body tracking and show that our method accurately tracks a diverse range of body motions. XR-MBT tracks legs in XR for the first time, whereas traditional synthesis approaches based on partial body tracking are blind.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge