Jason Saragih
REWIND: Real-Time Egocentric Whole-Body Motion Diffusion with Exemplar-Based Identity Conditioning
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:We present REWIND (Real-Time Egocentric Whole-Body Motion Diffusion), a one-step diffusion model for real-time, high-fidelity human motion estimation from egocentric image inputs. While an existing method for egocentric whole-body (i.e., body and hands) motion estimation is non-real-time and acausal due to diffusion-based iterative motion refinement to capture correlations between body and hand poses, REWIND operates in a fully causal and real-time manner. To enable real-time inference, we introduce (1) cascaded body-hand denoising diffusion, which effectively models the correlation between egocentric body and hand motions in a fast, feed-forward manner, and (2) diffusion distillation, which enables high-quality motion estimation with a single denoising step. Our denoising diffusion model is based on a modified Transformer architecture, designed to causally model output motions while enhancing generalizability to unseen motion lengths. Additionally, REWIND optionally supports identity-conditioned motion estimation when identity prior is available. To this end, we propose a novel identity conditioning method based on a small set of pose exemplars of the target identity, which further enhances motion estimation quality. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that REWIND significantly outperforms the existing baselines both with and without exemplar-based identity conditioning.
FRESA:Feedforward Reconstruction of Personalized Skinned Avatars from Few Images
Mar 24, 2025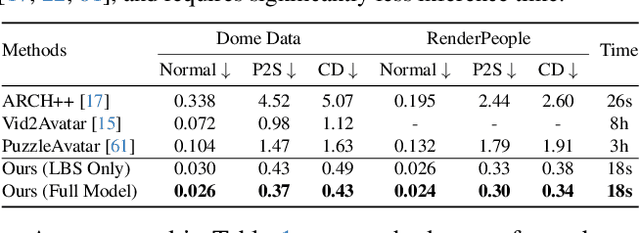
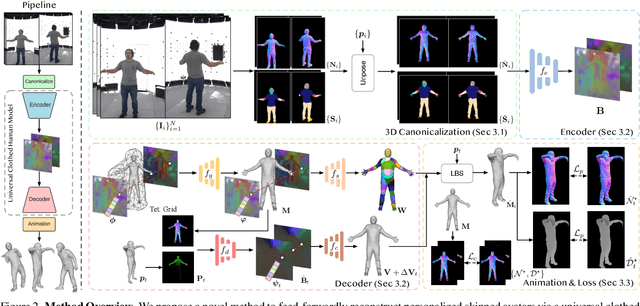
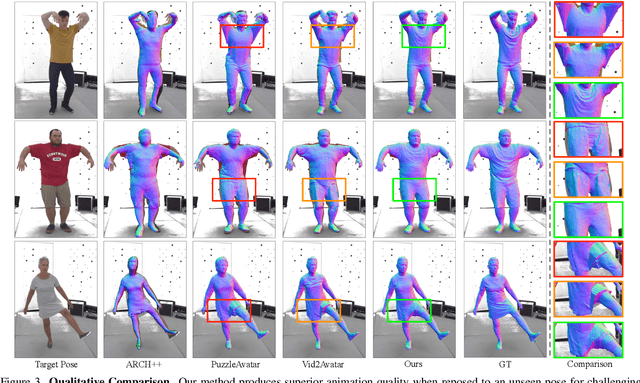
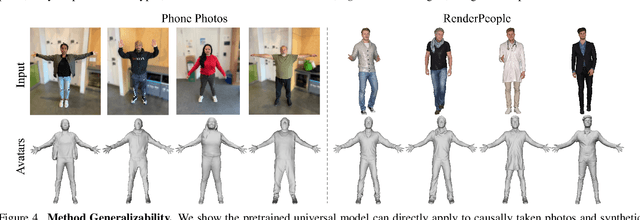
Abstract:We present a novel method for reconstructing personalized 3D human avatars with realistic animation from only a few images. Due to the large variations in body shapes, poses, and cloth types, existing methods mostly require hours of per-subject optimization during inference, which limits their practical applications. In contrast, we learn a universal prior from over a thousand clothed humans to achieve instant feedforward generation and zero-shot generalization. Specifically, instead of rigging the avatar with shared skinning weights, we jointly infer personalized avatar shape, skinning weights, and pose-dependent deformations, which effectively improves overall geometric fidelity and reduces deformation artifacts. Moreover, to normalize pose variations and resolve coupled ambiguity between canonical shapes and skinning weights, we design a 3D canonicalization process to produce pixel-aligned initial conditions, which helps to reconstruct fine-grained geometric details. We then propose a multi-frame feature aggregation to robustly reduce artifacts introduced in canonicalization and fuse a plausible avatar preserving person-specific identities. Finally, we train the model in an end-to-end framework on a large-scale capture dataset, which contains diverse human subjects paired with high-quality 3D scans. Extensive experiments show that our method generates more authentic reconstruction and animation than state-of-the-arts, and can be directly generalized to inputs from casually taken phone photos. Project page and code is available at https://github.com/rongakowang/FRESA.
LUCAS: Layered Universal Codec Avatars
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Photorealistic 3D head avatar reconstruction faces critical challenges in modeling dynamic face-hair interactions and achieving cross-identity generalization, particularly during expressions and head movements. We present LUCAS, a novel Universal Prior Model (UPM) for codec avatar modeling that disentangles face and hair through a layered representation. Unlike previous UPMs that treat hair as an integral part of the head, our approach separates the modeling of the hairless head and hair into distinct branches. LUCAS is the first to introduce a mesh-based UPM, facilitating real-time rendering on devices. Our layered representation also improves the anchor geometry for precise and visually appealing Gaussian renderings. Experimental results indicate that LUCAS outperforms existing single-mesh and Gaussian-based avatar models in both quantitative and qualitative assessments, including evaluations on held-out subjects in zero-shot driving scenarios. LUCAS demonstrates superior dynamic performance in managing head pose changes, expression transfer, and hairstyle variations, thereby advancing the state-of-the-art in 3D head avatar reconstruction.
Relightable Full-Body Gaussian Codec Avatars
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:We propose Relightable Full-Body Gaussian Codec Avatars, a new approach for modeling relightable full-body avatars with fine-grained details including face and hands. The unique challenge for relighting full-body avatars lies in the large deformations caused by body articulation and the resulting impact on appearance caused by light transport. Changes in body pose can dramatically change the orientation of body surfaces with respect to lights, resulting in both local appearance changes due to changes in local light transport functions, as well as non-local changes due to occlusion between body parts. To address this, we decompose the light transport into local and non-local effects. Local appearance changes are modeled using learnable zonal harmonics for diffuse radiance transfer. Unlike spherical harmonics, zonal harmonics are highly efficient to rotate under articulation. This allows us to learn diffuse radiance transfer in a local coordinate frame, which disentangles the local radiance transfer from the articulation of the body. To account for non-local appearance changes, we introduce a shadow network that predicts shadows given precomputed incoming irradiance on a base mesh. This facilitates the learning of non-local shadowing between the body parts. Finally, we use a deferred shading approach to model specular radiance transfer and better capture reflections and highlights such as eye glints. We demonstrate that our approach successfully models both the local and non-local light transport required for relightable full-body avatars, with a superior generalization ability under novel illumination conditions and unseen poses.
Universal Facial Encoding of Codec Avatars from VR Headsets
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:Faithful real-time facial animation is essential for avatar-mediated telepresence in Virtual Reality (VR). To emulate authentic communication, avatar animation needs to be efficient and accurate: able to capture both extreme and subtle expressions within a few milliseconds to sustain the rhythm of natural conversations. The oblique and incomplete views of the face, variability in the donning of headsets, and illumination variation due to the environment are some of the unique challenges in generalization to unseen faces. In this paper, we present a method that can animate a photorealistic avatar in realtime from head-mounted cameras (HMCs) on a consumer VR headset. We present a self-supervised learning approach, based on a cross-view reconstruction objective, that enables generalization to unseen users. We present a lightweight expression calibration mechanism that increases accuracy with minimal additional cost to run-time efficiency. We present an improved parameterization for precise ground-truth generation that provides robustness to environmental variation. The resulting system produces accurate facial animation for unseen users wearing VR headsets in realtime. We compare our approach to prior face-encoding methods demonstrating significant improvements in both quantitative metrics and qualitative results.
* SIGGRAPH 2024 (ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG))
Rasterized Edge Gradients: Handling Discontinuities Differentiably
May 03, 2024



Abstract:Computing the gradients of a rendering process is paramount for diverse applications in computer vision and graphics. However, accurate computation of these gradients is challenging due to discontinuities and rendering approximations, particularly for surface-based representations and rasterization-based rendering. We present a novel method for computing gradients at visibility discontinuities for rasterization-based differentiable renderers. Our method elegantly simplifies the traditionally complex problem through a carefully designed approximation strategy, allowing for a straightforward, effective, and performant solution. We introduce a novel concept of micro-edges, which allows us to treat the rasterized images as outcomes of a differentiable, continuous process aligned with the inherently non-differentiable, discrete-pixel rasterization. This technique eliminates the necessity for rendering approximations or other modifications to the forward pass, preserving the integrity of the rendered image, which makes it applicable to rasterized masks, depth, and normals images where filtering is prohibitive. Utilizing micro-edges simplifies gradient interpretation at discontinuities and enables handling of geometry intersections, offering an advantage over the prior art. We showcase our method in dynamic human head scene reconstruction, demonstrating effective handling of camera images and segmentation masks.
Fast Registration of Photorealistic Avatars for VR Facial Animation
Jan 19, 2024



Abstract:Virtual Reality (VR) bares promise of social interactions that can feel more immersive than other media. Key to this is the ability to accurately animate a photorealistic avatar of one's likeness while wearing a VR headset. Although high quality registration of person-specific avatars to headset-mounted camera (HMC) images is possible in an offline setting, the performance of generic realtime models are significantly degraded. Online registration is also challenging due to oblique camera views and differences in modality. In this work, we first show that the domain gap between the avatar and headset-camera images is one of the primary sources of difficulty, where a transformer-based architecture achieves high accuracy on domain-consistent data, but degrades when the domain-gap is re-introduced. Building on this finding, we develop a system design that decouples the problem into two parts: 1) an iterative refinement module that takes in-domain inputs, and 2) a generic avatar-guided image-to-image style transfer module that is conditioned on current estimation of expression and head pose. These two modules reinforce each other, as image style transfer becomes easier when close-to-ground-truth examples are shown, and better domain-gap removal helps registration. Our system produces high-quality results efficiently, obviating the need for costly offline registration to generate personalized labels. We validate the accuracy and efficiency of our approach through extensive experiments on a commodity headset, demonstrating significant improvements over direct regression methods as well as offline registration.
A Local Appearance Model for Volumetric Capture of Diverse Hairstyle
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:Hair plays a significant role in personal identity and appearance, making it an essential component of high-quality, photorealistic avatars. Existing approaches either focus on modeling the facial region only or rely on personalized models, limiting their generalizability and scalability. In this paper, we present a novel method for creating high-fidelity avatars with diverse hairstyles. Our method leverages the local similarity across different hairstyles and learns a universal hair appearance prior from multi-view captures of hundreds of people. This prior model takes 3D-aligned features as input and generates dense radiance fields conditioned on a sparse point cloud with color. As our model splits different hairstyles into local primitives and builds prior at that level, it is capable of handling various hair topologies. Through experiments, we demonstrate that our model captures a diverse range of hairstyles and generalizes well to challenging new hairstyles. Empirical results show that our method improves the state-of-the-art approaches in capturing and generating photorealistic, personalized avatars with complete hair.
Auto-CARD: Efficient and Robust Codec Avatar Driving for Real-time Mobile Telepresence
Apr 24, 2023



Abstract:Real-time and robust photorealistic avatars for telepresence in AR/VR have been highly desired for enabling immersive photorealistic telepresence. However, there still exists one key bottleneck: the considerable computational expense needed to accurately infer facial expressions captured from headset-mounted cameras with a quality level that can match the realism of the avatar's human appearance. To this end, we propose a framework called Auto-CARD, which for the first time enables real-time and robust driving of Codec Avatars when exclusively using merely on-device computing resources. This is achieved by minimizing two sources of redundancy. First, we develop a dedicated neural architecture search technique called AVE-NAS for avatar encoding in AR/VR, which explicitly boosts both the searched architectures' robustness in the presence of extreme facial expressions and hardware friendliness on fast evolving AR/VR headsets. Second, we leverage the temporal redundancy in consecutively captured images during continuous rendering and develop a mechanism dubbed LATEX to skip the computation of redundant frames. Specifically, we first identify an opportunity from the linearity of the latent space derived by the avatar decoder and then propose to perform adaptive latent extrapolation for redundant frames. For evaluation, we demonstrate the efficacy of our Auto-CARD framework in real-time Codec Avatar driving settings, where we achieve a 5.05x speed-up on Meta Quest 2 while maintaining a comparable or even better animation quality than state-of-the-art avatar encoder designs.
MEGANE: Morphable Eyeglass and Avatar Network
Feb 09, 2023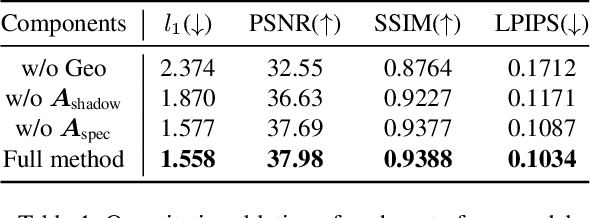
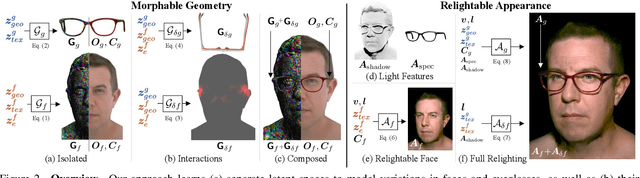
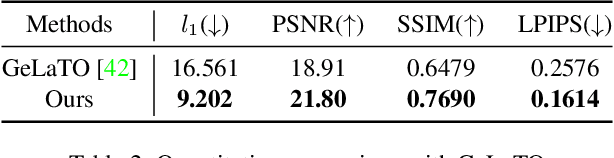
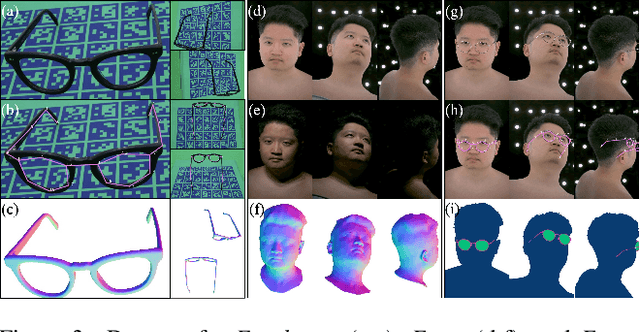
Abstract:Eyeglasses play an important role in the perception of identity. Authentic virtual representations of faces can benefit greatly from their inclusion. However, modeling the geometric and appearance interactions of glasses and the face of virtual representations of humans is challenging. Glasses and faces affect each other's geometry at their contact points, and also induce appearance changes due to light transport. Most existing approaches do not capture these physical interactions since they model eyeglasses and faces independently. Others attempt to resolve interactions as a 2D image synthesis problem and suffer from view and temporal inconsistencies. In this work, we propose a 3D compositional morphable model of eyeglasses that accurately incorporates high-fidelity geometric and photometric interaction effects. To support the large variation in eyeglass topology efficiently, we employ a hybrid representation that combines surface geometry and a volumetric representation. Unlike volumetric approaches, our model naturally retains correspondences across glasses, and hence explicit modification of geometry, such as lens insertion and frame deformation, is greatly simplified. In addition, our model is relightable under point lights and natural illumination, supporting high-fidelity rendering of various frame materials, including translucent plastic and metal within a single morphable model. Importantly, our approach models global light transport effects, such as casting shadows between faces and glasses. Our morphable model for eyeglasses can also be fit to novel glasses via inverse rendering. We compare our approach to state-of-the-art methods and demonstrate significant quality improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge