Maria Escobar
EgoCast: Forecasting Egocentric Human Pose in the Wild
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Accurately estimating and forecasting human body pose is important for enhancing the user's sense of immersion in Augmented Reality. Addressing this need, our paper introduces EgoCast, a bimodal method for 3D human pose forecasting using egocentric videos and proprioceptive data. We study the task of human pose forecasting in a realistic setting, extending the boundaries of temporal forecasting in dynamic scenes and building on the current framework for current pose estimation in the wild. We introduce a current-frame estimation module that generates pseudo-groundtruth poses for inference, eliminating the need for past groundtruth poses typically required by current methods during forecasting. Our experimental results on the recent Ego-Exo4D and Aria Digital Twin datasets validate EgoCast for real-life motion estimation. On the Ego-Exo4D Body Pose 2024 Challenge, our method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches, laying the groundwork for future research in human pose estimation and forecasting in unscripted activities with egocentric inputs.
SuperFormer: Volumetric Transformer Architectures for MRI Super-Resolution
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel framework for processing volumetric medical information using Visual Transformers (ViTs). First, We extend the state-of-the-art Swin Transformer model to the 3D medical domain. Second, we propose a new approach for processing volumetric information and encoding position in ViTs for 3D applications. We instantiate the proposed framework and present SuperFormer, a volumetric transformer-based approach for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Super-Resolution. Our method leverages the 3D information of the MRI domain and uses a local self-attention mechanism with a 3D relative positional encoding to recover anatomical details. In addition, our approach takes advantage of multi-domain information from volume and feature domains and fuses them to reconstruct the High-Resolution MRI. We perform an extensive validation on the Human Connectome Project dataset and demonstrate the superiority of volumetric transformers over 3D CNN-based methods. Our code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/BCV-Uniandes/SuperFormer.
Ego-Exo4D: Understanding Skilled Human Activity from First- and Third-Person Perspectives
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:We present Ego-Exo4D, a diverse, large-scale multimodal multiview video dataset and benchmark challenge. Ego-Exo4D centers around simultaneously-captured egocentric and exocentric video of skilled human activities (e.g., sports, music, dance, bike repair). More than 800 participants from 13 cities worldwide performed these activities in 131 different natural scene contexts, yielding long-form captures from 1 to 42 minutes each and 1,422 hours of video combined. The multimodal nature of the dataset is unprecedented: the video is accompanied by multichannel audio, eye gaze, 3D point clouds, camera poses, IMU, and multiple paired language descriptions -- including a novel "expert commentary" done by coaches and teachers and tailored to the skilled-activity domain. To push the frontier of first-person video understanding of skilled human activity, we also present a suite of benchmark tasks and their annotations, including fine-grained activity understanding, proficiency estimation, cross-view translation, and 3D hand/body pose. All resources will be open sourced to fuel new research in the community.
EgoCOL: Egocentric Camera pose estimation for Open-world 3D object Localization @Ego4D challenge 2023
Jun 29, 2023



Abstract:We present EgoCOL, an egocentric camera pose estimation method for open-world 3D object localization. Our method leverages sparse camera pose reconstructions in a two-fold manner, video and scan independently, to estimate the camera pose of egocentric frames in 3D renders with high recall and precision. We extensively evaluate our method on the Visual Query (VQ) 3D object localization Ego4D benchmark. EgoCOL can estimate 62% and 59% more camera poses than the Ego4D baseline in the Ego4D Visual Queries 3D Localization challenge at CVPR 2023 in the val and test sets, respectively. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/BCV-Uniandes/EgoCOL
BoDiffusion: Diffusing Sparse Observations for Full-Body Human Motion Synthesis
Apr 21, 2023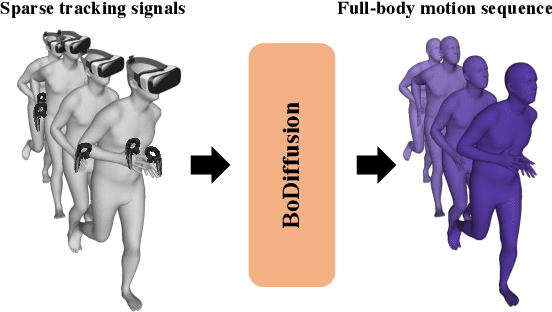
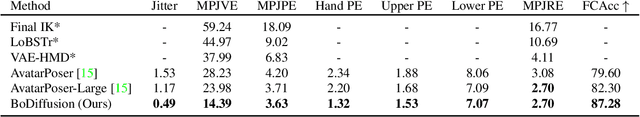
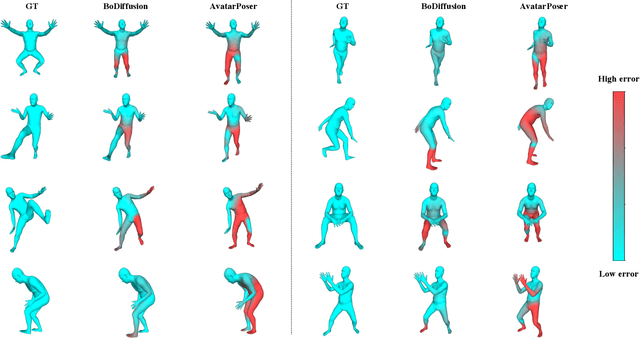
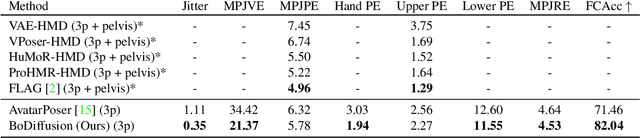
Abstract:Mixed reality applications require tracking the user's full-body motion to enable an immersive experience. However, typical head-mounted devices can only track head and hand movements, leading to a limited reconstruction of full-body motion due to variability in lower body configurations. We propose BoDiffusion -- a generative diffusion model for motion synthesis to tackle this under-constrained reconstruction problem. We present a time and space conditioning scheme that allows BoDiffusion to leverage sparse tracking inputs while generating smooth and realistic full-body motion sequences. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach that uses the reverse diffusion process to model full-body tracking as a conditional sequence generation task. We conduct experiments on the large-scale motion-capture dataset AMASS and show that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches by a significant margin in terms of full-body motion realism and joint reconstruction error.
Video Swin Transformers for Egocentric Video Understanding @ Ego4D Challenges 2022
Jul 22, 2022
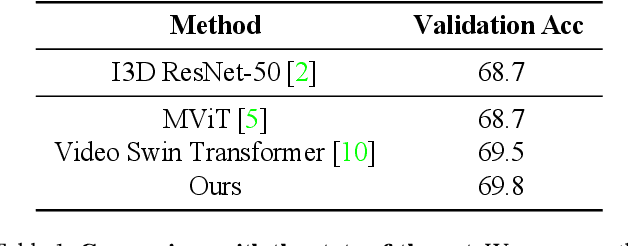
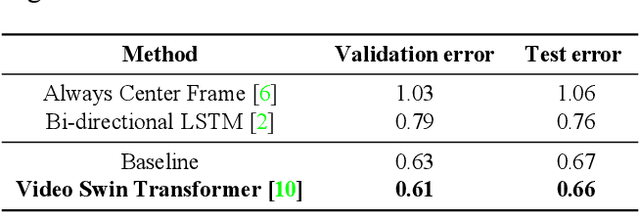
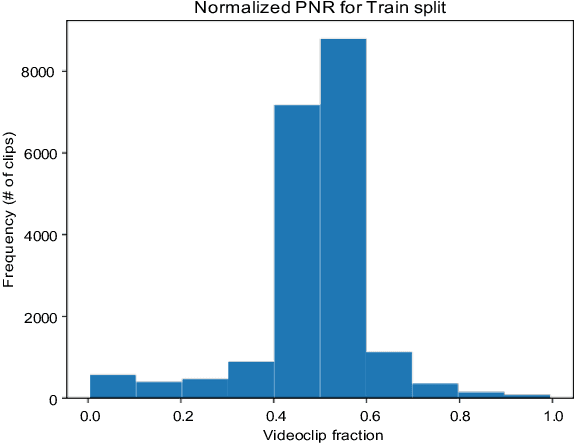
Abstract:We implemented Video Swin Transformer as a base architecture for the tasks of Point-of-No-Return temporal localization and Object State Change Classification. Our method achieved competitive performance on both challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge