Pablo Arbelaez
Center for Research and Formation in Artificial Intelligence, Universidad de los Andes, Colombia
Completing Spatial Transcriptomics Data for Gene Expression Prediction Benchmarking
May 05, 2025Abstract:Spatial Transcriptomics is a groundbreaking technology that integrates histology images with spatially resolved gene expression profiles. Among the various Spatial Transcriptomics techniques available, Visium has emerged as the most widely adopted. However, its accessibility is limited by high costs, the need for specialized expertise, and slow clinical integration. Additionally, gene capture inefficiencies lead to significant dropout, corrupting acquired data. To address these challenges, the deep learning community has explored the gene expression prediction task directly from histology images. Yet, inconsistencies in datasets, preprocessing, and training protocols hinder fair comparisons between models. To bridge this gap, we introduce SpaRED, a systematically curated database comprising 26 public datasets, providing a standardized resource for model evaluation. We further propose SpaCKLE, a state-of-the-art transformer-based gene expression completion model that reduces mean squared error by over 82.5% compared to existing approaches. Finally, we establish the SpaRED benchmark, evaluating eight state-of-the-art prediction models on both raw and SpaCKLE-completed data, demonstrating SpaCKLE substantially improves the results across all the gene expression prediction models. Altogether, our contributions constitute the most comprehensive benchmark of gene expression prediction from histology images to date and a stepping stone for future research on Spatial Transcriptomics.
EgoCast: Forecasting Egocentric Human Pose in the Wild
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Accurately estimating and forecasting human body pose is important for enhancing the user's sense of immersion in Augmented Reality. Addressing this need, our paper introduces EgoCast, a bimodal method for 3D human pose forecasting using egocentric videos and proprioceptive data. We study the task of human pose forecasting in a realistic setting, extending the boundaries of temporal forecasting in dynamic scenes and building on the current framework for current pose estimation in the wild. We introduce a current-frame estimation module that generates pseudo-groundtruth poses for inference, eliminating the need for past groundtruth poses typically required by current methods during forecasting. Our experimental results on the recent Ego-Exo4D and Aria Digital Twin datasets validate EgoCast for real-life motion estimation. On the Ego-Exo4D Body Pose 2024 Challenge, our method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches, laying the groundwork for future research in human pose estimation and forecasting in unscripted activities with egocentric inputs.
SuperFormer: Volumetric Transformer Architectures for MRI Super-Resolution
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel framework for processing volumetric medical information using Visual Transformers (ViTs). First, We extend the state-of-the-art Swin Transformer model to the 3D medical domain. Second, we propose a new approach for processing volumetric information and encoding position in ViTs for 3D applications. We instantiate the proposed framework and present SuperFormer, a volumetric transformer-based approach for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Super-Resolution. Our method leverages the 3D information of the MRI domain and uses a local self-attention mechanism with a 3D relative positional encoding to recover anatomical details. In addition, our approach takes advantage of multi-domain information from volume and feature domains and fuses them to reconstruct the High-Resolution MRI. We perform an extensive validation on the Human Connectome Project dataset and demonstrate the superiority of volumetric transformers over 3D CNN-based methods. Our code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/BCV-Uniandes/SuperFormer.
Multi-Center Fetal Brain Tissue Annotation (FeTA) Challenge 2022 Results
Feb 08, 2024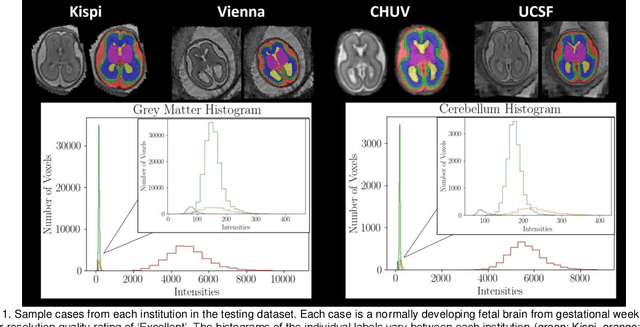
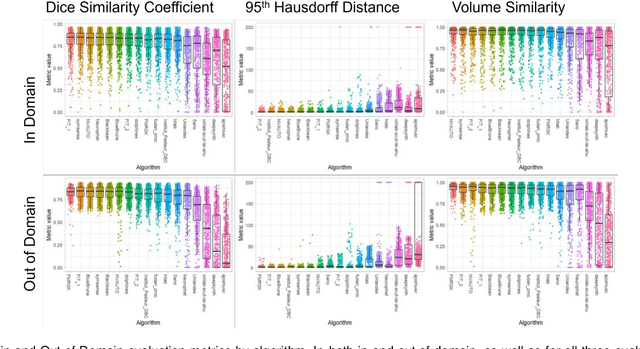
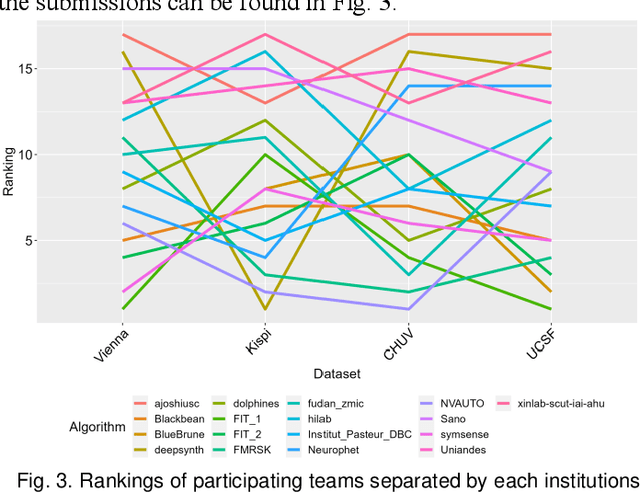
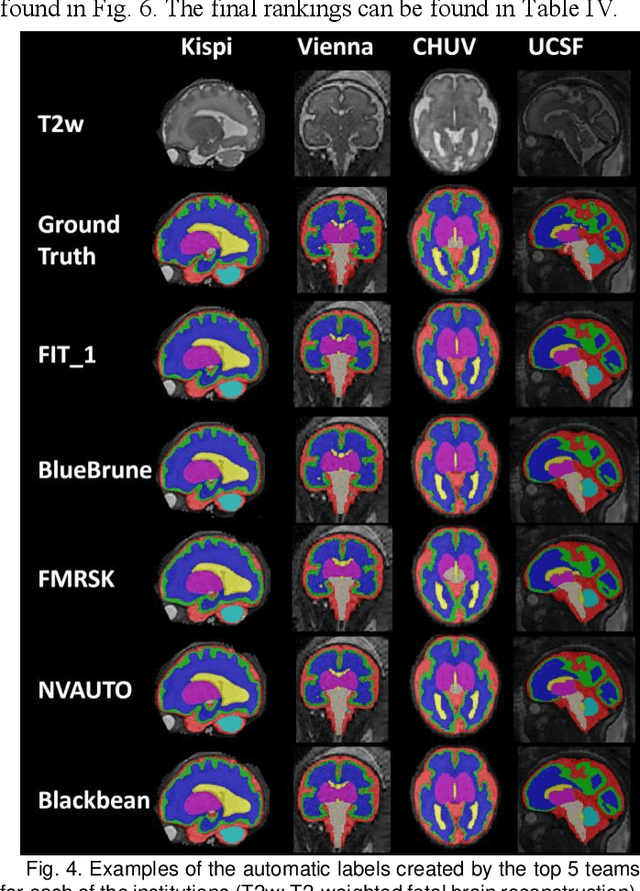
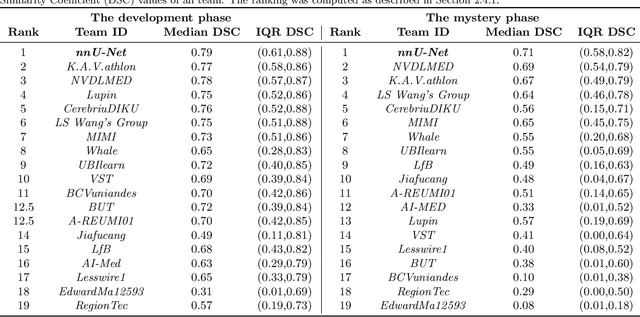
Abstract:Segmentation is a critical step in analyzing the developing human fetal brain. There have been vast improvements in automatic segmentation methods in the past several years, and the Fetal Brain Tissue Annotation (FeTA) Challenge 2021 helped to establish an excellent standard of fetal brain segmentation. However, FeTA 2021 was a single center study, and the generalizability of algorithms across different imaging centers remains unsolved, limiting real-world clinical applicability. The multi-center FeTA Challenge 2022 focuses on advancing the generalizability of fetal brain segmentation algorithms for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In FeTA 2022, the training dataset contained images and corresponding manually annotated multi-class labels from two imaging centers, and the testing data contained images from these two imaging centers as well as two additional unseen centers. The data from different centers varied in many aspects, including scanners used, imaging parameters, and fetal brain super-resolution algorithms applied. 16 teams participated in the challenge, and 17 algorithms were evaluated. Here, a detailed overview and analysis of the challenge results are provided, focusing on the generalizability of the submissions. Both in- and out of domain, the white matter and ventricles were segmented with the highest accuracy, while the most challenging structure remains the cerebral cortex due to anatomical complexity. The FeTA Challenge 2022 was able to successfully evaluate and advance generalizability of multi-class fetal brain tissue segmentation algorithms for MRI and it continues to benchmark new algorithms. The resulting new methods contribute to improving the analysis of brain development in utero.
SAR-RARP50: Segmentation of surgical instrumentation and Action Recognition on Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy Challenge
Dec 31, 2023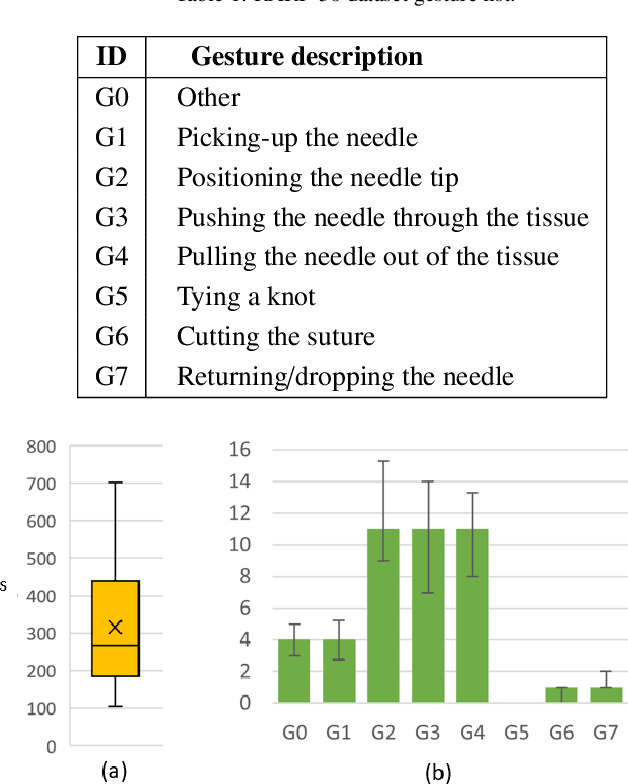
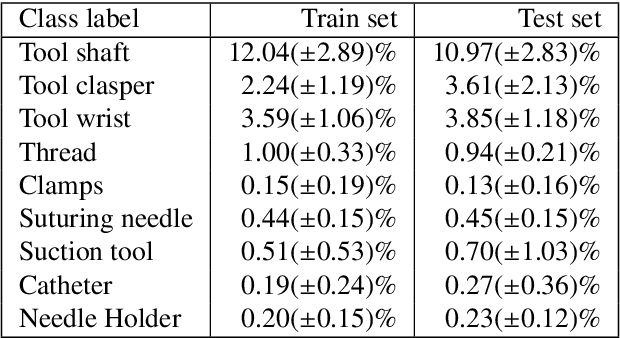
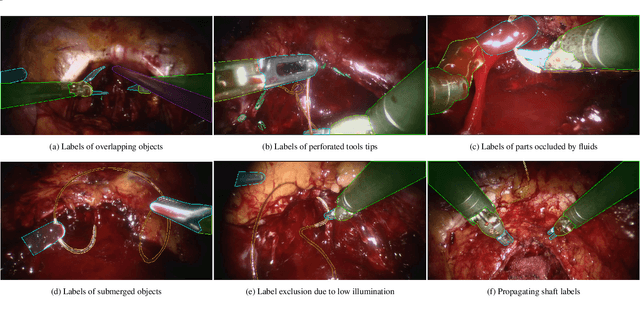
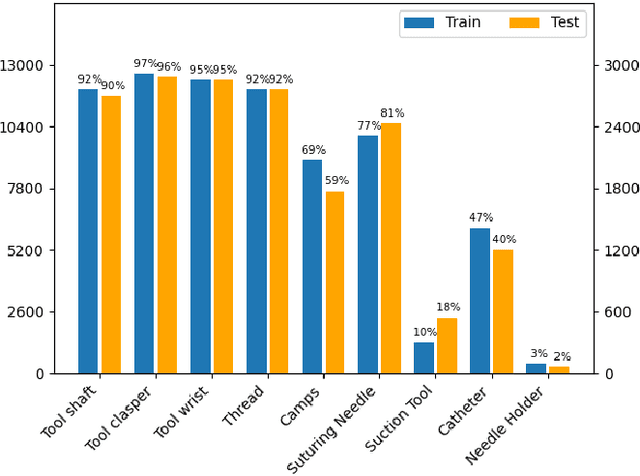
Abstract:Surgical tool segmentation and action recognition are fundamental building blocks in many computer-assisted intervention applications, ranging from surgical skills assessment to decision support systems. Nowadays, learning-based action recognition and segmentation approaches outperform classical methods, relying, however, on large, annotated datasets. Furthermore, action recognition and tool segmentation algorithms are often trained and make predictions in isolation from each other, without exploiting potential cross-task relationships. With the EndoVis 2022 SAR-RARP50 challenge, we release the first multimodal, publicly available, in-vivo, dataset for surgical action recognition and semantic instrumentation segmentation, containing 50 suturing video segments of Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP). The aim of the challenge is twofold. First, to enable researchers to leverage the scale of the provided dataset and develop robust and highly accurate single-task action recognition and tool segmentation approaches in the surgical domain. Second, to further explore the potential of multitask-based learning approaches and determine their comparative advantage against their single-task counterparts. A total of 12 teams participated in the challenge, contributing 7 action recognition methods, 9 instrument segmentation techniques, and 4 multitask approaches that integrated both action recognition and instrument segmentation.
Ego-Exo4D: Understanding Skilled Human Activity from First- and Third-Person Perspectives
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:We present Ego-Exo4D, a diverse, large-scale multimodal multiview video dataset and benchmark challenge. Ego-Exo4D centers around simultaneously-captured egocentric and exocentric video of skilled human activities (e.g., sports, music, dance, bike repair). More than 800 participants from 13 cities worldwide performed these activities in 131 different natural scene contexts, yielding long-form captures from 1 to 42 minutes each and 1,422 hours of video combined. The multimodal nature of the dataset is unprecedented: the video is accompanied by multichannel audio, eye gaze, 3D point clouds, camera poses, IMU, and multiple paired language descriptions -- including a novel "expert commentary" done by coaches and teachers and tailored to the skilled-activity domain. To push the frontier of first-person video understanding of skilled human activity, we also present a suite of benchmark tasks and their annotations, including fine-grained activity understanding, proficiency estimation, cross-view translation, and 3D hand/body pose. All resources will be open sourced to fuel new research in the community.
Ego4D: Around the World in 3,000 Hours of Egocentric Video
Oct 13, 2021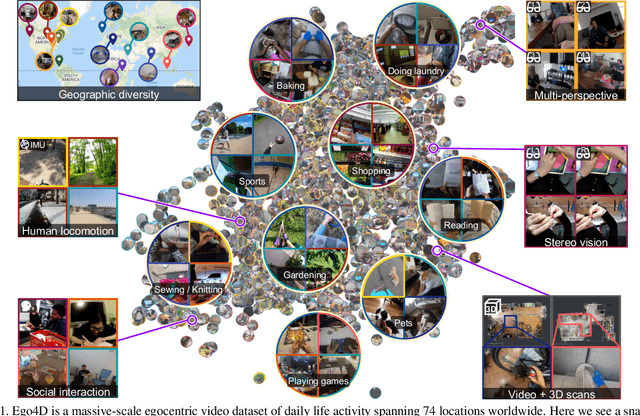
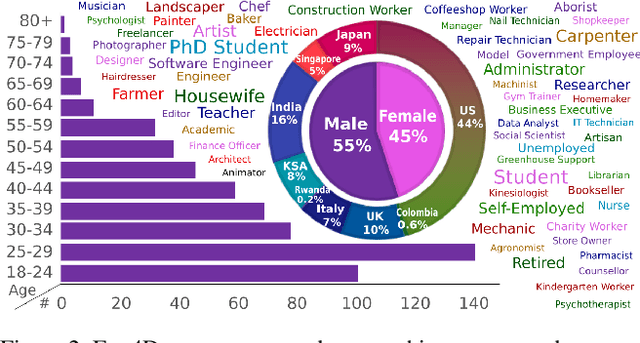

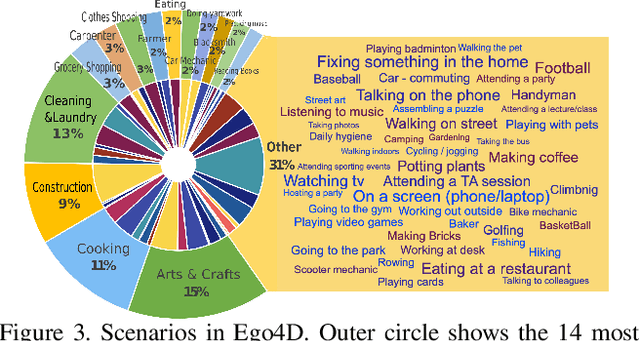
Abstract:We introduce Ego4D, a massive-scale egocentric video dataset and benchmark suite. It offers 3,025 hours of daily-life activity video spanning hundreds of scenarios (household, outdoor, workplace, leisure, etc.) captured by 855 unique camera wearers from 74 worldwide locations and 9 different countries. The approach to collection is designed to uphold rigorous privacy and ethics standards with consenting participants and robust de-identification procedures where relevant. Ego4D dramatically expands the volume of diverse egocentric video footage publicly available to the research community. Portions of the video are accompanied by audio, 3D meshes of the environment, eye gaze, stereo, and/or synchronized videos from multiple egocentric cameras at the same event. Furthermore, we present a host of new benchmark challenges centered around understanding the first-person visual experience in the past (querying an episodic memory), present (analyzing hand-object manipulation, audio-visual conversation, and social interactions), and future (forecasting activities). By publicly sharing this massive annotated dataset and benchmark suite, we aim to push the frontier of first-person perception. Project page: https://ego4d-data.org/
A Hierarchical Assessment of Adversarial Severity
Aug 26, 2021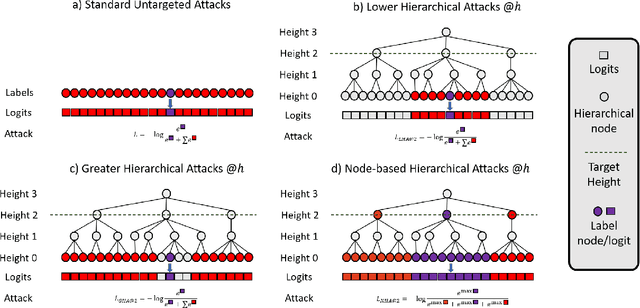

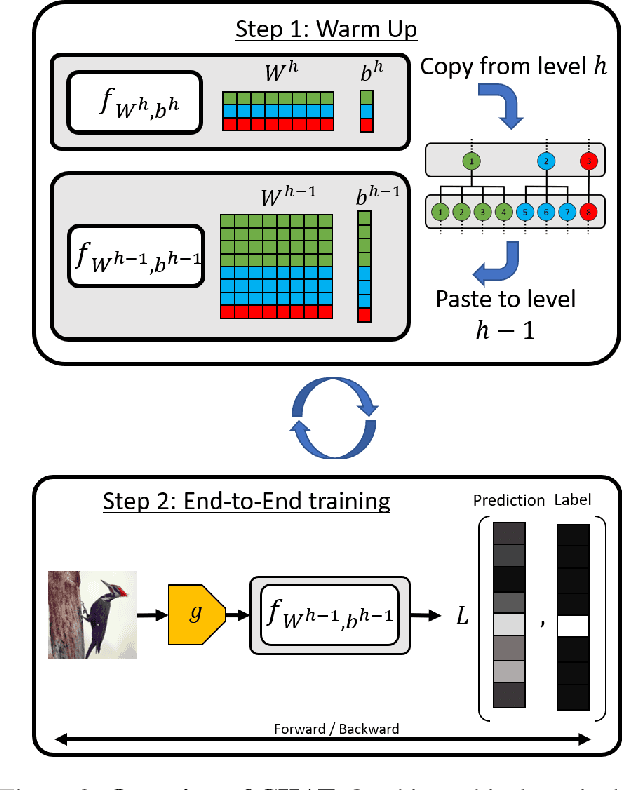

Abstract:Adversarial Robustness is a growing field that evidences the brittleness of neural networks. Although the literature on adversarial robustness is vast, a dimension is missing in these studies: assessing how severe the mistakes are. We call this notion "Adversarial Severity" since it quantifies the downstream impact of adversarial corruptions by computing the semantic error between the misclassification and the proper label. We propose to study the effects of adversarial noise by measuring the Robustness and Severity into a large-scale dataset: iNaturalist-H. Our contributions are: (i) we introduce novel Hierarchical Attacks that harness the rich structured space of labels to create adversarial examples. (ii) These attacks allow us to benchmark the Adversarial Robustness and Severity of classification models. (iii) We enhance the traditional adversarial training with a simple yet effective Hierarchical Curriculum Training to learn these nodes gradually within the hierarchical tree. We perform extensive experiments showing that hierarchical defenses allow deep models to boost the adversarial Robustness by 1.85% and reduce the severity of all attacks by 0.17, on average.
The Medical Segmentation Decathlon
Jun 10, 2021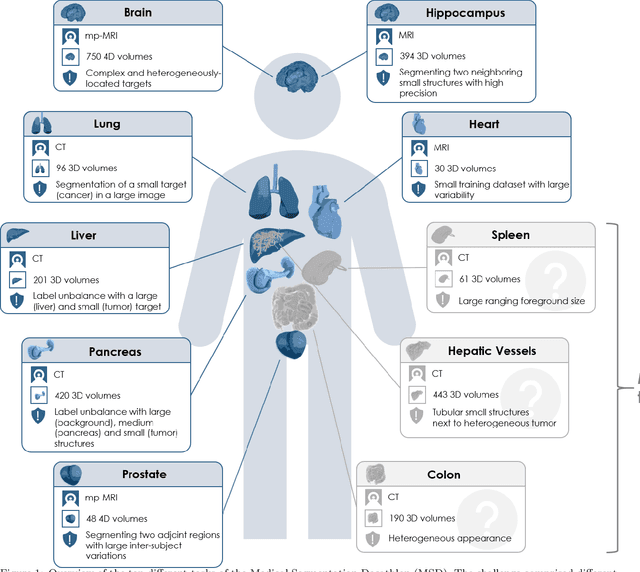
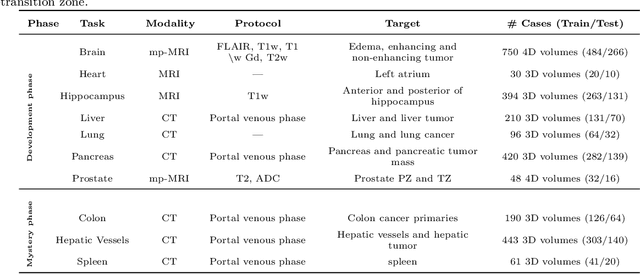
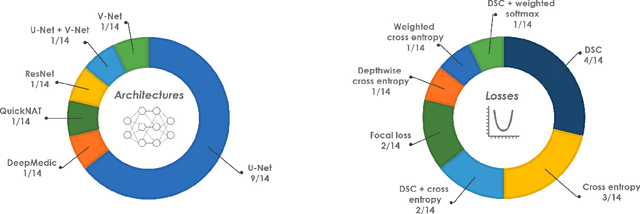
Abstract:International challenges have become the de facto standard for comparative assessment of image analysis algorithms given a specific task. Segmentation is so far the most widely investigated medical image processing task, but the various segmentation challenges have typically been organized in isolation, such that algorithm development was driven by the need to tackle a single specific clinical problem. We hypothesized that a method capable of performing well on multiple tasks will generalize well to a previously unseen task and potentially outperform a custom-designed solution. To investigate the hypothesis, we organized the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) - a biomedical image analysis challenge, in which algorithms compete in a multitude of both tasks and modalities. The underlying data set was designed to explore the axis of difficulties typically encountered when dealing with medical images, such as small data sets, unbalanced labels, multi-site data and small objects. The MSD challenge confirmed that algorithms with a consistent good performance on a set of tasks preserved their good average performance on a different set of previously unseen tasks. Moreover, by monitoring the MSD winner for two years, we found that this algorithm continued generalizing well to a wide range of other clinical problems, further confirming our hypothesis. Three main conclusions can be drawn from this study: (1) state-of-the-art image segmentation algorithms are mature, accurate, and generalize well when retrained on unseen tasks; (2) consistent algorithmic performance across multiple tasks is a strong surrogate of algorithmic generalizability; (3) the training of accurate AI segmentation models is now commoditized to non AI experts.
APES: Audiovisual Person Search in Untrimmed Video
Jun 03, 2021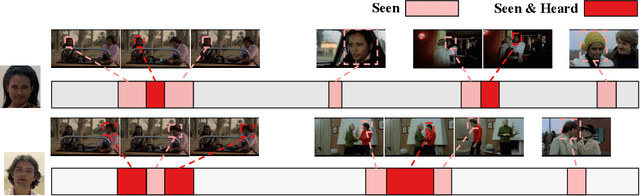
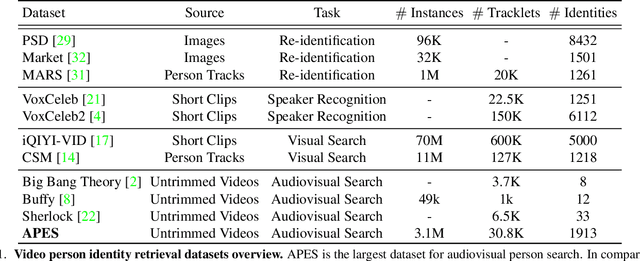


Abstract:Humans are arguably one of the most important subjects in video streams, many real-world applications such as video summarization or video editing workflows often require the automatic search and retrieval of a person of interest. Despite tremendous efforts in the person reidentification and retrieval domains, few works have developed audiovisual search strategies. In this paper, we present the Audiovisual Person Search dataset (APES), a new dataset composed of untrimmed videos whose audio (voices) and visual (faces) streams are densely annotated. APES contains over 1.9K identities labeled along 36 hours of video, making it the largest dataset available for untrimmed audiovisual person search. A key property of APES is that it includes dense temporal annotations that link faces to speech segments of the same identity. To showcase the potential of our new dataset, we propose an audiovisual baseline and benchmark for person retrieval. Our study shows that modeling audiovisual cues benefits the recognition of people's identities. To enable reproducibility and promote future research, the dataset annotations and baseline code are available at: https://github.com/fuankarion/audiovisual-person-search
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge